KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Bird Flu Lands as the Next Public Health Challenge
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
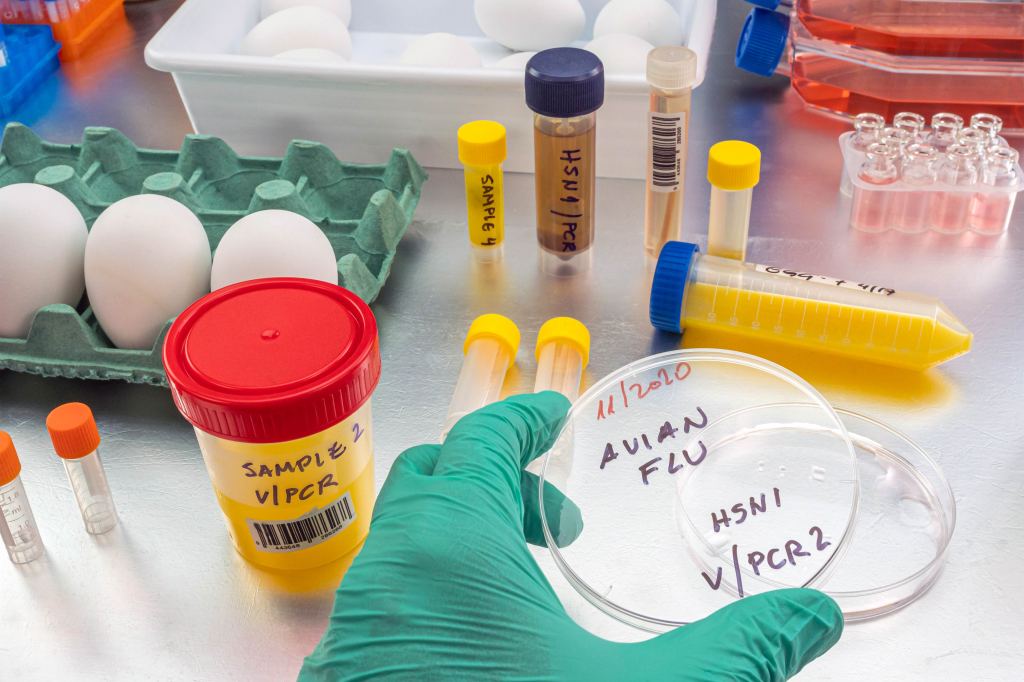
Public health officials are watching with concern since a strain of bird flu spread to dairy cows in at least nine states, and to at least one dairy worker. But in the wake of covid-19, many farmers are loath to let in health authorities for testing.
Meanwhile, another large health company — the Catholic hospital chain Ascension — has been targeted by a cyberattack, leading to serious problems at some facilities.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Rachel Cohrs Zhang of Stat, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, and Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Panelists
Rachel Cohrs Zhang
Stat News
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Sandhya Raman
CQ Roll Call
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Stumbles in the early response to bird flu bear an uncomfortable resemblance to the early days of covid, including the troubles protecting workers who could be exposed to the disease. Notably, the Department of Agriculture benefited from millions in covid relief funds designed to strengthen disease surveillance.
- Congress is working to extend coverage of telehealth care; the question is, how to pay for it? Lawmakers appear to have settled on a two-year agreement, though more on the extension — including how much it will cost — remains unknown.
- Speaking of telehealth, a new report shows about 20% of medication abortions are supervised via telehealth care. State-level restrictions are forcing those in need of abortion care to turn to options farther from home.
- And new reporting on Medicaid illuminates the number of people falling through the cracks of the government health system for low-income and disabled Americans — including how insurance companies benefit from individuals’ confusion over whether they have Medicaid coverage at all.
Also this week, Rovner interviews Atul Grover of the Association of American Medical Colleges about its recent analysis showing that graduating medical students are avoiding training in states with abortion bans and major restrictions.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: NPR’s “Why Writing by Hand Beats Typing for Thinking and Learning,” by Jonathan Lambert.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Time’s “‘I Don’t Have Faith in Doctors Anymore.’ Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control,” by Alana Semuels.
Rachel Cohrs Zhang: Stat’s “After Decades Fighting Big Tobacco, Cliff Douglas Now Leads a Foundation Funded by His Former Adversaries,” by Nicholas Florko.
Sandhya Raman: The Baltimore Banner’s “People With Severe Mental Illness Are Stuck in Jail. Montgomery County Is the Epicenter of the Problem,” by Ben Conarck.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- Stat’s “My Rendezvous With the Raw Milk Black Market: Quick, Easy, and Unchecked by the FDA,” by Nicholas Florko.
- The Stamford Advocate’s “Dan Haar: Hackers Stole a Disabled CT Couple’s SNAP Food Aid. Now They’re Out $1,373,” by Dan Haar.
- WKRN’s “‘Chaos’: Nurses, Visitors Describe Conditions Inside Ascension Hospitals After Cyberattack,” by Stephanie Langston.
- KFF Health News’ “Medicaid ‘Unwinding’ Decried as Biased Against Disabled People,” by Daniel Chang.
- KFF Health News’ “Why Medicaid’s ‘Undercount’ Problem Counts,” by Phil Galewitz.
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: Bird Flu Lands as the Next Public Health Challenge
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Mila Atmos: The future of America is in your hands.
This is not a movie trailer and it’s not a political ad, but it is a call to action. I’m Mila Atmos and I’m passionate about unlocking the power of everyday citizens. On our podcast “Future Hindsight,” we take big ideas about civic life and democracy and turn them into action items for you and me. Every Thursday we talk to bold activists and civic innovators to help you understand your power and your power to change the status quo. Find us at futurehindsight.com or wherever you listen to podcasts.
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, May 16, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this, so here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Rachel Cohrs Zhang of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs Zhang: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And we welcome back to the podcast following her sabbatical, Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Sandhya Raman: Hi, everyone.
Rovner: Later in this episode we’ll have my interview with Atul Grover of the Association of American Medical Colleges. He’s the co-author of the analysis we talked about on last week’s episode about how graduating medical students are avoiding applying for residencies in states with abortion bans or severe restrictions. But first this week’s news.
Well, I have been trying to avoid it, but I guess we finally have to talk about bird flu, which I think we really need to start calling “cow flu.” I just hope we don’t have to call it the next pandemic. Seriously, scientists say they’ve never seen the H5N1 virus spread quite like this before, including to at least one farmworker, who luckily had a very mild case. And public health officials are, if not actively freaking out, at least expressing very serious concern.
On the one hand, the federal government is providing livestock farmers tens of thousands of dollars each to beef up their protective measures — yes, I did that on purpose — and test for the avian flu virus in their cows, which seems to be spreading rapidly. On the other hand, many farmers are resisting efforts to allow health officials to test their herds, and this is exactly the kind of thing at the federal level that touches off those intra-agency rivalries between FDA [Food and Drug Administration] and USDA [United States Department of Agriculture] and the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention].
Is this going to be the first test of how weak our public health sector has become in the wake of covid? And how worried should we be both about the bird flu and about the ability of government to do anything about it? Rachel, you wrote about this this week.
Cohrs Zhang: I did, yes. It is kind of wild to see a lot of these patterns play out yet again, as if we’ve learned nothing. We still have a lot of challenges between coordinating with state and local health officials and federal agencies like CDC. We’re still seeing authorities that are exactly the same between USDA and FDA. USDA actually got $300 million from covid relief bills to try to increase their surveillance for these kind of diseases that spread among animals, but people are worried it could all potentially jump to humans.
So I think there was a lot of hope that maybe we would learn some lessons and learn to respond better, but I think we have seen some hiccups and just these jurisdictional issues that have just continued to happen because Congress didn’t really address some of these larger authorities in any meaningful way.
Rovner: I think the thing that worries me the most is looking at the dairy farmers who don’t want to let inspectors onto their farms. That strikes me as something that could seriously hamper efforts to know how widely and how fast this is spreading.
Cohrs Zhang: It could. And USDA does have more authority than they have had in other foodborne disease outbreaks like E. coli or salmonella to get on these farms, according to the experts that I’ve talked to. But we do see sometimes federal agencies don’t always want to use their full statutory authority because then it creates conflict. And obviously USDA has this dual mission of both ensuring food safety and promoting agriculture. And I think that comes into conflict sometimes and USDA just hasn’t been willing to enforce anything mandatory on farms yet. They’ve been kind of trying to use the carrot instead of the stick approach so far. So we’ll see how that goes and how much information they’re able to obtain with the measures they’ve used so far.
Rovner: Alice, you want to add something.
Ollstein: Yeah, I mean, like Rachel said, it’s sort of Groundhog Day for some of the bigger missteps of covid: inadequate testing, inadequate PPE [personal protective equipment]. But it’s also like a scary repeat of some of the specifics of covid, which really hit agricultural workers really hard. And a lot of that wasn’t known at the time, but we know it now. And a lot of workers in these agricultural, meatpacking, and other sectors, were just really devastated and forced to keep working during the outbreak.
This sector in particular has been resistant to public health enforcement and we’re just seeing that repeat once again with a potentially more deadly virus should it make the jump to humans.
Rovner: Basically, from what they can tell, this virus is in a lot of milk. It seems that pasteurization can kill it, but is this maybe what will get people to stop drinking raw milk, which isn’t that safe anyway? And if you need to know why you shouldn’t drink raw milk, I will link to a highly informative and entertaining story by Rachel’s colleague Nick Florko about how easy it is to buy raw milk and how dangerous it can be. This is one of those things where the public looks at the public health and goes, “Yeah, nah.”
Ollstein: Right, yeah. I think, at least anecdotally, the raw milk seller that Nick bought from indicated that business is good for him, business is booming. A lot of the people that maybe weren’t so concerned about covid aren’t so concerned about bird flu, and I think that will continue to drink that. Again, we haven’t seen a lot of data about how exactly that works with bird flu fragments or virus fragments: whether it’s showing up in raw milk?; what happens when people drink it? There’s so many questions we have right now because I think the FDA has been focused on pasteurized milk because that’s what most people drink. But certainly in terms of concern with transitions into humans, I think that’s an area to watch.
Raman: One of the things that struck me was that one of the benefits from what the USDA and HHS [Department of Health and Human Services] were doing was the benefit for workers to get a swab test and do an interview so they can study more and gauge the situation.
If $75 is enough to incentivize people to take off work, to maybe have to do transportation, to do those other things. And if they’ll be able to get some of the data, just as Rachel was saying, to just kind of continue gauging the situation. So I think that’ll be interesting to see.
Because even with when we had covid, there were so many incentives that we did just for vaccines that we hoped would be successful for different populations and money and prizes and all sorts of things that didn’t necessarily move the needle.
Rovner: Although some did. And nice pun there.
All right, well, moving on to less potentially-end-of-the-world health news, Congress is grappling with whether and how to extend coverage of telehealth and, if so, how to pay for it. Telehealth, of course, was practically the only way to get nonemergency health care throughout most of the pandemic, and both patients and providers got used to it and even, dare I say, came to like it. But as a Politico story succinctly put it this week, telehealth “has the potential to reduce expenses but also lead to more visits, driving up costs.”
Rachel, you’ve been watching this also this week. Where are we on these competing telehealth bills?
Cohrs Zhang: Well, we have some news this morning. The [House Committee on] Energy and Commerce Health Subcommittee is planning to mark up their telehealth bill. And the underlying bill will be a permanent extension of some of these Medicare telehealth flexibilities that matter a lot to seniors. But they’re planning to amend it today, so that they’re proposing a two-year extension, which does fall more in line with what the Ways and Means Committee, which is kind of the counterpart that makes policy on health care, marked up …
Rovner: Yes, they shared jurisdiction over Medicare.
Cohrs Zhang: … unanimously passed. They shared, yes, but it is surprising and remarkable for them to come to an agreement this quickly on a two-year extension. Again, I think industry would’ve loved to see a little bit more certainty on this for what these authorities are going to look like, but I think it is just expensive. Again, when these bills pass out of committee, then we’ll actually get formal cost estimates for them, which will be helpful in informing what our end-of-the-year December package is going to look like on health care. But we are seeing some alignment now in the House on a two-year telehealth extension for some of these very impactful measures for Medicare patients.
Rovner: Congress potentially getting things done months before they actually have to! Dare we hope?
Meanwhile, bridging this week’s topics between telehealth and abortion, which we will get to next, a new report from the family planning group WeCount! finds that not only are medication abortions more than half of all abortions being performed these days, but telehealth medication abortions now make up 20% of all medication abortions.
Some of this increase obviously is the pandemic relaxation of in-person medication abortion rules by the FDA, as well as shield laws that attempt to protect providers in states where abortion is still legal, who prescribe the pills for patients in states where abortion is banned.
Still, I imagine this is making anti-abortion activists really, really frustrated because it is certainly compromising their ability to really stop abortions in these states with bans, right?
Ollstein: Well, I think for a while we’ve seen anti-abortion activists really targeting the two main routes for people who live in states with bans to still have an abortion. One is ordering pills and the other is traveling out of state. And so they are exploring different policies to cut off both. Obviously both are very hard to police, both logistically and legally. There’s been a lot of debate about how this would be enforced. You see Louisiana moving to make abortion pills a controlled substance and police it that way. These pills are used for more than just abortions, so there’s some health care implications to going down that route. They’re used in miscarriage management, they’re used for other things as well in health care. And then of course, the enforcement question. Short of going through everyone’s mail, which has obvious constitutional problems, how would you ever know? These pills are sent to people’s homes in discreet packaging.
What we’ve seen so far with anti-abortion laws and their enforcement is that just the chilling effect alone and the fear is often enough to deter people from using different methods. And so that could be the goal. But actually cutting off people from telehealth abortions that, like you said, like the report said, have become very, very widely used, seems challenging.
Raman: And I would say that that really underscores the importance of the case we’d heard this year from the Supreme Court, and that we will get a decision coming up about the regulation of medication abortions. And how the court lands on that could have a huge impact on the next steps for all of these. So it’s in flux regardless of what’s happening here.
Cohrs Zhang: I want to emphasize, too, that mail-order abortion pills have been sort of held up as this silver bullet for getting around bans. And for a lot of people, that seems to be the case. But I really hear from providers and from patients that this is not a solution for everyone. A lot of people don’t have internet access or don’t know how to navigate different websites to find a reliable source for the pills. Or they’re too scared to do so, scared by the threat of law enforcement or scared that they could purchase some sort of counterfeit that isn’t effective or harms them.
Some people, even when they’re eligible for a medication abortion, prefer surgical or procedural because with a medication you take it and then you have to wait a few weeks to find out if it worked. And so some people would rather go into the clinic, make sure it’s done, have that peace of mind and security.
Also, these pills are delivered to people’s homes. Some people, because of a domestic violence situation or because they’re a minor who’s still at home with their parents, they can’t have anything sent to their homes. There’s a lot of reasons why this isn’t a solution for everyone, that I’ve been hearing about, but it is a solution, it seems, for a lot of people.
Rovner: In other abortion news this week, Democrats in the Missouri state Senate this week broke the record for the longest filibuster in history in an effort to block anti-abortion forces from making it harder for voters to amend the state constitution.
Alice, this feels pretty familiar, like it’s just about what happened in Ohio, right? And I guess the filibuster is over, but so far they’ve managed to be successful. What’s happening in Missouri?
Ollstein: So Missouri Democrats, with their filibuster that lasted for days, managed to stop a vote for now on a measure that would’ve made ballot measures harder to pass, including the abortion rights ballot measure that’s expected this fall. It’s not over yet. They sort of kicked it back to committee, but there’s only basically a day left in the legislature session, and so stay tuned over the next day to see what happens.
But what Democrats are trying to do is prevent what happened in Ohio, which is setting up a summer special election on a provision that would make all ballot measures harder to pass in the future. In Ohio, they did hold that summer vote, and voters defeated it and then went on to pass an abortion rights measure. And so even if Republicans push this through, it can still be scuttled later. But there, Democrats are trying to nip it in the bud to make sure that doesn’t happen in the first place.
Rovner: I thought that was very well explained. Thank you very much.
And speaking of misleading ballot measures, next door in Nebraska — and I did have to look at a map to make sure that Nebraska and Missouri do have a border, they do — anti-abortion forces are pushing a ballot measure they’re advertising as enshrining abortion rights in the state constitution, but which would actually enshrine the state’s current 12-week ban.
We’re seeing more and more of this: anti-abortion forces trying to sort of confuse voters about what it is that they’re voting on.
Raman: I mean, I think that that has been something that we have been seeing a little bit more of this. They’ve been trying different tactics to see — the same metaphor of throwing spaghetti at the wall and seeing what sticks. So with Nebraska right now, the proposal is to ban abortions after the first trimester, except in the trio of cases: medical emergencies, rape, incest.
And so that’s definitely different than a lot of the other ballot measures that we’ve seen in the last few years in that it’s being kind of pitched as a little bit of a middle ground and it has the backing of the different anti-abortion groups. But at the same time, it would allow state legislature to put additional bans on top of that. This is just kind of like the mark in the constitution and it would already keep in place the bans that you have in place.
So it’s a little bit more difficult to comprehend, especially if you’re just kind of walking in and checking a box, since there’s more nuance to it than some of the other measures. And I think that a lot of that is definitely more happening in states like that and others.
Rovner: I feel like we’re learning a lot more about ballot measures and how they work. And while we’re in the Great Plains, there’s a wild story out of South Dakota this week about an actual scam related to signatures on petitions for abortion ballot measures. Somebody tease this one apart.
Ollstein: So in South Dakota, they’ve already submitted signatures to put an abortion rights measure on the November ballot. The state is, as happens in most states, going through those signatures to verify it. What’s different than most states is that the state released the names of some of the people who signed the petition, and that enabled these anti-abortion groups to look up all those people and start calling them, and to try to convince them to withdraw their signatures to deny this from going forward.
What happened is that, in doing so, these groups are accused of misrepresenting themselves and impersonating government officials in the way they said, “Hey, we’re the ballot integrity committee of the something, something, something.” And they said it in a way that made it sound like they were with the secretary of state’s office. So the secretary of state put out a press release condemning this and referring it to law enforcement.
The group has admitted to doing this and said it’s done nothing wrong, that technically it didn’t say anything untrue. Of course there’s lying versus misleading versus this versus that. It’s a bit complicated here.
So regardless, I am skeptical that enough people will bother to go through the process of withdrawing their signature to make a difference. It’s a lot more work to withdraw your signature than to sign in the first place. You have to go in person or mail something in. And so I am curious to see if, one, whether this is illegal, and two, whether it makes a difference on the ground.
Rovner: Well, at some point, I think by the end of the summer we’ll be able to make a comprehensive list of where there are going to be ballot measures and what they’re going to be. In the meantime, we shall keep watching.
Let’s move on to another continuing story: health system cyberhacks. This week’s victim is Ascension, a large Catholic system with hospitals in 19 states. And the hack, to quote the AP, “forced some of its 140 hospitals to divert ambulances, caused patients to postpone medical tests, and blocked online access to patient records.”
You would think in the wake of the Change Healthcare hack, big systems like Ascension would’ve taken steps to lock things down more, or is that just me?
Cohrs Zhang: We’re still using fax machines, Julie. What are your expectations here? So cyberattacks have been a theoretical concern of health systems for a long time. I mean, back in 2019, 2020, Congress was kind of sliding provisions into spending bills to help support health systems in upgrading their systems. But again, we’re just seeing the scale. And I think these stories that came out this week really illustrate the human impact of these cyberattacks. And people are waiting longer in an ambulance to get to the hospital.
I mean, that’s a really serious issue. And I’m hoping that health systems will start taking this seriously. But I think it’s just exposing yet another risk that the failure to upgrade these systems isn’t just an inconvenience for people actually using the system. It isn’t just a disservice to all kind of the power of health care data and patients’ information that they could be leveraging better. But it’s also a real medical concern with these attacks. So I am optimistic. We’ll see. Sometimes it takes these sort of events to force change.
Rovner: Well, just before we started to tape this morning, I saw a story out of Tennessee about one of the hospitals that’s being affected. And apparently it is. I believe the word “chaos” was used in the headline and the lead. I mean, these are really serious things. It’s not just what’s going on in the back room, it’s what’s going on with patient care.
In maybe the most depressing hacking story ever, in Connecticut criminals are hacking and stealing the value of people’s electronic food stamp debit card. The Stamford Advocate wrote about one older couple whose card has been now hacked five times and who are out nearly $1,400 they can’t get back because the state can only reimburse people for two hacks. I remember when electronic funds transfers were going to make our lives so much easier. They do seem to be making lives so much easier for criminals.
Finally this week, more on the mess that is the Medicaid unwinding, from two of my colleagues. One story by Daniel Chang is about how people with disabilities, who shouldn’t really have been impacted by the unwinding anyway, are losing critical home care services in all of the administrative confusion. This seems a lot like the cases of eligible children losing coverage because their parents were deemed to have too-high income, even though children have different eligibility criteria.
I know the Biden administration has been trying to soft-pedal its pushes to some of these states. Rachel, you were talking about the USDA trying not to push too hard, but it does seem like in Medicaid a lot of eligible people are falling between the cracks.
Raman: Yeah, I mean states, as we’ve seen, have been really trying to see how fast that they can go to kind of reverify this huge batch of folks because it will be a cost saver for them to have fewer folks on the rolls. But as you’re saying, that a lot of people are falling through the cracks, especially when it’s unintentionally getting pulled from the program like your colleague’s story. And people with a lot of chronic disabilities already qualify for Medicaid, don’t need to be reverified each time because they’re continually qualified for it. And so there are some cases that have been filed already by the National Health Law Program in Colorado, and [Washington,] D.C., and Texas. And so we’ll kind of see as time goes on, how those go and if there’s any changes made to stop that.
Rovner: Also on the Medicaid beat, my colleague Phil Galewitz has a story that’s kind of the opposite. According to a study in the policy journal Health Affairs, a third of those enrolled in Medicaid in 2022, didn’t even know it. That’s 26 million people. And 3 million people actually thought they were uninsured when they in fact had Medicaid. That not only meant lots of people who didn’t get needed health services because they thought they couldn’t afford them because they thought they didn’t have insurance, but also managed-care companies who got paid for these enrollees who never got any care, and conveniently never bothered to inform them that they were covered. Rachel, you had a comment about this?
Cohrs Zhang: I did, yes. One part I really liked about this story is how Phil highlighted that it’s in insurance companies’ best interests for these people not to know that they can get health care services. Because a lot of Medicaid, they’re getting a payment for each member, capitated payments. And so if people aren’t using it, then the insurance companies are making more money. And so I think there has been some more, I think, political conversation about the incentives that capitated payments create especially in the Medicaid population. And so I think that was certainly just a disservice. I mean, these people have been done a disservice by someone. And I think that it’s a really interesting question of who should have been reaching them. And we’ll just, I guess, never know how much care they could have gotten and how their lives could be different had they known.
Rovner: It’s funny, we’ve known for a long time when they do the uninsured statistics that people don’t always know what kind of insurance they have. And they’ll say when they started asking a follow-up question, the Census Bureau started asking a follow-up question about insurance, suddenly the number of uninsured went down. This is the first time I’ve seen a study like this though, where people actually had insurance but didn’t know it. And it’s really interesting. And you’re right, it has real policy ramifications.
All right, well that’s the news for this week. Before we get to our interview, Sandhya, you’ve been gone for the last couple of months on sabbatical. Tell us what you saw in Europe.
Raman: Yeah, so it’s good to be back. I was gone for six weeks mostly to France, improving my French to see how I could get better at that and hopefully use it in my reporting at some point. It was interesting because I was trying to tune out of the news a little bit and stay away from health care. And of course when you try to do that, it comes right back to you. So I would be in my French class and we’d do a practice, let’s read an article or learn a historical thing, and lo and behold, one of the examples was about abortion politics in France over the years.
It was interesting to have to explain to my classmates, “Yes, I’m very familiar with this topic, and how much do you want me to talk about how this is in my country? But let me make sure I know all of those words.” So it pops up even when you think you’re going to sneak away from it.
Rovner: Yes, and we’re very obviously U.S.-centric here, but when you go to another country you realize none of their health systems work that well either. So the frustration continues everywhere.
All right, that is the news for this week. Now we will play my interview with Atul Grover, then we will come back and do our extra credits.
I am so pleased to welcome to the podcast Dr. Atul Grover, executive director of the Association of American [Medical] Colleges’ Research and Action Institute. I bet you have a very long business card.
And I want to offer him a public apology for not having him on sooner. Atul is the co-author of the report we talked about on last week’s episode on how graduating medical students are less likely to apply for residency in states with abortion bans and restrictions. Welcome at last to “What the Health?”
Grover: Better late than never.
Rovner: So there seems to be some confusion, at least in social media land, about some of the numbers here. Tell us what your analysis found.
Grover: First, Julie, is there ever not confusion in social media land? The numbers basically bear out the same thing that we saw last year — making it a very short but real trend — which is that when we look at where new U.S. medical school graduates are applying for residencies, and they apply to any number of programs, what they’re doing, it appears, is selectively avoiding those states in which abortion is either completely banned or severely restricted. And that’s not just in reproductive health-heavy specialties like OB-GYN, but it seems to be across the board.
Rovner: Now, can you explain why all of the numbers seem to be going down? It’s not that the number of applicants are falling, it’s the number of applications.
Grover: There’s about 20,000 people that graduate from U.S. MD [medical degree] schools every year. There are another 15[,000] to 20,000 applicants for residency positions that are DO [doctor of osteopathic medicine] graduates domestically or international graduates. Could be U.S. citizens or foreign citizens.
But what we’ve tried to do for a number of years is encourage applicants to apply to a fewer number of residency programs because we found that they were out-applying, they were over-applying. Where we did some data analyses a couple of years back on diminishing returns where we said, “Look, once you apply to 15, 20, 30 programs, your likelihood of matching, I know you’re nervous, but the likelihood of matching is not going to go up. You’re going to do fine. You don’t need to apply to 60, 70, 80 programs.”
So the good news is we’re actually seeing those numbers come down by about, for U.S. medical grads, about 7% this year, which is really the first time that I can remember in the last 10 years that this has happened. So that is good news.
Rovner: And that was an explicit goal.
Grover: That was an explicit goal. We want to make this cheaper, easier, and more rational for applicants and for programs, as they have to screen people and figure out who really wants to come to their program.
So overall, we were really pleased to see that the average applicant, as they applied to programs, applied to a few less programs, which meant that in many cases they were maybe not applying to one or two states that the average applicant might’ve applied to last year. So on average, each state saw about a 10% decrease in the number of unique applicants. But that decrease was much higher when we looked at those states that had banned abortion or severely limited it.
Rovner: Eventually, all these residency positions fill though, right, because there are more applicants as you point out, more graduating medical students and incoming graduates from other countries than there are slots. So why should we care, if all of these programs are filling?
Grover: So, I think you should always care about the number of residency spots, and I know you have a long history here, as do I, in that that is the bottleneck where we have to deal with why we have physician shortages, or one of the reasons why across the board we just don’t train enough physicians.
We have increased the number of medical school spots. We have people that are graduating from DO schools, as I said, international graduates. More are applying every year than we have space for. Which means that, yes, right now every spot will fill, because if the alternative for somebody applying is, look, I either won’t get in and actually be able to train in my specialty of choice. Or, I may have to go to my third choice or 10th choice or 50th choice or 100th choice. I’d rather go to someplace than no place at all.
So yes, everything is filling, but our look at the U.S. MD seniors was in part because we believe that they are the most competitive applicants, and in some ways the most desirable applicants. They have a 95% success in the match year after year. And so we thought they would be the most sensitive to look at in terms of, hey, I’ve got a little more choice here. Maybe I won’t apply to that state where I don’t feel like I can practice medicine freely for my patients.
And I think that’s a potential problem for a lot of these states and a lot of these programs is, if the people who might’ve been applying if the laws were different, who happened to be a better match for your program, for your specialty and your community, aren’t choosing to apply there, yes, you can fill it, but maybe not with the ideal candidate. And I think that’s going to affect patients and populations and local communities in the years to come.
Rovner: When we saw the beginning of this trend last year most of the talk was about a potential shortage of OB-GYNs going forward, since physicians often stay in practice where it is that they do their residency. But now, as you mentioned, we’re seeing a decrease in applications and specialties across the board. Why would that be?
Grover: So this is an informed opinion as to why people across specialties are choosing not to apply to residencies in these states. We didn’t ask the specific people who are matching this past year, “Why did you choose to apply or not to apply to this state?”
So what we know, though, from asking questions in other surveys is that about 70% of all health professions and health profession students believe that abortion should be legal at some point during a pregnancy. If you look at some specialties like adolescent medicine, that number goes up to 96%. So No. 1, I think it’s a potential violation of what people believe should be some freedom between doctors and patients as to allowing them to have the full range of reproductive health care.
No. 2, I think the potential penalties and the laws are often viewed as being incredibly punitive and somewhat unclear. And as much as doctors hate getting sued, we really don’t want to be indicted. I know some people are fine getting indicted. We really don’t want to be indicted. And that has implications because if we’re indicted, if we’re convicted of any kind of criminal offense, we could lose our license and not be able to care for patients. And we have a long investment in trying to do so.
The third thing that I think is relevant is certainly some of the specialties we’re looking at are heavily populated by women physicians, so OB-GYN, pediatrics. But again, across the board, it’s 50% women. So I think for the women themselves that happen to be applying, there is this issue of, think about their ages, 26, 27, 28 to the mid-30s, for the most part, and there are outliers on either end. But for the most part, they are of reproductive age, and I think they want to have control over their own lives and their own health care, and make sure that all services are available to them and their families if they need it. And I think even if it’s not relevant to you as an individual, it probably is relevant to your spouse or partner or somebody else in your family. And I think that makes a huge difference when people make these choices.
Rovner: So in the end, assuming these trends continue, I mean there really is concern for what the health professional community will look like in some of these states, right?
Grover: Yeah, and I think one of the things that I tried to look at last year in an editorial for JAMA was trying to overlay the states that have already significant challenges in recruiting and retaining physicians. They tend to be a lot of the heavily rural states, Southern states, parts of the Midwest. You overlay that on a map of the 14 states now that have basically banned abortion, and there’s a pretty close match.
So I think it’s critically important for state, local officials, legislatures, governors to think about their own potential impact of passing these laws on something that they may think is critically important, which is recruiting and retaining health professionals. And as you said, about half of people who train in a state will end up staying there to practice.
And for these pipeline programs, I know places like Mississippi and Alabama will really try and recruit individuals from underserved communities, get them through high school, get them into college, get them to stay in the state for med school, stay in the state for residency. They’re 80% likely to stay in those states. You lose them at any point along the way and they’re a lot less likely to come back.
So without even telling these states, I can’t tell you what’s good for you, but you should at least figure out how to collect the data at a local level to understand the implications of your policies on the health of everybody in a state, not just women of reproductive age.
Rovner: And I assume that we’ll be hearing more about this.
Grover: I would think so, yes.
Rovner: And asking more students about it.
Grover: Yes, we will. And we get to administer something called the Graduation Questionnaire every year for all these MD students. One of the questions we just added, and hopefully we’ll have some data, my colleagues will have that by probably August or so, is asking them specifically: What role did laws around some of these social issues have in your choice of where to do your residency? And again, there is some overlap here of states that have restricted reproductive rights, transgender care, and some other issues that are probably all kind of mixed in.
Rovner: Great. We’ll have you back to talk about it then.
Grover: Great. And I’m happy to come back and talk about market consolidation, about life expectancy, the quality of U.S. health, or anything else you want.
Rovner: Atul Grover, thank you so much.
Grover: Thanks for having me.
Rovner: OK, we are back. It’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device.
Sandhya, why don’t you go ahead and go first this week?
Raman: Great. So my story is from Ben Conarck at The Baltimore Banner, and it’s called “People With Severe Mental Illness Are Stuck in Jail. Montgomery County Is the Epicenter of the Problem.”
This is a really sad and impactful story about Montgomery County, Maryland, which is just outside of D.C., and how they are leading to this problem in this state. And many people are on the wait list for beds and psychiatric facilities, but they’re serving pretty short sentences of 90 days or less, and just a lot of the issues there. And just the problems for criminal defendants waiting in facilities for months on end for treatment.
Rovner: And I would add, because I live there, Montgomery County, Maryland, is one of the wealthiest counties in the country, and it’s kind of embarrassing that there are people who are not where they should be because they don’t have enough beds. Alice.
Ollstein: I have a piece from Time magazine called “‘I Don’t Have Faith in Doctors Anymore.’ Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control.” And it’s about something that I’ve been hearing about from providers for a bit now, which is that IUDs are this very effective form of birth control. It’s a device implanted in the uterus, and it was supposed to be this amazing way to help people avoid unwanted pregnancies. But as with many things, it is being used coercively, according to this report.
Because a physician has to implant it and remove it, people say that, one, they were pressured into having one often right after giving birth when they were sort of not in a place to make that kind of big decision. And then people who were given one struggled to have someone remove it when they wanted that done in the future.
And so I think it’s a good reminder that these tools are not inherently good or inherently bad. They can be used unethically or ethically by providers.
Rovner: And all reproductive health care is fraught. Rachel?
Cohrs Zhang: Yes. So Nick has been on quite the tear this week. My colleague Nick Florko at Stat and I wanted to highlight a profile that he wrote. The headline is, “After Decades Fighting Big Tobacco, Cliff Douglas Now Leads a Foundation Funded by His Former Adversaries.”
And I think it just has so much nuance into just a figure who fought Big Tobacco to bring to light what they were doing over decades. And now he’s chosen to take over this organization that had, in the past, been entirely funded by a tobacco company. And so I think it’s this really interesting … what we see all the time in Washington, how people contort themselves to make that transition into the private sector, or what they choose to do with their careers after public service. This is a nontraditional public service, obviously, being an advocate in this way. But I think it will be a really interesting dynamic to watch to see how much he chooses to change the direction of the organization, how long that arrangement lasts, if he chooses to do that.
I learned a lot reading this profile, and I think it’s even more rare to see people sit down for lengthy interviews for an old-fashioned profile. So I really enjoyed the piece.
Rovner: Full disclosure, I’ve known Cliff Douglas since the 1980s when he was just a young advocate starting out on his antismoking career. It really is good piece. I also thought Nick did a really good job.
Well, my story this week is from the NPR Shots blog. It’s by Jonathan Lambert and it’s called “Why Writing by Hand Beats Typing for Thinking and Learning.” And it made me feel much better for often being the only person in a room taking notes by hand in a notebook when everyone else is on their laptop. In fact, I can type as fast as anyone, and I can definitely type faster than I can write in longhand, but I actually find I take better notes if I have to boil down what I’m listening to. And it turns out there’s science that bears that out. Now, if only we could get the schools to go back to teaching cursive, but that’s a whole different issue.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. And happy birthday today to half of my weekly live audience: Aspen the corgi turns 4 today.
As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org, or you can still find me at X or Twitter, whatever you want to call it, @jrovner. Sandhya, where are you?
Raman: @SandhyaWrites.
Rovner: Alice.
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein.
Rovner: Rachel.
Cohrs Zhang: @rachelcohrs.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 2 months ago
Health Industry, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Public Health, Health IT, Hospitals, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Podcasts, Telemedicine, U.S. Congress
FDA Said It Never Inspected Dental Lab That Made Controversial AGGA Device
The FDA never inspected Johns Dental Laboratories during more than a decade in which it made the Anterior Growth Guidance Appliance, or “AGGA,” a dental device that has allegedly harmed patients and is now the subject of a criminal investigation.
According to FDA documents obtained through the Freedom of Information Act, the agency “became aware” of the AGGA from a joint investigation by KFF Health News and CBS News in March 2023, then responded with its first-ever inspection of Johns Dental months later.
That inspection found that the Indiana dental device manufacturer didn’t require all customer complaints to be investigated and the company did not investigate some complaints about people being hurt by products, including the AGGA, the FDA documents state. The FDA requires device companies to investigate complaints and forward them to the agency. Johns Dental had “never” alerted the FDA to any such complaints, according to the documents.
The AGGA, which its inventor testified has been used on more than 10,000 patients, was promoted by dentists nationwide, some of whom said it could “grow” or “expand” an adult’s jaw without surgery and treat common ailments like sleep apnea. But these claims were not backed by peer-reviewed research, and Johns Dental has settled lawsuits from 20 patients who alleged the AGGA caused them grievous harm. The company has not admitted liability.
Two former FDA officials said the AGGA was likely able to stay on the market — and off the FDA’s radar — for so long because of the lack of inspections and investigations at Johns Dental. Madris Kinard, a former FDA manager who founded Device Events, which analyzes FDA data, said it defies belief that Johns Dental never received a complaint worthy of relaying to the FDA.
“That’s a red flag for me. If I don’t see a single report to the FDA, I typically think there is something going on,” Kinard said. “When they don’t report, what you have is devices that stay on the market much longer than they should. And patients get harmed.”
Johns Dental Laboratories declined to comment when reached by phone and its lawyers did not respond to requests for an interview. The family-owned company, which has operated since 1939 in the western Indiana city of Terre Haute, sells dozens of products to dentists and makes hundreds of retainers and sleep apnea appliances each month, according to its website.
Twelve of Johns Dental’s products are registered with the FDA as Class II medical devices, meaning they carry at least a moderate risk, and some have been featured on the company website for at least two decades, according to screen captures preserved by the Internet Archive.
The AGGA, which was invented by Tennessee dentist Steve Galella in the 1990s, was not registered with the FDA like Johns Dental’s other devices. Company owner Jerry Neuenschwander has said in sworn court depositions that Johns Dental started making the AGGA in 2012 and became Galella’s exclusive manufacturer in 2015 and that at one point the AGGA was responsible for about one-sixth of Johns Dental’s total sales revenue.
In another deposition, Johns Dental CEO Lisa Bendixen said the company made about 3,000 to 4,000 AGGAs a year and paid Galella’s company a “royalty” of $50 to $65 for every sale.
“We are not dentists. We do not know how these appliances work. All we do is manufacture to Dr. Galella’s specifications,” she said, according to a deposition transcript.
The FDA’s lack of knowledge about the AGGA likely contributed to its loose oversight of Johns Dental. When asked to explain the lack of inspection, the FDA said that, based on what it knew at the time, it was not required to inspect Johns Dental until 2018 when the company registered as a “contract manufacturer” of other medical devices. Prior to 2018, the FDA was only aware of Johns Dental operating as a “dental laboratory,” which normally do not manufacture their own products and only modify devices made by other companies to fit dentists’ specifications. The FDA does not regularly inspect dental labs, although it can if it has concerns or gets complaints, the agency said.
Kinard said that based on her experience at the FDA she believes the agency prioritizes medical devices over dental devices, which may have contributed to the lack of inspections at Johns Dental.
“There hasn’t been much attention to dental devices in the past,” Kinard said. “Hopefully that’s going to change because of dental implant failures, as well as this device, which has quite obviously had serious issues.”
The AGGA resembles a retainer and uses springs to apply pressure to the front teeth and upper palate, according to a patent application. Last year, the KFF Health News-CBS News investigation revealed the AGGA was not backed by any peer-reviewed research and had never been submitted to the FDA for review. At the time, at least 20 patients had alleged in lawsuits that the AGGA had caused grievous harm to their teeth, gums, and bone — and some said they’d lost teeth. Multiple dental specialists said in interviews that they had examined AGGA patients whose teeth had been shoved out of position by the device, sometimes causing tens of thousands of dollars in damage.
“The entire concept of this device, of this treatment, makes zero sense,” said Kasey Li, a maxillofacial surgeon who published research on AGGA patients that appeared on a National Institutes of Health website. “It doesn’t grow the jaw. It doesn’t widen the jaw. It just pushes the teeth out of their original position.
Johns Dental and Galella have negotiated out-of-court settlements with the original 20 AGGA plaintiffs without publicly admitting fault. At least 13 more AGGA patients have filed similar lawsuits since the KFF Health News-CBS News investigation. Johns Dental and Galella denied wrongdoing or have not yet responded to the allegations in the newer lawsuits.
Galella declined to be interviewed in 2023 and neither he nor his attorneys responded to recent requests for comment. One of his attorneys, Alan Fumuso, said in a 2023 statement that the AGGA “is safe and can achieve beneficial results” when used properly.
In the wake of the KFF Health News-CBS News report, Johns Dental abruptly stopped making the AGGA, according to the newly released FDA documents. The Department of Justice soon after opened a criminal investigation into the AGGA that was ongoing as of December, according to court filings. No charges have been filed. A DOJ spokesperson declined comment.
Spurred by the March 2023 news report, the FDA inspected Johns Dental in July. The FDA’s website shows that Johns Dental was issued seven citations, but the substance of the agency’s findings was not known until the inspection report was obtained this year.
FDA investigator David Gasparovich wrote in that report that he arrived unannounced at Johns Dental last July and was met by five attorneys who instructed employees not to answer any questions about the AGGA or the company’s complaint policies. Neuenschwander was told by his attorney not to talk to the inspector, the report states.
“He asked if he could photograph my credentials,” Gasparovich wrote in his report. “This was the last conversation I would have with Mr. Neuenschwander at the request of his attorney.”
The FDA requires device companies to investigate product complaints and submit a “medical device report” to the agency within 30 days if the products may have contributed to serious injury or death. Gasparovich’s inspection report states that Johns Dental had “not adequately investigated customer complaints,” and its complaint policies were “not adequately established,” allowing employees to not investigate if the product was not first returned to the company.
Johns Dental received four complaints about the AGGA after the KFF Health News-CBS News report, including one that came after the FDA announced “safety concerns” about the device, according to the inspection report.
“Zero (0) out of the four (4) complaints were investigated,” Gasparovich wrote in the report. “Each complaint was closed on the same day it was received.”
In the months after Gasparovich’s inspection, Johns Dental sent letters to the FDA saying it revised its complaint policies to require more investigations and hired a consultant and an auditor to address other FDA concerns, according to the documents obtained through FOIA.
Former FDA analyst M. Jason Brooke, now an attorney who advises medical device companies, said the FDA uses an internal risk-based algorithm to determine when to inspect manufacturers and he advises his clients to expect inspections every three to five years.
Brooke said the AGGA is an example of how the FDA’s oversight can be hamstrung by its reliance on device manufacturers to be transparent. If device companies don’t report to the agency, it can be left unaware of patient complaints, malfunctions, or even entire products, he said.
When a company “doesn’t follow the law,” Brooke said, “the FDA is in the dark.”
“If there aren’t complaints coming from patients, doctors, competitors, or the company itself, then in a lot of ways, there’s just a dearth of information for the FDA to consume to trigger an inspection,” Brooke said.
CBS News producer Nicole Keller contributed to this article.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 2 months ago
Health Industry, Dental Health, FDA, Indiana, Investigation, Tennessee, When Medical Devices Malfunction
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Newly Minted Doctors Are Avoiding Abortion Ban States
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
A new analysis finds that graduating medical students were less likely to apply this year for residency training in states that ban or restrict abortion. That was true not only for aspiring OB-GYNs and others who regularly treat pregnant patients, but for all specialties.
Meanwhile, another study has found that more than 4 million children have been terminated from Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program since the federal government ended a covid-related provision barring such disenrollments. The study estimates about three-quarters of those children were still eligible and were kicked off for procedural reasons.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Lauren Weber of The Washington Post, Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University schools of nursing and public health and Politico Magazine, and Anna Edney of Bloomberg News.
Panelists
Anna Edney
Bloomberg
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins University and Politico
Lauren Weber
The Washington Post
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- More medical students are avoiding applying to residency programs in states with abortion restrictions. That could worsen access problems in areas that already don’t have enough doctors and other health providers in their communities.
- New threats to abortion care in the United States include not only state laws penalizing abortion pill possession and abortion travel, but also online misinformation campaigns — which are trying to discourage people from supporting abortion ballot measures by telling them lies about how their information might be used.
- The latest news is out on the fate of Medicare, and a pretty robust economy appears to have bought the program’s trust fund another five years. Still, its overall health depends on a long-term solution — and a long-term solution depends on Congress.
- In Medicaid expansion news, Mississippi lawmakers’ latest attempt to expand the program was unsuccessful, and a report shows two other nonexpansion states — Texas and Florida — account for about 40% of the 4 million kids who were dropped from Medicaid and CHIP last year. By not expanding Medicaid, holdout states say no to billions of federal dollars that could be used to cover health care for low-income residents.
- Finally, the bankruptcy of the hospital chain Steward Health Care tells a striking story of what happens when private equity invests in health care.
Also this week, Rovner interviews KFF Health News’ Katheryn Houghton, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month” feature, about a patient who went outside his insurance network for a surgery and thought he had covered all his bases. It turned out he hadn’t. If you have an outrageous or incomprehensible medical bill you’d like to share with us, you can do that here.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The Nation’s “The Abortion Pill Underground,” by Amy Littlefield.
Joanne Kenen: The New York Times’ “In Medicine, the Morally Unthinkable Too Easily Comes to Seem Normal,” by Carl Elliott.
Anna Edney: ProPublica’s “Facing Unchecked Syphilis Outbreak, Great Plains Tribes Sought Federal Help. Months Later, No One Has Responded,” by Anna Maria Barry-Jester.
Lauren Weber: Stat’s “NYU Professors Who Defended Vaping Didn’t Disclose Ties to Juul, Documents Show,” by Nicholas Florko.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- KFF Health News’ “Medical Residents Are Increasingly Avoiding States With Abortion Restrictions,” by Julie Rovner and Rachana Pradhan.
- CNBC’s “Abortion Bans Drive Away up to Half of Young Talent, New CNBC/Generation Lab Youth Survey Finds,” by Jason Gewirtz.
- The Washington Post’s “Texas Man Files Legal Action To Probe Ex-Partner’s Out-of-State Abortion,” by Caroline Kitchener.
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: Newly Minted Doctors Are Avoiding Abortion Ban States
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, May 9, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this, so here we go. We are joined today via video conference by Lauren Weber of The Washington Post.
Lauren Weber: Hello. Hello.
Rovner: Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University schools of public health and nursing and Politico Magazine.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And Anna Edney of Bloomberg News.
Anna Edney: Hi there.
Rovner: Later in this episode we’ll have my interview with KFF Health News’ Katheryn Houghton, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month.” This month’s patient went out of network for surgery and thought he did everything right. Things went wrong anyway. But first, this week’s news. We are going to start again with abortion this week with a segment I’m calling, “The kids are all right, but they don’t want to settle in states with abortion bans.”
This morning we got the numbers from the Association of American Medical Colleges on the latest residency match. And while applications for residency positions were down in general — more on that in a minute — for the second year in a row, they were down considerably more in states with abortion bans, and to a lesser extent, in states with other abortion restrictions, like gestational limits. And it’s not just in OB-GYN and other specialties that interact regularly with pregnant people. It appears that graduating medical students are trying to avoid abortion ban states across the board. This could well play out in ways that have nothing to do with abortion but a lot more to do with the future of the medical workforce in some of those states.
Edney: I think that’s a really good point. We know that even on just a shortage of primary care physicians and if you’re in a rural area already and you aren’t getting enough of those coming — because you could end up dealing with these issues in primary care and ER care and many other sections where it’s not just dealing with pregnant women all the time, but a woman comes in because it’s the first place she can go when she’s miscarrying or something along those lines. So it could lower the workforce for everybody, not just pregnant women.
Rovner: A lot of these graduating medical students are of the age where they want to start their own families. If not them, they’re worried about their partners. Somebody also pointed out to me — this isn’t even in my story — that graduating medical students tend to wait longer to have their children, so they tend to be at higher risk when they are pregnant. So that’s another thing that makes them worry about being in states where if something goes wrong, they would have trouble getting emergency care.
Weber: I would just add, I mean, you know, a lot of these states also overlap with states that have severe health professional shortages as well. You know, my reporting in St. Louis for KFF Health News — we did a lot of work on how there are just huge physician shortages to start with. So the idea that you’re combining massive gaps in primary care or massive gaps in reproductive health deserts with folks that are going to choose not to go to these places is really a double whammy that I don’t necessarily think people fully grasp at this current point in time.
Rovner: I promised I would explain the reason that applications are down. This is something that’s happening on purpose. There are still more graduating medical students from MD programs and DO [Doctor of Osteopathy] programs and international medical graduates than there are residency slots, but graduating students had been applying to literally dozens and dozens of residencies to make sure they got matched somewhere, and they’re trying to deter that. So now I think students are applying to an average of 30 programs instead of an average of 60 programs.
That’s why it takes so long for them to crunch the numbers because everybody’s doing multiple applications in multiple states and it’s hard to sort the whole thing out. Of course, it may be that they don’t need all of those doctors. Because according to a separate survey from CNBC and Generation Lab, 62% of those surveyed said they probably wouldn’t or definitely wouldn’t live in a state that banned abortion. Seriously, at some point, these states are going to have to balance their state economies against their abortion positions. Now we’re talking about not just the medical workforce, but the entire workforce, at least for younger people.
Edney: Yeah. I was thinking about this recently because during the pandemic you had tech or Wall Street companies looking at Texas or Florida for where they wanted to move their headquarters or move a substantial amount of their company. And then when Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] happened, how is the workforce going to play out? I’m curious what that ends up looking like because many of the people that might want to work for those companies might not want to live there in those states, and I think it could affect how the country is made up at some point. I think what’s still to play out is that over 60% that wouldn’t want to move to a state with abortion restrictions, whether that is something that plays out or whether some people say, “Well, that job’s really good, so maybe I do want to go make a lot more money in this place or whenever.” I’m curious how all of this I think, you know, over the next five years or something, plays out.
Rovner: Yeah. I mean, at some point, this something is better than nothing, that’s true of the residency numbers, too. If the only place you can match is in a state that you’d rather not go, I think most people would rather go somewhere than not be able to pursue their career, and I suspect that’s true for people in other lines of work as well. Well, meanwhile, anti-abortion states are continuing to push the envelope as far as they can. In Louisiana, legislation is moving, it passed the Senate already, to criminalize the act of ordering abortion pills from out of state. It’s scheduling mifepristone and misoprostol in the same category as opioids and other addictive drugs.
Simple possession of either abortion drug without a prescription could result in a $5,000 fine or five years in prison. And in a wild story out of Texas, the ex-partner of a woman who traveled to Colorado for an abortion is attempting to pursue wrongful death claims against anyone who helped her, by helping her with travel or providing money or anything else associated with the abortion. Both of these cases seem like they’re trying to more chill people from attempting to obtain abortions than they are really actually pursuing legal action, right?
Kenen: Well, in that case, he’s pursuing legal action. We don’t know how that’s playing out, but I mean, it’s this accumulation of barriers and threats and making it both more difficult and more risky to obtain an out-of-state abortion or obtain medication abortion in-state. But there’s a big thicket and a lot of it, because it’s in court and it takes years to straighten things out, we don’t know what the final landscape’s going to look like, but obviously the trend is toward greater restriction.
Rovner: And I would point out that the lawyer who’s representing the ex-partner who’s trying to find everyone involved with the ex-partner’s abortion is the lawyer who brought us SB 8 [Senate Bill 8] the law, the “bounty hunter law,” that makes it a crime for people to aid and abet somebody getting an abortion in Texas. Lauren.
Weber: Yeah. I just would add too that tactics like this, whether or not — however they do play out in court, they do have a deterrence effect, right? There’s no way to absolutely tell someone XYZ is legally safe or not. At the end of the day, that can lead to a heck of a lot of misinformation, misconceptions, and different life choices. So I mean, I think the different things that Joanne and Julie are describing lead to people making different choices as all this plays out.
Kenen: I think one of the stories that Julie shared this week — there was an interesting little aside about disinformation, which is the petition to get an abortion rights ballot initiative in, I think it was Missouri. And one of the things in that article was that the anti-abortion forces were telling people that if you sign this petition, you’re vulnerable to identity theft. Now, so that is not true, but it’s just like this misinformation world we’re living in is spilling over into things like, you know, democratic issues of, “Can you get something on the ballot in your state?” It may lose. Missouri is a very conservative state. I don’t know what the threshold is for passage there. I don’t know that it’s as high as the 60% in Florida. But who knows what’s going to happen?
Rovner: That story was interesting, though, because it was the anti-abortion groups were trying to get people not just to not sign the petition.
Kenen: Unsign.
Rovner: Right. They were trying to get people to take their signatures off. And when all was said and done, they had twice as many signatures as they needed to get it on the ballot, so it will be on the ballot. I don’t know either what the threshold is in Missouri ’cause they were playing with that. Lauren, do you know?
Weber: I don’t know what the threshold is, but I will say what I found interesting about that story was that they said they were going to activate the Catholic Church. And as someone who is Catholic and went to Mass during the Missouri eras of Todd Akin and the stem cell fights, activating the Catholic Church could be very effective on changing how the abortion ballot plays out because I’ve seen what that looks like. So I’ll be very curious to see how that plays out in the weeks and months to come.
Kenen: Right. States doing physician-assisted suicide, aid-in-dying bills, have also — people fighting them have activated the church and they’re quite effective.
Rovner: Yeah. But I think Ohio also activated the Catholic Church and it didn’t work out. So I mean, we obviously know from polling Catholics, they’re certainly in favor of contraception and more American Catholics are in favor of abortion rights than I think their priests would like to know, at least that’s what they tell pollsters.
Edney: I also think that activating the church, whatever church it is, is at least a above-the-board tactic where in a lot of ways you never know, but this was so scary because they’re really going out and, not assaulting, but like verbally trying to keep these people from even being able to get signatures, saying that why should we let people vote on something that’s bad for them. Like not giving the electorate the right to make their voices heard. It was pretty scary to see that because of things like Ohio and other abortion rights movements that won that this is what they’re resorting to to try to make sure Missouri goes a different way.
Rovner: Yeah. I think this is going to be a really interesting year to watch because there are so many of them. Well, in abortion travel news, a federal district judge in Alabama green-lighted a suit by abortion rights groups against the state’s attorney general, who was threatening to prosecute those who “aid and abet” Alabama residents trying to leave the state for an abortion. “The right to interstate travel is one of our most fundamental constitutional rights,” Judge Myron Thompson wrote. On the other hand, Idaho was in federal appeals court in Seattle this week arguing just the opposite. They want to have an injunction lifted on its law that would make it a crime to help a minor cross state lines for an abortion. So I guess this particular fight about whether states can have control over their residents’ trying to leave the state for reproductive health care is a fight that’s going to continue for a while.
Edney: I mean, I think that — and sure it’ll continue for a while — you know, my thought when hearing about these cases is sort of just like, I know people that, when there wasn’t really gambling in Maryland, that would get in the bus and the seniors would all go to Delaware and go to the casino and go gambling. Like, we do this all the time. We go to other states for other things — for alcohol, in some cases. It’s just interesting that now they’re trying to make sure that people can’t do that when it comes to women’s rights.
Rovner: Yeah. I know. I mean, there are lots of things that are legal in some states and not legal in others.
Edney: Right.
Rovner: This seems to be, again, pushing the envelope to places we have not yet seen. Well, moving on, it is May, which means it’s time for the annual report of the Medicare and Social Security trustees about the financial solvency of the trust funds, and the news is good, sort of. Medicare’s Hospital Insurance Trust Fund can now pay full benefits until 2036. That’s five years more than the trustees estimated last year, thanks largely to a strong economy, more people paying payroll taxes, and fewer people seeking expensive medical care. But of course, Washington being Washington, good news is also bad news because it makes it less likely that Congress will take on the distasteful task of figuring out how to keep the program solvent for the long term. Are we ever going to get to this or is Congress just going to kick the can down the road until it’s like next year that the trust fund’s going bankrupt?
Kenen: I mean, of all the can-kicking — you know, we’ve used that phrase about Congress frequently — this is the distillation of the essence of kicking the can when it comes to entitlements, right? Both Social Security and Medicare need congressional action to make them viable and sustainable and secure for decades, not years, and we don’t expect that to happen. I mean, even when things are less partisan than they are now, because obviously we’re in a hyperpartisan era, even when Washington functioned better, this was still a kick-the-can issue. Not only was it kick the can, but everybody fought over how to kick the can and where to kick the can and who could kick it furthest. So five extra years is a long time. I mean, it is. But again, the economy changes. Tax revenues change. It’s a cyclical economy. Next year, we could lose the five years or lose two years or gain one year. Who knows? But in terms of a sustained, bipartisan, sensible — no, I’m not holding my breath, because I would get very, very red, very fast.
Rovner: Yeah. And also, I mean, the thing about fixing both Medicare and Social Security is that somebody has to pay more. Either there will be fewer benefits or more taxes, or in the case of Medicare, providers will be paid less. So somebody ends up unhappy. Usually in these compromises, everybody ends up a little bit unhappy. That’s kind of the best possible world. Lauren, you wanted to add something?
Weber: Yeah. I mean, I just wanted to add that if it goes insolvent by 2036, it’s not looking very good for my ability to access these programs.
Kenen: But they always fix it. They always fix it. They just fix it at the last minute.
Weber: That’s true. I mean, I think that’s a fair point, but I do think overall, the concern, it does seem like something will have to change. I don’t think that when I — hope, God willing — live long enough to access this Medicare benefits, that I think they’ll look very different. Because when there is a compromise or there is something like this, there’s just no way the program can continue as it is, currently.
Kenen: The other thing though is this Medicare date probably means there’ll be less campaign. You know, it was beginning to bubble up a little bit on the presidential campaign. I mean, there were plenty of other health care issues to fight about, but it probably means that there’ll be a little bit of token talk about saving Medicare and so forth, but unlikely that there will become a really hot-button issue with either Trump or Biden putting out a detailed plan about it. There’ll be some verbal, “Yes, I’ll protect Medicare,” but I don’t think it’ll be elevated. If it was the other way, if it had lost five years or lost three years, then we would’ve had yet another Medicare election. I think probably we won’t.
Rovner: Yeah. I think that’s exactly right. If the insolvency date had gotten closer, it would’ve been a bigger issue.
Kenen: And remember that the trend toward Medicare Advantage, which is more than people had anticipated, I mean, it is revolutionizing what Medicare looks like. It’s more than half the people now. So there’s many, many sub-cans to kick on that, with private equity and access and prior authorization. I mean, there’s a million things going on there, and payment rates and everything, but that is a slow-motion, dramatic change to Med[icare], not so slow, but that is a dramatic change to Medicare.
Rovner: We’re figuring out how to do sort of a special episode just on Medicare Advantage because there’s so much there. But meanwhile, let’s catch up on Medicaid, ’cause it’s been a while. As one of my colleagues put it on Slack this week, it was a swing and a miss in Mississippi, where some pretty serious efforts to expand Medicaid came to naught as the legislature closed the books on its 2024 session last week. Mississippi is one of the 10 remaining states that have not expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, which could expand health coverage to an estimated 200,000 low-income residents there who lack it now. It feels like these last states, mostly in the South, are going to hold out as long as they can, even though they’re basically giving up a gigantic handout from the federal government.
Edney: It’s billions of dollars they’re leaving on the table and it doesn’t really make sense. This seemed to maybe come down to a work requirement. Maybe there was more there. It was more of a poison pill in that Senate bill instead, but it doesn’t seem to make sense. I mean, even one of the earlier bills the Senate in Mississippi had come up with would have left billions of dollars on the table as well. So I think the idea of this being the central part of Obamacare is still strong in some places.
Kenen: And it also is worth pointing out that these are states not just with the gap in coverage, but most of these states don’t have great health status. They have a lot of chronic disease, a lot of obesity, a lot of addiction, a lot of diabetes, etc. The se are not the healthiest states in the country. You’re not just leaving money on the table; you’re leaving an opportunity to get people care on the table and —
Rovner: And exacerbating health inequities that we already have.
Kenen: Yes. Yes. And when North Carolina decided to, which took many years of arguing about it — that’s a purple state; there were some people who thought it would be a domino: OK, North Carolina stopped holding out; the rest of the South will now. I, never having reported in North Carolina on that, you know, having spent time in the state, I never thought it was a domino. I thought it was just something that went on in North Carolina. Do I think eventually most or all of them will accept Medicaid? Yes. But, you know, we’ve mentioned this before: It took almost 20 years for the original Medicaid to go to all 50 states.
And it’s not just — because North Carolina is North Carolina and South Carolina is different. They have different dynamics. And it’s not over by any means, and there’s no … Mississippi got close. Are they going to pick up where they left off and sort it out next year? Who knows? There’s elections between now and then. We don’t know what the makeup and who is the driver of this, and which chamber there, and who’s retiring, and who’s going to get reelected. We just don’t know exactly. It’s not going to be a dramatic shift, but in these close fights, a couple of seats shifting in state government can change things.
Rovner: That’s what happened in Kansas, although Wyoming came close, I think it was a couple of years ago, and then there I haven’t seen any action either, so.
Kenen: You still hear talk about Wyoming considering it. Like, that’s not off the … I don’t think any of us would be totally shocked if Wyoming is the next one, but I mean it didn’t happen this year, so.
Rovner: Well the other continuing Medicaid story is the “unwinding,” dropping those from coverage who were kept on during the pandemic emergency by a federal requirement. A new report from the Georgetown Center for Children and Families finds that as of the end of 2023, the number of children covered by Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program was down by 10%, or about 4 million. Yet an estimated three-quarters of those kids are actually still eligible. They were struck from the rolls because of a breakdown in paperwork. Texas alone was responsible for more than a million of those disenrollments, a quarter of the total. Texas and Florida together accounted for nearly 40% of those dropped. And Texas and Florida are also the largest states that haven’t expanded Medicaid to the working poor. At some point the problem with the uninsured is going to be back on our radar, right? I mean, we haven’t talked about it for a while because we haven’t sort of needed to talk about it for a while because uninsurance rate has been the lowest it’s been since we’ve been keeping track.
Weber: I just can’t get over that three-quarters of kids lost their coverage due to paperwork issues. I mean, I know we talk about it many times on this podcast, but just to go back to it again: I miss mail. We all miss mail. I’m not someone also that’s moving frequently. That would make it easier to miss mail. I mean, that is just …
Kenen: You speak English.
Weber: Yeah, and I speak English. That is a wild stat, that 75% of these children lost this coverage because of paperwork issues. And as that report discusses, you know, some states did work to mitigate that and other states worked to not mitigate it. And I think that’s an important distinction to be clear about.
Rovner: And I will link to the report because the report shows the huge difference in states, the ones that sort of did it slowly and carefully. I think the part of it that made my hair stand on end was not so much the kids who came off because, you know, the whole family did, because the paperwork issues, but it’s the kids, particularly kids in CHIP who were still eligible when their parents aren’t. And there were some states that just struck families entirely because the parents were no longer eligible without realizing in their own state that parents’ eligibility and kids’ eligibility isn’t the same. And that apparently happened in a lot of cases. And I think the federal government tried to intercede in some of those because those were kids who, by definition of how these programs work, would still be eligible when their parents were not.
Kenen: The one thing it’s always good to remind people that, I mean, this is an extraordinary mess. I mean, it’s not the unwinding, it’s the unraveling. But unlike employer-sponsored insurance and the Obamacare exchanges, there’s no enrollment season for Medicaid. You can get in if you qual … so it can be the unwinding could be rewound. If a child gets sick and they are in an ER or they’re in a hospital or in a doctor’s or whatever, they can get back in quickly. It is a 365-day, always-open, for both Medicaid and CHIP in I believe every state. There may be an exception I’m not aware of, but I think it’s everywhere.
Rovner: I think it’s everywhere. I think it’s a requirement that it’s everywhere.
Kenen: I think it’s federal, right. So yes, it’s a mess, but unlike many messes in health care, it is a mess that can be improved. Although of course not everybody knows that and somebody will be afraid to go to the doctor ’cause they can’t pay, etc., etc. I’m not minimizing what a mess it is. But if you get word out, you can get word out to people that, you know, if you’re sick, go to the doctor. You’re still being taken care of.
Rovner: And also when people do go to the doctor, at the same time they’re told, uh-oh, your Medicaid’s been canceled, they can be reenrolled if they’re still eligible.
Kenen: Yeah, right. I mean, community health clinics know that. Hospitals know that. I don’t know that all private physicians’ offices know that, but …
Rovner: Although they should —
Kenen: They should.
Rovner: — because that’s how they’ll get paid.
Kenen: They should.
Rovner: So I suspect — providers have an incentive to know who’s eligible because otherwise they’re not going to get paid.
Kenen: So that should be the next public campaign. If you lost your Medicaid, here’s how you get it back. And we don’t see enough of that.
Rovner: Last week we talked about a lot of health-related regulations the Biden administration is trying to finalize. If it seems they’re all happening at once, there is an actual reason for that. It’s called the Congressional Review Act. Basically the CRA lets a new Congress and administration easily undo regulations put in place by an earlier administration towards the end of a presidential term. Basically that means any regulations the Biden administration doesn’t want easily overturned by the next Congress and president, should it return to Republican hands, those regulations need to be completed roughly by the end of this month. Towards that end, and as I said, speaking of looking at the problem of the uninsured, last week the administration finalized a rule that would give people here under DACA, that’s the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals immigration program, access to subsidized coverage under the Affordable Care Act.
These are about 100,000 so-called Dreamers, those who are not here legally but were brought over as children. In general, those who are not in the country legally are not able to access Affordable Care Act coverage. That was a gigantic fight when the Affordable Care Act was being passed. In some ways, though, I feel like this addition of Dreamers to the ACA is an acknowledgement that they’re not going to get full legal status anytime soon, which has also been a fight that’s been going on for years and years.
Kenen: Yes. And I was wondering, like, who’s going to sue to stop this or introduce legislation? I mean, somebody will do something. I’m not sure what yet. I mean, I would be surprised if nobody tries to block this because there’s obviously controversy about normalizing the status of the Dreamers or the DACA population and it’s been going on for years. We’ll see. I mean, it’s just another, I mean, immigration is such a flash point in this year’s election. Maybe people will say, “OK, this portion of the Dreamers has legal status and they can get health insurance” and people won’t fight about it. But usually nowadays people fight about — I mean, if the intersection of health care and immigration, I would think somebody will fight about it.
Rovner: Yeah. I would, too. And also, I mean obviously the people who are preventing legislation from getting through to legalize the Dreamers’ status, there seems to be, I believe, there is overwhelming support in both houses, but not quite enough to get it through. I suspect those people on the other side might not be very happy about this. Well, finally this week in business, or more specifically this week in private equity in health care, the multistate hospital chain Steward Health [Care] filed for bankruptcy this week, putting up for sale all 31 of its hospitals, which normally wouldn’t be really big news. Lots of hospitals are having trouble keeping their doors open. But in this case, we’re talking about a chain that was pretty large and stable until it was bought by Cerberus Capital Management, a private equity firm.
Cerberus sold off the land the hospitals were on, requiring them to pay rent to yet another company, and then Cerberus got out. The details of the many transactions that took place are still kind of murky, but it appears that many investors did quite well, including acquisitions of some private yachts, while the hospitals, well, did not do so well. This all has yet to play out fully. But this seems to be pretty much how private equity often works, right? They buy something, take the profit that they can, and leave the rest to the whims of the marketplace, or in this case billions of dollars in debt now owed by these hospitals.
Weber: Yeah. I mean, I think when you look at private equity the question is always when is the multipliers going to run out? Like, when are you going to run out of things to sell to get the multipliers out? And the question is, when you do this with health care, you know, we’ve seen some emerging research show that the patient outcomes for private equity-owned health care systems can be impacted by infection rates and so on. And I mean, I thought it was particularly interesting at the end of this Wall Street Journal story, they also noted how UnitedHealthcare, there is some investigations over —
Rovner: They’re tangentially involved.
Weber: They’re tangentially involved, but the government appeared — the story seems to allude to the government is interested in whether there’s some antitrust concerns on selling the doctors’ practices, which is obviously an ongoing issue as well as we talk about health care and acquisitions and consolidation in the country. So, 31 hospitals’ being insolvent is a lot of hospitals in a lot of states.
Rovner: Yeah. And I mean, the idea, I think, was that one of the ways they were going to pay off some of their debts was by selling the doctor practices to United. United, of course, now under the microscope for antitrust, might not be such an eager buyer, which leaves Steward holding the bag again with all of this debt. They owe literally billions of dollars to this company that now owns the land that their hospitals are on. It is quite the saga.
Kenen: It’s very complicated. I mean, I had to read everything more than once to understand it, and I’m not sure I totally understood all of it. It’s also sort of like the, you know, if you were writing, if you were teaching business school about what can go wrong when private equity buys a health system, this would be your final exam question. It is very complicated, extremely damaging, and the critics of PE in health care — I mean this is everything they warn about. And I would also, since all of us are journalists, I mean the same thing is going on with private equity in owning newspapers or newspaper chains: wreckage. Not everyone is a bad actor. There’s wreckage in health care and there’s wreckage in the media.
Rovner: Yeah. We will watch this one to see how it plays out. All right, that is this week’s news. Now we will play my “Bill of the Month” interview with Katheryn Houghton and then we will be back with our extra credits. I am pleased to welcome to the podcast my KFF Health News colleague, in person, here in our Washington, D.C., studio, Katheryn Houghton, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month.” It’s about an out-of-network surgery the patient knew would be expensive, but not how expensive it would be. Welcome, Katheryn.
Houghton: Hi.
Rovner: So tell us about this month’s patient, who he is, and what kind of treatment he got.
Houghton: So I spoke with Cass Smith-Collins. He’s a 52-year-old transgender man from Vegas, and he wanted to get surgery to match his chest to his gender identity, so he got top surgery.
Rovner: This was a planned surgery and he knew he was going to go out of network. So what kind of steps did he take in preparation to make sure that the surgery would be at least partially covered by his health insurance?
Houghton: Well, he actually took a really key step that some patients miss, and it’s making sure that you get prior authorization from insurance, so a letter from them saying we’re going to cover this. And he got that. He also talked with his surgeon beforehand, saying what do I need to do to make sure we can submit a claim with insurance? And he signed paperwork saying how that would happen.
Rovner: Then, as we say, the bill came. What went awry?
Houghton: Yeah. Or in this case the reimbursement didn’t come. For Cass’ case there are two key things that kind of went awry here. First off, covered doesn’t necessarily mean the entire bill. So what insurance says is a fair price is not going to match up with what the surgeon always says is a fair price. So when Cass saw that his procedure was covered, it didn’t say the entire amount. It didn’t say how much was covered. The second thing is that that provider agreement that he signed with the surgeon beforehand actually says you’re not guaranteed reimbursement. And that provider agreement also stated there are two different bills here. One is the cost that Cass paid up-front for his surgery, and the other was the bill submitted to insurance.
Rovner: And how much money are we actually talking about here?
Houghton: We’re talking about $14,000. And he expected to get about half of that back.
Rovner: Because he assumed that when he got to his out-of-network maximum the insurance would cover, right?
Houghton: Exactly.
Rovner: And that’s not what happened.
Houghton: Not at all.
Rovner: How much did the surgeon end up charging for the surgery and what did his insurance say about that?
Houghton: If you’re looking at both bills, the surgeon charged more than $120,000 for the surgery and insurance said ah, no, we’re not going to cover that. And it was a little over $4,000 that insurance said, this is the fair price.
Rovner: So that’s a big difference.
Houghton: A very big difference.
Rovner: Was Cass expected to pay the rest?
Houghton: He could have. The agreement that he signed actually said that he could be on the hook for whatever insurance didn’t cover. That being said, he didn’t get a bill this time around.
Rovner: So what eventually happened?
Houghton: So eventually, when KFF Health News started asking questions about this, insurance increased how much that they paid the provider. And with that increased reimbursement, which was $97,000, the provider gave Cass a reimbursement of about $7,000.
Rovner: So he ended up paying about $7,000 out-of-pocket.
Houghton: It was more towards the line of what he was expecting to pay for this.
Rovner: Right. I was just going to say that was about what his out-of-pocket maximum was. But in this case he was kind of just lucky, right?
Houghton: Yes. I mean the paperwork that he signed in advance — it was really confusing paperwork. We had several experts look over this and say, yeah, there are things in this we don’t fully understand what it means.
Rovner: What’s the takeaway here? A lot of people want to go to a particular provider who may be very good at what they do but don’t take insurance. Is there any way that he could have better prepared for this financially or that somebody looking at a similar kind of situation and doesn’t want to end up having someone say, oh, you owe us $80,000?
Houghton: Right. Yeah. So for this case it was really important for Cass to go to a surgeon that he felt like he could trust. And so if you do have that out-of-network provider, there are a few steps you can actually take. There’s still no guarantees, but there are steps. First off, patients should always ask their insurance company what covered actually means. Are you talking the entire bill here? Are you talking just a portion of it? Try to get that outlined. You can also ask your insurance company to spell out the dollar amount that they’re willing to pay for this. That’s a really helpful step. And lastly, on the provider side, you can also say, “Hey, whatever insurance deems as a fair payment, can we count that as the total bill?” You can always ask that. They’re not required, but it’s worth checking.
Rovner: Yeah. So at least you go in with your eyes open knowing what your maximum is going to be.
Houghton: Exactly. Especially if you’re paying out-of-pocket to begin with. You really want to know what is insurance reimbursing for this? What is the provider going to charge me more at the end of this?
Rovner: Well, I’m glad this one had a happy ending. Katheryn Houghton, thank you very much.
Houghton: Thank you so much.
Rovner: OK, we are back. It’s time for our “extra credit” segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Anna, why don’t you go first this week?
Edney: Sure. So mine is from ProPublica by Anna Maria Barry-Jester and it’s “Facing Unchecked Syphilis Outbreak, Great Plains Tribes Sought Federal Help. Months Later, No One Has Responded.” And I think we have even heard over the last few years the story of syphilis rates rising and in this specific look at the Great Plains, there are Native Americans there, that the syphilis rates are even worse. And this is resulting in deaths of babies, like wanted children. And it seems like the federal government has been pretty lackluster in its response, to put it mildly, sending a few CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] workers for a couple of weeks, and the tribes have been asking for basically a national emergency so they can get more help. And they’ve gone straight to HHS [Health and Human Services] Secretary [Xavier] Becerra, and at least in the last several weeks as this was being reported, they haven’t gotten any response or any help. So I think it’s an important story to spread far and wide.
Rovner: It is. Joanne?
Kenen: There was a very interesting op-ed in The New York Times this week by Dr. Carl Elliott, who is a physician and bioethicist at the University of Minnesota: “In Medicine, the Morally Unthinkable Too Easily Comes to Seem Normal.” It’s a little hard to summarize, but it’s very subtle. It’s the culture of medicine, of being a medical student or a resident, and the things you see, so much of what you see, shocks you anyway because it’s something you have to get used to. But there are outrages. He begins, the opening anecdote is a woman is unconscious and anesthetized before her surgery and the doctor in charge invites all the med students to come and like, “Oh, why don’t you come touch her cervix? She’ll never know. See what it’s like.”
And to that, to really the larger, even larger questions about how did Willowbrook [State School] survive for all those years? How did the Tuskegee studies go on for all those years? You know, at what point, what are the sort of cultural and peer pressure and dynamics of these outrages, big and large, becoming normalized? And, you know, as we know, like recently HHS just said you have to have a written consent for a pelvic exam, particularly if you’re going to be unconscious. But that’s only one example — it was a very disturbing piece actually.
Rovner: Yeah. It really was. Lauren?
Weber: I chose Nicholas Florko’s piece on how “NYU Professors Who Defended Vaping Didn’t Disclose Ties to Juul, Documents Show,” in Stat. Great piece. He dug through a bunch of the Juul legal documents that have been revealed to show how two prominent NYU public health professors were communicating with Juul about their comments in both a congressional hearing and then public comments to many, many journalists defending vaping and saying that, you know, it had public health benefits because it got people off of cigarettes. And it raises up a lot of thorny questions about conflict of interest. These public health officials say they were not paid by Juul, but they did accept dinners. And the question is, you know, a lot of the studies they submitted, one of them they even sent to Juul. It’s a lot of thorny questions about academic review and disclosures. It’s a great piece, too, and a warning for all journalists of who are you interviewing, what are their ties, and what are the disclosures that they may or may not be sharing? It was a great story.
Rovner: Yeah. Super thought-provoking. I will say, every time I speak — and we don’t take money for speaking — all of my speeches are for free. But I constantly, you know, they now have to fill out that, “Do you have any conflicts of interest?” And it’s like, no, I don’t take any money from any industry. But it’s all basically self-reported, and I think that’s one of the big problems with this whole issue. Well, my story this week is from The Nation. It’s by Amy Littlefield. It’s called “The Abortion Pill Underground.” And it’s not the first story like this, but it’s a very comprehensive look at the fight that’s shaping up between blue states that are passing shield laws to protect doctors who are providing abortion medication to patients in red states where, as we discussed earlier, prosecutors would like to reach back to punish those blue-state providers. It’s a fairly small group of providers operating in what is still a legally gray area.
As we mentioned, this is all still under — in court, in various places at various levels — but I do think it’s one of the next big battles that are shaping up in reproductive health. It’s a really good piece. OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org, or you can still find me at Twitter, @jrovner, or @julierovner at Bluesky and @julie.rovner at Threads. Joanne, are you hanging anywhere on social media?
Kenen: A little bit on Twitter @JoanneKenen, not even that much. But more on Threads @joannekenen1.
Rovner: Anna?
Edney: @annaedney on Twitter and @anna_edneyreports on Threads.
Rovner: Lauren?
Weber: Still only on Twitter, @LaurenWeberHP. HP is for health policy.
Rovner: Don’t apologize. You can find us all if you really want to. We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 2 months ago
Courts, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Abortion, Doctors, Hospitals, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Medical Education, Missouri, Podcasts, reproductive health, texas, Women's Health
La gripe aviar es mala para las aves de corral y las vacas lecheras. No es una amenaza grave para la mayoría de nosotros… por ahora
Los titulares explotaron después que el Departamento de Agricultura confirmara que el virus de la gripe aviar H5N1 ha infectado a vacas lecheras en todo el país.
Las pruebas han detectado el virus en el ganado en nueve estados, principalmente en Texas y Nuevo México, y más recientemente en Colorado, dijo Nirav Shah, director principal adjunto de los Centros para el Control y Prevención de Enfermedades (CDC), en un evento del 1 de mayo.
Otros animales, y al menos una persona en Texas, también se infectaron con el H5N1. Pero lo que más temen los científicos es si el virus se propagara de manera eficiente de persona a persona. Eso no ha sucedido y podría no suceder. Shah dijo que los CDC consideran que el brote de H5N1 “es un riesgo bajo para el público en general en este momento”.
Los virus evolucionan y los brotes pueden cambiar rápidamente. “Como con cualquier brote importante, esto se mueve a la velocidad de un tren bala”, dijo Shah. “De lo que hablamos ahora es de un instantánea de ese tren que se mueve rápidamente”. Lo que quiere decir es que lo que hoy se sabe sobre la gripe aviar H5N1 seguramente cambiará.
Con eso en mente, KFF Health News explica lo que se necesita saber ahora.
¿Quién contrae el virus que causa la gripe aviar?
Principalmente las aves. Sin embargo, en los últimos años, el virus de la gripe aviar H5N1 ha estado saltando cada vez más de las aves a los mamíferos en todo el mundo. La creciente lista, de más de 50 especies, incluye focas, cabras, zorrinos, gatos y perros salvajes en un zoológico en el Reino Unido. Al menos 24,000 leones marinos murieron en brotes de gripe aviar H5N1 en Sudamérica el año pasado.
Lo que hace que el brote actual en el ganado sea inusual es que se está propagando rápidamente de vaca a vaca, mientras que los otros casos, excepto las infecciones de leones marinos, parecen limitados. Los investigadores saben esto porque las secuencias genéticas de los virus H5N1 extraídos de las vacas este año eran casi idénticas entre sí.
El brote de ganado también preocupa porque agarró al país desprevenido. Los investigadores que examinan los genomas del virus sugieren que originalmente se transmitió de las aves a las vacas a finales del año pasado en Texas, y desde entonces se ha propagado entre muchas más vacas de las que se han examinado.
“Nuestros análisis muestran que esto ha estado circulando en vacas durante unos cuatro meses, bajo nuestras narices”, dijo Michael Worobey, biólogo especializado en evolución de la Universidad de Arizona en Tucson.
¿Es este el comienzo de la próxima pandemia?
Aún no. Pero es algo que vale la pena considerar porque una pandemia de gripe aviar sería una pesadilla. Más de la mitad de las personas infectadas por cepas anteriores del virus de la gripe aviar H5N1 de 2003 a 2016 murieron.
Incluso si las tasas de mortalidad resultan ser menos severas para la cepa H5N1 que circula actualmente en el ganado, las repercusiones podrían implicar muchas personas enfermas y hospitales demasiado abrumados para manejar otras emergencias médicas.
Aunque al menos una persona se infectó con el H5N1 este año, el virus no puede provocar una pandemia en su estado actual.
Para alcanzar este horrible estatus, un patógeno necesita enfermar a muchas personas en varios continentes. Y para lograrlo, el virus H5N1 necesitaría infectar a toneladas de personas. Eso no sucederá a través de saltos ocasionales del virus de los animales de granja a las personas. Más bien, el virus debe adquirir mutaciones para propagarse de persona a persona, como la gripe estacional, como una infección respiratoria transmitida principalmente por el aire cuando las personas tosen, estornudan y respiran.
Como aprendimos de covid-19, los virus transmitidos por el aire son difíciles de frenar.
Eso aún no ha sucedido. Sin embargo, los virus H5N1 ahora tienen muchas oportunidades para evolucionar a medida que se replican dentro de los organismos de miles de vacas. Como todos los virus, mutan a medida que se replican, y las mutaciones que mejoran la supervivencia del virus se transmiten a la próxima generación. Y debido a que las vacas son mamíferos, los virus podrían estar mejorando en reproducirse dentro de células más cercanas a las nuestras que las de las aves.
La evolución de un virus de gripe aviar listo para una pandemia podría facilitarse por una especie de superpoder que poseen muchos virus. Es decir, a veces intercambian sus genes con otras cepas en un proceso llamado recombinación.
En un estudio publicado en 2009, Worobey y otros investigadores rastrearon el origen de la pandemia del virus de la gripe porcina H1N1 en eventos en los que diferentes virus que causaban esta gripe, la gripe aviar y la gripe humana mezclaban y combinaban sus genes dentro de cerdos que se estaban infectando simultáneamente. Los cerdos no necesitan estar involucrados esta vez, advirtió Worobey.
¿Comenzará una pandemia si una persona bebe leche contaminada con el virus?
Aún no. La leche de vaca, así como la leche en polvo y la fórmula infantil, que se venden en tiendas se consideran seguras porque la ley requiere que toda la leche vendida comercialmente sea pasteurizada. Este proceso de calentar la leche a altas temperaturas mata bacterias, virus y otros microorganismos.
Las pruebas han identificado fragmentos de virus H5N1 en la leche comercial, pero confirman que los fragmentos del virus están muertos y, por lo tanto, son inofensivos.
Sin embargo, la leche “cruda” no pasteurizada ha demostrado contener virus H5N1 vivos, por eso la Administración de Drogas y Alimentos (FDA) y otras autoridades sanitarias recomiendan firmemente a las personas que no la tomen, porque podrían enfermarse de gravedad o algo peor.
Pero, aún así, es poco probable que se desate una pandemia porque el virus, en su forma actual, no se propaga eficientemente de persona a persona, como lo hace, por ejemplo, la gripe estacional.
¿Qué se debe hacer?
¡Mucho! Debido a la falta de vigilancia, el Departamento de Agricultura (USDA) y otras agencias han permitido que la gripe aviar H5N1 se propague en el ganado, sin ser detectada. Para hacerse cargo de la situación, el USDA recientemente ordenó que se sometan a pruebas a todas las vacas lecheras en lactancia antes que los ganaderos las trasladen a otros estados, y que se informen los resultados de las pruebas.
Pero al igual que restringir las pruebas de covid a los viajeros internacionales a principios de 2020 permitió que el coronavirus se propagara sin ser detectado, testear solo a las vacas que se mueven entre estados dejaría pasar muchos casos.
Estas pruebas limitadas no revelarán cómo se está propagando el virus entre el ganado, información que los ganaderos necesitan desesperadamente para frenarlo. Una hipótesis principal es que los virus se están transfiriendo de una vaca a la siguiente a través de las máquinas utilizadas para ordeñarlas.
Para aumentar las pruebas, Fred Gingrich, director ejecutivo de la American Association of Bovine Practitioners, dijo que el gobierno debería ofrecer fondos a los ganaderos para que informen casos y así tengan un incentivo para hacer pruebas. De lo contrario, dijo, informar solo daña la reputación por encima de las pérdidas financieras.
“Estos brotes tienen un impacto económico significativo”, dijo Gingrich. “Los ganaderos pierden aproximadamente el 20% de su producción de leche en un brote porque los animales dejan de comer, producen menos leche, y parte de esa leche es anormal y no se puede vender”.
Gingrich agregó que el gobierno ha hecho gratuitas las pruebas de H5N1 para los ganaderos, pero no han presupuestado dinero para los veterinarios que deben tomar muestras de las vacas, transportar las muestras y presentar los documentos. “Las pruebas son la parte menos costosa”, explicó.
Si las pruebas en las granjas siguen siendo esquivas, los virólogos aún pueden aprender mucho analizando secuencias genómicas del virus H5N1 de muestras de ganado. Las diferencias entre las secuencias cuentan una historia sobre dónde y cuándo comenzó el brote actual, el camino que recorre y si los virus están adquiriendo mutaciones que representan una amenaza para las personas.
Sin embargo, esta investigación vital se ha visto obstaculizada porque el USDA publica los datos incompletos y con cuentagotas, dijo Worobey.
El gobierno también debería ayudar a los criadores de aves de corral a prevenir brotes de H5N1, ya que estos matan a muchas aves y representan una amenaza constante de potenciales saltos de especies, dijo Maurice Pitesky, especialista en enfermedades de aves de la Universidad de California-Davis.
Las aves acuáticas como los patos y los gansos son las fuentes habituales de brotes en granjas avícolas, y los investigadores pueden detectar su proximidad mediante el uso de sensores remotos y otras tecnologías. Eso puede significar una vigilancia rutinaria para detectar signos tempranos de infecciones en aves de corral, usar cañones de agua para ahuyentar a las bandadas migratorias, reubicar animales de granja o llevarlos temporalmente a cobertizos. “Deberíamos estar invirtiendo en prevención”, dijo Pitesky.
Bien, no es una pandemia, pero ¿qué podría pasarle a las personas que contraigan la gripe aviar H5N1 de este año?
Realmente nadie lo sabe. Solo una persona en Texas fue diagnosticada con la enfermedad este año, en abril. Esta persona trabajaba con vacas lecheras, y tuvo un caso leve con una infección en el ojo. Los CDC se enteraron de esto debido a su proceso de vigilancia. Las clínicas deben alertar a los departamentos de salud estatales cuando diagnostican a trabajadores agrícolas con gripe, utilizando pruebas que detectan virus de la influenza en general.
Los departamentos de salud estatales luego confirman la prueba y, si es positiva, envían una muestra de la persona a un laboratorio de los CDC, donde se verifica específicamente la presencia del virus H5N1. “Hasta ahora hemos recibido 23”, dijo Shah. “Todos menos uno resultaron negativos”.
Agregó que funcionarios del departamento de salud estatal también están monitoreando a alrededor de 150 personas que han pasado tiempo alrededor de ganado. Están en contacto con estos trabajadores agrícolas con llamadas telefónicas, mensajes de texto o visitas en persona para ver si desarrollan síntomas. Y si eso sucede, les harán pruebas.
Otra forma de evaluar a los trabajadores agrícolas sería testear su sangre en busca de anticuerpos contra el virus de la gripe aviar H5N1; un resultado positivo indicaría que podrían haberse infectado sin saberlo. Pero Shah dijo que los funcionarios de salud aún no están haciendo este trabajo.
“El hecho de que hayan pasado cuatro meses y aún no hayamos hecho esto no es una buena señal”, dijo Worobey. “No estoy muy preocupado por una pandemia en este momento, pero deberíamos comenzar a actuar como si no quisiéramos que sucediera”.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 2 months ago
Health Industry, Noticias En Español, Public Health, Rural Health, Colorado, FDA, Food Safety, New Mexico, texas
An Arm and a Leg: The Hack
When Change Healthcare, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group, got hit by a cyberattack this winter, a big chunk of the nation’s doctors, pharmacists, hospitals, and therapists stopped getting paid.
When Change Healthcare, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group, got hit by a cyberattack this winter, a big chunk of the nation’s doctors, pharmacists, hospitals, and therapists stopped getting paid. The hack also limited health providers’ ability to share medical records and other information critical to patient care.
The cyberattack revealed an often overlooked part of how health care is paid for in the United States and raised concerns for antitrust advocates about how large UnitedHealth has grown.
Host Dan Weissmann speaks with reporters Brittany Trang of Stat News and Maureen Tkacik of The American Prospect about their reporting on the hack and what it says about antitrust enforcement of health care companies.
Dan Weissmann
Host and producer of "An Arm and a Leg." Previously, Dan was a staff reporter for Marketplace and Chicago's WBEZ. His work also appears on All Things Considered, Marketplace, the BBC, 99 Percent Invisible, and Reveal, from the Center for Investigative Reporting.
Credits
Emily Pisacreta
Producer
Adam Raymonda
Audio wizard
Ellen Weiss
Editor
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: The Hack
Note: “An Arm and a Leg” uses speech-recognition software to generate transcripts, which may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
Dan: Hey there.
Brittany Trang is a reporter at STAT News– that’s a health care news outlet. We talked with Brittany’s colleague Bob Herman in our last episode. Like Bob, she’s been covering the business of health care.
And for Brittany, this story starts with Bob flagging a story to their team. He…
Brittany Trang: Dropped a link in the chat that said like, hey guys, I think we should write about this, question mark, and nobody replied,
Dan: The story was about a cyber-attack against a company called Change Healthcare.
Brittany Trang: I was like that sounds like a startup and I was like who cares about some sort of health tech startup
Dan: But Bob kept bringing it up.
Brittany Trang: And I finally clicked on the link, and I was like, oh no, this is a big deal. This touches most of the American healthcare system.
Dan: Yeah, and it’s no joke. Change Healthcare is what’s called a data clearinghouse. And it’s a big one. It’s an important part of health care’s financial plumbing. Someone had gone in and basically hijacked their computer system and said, Unless we get $22 million dollars, we’re not giving it back. So Change went offline, and a huge chunk of the country’s Pharmacists, doctors, therapists, hospitals just stopped getting paid. And Change Healthcare stayed offline for weeks and weeks. As we record this, seven weeks in, big parts of it remain offline. And here’s this other thing: Change Healthcare is not a startup. It’s been around for like 20 years. And in late 2022, Change got purchased by another company– a company that’s starting to become a real recurring character on this show: UnitedHealth Group.
You may remember: They’re the country’s biggest insurance company AND they’ve got their hands in just about every other part of health care, in a big way. For instance, they’re the very biggest employer of physicians in the country, by a huge margin. They’ve got their own bank, which– among other things– offers payday loans to doctors. And they have a huge collection of companies that do back-end services. In our last episode we heard about Navi Health— and how, under United’s ownership, insurance companies have been using NaviHealth’s algorithm to cut off care for people in nursing homes. [Boy, yeah– that was a fun story…] And as we’ve been learning: When one company like this gets so big, their problems– like this cyber-attack– become everybody’s problem. And in this case, everybody’s problem seems to create an opportunity for United. We’ll break down how THAT could possibly work, but obviously it doesn’t seem like the way a lot of us would WANT things to work.. And we’ll end up talking about what we can maybe do about it. Not “we” as in a bunch of individuals trying to tackle an opponent this big. Good luck with that. But “we” as in the “We the people” of the United States Constitution. We may already be on the case.
This is An Arm and a Leg– a show about why health care costs so freaking much, and what we can maybe do about it. I’m Dan Weissmann. I’m a reporter, and I like a challenge. So our job on this show is to take one of the most enraging, terrifying, depressing parts of American life, and bring you a show that’s entertaining, empowering, and useful.
We’ll start with an attempt to answer what you’d think would be a simple question: What does Change Healthcare do?
Here’s Brittany Trang from STAT News again.
Brittany Trang: It’s kind of like Visa or Mastercard or something. Like, when you go to the grocery store and you pay with a credit card, you are not putting your money directly into the pockets of the grocery store. There’s a middleman in there and change is that middleman, but for a ton of different things.
Dan: Like insurance claims. Brittany says hospitals and doctors offices often don’t submit claims directly to insurance companies. They send the claim to a middleman like Change. And then Change figures out where that claim needs to go next. Like: I’m sending a bunch of mail– I put it all in one mailbox, and the post office figures out how to get it where it goes. Except of course, there’s no paper here, no envelopes, no physical packages: All those claims are basically data. Which is why a company like Change is called a data clearinghouse. And even if a given provider uses some other clearinghouse– and of course there are others– Change may still be involved. Because INSURANCE companies like Aetna also use Change as a place to COLLECT claims from providers. On that side, Change is kind of like a post-office box. But claims are just one of the types of data that Change handles. For instance…
Brittany Trang: when you went to the pharmacy counter or when you would check in at the doctor’s office and they take your insurance information and figure out like what you’re going to pay for this visit. Both of those processes were messed up.
Dan: Yeah, and there’s more! Prior authorizations– like when your doctor checks in advance to make sure your insurance company is OK with paying for whatever. Those all go through companies like Change. So, if change is offline, do they do your MRI, or your surgery– and just hope it doesn’t get denied when Change comes back? And once claims get approved, data for payments goes through Change too. So payments– a lot of payments– just stopped going out. Here’s Brittany Trang.
Brittany Trang: it’s just kind of flabbergasting how big this is. This collapsed most of healthcare in some way or another.
Dan: Overall, the numbers are wild: Change reportedly processes 1.5 trillion dollars a year in claims. Maybe a third of everything that happens in healthcare. According to the American Hospital Association, 94 percent of hospitals said they were affected. Some more than others. Not all providers use Change as their primary clearinghouse. But lots do. And for them, everything just stopped.
Brittany Trang: I talked to one provider she’s like, Oh, I can, I can talk. I’m, here today and tomorrow before we close. And I was like, before we close for spring break. And she said, no, we have 3 and 13 cents left in our bank account. Brittany says that provider got a last minute reprieve– an emergency loan from United. There have been two or three rounds of these loans so far, plus some advance payments from Medicare. But as the outage has dragged on– it started in February, and we’re recording this seven weeks later– it’s hard to know if those are going to be enough. At the end of March, I talked with Emily Benson. She runs a therapy practice in a Minneapolis suburb. Eight clinicians, mostly treating kids. She says the practice does maybe 70 or 80 thousand dollars worth of business a month. But then in February… Emily Benson: essentially everything went dark for us.
Dan: United publicly acknowledged the Change hack on February 21st. But Emily Benson says she didn’t actually get a heads-up until almost a week later.
Emily Benson: a lot of alarm bells went off, that was the end of the month. And so a lot of payments came due
Dan: Her rent. Paychecks for her colleagues, and herself.
Emily Benson: I mean, I was in a panic. Y’know, I didn’t know where I was going to go.
Dan: She says she usually gets two payments a week from insurance, with everything passing through Change. But it’s not just the payments from insurance. Change also provides the documents that say how much an insurance company is GOING to pay for any given claim.
Emily Benson: That’s a critical document because that tells me what does the family owe us. And then the beneficiary is also going to get that information. So they’re not surprised by what we charge them. So now every week we’re stacking up and stacking up these amounts that the family’s going to owe us.
Dan: By the time we talked, Emily Benson had gotten two loans from United. About 40,000 each: maybe a month’s worth of billing for her, between the two loans.
Emily Benson: That first one was wiped out. Pretty quickly because now we’re on week five I’m working on the second, um, installment that I got from united. But, you know, that’s half gone now too. So I don’t know what the next step is. We’re nowhere near. Getting claims processing yet and so. I’m kind of panicking Yeah.
Emily Benson: it looks like the terms are within 45 days. You have to pay back that temporary loan. How am I going to do that if I don’t have claims coming?
Dan: God.
Emily Benson: I’m still panicking.
Dan: I’ll bet. Oh my God. You’re very, you’re very calm for somebody in this situation.
Emily Benson: Well, you know, I’ve had a lot of therapy of my own. That’s how you become a therapist. So panicking doesn’t help anyone.
Dan: I guess that’s, I’ll take that under advisement.
Dan: So, to pay back those loans– which are supposed to be repaid within 45 days– Emily Benson is gonna have to start getting paid again. As we spoke, she’d had been living without systems for filing claims and getting paid for five weeks. And even when those systems get moving again, she’s not gonna see all that money right away.
Emily Benson: Imagine the backlog and the clog. Five weeks worth of insurance claims I mean, we’re looking at a major traffic jam.
Dan: Oh myGod.Andif everybody were to work double time for the next five weeks, then it would be 10 weeks. But people can’t really work double time.
Emily Benson: When you say that out loud,
Dan: Sorry.
Emily Benson: I don’t feel as grounded,
Dan: I’m so sorry.
Emily Benson: but, but, but it’s probably realistic.
Dan: Other news outlets are talking to providers like Emily Benson all over the country. We’re recording this in mid-April. United hasn’t responded to our questions on this story, but their website says “We’re determined to make this right.” It says they’ve put out 4 point 7 billion dollars in emergency loans to providers so far. And it says that for the vast majority of Change Healthcare’s services, a restoration date is “still pending.” We have no idea what’s going to happen. What it’ll mean for our doctors, our therapists, our local hospitals. And look, there are elements of this story that go beyond health care. How many of us have personal health information– maybe financial information– that got seized by who the heck knows who in this? And yes, United’s getting some heat. They got a list of pointed questions from U.S. Representative Jamie Raskin. Their CEO is supposed to testify in a Senate hearing at the end of April. But as we’ll get into in a minute, this disaster– United’s disaster– could turn out to have a silver lining– for United: An opportunity to keep on growing. And that opportunity arises precisely because they’re so big, and doing so much business in so many parts of the medical-industrial complex. Which doesn’t sound great. It raises questions about the, uh, potential downsides for a lot of people, when individual companies get this freaking big. And it raises questions about what we can maybe do about it. And the answer is: Maybe more than we think. That’s all coming right up.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News. That’s a nonprofit newsroom covering health care in America. Their reporters do amazing work, and we’re honored to be in cahoots with them. So, as we’ve seen, a company like United is so big that their problems become everybody’s problem. And at least in one case that I’ve seen so far, everybody’s problem can become United’s opportunity. That’s what happened in Oregon, and a reporter from Washington, DC, was in a position to make it a national story.
Maureen Tkacik: My name is Maureen Tkacik, but you can call me Mo and I am the Investigations Editor at the American Prospect, and a Senior Fellow at the American Economic Liberties Project.
Dan: The Prospect is a politically-progressive news magazine, and the Economic Liberties Project is a non-profit that pushes an anti-monopoly agenda. A lot of Mo’s reporting looks at how financial behemoths are looking like monopolists– especially in health care. So…
Maureen Tkacik: have come to know United Healthcare, pretty well, over past, year or so,
Dan: Looking at, for instance, how they gobble up medical practices. And as we mentioned, that kind of gobbling has made United the biggest employer of physicians in the country– by huge margins– in just the last few years. About one doc in ten now works for them, as employees or “affiliates.” As we’ve reported before, big players– like United, like big hospital systems, and like private equity groups– have been gobbling up medical practices for years. And: that kind of consolidation often leads to us paying more– and often for lousier healthcare. Moe Tkacik has been reporting on that kind of gobbling– and recently, she’d been looking at how the state of Oregon had been trying to slow it down. Then, in January 2024, a good-size medical group in Corvallis, Oregon said they were ready for United to gobble them up. The group is called the Corvallis Clinic, and it’s got more than a hundred docs. But United and the Clinic would have to go through a whole process to get approval from state regulators. That process includes: regulators asking the public for comments on the transaction. And in this case…
Maureen Tkacik: they were. inundated with comments.
Dan: Like 378 of them in just a few weeks. And the comments were overwhelmingly AGAINST the sale. In February, the regulators sent United and Corvallis a 5-page list of conditions under which they might approve a deal. A source of Moe’s sent me the document, which he got through a public-records request. The conditions are like, to not reduce service levels in the community for at least 10 years. To keep accepting non-United insurance. And to submit to a lot of monitoring. Then, as negotiations were starting, Change Healthcare went offline. And in early March, Moe got a tip: The clinic and United were gonna make an end run around this process. She talked with an anonymous insider at the clinic. Who told her: It turns out that all of the clinic’s billing had been connected to Change.
Maureen Tkacik: So we’re talking about just a calamitous cash crunch. Their revenue came to a standstill
Dan: And by the time Moe’s insider source learned what was up– this had been going on for two weeks.
Maureen Tkacik: this source said that , Thursday, they all had a meeting and they were not sure they were going to be able to open their doors the following Monday.
Dan: That was Thursday March 7. The next day, March 8th, lawyers for Corvallis Clinic filed an application for an emergency exemption from the normal review process. A week later, they got that exemption. And this time regulators had not demanded any conditions. As Moe’s story laid out, United’s problem– the Change Healthcare hack– became everybody’s problem, including Corvallis. And their problem seemed to have become United’s opportunity. To gobble up the practice without having to agree to any conditions from pesky regulators. And a postscript to the Corvallis Clinic story: Shortly after regulators approved that deal, United sent notices to thousands of patients at another clinic it had taken over in nearby Eugene, saying basically: We don’t have a doctor for you anymore. Goodbye and good luck. News reports said that clinic had lost more than 30 doctors since United took over. And among the public comments urging regulators to kibosh the Corvallis clinic, a bunch of people cited lousy experiences at that Eugene clinic under United’s ownership. This is the kind of thing that Moe Tkacik and her colleagues at the American Economic Liberties Project– and what’s become a kind of anti-monopoly movement– want to change. And here’s where this episode becomes maybe just a little less of a horror story, and maybe a little more of an action movie. Because the anti-monopoly movement has gotten a big backer in the last three years: The Biden Administration. In 2017, a woman named Lina Khan made a name for herself in legal circles when she published a paper arguing that Amazon had become the kind of super-dominant company that antitrust laws were designed to constrain. Lina Khan was a law student when she published that paper. In 2021, Joe Biden appointed her to lead the Federal Trade Commission. The FTC and the Department of Justice split the job of antitrust enforcement, and they’ve both become super-aggressive. They’ve filed big lawsuits against Google, Amazon, and– in March of this year– Apple. And gotten a fair amount of attention. As we were writing up this episode, Jon Stewart interviewed Lina Khan on “The Daily Show.” And here’s how she described her approach in that conversation.
LK: We’ve really focused on how companies are behaving. Are they behaving in ways that suggest they can harm their customers, harm their suppliers, harm their workers, and get away with it? And that type of too big to care type approach is really what ends up signaling that a company has monopoly power because they can start mistreating you, but they know you’re stuck.
Dan: Earlier this year, the Wall Street Journal reported that Lina Khan’s allies– antitrust folks at the Department of Justice are investigating United. Neither the Justice Department nor United has commented on that report. Meaning: Nobody’s denied it. So far, some of the Biden administration’s antitrust lawsuits have pan out, and some haven’t. Actually, in 2021, the Justice Department sued to prevent UnitedHealth Group from buying Change Healthcare. That one, they lost. But when the sued to block Penguin Random House from buying another giant publisher, Simon and Schuster, they won. And as Lina Khan told Jon Stewart, she and her colleagues aren’t just suing to prevent mergers. They sued to get infamous Pharma Bro Martin Skhreli banned for life from the pharma trade. And they won. And they’re looking at other ways big companies, especially in health care, screw people.
LK: Just to give you one example, inhalers. They’ve been around for decades, but they still cost hundreds of dollars. So our staff took a close look and we’ve realized the, some of the patents that had been listed for these inhalers were improper. There were bogus. And so we sent hundreds of warning letters around these patents. And in the last few weeks, we’ve seen companies deal list these patents and three out of the four major manufacturers have now said, Within a couple of months, they’re going to cap how much Americans pay to just 35.
Dan: I think we should start paying a lot more attention to what Lina Khan and her colleagues are up to– and what their chances are. I’ve started reading up, and getting in touch with folks who are in this fight, and who are watching it closely. Because this is looking like the kind of action movie I kind of like. Meanwhile, I’m posting a link to Jon Stewart’s interview with Lina Khan wherever you’re listening to this. I’ll have a few other links for you in our newsletter– you can sign up for that at arm and a leg show dot com, slash, newsletter. And I’ll catch you in a few weeks. Till then, take care of yourself.
This episode of an arm and a leg was produced by me, Dan Weissmann, with help from Emily Pisacreta, and edited by Ellen Weiss. Big thanks this time to the novelist, journalist and activist Cory Doctorow, who has been writing about the antitrust revival for years, breaking down complex, technical stories in clear, accessible ways. Thanks to professor Spencer Waller from the Loyola University Chicago law school for talking about antitrust with me. And thanks to Dr. John Santa in Oregon– for sharing material he got via a public-records request to the state, and for his observations. Adam Raymonda is our audio wizard. Our music is by Dave Weiner and blue dot sessions. Extra music in this episode from Epidemic Sound. Gabrielle Healy is our managing editor for audience. She edits the first aid kit newsletter. Bea Bosco is our consulting director of operations. Sarah Ballama is our operations manager. And Armand a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News. That’s a national newsroom producing in depth journalism about healthcare in America and a core program at KFF, an independent source of health policy research, polling and journalism. Zach Dyer is senior audio producer at KFF Health News. He’s editorial liaison to this show. And thanks to the Institute for Nonprofit News for serving as our fiscal sponsor, allowing us to accept tax exempt donations. You can learn more about INN at INN. org. Finally, thanks to everybody who supports this show financially– you can join in any time at arm and a leg show dot com, slash, support– and thanks for listening.
“An Arm and a Leg” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Public Road Productions.
To keep in touch with “An Arm and a Leg,” subscribe to the newsletter. You can also follow the show on Facebook and the social platform X. And if you’ve got stories to tell about the health care system, the producers would love to hear from you.
To hear all KFF Health News podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to “An Arm and a Leg” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 2 months ago
Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Multimedia, An Arm and a Leg, Podcasts
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Abortion — Again — At the Supreme Court
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Some justices suggested the Supreme Court had said its piece on abortion law when it overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022. This term, however, the court has agreed to review another abortion case. At issue is whether a federal law requiring emergency care in hospitals overrides Idaho’s near-total abortion ban. A decision is expected by summer.
Meanwhile, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid finalized the first-ever minimum staffing requirements for nursing homes participating in the programs. But the industry argues that there are not enough workers to hire to meet the standards.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University’s nursing and public health schools and Politico Magazine, Tami Luhby of CNN, and Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Panelists
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins University and Politico
Tami Luhby
CNN
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- This week’s Supreme Court hearing on emergency abortion care in Idaho was the first challenge to a state’s abortion ban since the overturn of the constitutional right to an abortion. Unlike previous abortion cases, this one focused on the everyday impacts of bans on abortion care — cases in which pregnant patients experienced medical emergencies.
- Establishment medical groups and doctors themselves are getting more vocal and active as states set laws on abortion access. In a departure from earlier political moments, some major medical groups are campaigning on state ballot measures.
- Medicaid officials this week finalized new rules intended to more closely regulate managed-care plans that enroll Medicaid patients. The rules are intended to ensure, among other things, that patients have prompt access to needed primary care doctors and specialists.
- Also this week, the Federal Trade Commission voted to ban most “noncompete” clauses in employment contracts. Such language has become common in health care and prevents not just doctors but other health workers from changing jobs — often forcing those workers to move or commute to leave a position. Business interests are already suing to block the new rules, claiming they would be too expensive and risk the loss of proprietary information to competitors.
- The fallout from the cyberattack of Change Healthcare continues, as yet another group is demanding ransom from UnitedHealth Group, Change’s owner. UnitedHealth said in a statement this week that the records of “a substantial portion of America” may be involved in the breach.
Plus for “extra credit” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: NBC News’ “Women Are Less Likely To Die When Treated by Female Doctors, Study Suggests,” by Liz Szabo.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: States Newsroom’s “Loss of Federal Protection in Idaho Spurs Pregnant Patients To Plan for Emergency Air Transport,” by Kelcie Moseley-Morris.
Tami Luhby: The Associated Press’ “Mississippi Lawmakers Haggle Over Possible Medicaid Expansion as Their Legislative Session Nears End,” by Emily Wagster Pettus.
Joanne Kenen: States Newsroom’s “Missouri Prison Agency To Pay $60K for Sunshine Law Violations Over Inmate Death Records,” by Rudi Keller.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- American Economic Review’s “Is There Too Little Antitrust Enforcement in the U.S. Hospital Sector?” by Zarek Brot-Goldberg, Zack Cooper, Stuart Craig, and Lev Klarnet.
- KFF Health News’ “Medical Providers Still Grappling With UnitedHealth Cyberattack: ‘More Devastating Than Covid,” by Samantha Liss.
CLICK TO OPEN THE TRANSCRIPT
Transcript: Abortion — Again — At the Supreme Court
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, April 25, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this, so here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Tami Luhby of CNN.
Tami Luhby: Hello.
Rovner: And Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University schools of public health and nursing and Politico Magazine.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: No interview this week, but wow, tons of news, so we are going to get right to it. We will start at the Supreme Court, which yesterday heard oral arguments in a case out of Idaho over whether the federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act, or EMTALA, trumps Idaho’s almost complete abortion ban. This is the second abortion case the high court has heard in as many months and the first to actively challenge a state’s abortion ban since the overturn of Roe v. Wade in 2022. Last month’s case, for those who have forgotten already, was about the FDA approval of the abortion pill mifepristone. Alice, you and I both listened to these arguments. Did you hear any hints on which way the court might be leaning here?
Ollstein: The usual caveat that you can’t always tell by the questions they ask. Sometimes they play devil’s advocate or it’s not indicative of how they will rule on the case, but it did seem that at least a couple of the court’s conservatives were interested in really taking a tough look at Idaho’s argument. Obviously, some of the other conservatives were very much in support of Idaho’s argument that its doctors should not be compelled to perform abortions for patients experiencing a medical emergency. It really struck me from the arguments how much it focused on what’s actually going on on the ground.
That was a huge departure from a lot of other Supreme Court arguments and a lot of Supreme Court arguments on abortion where it’s a lot of hypotheticals and getting into the legal weeds. This was just like they were reading these concrete, reported stories of what’s been happening in Idaho and other states because of these abortion bans. People turned away while they were actively miscarrying, people being flown across state lines to receive timely care. I think whether that will make a difference that the justices are sort of being confronted with the concrete ramifications of the Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] decision or not remains to be seen.
Rovner: I thought one of the things that it looked like very much like last month’s argument is that the women justices were very much about real details and talking about medical conditions, about ectopic pregnancies and premature rupture of membranes and things that none of the men mentioned at all. The men were sort of very legalistic and the women, including Amy Coney Barrett, who voted to overturn Roe v. Wade, were very much all about, as you said, what’s going on on the ground and what this distinction means. I mean, where we are is that Idaho has an exception in its abortion ban, but only for the life of the woman. Whereas EMTALA says you have to stabilize someone in an emergency situation and it’s been interpreted by the federal government to say sometimes that stabilization means terminating a pregnancy, as in the case of premature rupture of membranes or an ectopic pregnancy or a case where the woman is going to hemorrhage and is actively hemorrhaging.
That question of where that line is, between what’s an immediate threat to life and what’s just a threat to health or a threat to life soon, was the crux of this case. And it really does feel uncomfortably like we have nine Supreme Court justices making, really, medical decisions.
Ollstein: Yeah, it struck me how Amy Coney Barrett seemed to get pretty frustrated with Idaho’s attorney at a couple points. Idaho’s attorney was saying kind of, “Nothing to see here. There’s no problem. Since we allow lifesaving abortions and that’s what is required under EMTALA, there’s no conflict.” So Amy Coney Barrett was like, “Well, why are you here then? Why are you before us?” The reason is that they’re trying to get this lower-court injunction lifted even though it’s not in effect right now. The other point she got kinda testy was when Idaho was saying that their law is clear, doctors know what to do, and Amy Coney Barrett asked, “Well, couldn’t a prosecutor come in later and disagree and said, “Oh, you performed an abortion you said was to save someone’s life, but I don’t think it was necessary to save her life and I’m going to charge you criminally?” And the Idaho attorney conceded that that could happen.
So I think her vote could potentially be in play, but I don’t know if it’s going to be enough to overcome the court’s conservatives who are very skeptical that EMTALA should compel states to do anything.
Rovner: So the medical community has been quite outspoken in this case. The American Medical Association, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American College of Emergency Physicians have all filed briefs saying the Idaho ban could require them to violate professional ethics, wrote the immediate president of the AMA, Jack Resnick, in an op-ed. “It is reckless for Idaho to tell emergency physicians that they must ignore their moral and ethical standards and stand by while a septic patient begins to lose kidney function or when a hemorrhaging patient faces only a 30% chance of death.” But I feel like the medical profession has long since lost control of the abortion issue. I mean, is there any chance here that they might prevail? I have to say this week I’ve gotten so many emails from so many doctor groups saying, “Oh my goodness, look what’s happening. They’re going to put us in this impossible situation.” To which I want my response to be, “Where have you been for the last 20 years?”
Ollstein: I mean, I think it is notable that these establishment medical groups are becoming more vocal. I mean, some might say better late than never, and I think in some instances they are having an impact at the state level. They have pushed some state legislatures to add or expand exemptions to abortion bans. But a lot of times Republican lawmakers have rejected calls from state medical associations to do that, and so I think filing amicus briefs is a way to have your say, lobbying at the state level is a way to have your say. Some doctors are even running for office specifically on this issue. And also, medical groups are campaigning hard on these state abortion referendums. I reported on doctor groups door-knocking in Ohio, for instance, before that referendum won big.
I think it’s really interesting to see the medical community get a lot more vocal on something they’ve either tried to stay out of or been vocal on the other side on in the past, but we’ll have to see how much impact that actually has.
Rovner: Well, one thing this case highlights is how pregnant women who experience complications that can threaten their health or future fertility, but are not immediately life-threatening, can end up in really terrible circumstances, as we heard in a number of anecdotes at the oral arguments. The Associated Press “FOIA’d”[requested Freedom of Information Act] EMTALA pregnancy complaint records from several states with abortion bans and found some pretty horrific examples, including one woman who miscarried in the emergency room lobby restroom after she was turned away from the registration desk. Another who was turned away and ended up giving birth in a car on the way to another hospital. That baby died. These are not people who go to the emergency room in search of abortions. They’re women who are trying to maintain pregnancies. Is the concept that people ending up in the most horrific situations are often those who most want children, is that finally getting through here?
Ollstein: What struck me most about that reporting is that the documents they got were just from the first few months after Roe v. Wade was overturned, so we have no idea what’s happening now. It could be better, it could be much worse, it could be the same. I think that lack of transparency makes this really hard to report on accurately. And the fact that it took The AP a year to even get those few heavily redacted documents speaks to the challenge here. We want an accurate picture of how these bans are impacting the provision of health care around the country, and it’s really hard to get.
Rovner: I know the Biden administration has been kind of trying to keep this quiet. I mean, not out there sort of blaring what’s happening. They’ve been sort of leaving that to the politics side and this is obviously the policy side. Obviously on the politics side, the Biden administration is getting bolder about using abortion as a campaign issue. The president himself gave a speech in Florida where a six-week ban is set to take effect next week and pinned all the abortion restrictions directly on former President Trump, who he pointed out has taken credit for them. Biden actually said the word abortion twice in that speech. I was listening very closely and went back and counted. I think that’s a first. They’re definitely stepping up the pressure politically, right?
Ollstein: Yes. The Biden campaign is leaning very hard on this. Even in states where it’s debatable whether they have a chance, like Florida, I think that there’s an interest, especially after seeing all of these referendums and ballot measures win big. It’s really shown Democrats that this is a very popular issue to run on, that they shouldn’t be afraid of it, that they should lean into it. I think you are seeing attempts to do that. It’s not always the language that the abortion rights advocacy community wants to hear, but it’s definitely more than we’ve heard from the Biden administration in the past.
I think you’re also seeing an attempt to sort of take the air out of Trump’s “Let’s leave it to states. I am reasonable and moderate” sort-of pitch. By highlighting what’s happening on the ground in certain states, it’s an attempt to say, “OK, you want to leave it to states? Then you own all of this. You own every woman being turned away from a hospital while she’s miscarrying. You own every instance of a ban going into effect and people having to travel across state lines,” et cetera. But whether just blaming Trump and arguing that he would be worse is enough versus saying what Biden would actually do and continue to do, I think that’s what we’ve heard people want to hear more of. Although there has been some action from the Biden administration recently.
Rovner: That was just going to be my next question. The one policy change the Biden administration did do this week was finalized a rule expanding the health records protections under HIPAA to abortion information. Why was this important? It sounds pretty nerdy.
Ollstein: This has been in the works for more than a year. A lot of people have been wondering why it’s been taking so long and worried that if it took even longer, it would be easier to get rid of it if a new administration takes over. But essentially this is to make it harder for states to reach across state lines to try to obtain information and use it to prosecute for having an abortion. It’s an attempt to better protect that data and so we heard a lot of praise after the announcement came out from abortion rights groups and some medical groups, and I would anticipate some groups on the right would sue. I’ve seen some complaints saying this will prevent law enforcement from investigating actual crimes against people, and so I expect to see some legal challenges soon.
Kenen: There are all sorts of efforts to stop both travel for abortion. There are also laws on books already, there have been for a number of years, about helping a minor cross state lines for abortion. There’s the attempts to stop the shipment of abortion pills from a legal state into a state that has a ban. There’s all sorts of things where, whether the intent is to actually prosecute a woman or a pregnant person, versus collecting evidence for some kind of larger crackdown or prosecution, this is potentially a piece … patient records are potentially a piece of that. We’ve talked a few weeks ago, maybe a month or two ago by now, about some Texas communities that wanted to say, “If you drive on the road in our town on the way to an abortion, we’re going to arrest you.” How they figure out logistically and practically … What are you going to do? Stop everybody on the road and give them a pregnancy test?
I mean, I don’t know how you enforce that, but just that these ideas are out there and on the books through this privacy shield. We have privacy under HIPAA, all of us, so to interpret it this way, or reinforce it depending on your political point of view, undermine excessively, whatever, but this is sort of pivotal because there’s so many ways these records could be used in various kinds of legislative and prosecutorial ways.
Rovner: As you point out, it’s not theoretical. We’ve seen attorneys general — Indiana and Kansas — and some other states, actually, and Texas say that they want to go after these records, so it’s not …
Kenen: Right and we’ve seen cases of the child rape victim and the prosecutor, what happened with the doctor, and so it’s not theoretical. It’s not widespread right now, but it’s not theoretical. Whether the pregnancy was planned and wanted or it was unplanned and ended up being wanted, going through a pregnancy loss is not just medically difficult, depending on when in pregnancy it occurs and under what circumstances. It can be medically quite complicated and it’s emotionally devastating. So to just get pulled into these political legal fights when you’ve already been bleeding in the parking lot or whatever, or having lost a pregnancy, it’s like you forget these are human beings. These are people going through medical crises.
Rovner: Indeed. Well, abortion is far from the only big health news this week. On Monday, the Biden administration finalized more long-awaited rules regarding staffing in nursing homes that participate in Medicare or Medicaid. Tami, what’s in these rules and why is the concept that nursing homes should have nurses on duty so controversial?
Luhby: It is very controversial and it’s also very consequential. So on Monday, as you said, the Biden administration finalized the first-ever minimum staffing rules at nursing homes involved in Medicare and Medicaid, and they say it’s crucial for patient safety and quality of care. It requires that all nursing homes provide a total of at least 3.48 hours of nursing care per resident per day, including defined periods of care from registered nurses and from nurses’ aides. Plus, nursing homes must have a registered nurse on-site at all times, which is different than the rules now. Now, CMS [Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] is giving the nursing homes some time to staff up. The mandate will be phased in over three years with rural communities having up to five years and they’re also giving temporary exemptions for facilities in areas with workforce shortages that demonstrate a good faith effort to hire. When I spoke to [Department of Health and Human Services] Secretary [Xavier] Becerra about the nursing home industry’s vocal concerns that this could cause a lot of nursing homes to close or limit admissions, he said, “Well, a business model that is based on understaffing is not a very good business model and is dangerous for patients.”
So, it’s going to be a heavy lift for nursing homes. According to HHS, 75% of them will have to hire staff, including 12,000 registered nurses and 77,000 aides. And also, 22% of them will need to hire registered nurses to meet the around-the-clock mandate. The nursing home operators, not surprisingly, have strongly pushed back on this rule even back when it was first proposed in September, saying that they’re already having staffing problems amid a nationwide shortage of nurses. The American Health Care Association called the mandate an unreasonable standard that only threatens to shut down more nursing homes, displace hundreds of thousands of residents, and restrict seniors’ access to care.
Rovner: We should point out the American Health Care Association is the lobbying group for nursing homes.
Luhby: Yes. What’s interesting also, though, is that on the other side, you have advocacy groups that are saying that it doesn’t go far enough and they’re citing a 2001 CMS study that found that nursing home residents need at least 4.1 hours of daily care. To add to all of this, if it’s not complicated and controversial enough, Congress is getting involved and is also split over the rules. Some lawmakers, like Sens. Elizabeth Warren and Bob Casey, generally support it, but nearly a hundred House members from both parties wrote to HHS Secretary Becerra expressing their concern that the mandate could lead to nursing home closures. And there’s a bipartisan Senate bill and a House Republican bill that would prohibit HHS from finalizing the rule. So we have time before this goes into effect. It goes into effect in phases, and we’ll see if lawmakers move to block the mandate or if the courts do, but it’s going to be interesting to watch how this plays out.
Rovner: Joanne wanted to add something.
Kenen: Well, first of all, as we say frequently, there’s always lawsuits. We have a health care/lawsuit system, so it’s not over. But I think the other thing is I think families who put a loved one in a nursing home don’t understand how little nursing, let alone doctoring, goes on. The name is “nursing” home and people expect there to be a nurse there, meaning a registered nurse. I think people often think there’s a doctor there, where the doctors are not there very much. That’s one reason the lack of medical care on-site, not only could there be emergencies, but I mean even things that could be treated in place if there is a physician. I mean, it’s just dial 911 and put them in an ambulance and send them to the hospital. And we do have this problem with hospital readmission, which is not just a cost problem and a regulatory problem, it’s really bad for patients to … the continuity of care is good and lack of continuity and handoffs and change, sending people back-and-forth is not good for them.
Obviously, there are times there’s an emergency and you need to send someone to a hospital, but not always. If there was a doctor or nurse, there’s some things that you don’t have to call 911 for. Because you don’t know or don’t learn about nursing homes until you have a relative there or until you’re a reporter who has to write about them. You don’t realize that they’re very custodial and there’s not a lot of taken care of in terms of getting assistance in bathing and walking and things like that. There’s less medical care, including nursing care, than people realize until your loved one is there. I mean, when I covered them the first time, I was really shocked. I mean, it’s 20 years ago the first time I wrote about it, but my assumption of what was there and what is actually there was a big gap.
Rovner: Tami.
Luhby: One thing also, though is … I mean, yes, that is definitely true about the medical care, but we’re also talking about just the care, not only the nursing. But that’s why so many aides need to be hired because you also have situations in nursing homes where people aren’t getting help to go to the bathroom, aren’t getting showered regularly, aren’t being watched. Maybe they’re trying to go to the bathroom themselves and they’re falling because they have to go. I mean, unfortunately, I’ve had experience with nursing homes with my family and I’ve seen this. But also I think it’s been pretty well reported in a lot of publications and studies and such. But there are a lot of problems in nursing homes, in general, and staffing.
Rovner: Well, just to talk about how long this is going on, former Sen. David Pryor died this week. When he was a House member, he rather famously went undercover at a nursing home to try and spotlight. That was when we first started to hear about some of the conditions in nursing homes. He was instrumental in doing the work that got the original federal nursing home standards passed in 1987, which was the first time I covered this issue, and even then there was a big fight in 1987 about should there be a staffing mandate? It’s like, hello, if we’re going to improve care in nursing homes, maybe we should make sure there are enough people to provide care. Even then the nursing home industry was saying, “But we have a shortage. We can’t hire enough people to actually do this if you give us a staffing mandate.” So literally, this has gone back-and-forth since 1987. And, as Joanne points out, it’s still in all likelihood not over, but one could sort of think, gee, they’ve had two generations now to come up with enough people to work in these nursing homes. Maybe Becerra is right. Maybe there’s something wrong with the business model?
Luhby: I was going to say, we know the business model is also moving more towards private equity, which is not necessarily going to be as concerned with the staffing levels. We know that the staffing levels … I think there’ve been studies that show that staffing levels are generally lower in investor-owned nursing homes. So there’s that.
Kenen: There’ve been a lot of demographic changes. I mean, you live longer, but you don’t always live healthier. We have families that are spread out. Not everybody’s living in the same town anymore. I mean, they haven’t for a number of decades now, but your daughter-in-law is 3,000 miles away. She can’t come to your house every day. At the same time, we do have a push and it’s not brand-new, it’s a number of years now, to do more home- and community-based care, but there are shortages and waiting lists and problems there, too. So there are a lot of people who need institutional care. Whether they wanted to have that or not, that’s where they go because either there’s not enough community support or they don’t have the family to fill in the gaps or they’re too medically complicated or whatever. Given the demographic trends and the degree of chronic disease and disability, this is not going away. It’s like Julie said, it’s way overdue. We need to figure it out. There are workforce shortages to train more CRNAs [certified registered nurse anesthetists] like the trained aides. It’s not a five-, six-year program. I mean, this can be done and is done somewhere in community colleges. You can do this. You can improve at all levels. You need more nurse RNs, nurses or advanced practice nurses, but you also need more of everything else. People who go to work in these jobs, by and large, do want to provide quality, compassionate care, and it’s hard to do if there are not enough of you.
Rovner: But they’re also super hard jobs and super stressful and super physically demanding.
Kenen: Hoisting and …
Rovner: Yeah, yeah. And not well-paid.
Kenen: Keeping track of a lot of stuff.
Rovner: Well, in a related move, the Biden administration this week also finalized rules that will attempt to make the quality of Medicaid managed-care plans more transparent. Among other things, the rules establish national wait time limits for certain types of medical care and require states to conduct secret shopper surveys of insurance provider networks to make sure there are enough practitioners available to serve the patient population. The administration says these rules are needed because so many Medicaid patients are now in managed care and regulations just haven’t kept up. Will these be enough to actually protect these often very vulnerable populations? I mean, obviously these people are not quite as vulnerable as people in nursing homes, but they’re kind of the next level down.
Kenen: Well, I think that we’ve seen a history of waves of regulation. Then whatever the status quo becomes, it doesn’t stay the status quo. Whether, as Tami mentioned, there’s more private equity or there’s monopolization and consolidation or just new state regulation. I mean, it’s not static. Do we know how this move is going to play out? No. Do we assume that the bad actors who don’t want to comply will find new ways of doing things that in five years we’ll have another set of regulations that we’ll be talking about? I mean, unfortunately, that’s the way things work. Some regulatory approaches or legal approaches work and others just sort of morph. There’s a lot of history of innovative great actors and lousy bad actors.
Rovner: I say it’s been a big week for federal regulation because we also have breaking news from the Federal Trade Commission, of all places. On Tuesday, the commissioners voted to finalize rules banning most noncompete clauses in employment contracts. At an event here at KFF, the FTC chair, Lina Kahn, said a surprisingly large number of comments about that proposed rule came from health care workers. Here’s a snippet from that conversation.
Lina Khan: There were a whole bunch of comments that said, “I signed this, but it’s not like I was exercising real choice. It felt coercive.” We also heard a lot about the effect of these noncompetes and the way that, especially in rural areas, if you want to switch employers and there’s really only one other option locally, if a noncompete is barring you from taking a job with that other hospital, practically to change jobs you have to leave the state. Right? And just how destructive and devastating that is for people and their families, especially if they’re choosing between staying in a job where the employer realizes that this is a captive employee and they don’t really have to compete in offering them better opportunities, better wages, and having to instead think about uprooting their family. We also heard from doctors who did not uproot their families, but instead just commuted hours and hours a day driving. People saying, “For five years I didn’t really see my kids at all awake, ever, because I was always on the road because of this noncompete.” So just really vivid stories from people.
Rovner: So even though the vote was less than 48 hours ago, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce has already filed suit to block the rules as have some smaller business groups. Why do businesses think they need to prevent workers from changing jobs near where they live? I mean, you could see it for people who’ve invented something. You don’t want them to walk out the door with proprietary secrets, but baristas at Starbucks and even nurses are not walking out with trade secrets.
Kenen: Well, I mean, this is common in doctors’ employment contracts, nurses, it’s everything. I think it’s partly because there are provider shortages in some places and they want to keep the workforce they have instead of having them be lured across town to a competitor where they could be paid more and then you have to pay even more to hire the next one. So that’s part of it. It’s economic. A lot of it’s economic. I mean, there’s some fear of patients going with a certain beloved provider, a doctor goes somewhere else. But I think it’s basically they don’t want churn. They don’t want to have to keep paying more. Somebody gets a job offer across the street and they don’t want to take it. They like where they are, but they’re going to ask for more money. It’s largely economic in a market where there’s scarcity of some specialties and certainly nursing. I mean, there’s questions about are there are not enough nurses? Or are we just putting them in the wrong places? But speaking generally, there’s a nursing shortage and physicians, we don’t have enough primary care providers. We certainly don’t have enough geriatricians. We don’t have enough mental health providers. We don’t have enough of a lot of things. This helps the employer, in this case, the health system, usually.
Rovner: I have to say it was only in the last couple of years that I even became aware there were noncompetes in health care. I mean, I knew about them for weathercasters on local stations. It’s like if you leave, you have to go to another station in another city. I had absolutely no idea that they were so common, as you point out, for so many economic reasons. Obviously this has also already been challenged in court, so we’ll have to see how that plays out.
Also this week on the antitrust front, we have a paper from three health economists published in the American Economic Review who calculated that if the Federal Trade Commission had been more aggressive about flagging and potentially blocking hospital mergers just between 2010 and 2015, health care prices could have been 5% lower. Researchers blame the FTC’s limited budget, but you have to wonder if that budget is limited because business has so much clout in Washington and really doesn’t want eager regulators snooping into their potentially anticompetitive practices. I mean, the FTC has been around for 120-some years now. Occasionally it tries to do big things like with these noncompetes, but mostly it doesn’t do as much as obviously economists and people who study it think that it could do. I mean, we certainly have problems with lack of competition in health care.
Ollstein: I think we have an unusually aggressive FTC right now, so it’ll be really interesting to see what they can accomplish in whatever time this administration has remaining to it, which remains to be seen. I have seen some more aggressive action from the agency in the past on things like payday lending and some of these other sort of maybe more fringy sectors of the economy. So to take on health care, which is so central and such a behemoth and, like you said, there’s so much political power behind it, as Joanne said, guarantee of lawsuits and coverage from us forever basically.
Kenen: The other point that’s worth making, I don’t think any of us have said this, it doesn’t apply to nonprofit hospitals or health systems, and that’s a lot of … market-dominant health care systems that are nonprofits, nominally their tax status is nonprofit. It’s a very confusing term to normal people, but these bans on noncompetes do not apply to the nonprofit sector, which is a lot of health care.
Rovner: Yet still it’s set off quite a conflagration since they passed this on Tuesday. Well, finally this week, speaking of big health care business, we are still seeing ramifications from that Change Healthcare hack back in February. While UnitedHealth Group, which owns Change, says things are approaching normality, that’s not the case for providers who still can’t submit bills or collect payments except doing it on paper. Meanwhile, in what’s going to be some kind of movie or miniseries someday, a second group is now demanding ransom after publishing some of the stolen data. If you’ve been following this story along with us, you’ll remember that United reportedly already paid a ransom of $22 million, except that it appears that the group that got that money stiffed the group that actually has control of the pirated data.
Oh, and buried in UnitedHealthcare’s news “update” posted on its website, it says protected health information, “which could cover a substantial proportion of people of America,” is involved in the hack. Can this get any worse?
Kenen: Snakes? I don’t think any of us journalists can quite comprehend. I mean, we understand intellectually, but I don’t think we understand what it’s like to be the billing clerk at a major practice right now trying to figure out what’s where and how to get paid and what it means for patients and what’s next. I mean, this is a tremendous hack, but it’s not the last.
Rovner: Yeah, and the idea that I think — what did they say? — 1 out of every 3 health care transactions goes through Change, I certainly wasn’t aware of. I think most reporters who are covering this weren’t aware of. I think certainly none of the public was aware of, that there’s that much of the money-changing that goes on from one, as we now know, vulnerable organization is a little bit scary.
Luhby: It shows the power of UnitedHealth[care] in the market. I mean, it’s the largest insurer and people think of it, “OK, I have insurance through it,” but they don’t realize all of the other tentacles that are attached.
Kenen: It also shows that there’s hack after hack after hack after hack. This company knew that they were big and powerful and central, and many of us never heard of them or barely knew what they were. But they knew what they were and despite all the warnings of the need for better and higher protection, cybersecurity protections, these things are going on still. I don’t have the technical expertise to know, well, OK, everybody’s doing everything they’re supposed to do as a health system, but the hackers are just always a step ahead. Or whether they’re really not doing everything they’re supposed to do and weak links in their own chains. Is it the diabolical geniuses? Or is it people still not taking this seriously enough?
Rovner: I will add that in our discussion with FTC Chair Lina Kahn, she did talk about cybersecurity as something that the FTC is going to be looking at in deciding whether there is unfair competition going on. Also, she has promised to come on the podcast, so hopefully we will get her in the next several weeks.
All right, that is the news for this week. Now it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Tami, you were the first in, why don’t you go first this week?
Luhby: Well, my extra credit is an AP story by Emily Wagster Pettus titled “Mississippi Lawmakers Haggle Over Possible Medicaid Expansion as Their Legislative Session Nears End.” This story brings us up to date on the negotiations between the House and Senate in Mississippi over expanding Medicaid. Just a quick refresher for listeners: Mississippi is one of 10 states that hasn’t expanded Medicaid yet, and this is the first time, and it’s really very consequential that the Republican-led legislature has seriously considered doing so. The problem is the House and Senate versions are very, very different. The House bill is more like a traditional Medicaid expansion, providing coverage for those earning up to 138% of the poverty level, although it would also try to institute a work requirement, and about 200,000 people would gain coverage. But the Senate version would only extend coverage to those earning up to 100% of the poverty level, which the Senate Medicaid committee chair thought would add about 40,000 to the program, and it would also come with a very strict work requirement.
So on Tuesday, lawmakers met to try to hash out a compromise. They did so in public. It was a public meeting recorded, which was very unusual, and apparently there were people waiting hours to get in. It was standing room only. The House offered a plan that would cover people earning up to 100% of the poverty level under Medicaid, while those earning between 100% and 138% would receive subsidies to buy insurance through the ACA exchange. But the Senate did not offer a proposal nor immediately respond to the one in the House. There are more meetings scheduled. I think there was another one yesterday. It remains to be seen what will happen, but the clock is ticking. The state legislature only is in session until May 5, and it doesn’t give them much time.
Another wrinkle is that it’s important to note that Gov. Tate Reeves, a Republican, has repeatedly voiced his opposition to Medicaid expansion in recent months and is likely to veto any bill. So if lawmakers do eventually agree on a compromise, they may very well also have to vote on whether to override the veto by the governor. This happened in Kansas in 2017 where the legislature did pass Medicaid expansion, Republican governor vetoed it, and the legislature was not able to override the veto and it never got that far again.
Rovner: So yes, we will keep our eyes on Mississippi. Thank you for the update. Alice, why don’t you go next?
Ollstein: I have a piece from States Newsroom related to the Supreme Court arguments on Idaho’s abortion ban and its impact on pregnant patients. The piece [“Loss of Federal Protection in Idaho Spurs Pregnant Patients To Plan for Emergency Air Transport”] is about the increase in patients being airlifted out of the state on these Life Flight [Network] emergency transports and the situation and doctors’ hesitancy to provide abortion care, even when they feel it’s medically necessary, is leading to this increase in flying patients to Oregon and Washington and Utah and neighboring states. It’s getting to the point where some doctors are even recommending people who are pregnant or planning to be pregnant purchase memberships in these flight companies, which normally is only recommended for people who do extreme outdoor sports who may need to be rescued or who ride motorcycles. So the fact that just being pregnant is becoming a category in which you are recommended to have this kind of insurance is pretty wild.
Rovner: Yeah. Welcome to 2024. Joanne.
Kenen: This is a piece from the Missouri Independent, which is also part of the States Newsroom, by Rudi Keller, and the headline is “Missouri Prison Agency To Pay $60K for Sunshine Law Violations Over Inmate Death Records.” That doesn’t sound quite as dramatic as this story really is. It’s about a mother who’s been trying to find out how her son was left unprotected, and he died by suicide, hanged himself in solitary confinement, when he had a history of mental illness. He was serving time for robbery. He wasn’t a murderer. I mean, he was obviously in prison. He had done something wrong, very wrong. He had had a 13-year sentence. But he had a history of mental illness. He had a history of past suicide attempts. He had been taken off some of his drugs, and she has been trying to find out what happened. But it’s not just her. There are other cases. The number of deaths in Missouri prisons has actually gone up in the last few years, even though the prison population itself has gone down. The headline is sort of the tip of a rather sad iceberg.
Rovner: Prison health care, I think, is something that people are starting to look at more closely, but there’s a lot of stories there to be done. Well, my story this week is from my friend and former colleague Liz Szabo, and it’s called “Women Are Less Likely To Die When Treated by Female Doctors, Study Suggests.” Now, this was a study of women on Medicare who were hospitalized, so not everybody, and the difference was small, but statistically significant. Those women treated by women doctors were slightly less likely to die in the ensuing 30 days than those treated by male doctors. It’s not entirely clear why, but at least part of it is that women tend to take other women’s problems more seriously, and women patients may be more likely to open up to other women doctors.
It’s another data point in trying to close the gap between women and men and the gap between people of color and white people when it comes to health care. So more studies to come.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions to whatthehealth, all one word, @kff.org. Or you can still find me at X, I’m @jrovner. Joanne, where do you hang these days?
Kenen: Occasionally on X @JoanneKenen, but not very much, and on threads @joannekenen1.
Rovner: Tami?
Luhby: Best place is cnn.com.
Rovner: There you go. Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein on X, and @alicemiranda on Bluesky.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 3 months ago
Courts, Elections, Health Industry, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, States, Abortion, Health IT, Hospitals, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Legislation, Podcasts, reproductive health, Women's Health
California Health Workers May Face Rude Awakening With $25 Minimum Wage Law
SACRAMENTO, Calif.
— Nearly a half-million health workers who stand to benefit from California’s nation-leading $25 minimum wage law could be in for a rude awakening if hospitals and other health care providers follow through on potential cuts to hours and benefits.
A medical industry challenge to a new minimum wage ordinance in one Southern California city suggests layoffs and reductions in hours and benefits, including cuts to premium pay and vacation time, could be one result of a state law set to begin phasing in in June. However, some experts are skeptical of that possibility.
The California Hospital Association brought a partly successful legal challenge to Inglewood’s $25 minimum wage ordinance, which barred employers from taking those sorts of steps to offset their higher costs.
“Layoffs, reductions in premium pay rates, reductions in non-wage benefits, reductions in hours, and increased charges are consequences of an employer having less money to spend—which will necessarily be the case given the significant increase in spending on wages due to the minimum wage,” the association said in its lawsuit. Additional examples include reducing health coverage and charging for parking or work-related equipment.
Inglewood voters approved the ordinance in November 2022, nearly a year before California legislators enacted a $25 minimum wage for health workers. Those statewide higher wages are to be phased in starting in June under California’s first-in-the-nation law, but Gov. Gavin Newsom has since said they are too expensive as the state faces a deficit estimated between $38 billion and $73 billion. It’s unclear if lawmakers will agree to a delay or take other steps to reduce the cost.
U.S. District Judge Dale S. Fischer agreed with the hospital industry in a March 11 tentative ruling when he shot down the portion of Inglewood’s ordinance banning layoffs and clawbacks by employers, while allowing the rest of the ordinance to remain in effect. He gave the sides time to object to his preliminary decision, though none did.
The California Hospital Association represents more than 400 hospitals and was a key backer of the state’s carefully crafted compromise law, which notably contains none of the employee safeguards included in the Inglewood ordinance.
Spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea said the association doesn’t know how providers will react once the state law takes effect. “We don’t have any insights,” she said.
“The challenge for any health care organization is figuring out how to pay for the higher wages,” said Joanne Spetz, director of the Philip R. Lee Institute for Health Policy Studies at the University of California-San Francisco. “Since labor costs are the largest part of any health care organization’s costs, it’s hard to figure out how to reduce spending without looking at labor costs.”
Providers can try to increase revenues by bargaining for higher reimbursements from commercial insurers, she said. Public hospitals, nursing homes, and community clinics get most of their money through Medi-Cal, the state’s Medicaid program.
Providers could reduce the services they offer, pare back charity care, and cut or delay capital investments, Spetz said. In the long term, she expects some combination of spending cuts and revenue increases.
Both the state law and local ordinance cover far more than doctors and nurses, with a definition of health worker that includes janitors, housekeepers, groundskeepers, security guards, food service workers, laundry workers, and clerical staff.
The most recent estimate by the Health Care Program at the University of California-Berkeley Labor Center is that as many as 426,000 health workers would make an average of $6,400 extra in the law’s first year, a 19% average pay bump mainly benefiting lower-income workers of color and women. State finance officials project that well over 500,000 workers will benefit.
Researchers didn’t include layoffs and other potential staffing and benefit reductions when they projected the state law’s costs and benefits, said Laurel Lucia, the program’s director. But she pointed to initial projections by hospitals, doctors, and business and taxpayer groups that the wage hike would cost $8 billion annually, thereby imperiling services and resulting in higher premiums and higher costs for state and local governments.
“It seems like a contradiction to say this law’s going to cost billions of dollars while at the same time saying it’s going to reduce workers’ total compensation,” said Lucia, who projects a far lower price tag.
She added that state finance officials had anticipated that Medi-Cal reimbursements would reflect the increased labor costs, while Medicare would eventually at least partially compensate for the higher labor costs.
Michael Reich, chair of the Center on Wage and Employment Dynamics at UC Berkeley’s Institute for Research on Labor and Employment, and affiliated economist Justin Wiltshire recently argued that California’s new $20 minimum wage law for fast-food workers won’t result in mass layoffs and price increases, as some have predicted.
Health care is much different than fast food, Reich acknowledged, but he argued for much the same positive result.
“A higher minimum wage will make it easier and cheaper for hospitals to recruit and retain these workers. The cost savings, and the productivity benefits of more experienced workers, could offset much of the labor cost increase,” Reich said.
The hospital association filed its lawsuit against Inglewood’s ordinance in July, while it was still opposing early versions of the statewide minimum wage legislation. Among many other provisions, the statewide law put on hold an initiative to cap hospital executives’ salaries in Los Angeles.
The hospital association’s legal challenge referenced in part layoffs and reduced working hours imposed by Centinela Hospital Medical Center after Inglewood’s ordinance took effect.
But Centinela said the reduction was entirely unrelated to the ordinance and that all staff were offered alternate positions, which many accepted.
“Centinela Hospital also has since added many more jobs in new clinical positions above minimum wage scale,” the hospital said in a statement.
Service Employees International Union-United Healthcare Workers West, the prime backer of both the local ordinance and the statewide law, sued the hospital in April 2023 alleging that it cut workers’ hours to offset the higher minimum wage. The case is still pending.
The union did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
In a court filing, however, the union and city of Inglewood said similar employer restrictions in previous minimum wage laws have survived.
The ordinance “merely sets the backdrop for collective bargaining negotiations,” and does not bar employers from locking out employees or hiring replacement workers during a strike. Employers can still lay off workers or reduce their hours, they said, so long as they don’t do so to fund the higher minimum wage.
But Fischer agreed with the hospital association that layoffs and reductions in employees’ total compensation packages are “obvious responses by an employer to rising compensation costs.”
Restricting employers’ options would violate federal labor relations rules, he said.
“The minimum wage an employer has to pay its employees will invariably affect the total amount of compensation it is able or willing to pay,” he wrote “This will then invariably affect the number of employees it can retain and the number of hours those employees will be scheduled to work.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 3 months ago
california, Health Industry, States, Cost of Living, Hospitals, Legislation
An Arm and a Leg: Attack of the Medicare Machines
Covering the American health care system means we tell some scary stories. This episode of “An Arm and a Leg” sounds like a real horror movie.
It uses one of Hollywood’s favorite tropes: machines taking over. And the machines belong to the private health insurance company UnitedHealth Group.
Covering the American health care system means we tell some scary stories. This episode of “An Arm and a Leg” sounds like a real horror movie.
It uses one of Hollywood’s favorite tropes: machines taking over. And the machines belong to the private health insurance company UnitedHealth Group.
Host Dan Weissmann talks to Stat News reporter Bob Herman about his investigation into Medicare Advantage plans that use an algorithm to make decisions about patient care. The algorithm is owned by a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group.
Herman tells Weissmann that some of UnitedHealth’s own employees say the algorithm creates a “moral crisis” in which care is unfairly denied.
Scary stuff! Such reporting even has caught the eye of powerful people in government, putting Medicare Advantage plans under scrutiny.
Dan Weissmann
Host and producer of "An Arm and a Leg." Previously, Dan was a staff reporter for Marketplace and Chicago's WBEZ. His work also appears on All Things Considered, Marketplace, the BBC, 99 Percent Invisible, and Reveal, from the Center for Investigative Reporting.
Credits
Emily Pisacreta
Producer
Adam Raymonda
Audio Wizard
Ellen Weiss
Editor
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: Son of Medicare: Attack of the Machines
Note: “An Arm and a Leg” uses speech-recognition software to generate transcripts, which may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
Dan: Hey there–
So this is kind of a horror story. But it’s not quite the kind of story it might sound like at first.
Because at first, it might sound like a horror story about machines taking over, making all the decisions– and making terrible, horrifying choices. Very age-of-Artificial Intelligence.
But this is really a story about decisions made by people. For money.
It’s also kind of a twofer sequel– like those movies that pit two characters from earlier stories against each other. Like Godzilla vs King Kong, or Alien vs Predator.
Although in this case, I’ve gotta admit, the two monsters are not necessarily fighting each other.
Let’s get reacquainted with them.
On one side, coming back from our very last episode, we’ve got Medicare Advantage: This is the version of Medicare that’s run by private insurance companies.
It’s got a bright and appealing side, compared to the traditional Medicare program run by the federal government, because: It can cost a lot less, month to month — saving people money on premiums. And it often comes with extra benefits, like dental coverage, which traditional Medicare doesn’t offer. [I know.]
But Medicare Advantage can have a dark side, which is basically: Well, you end up dealing with private insurance companies for the rest of your life. You need something — a test, a procedure, whatever — they might decide not to cover it.
Which can be scary.
Our other returning monster — am I really calling them a monster? — well, last time we talked about them, in 2023, we had an expert calling them a behemoth. That’s United HealthGroup. You might remember, they’re not only one of the biggest insurance companies
— and maybe not-coincidentally the very biggest provider of Medicare Advantage plans —
they’ve also got a whole other business– under the umbrella name Optum. And Optum has spent the last bunch of years buying up a gazillion other health care companies of every kind.
That includes medical practices — they employ more doctors than anyone else, by a huge margin. It includes surgery centers, and home-health companies, and every kind of middleman company you can imagine that works behind the scenes — and have their hands in a huge percentage of doctor bills and pharmacy visits.
A few years ago, United bought a company called NaviHealth, which provides services to insurance companies that run Medicare Advantage plans.
NaviHealth’s job is to decide how long someone needs to stay in a nursing home, like if you’re discharged from a hospital after surgery, but you’re not ready to go home yet.
And the horror story– the stories, as dug up by reporters — starts after United bought NaviHealth.
And according to their reports, it involves people getting kicked out of those nursing homes who aren’t ready to go home.
People getting sent home who can’t walk up the stairs in their house. Who can’t walk at all. Who are on feeding tubes. People who NaviHealth’s own employees are saying, “Wait. This person isn’t ready to go home.”
But their new bosses have told them: You’re not really making these decisions anymore.
This is where machines do enter the picture.
NaviHealth’s distinctive offering has always been its proprietary algorithm– an algorithm that makes predictions about how long any given patient might need to stay.
Before United bought the company, that algorithm was used as a guide, a first-guess. Humans weighed in with their own judgment about what patients needed.
After United bought the company, people inside have told reporters, that changed: The new owners basically told their employees, If the algorithm says someone can go home after x days, that’s when we’re cutting them off.
Like pretty much any horror movie, this story’s got people running around trying to tell everyone: HEY, WATCH OUT! THERE’S SOMETHING BIG AND DANGEROUS HAPPENING HERE.
And in this case, they’ve actually gotten the attention of some people who might have the power to do something about it. Now, what those people will do? We don’t know yet.
And, by the way: Yes, I said at the end of our last episode that we’d be talking about Medicaid this time around. That’s coming! But for now, strap in for this one.
This is An Arm and a Leg, a show about why health care costs so freaking much, and what we can maybe do about it. I’m Dan Weissmann. I’m a reporter, and I like a challenge. So our job on this show is to take one of the most enraging, terrifying, depressing parts of American life, and bring you something entertaining, empowering, and useful.
So. I said that, like every horror movie, this one has people who are seeing what’s going on and are trying to warn everybody?
Like those movies, we’re gonna follow one of those people, watch them discover the problem, see how deep it goes, and start ringing alarm bells. Let’s meet our guy.
Bob Herman: My name is Bob Herman. I’m a reporter at STAT News
Dan: Stat is an amazing medical news publication. Bob covers the business of medicine there. Bob started working on this story in November 2022, after talking to a source who runs nursing homes. Bob’s source was complaining about Medicare Advantage.
Bob Herman: There were a lot of payment denials. They just weren’t able to get paid. And just offhandedly, the source mentioned like, um, you know, and they’re attributing everything to this algorithm. This algorithm said, You know, only 17 days for our patients and then time’s up and I went running to Casey Ross
Dan: Casey is a reporter at Stat who focuses on tech and AI in healthcare. Bob said, hey, what do you think of this? Wanna team up?
Bob Herman: And he was hooked.
Dan: They started talking to people who worked at nursing homes, talking to experts, and talking to families. And it was clear: They were onto something.
Bob Herman: It took so many families by surprise to be like, what do you mean we’re going home? The, you know, my husband, my wife, my grandma, my grandpa, they can’t go to the bathroom on their own. Like, what do you? It was just, it was so confusing to people. It seemed like such a, a cold calculation,
Dan: One person they ended up talking with was Gloria Bent. Her husband Gary was sent to a nursing home for rehab after brain surgery for cancer. He was weak. He couldn’t walk. And he had something called “left neglect”: His brain didn’t register that there was a left side of his body. Here’s Gloria testifying before a Senate committee about how — when Gary arrived at the nursing home — the first thing he got was a discharge date. That is…
Gloria Bent: Before the staff of the facility could even evaluate my husband or develop a plan of care, I was contacted by someone who identified themselves as my Navi Health Care Coordinator
Dan: Gloria says when she told the nursing home staff she’d heard from NaviHealth, they groaned. And told her what to expect.
Gloria Bent: I was told that I had just entered a battlefield, that I could expect a series of notices of denial of Medicare payment accompanied by a discharge date that would be two days after I got that notice.
Dan: Yeah, they said she’d get two days notice. Gloria says the nursing home staff told her she’d have 24 hours to appeal each of those, but even if she won, the denials would keep coming. In fact, they said,
Gloria Bent: If we won a couple of appeals, then we could expect that the frequency with which these denials were going to come would increase.
Dan: All of which happened. NaviHealth started issuing denials July 15, 2022, after Gary had been at the home for a month.
Gloria appealed. She told senators what the doctor who evaluated the appeal found: Gary couldn’t walk. He couldn’t even move — like from bed to a chair — without help from two people.. That reviewer took Gloria’s side.
Her husband’s next denial came a week after the first. Gloria won that appeal too. She says the reviewer noted that Gary needed maximum assistance with activities of daily living.
The third denial came four days later, and this time Gloria lost.
Gary came home in an ambulance: As Gloria testified, he couldn’t get into or out of a car without assistance from someone with special training.
And when he got into the ambulance, he had a fever. The next morning, he wound up in another ambulance — headed to a hospital with meningitis. He lost a lot of the functioning he’d picked up at the nursing home.
He died at home a few months later. When Gloria testified in the Senate, all of it was still fresh. She told them that as awful as Gary’s illness and decline had been, the fights with insurance were an added trauma.
Gloria Bent: This should not be happening to families and patients. It’s cruel. Our family continues to struggle with the question that I hear you asking today. Why are people who are looking at patients only on paper or through the lens of an algorithm
making decisions that deny the services judged necessary by health care providers who know their patients.
Dan: Bob Herman calls Gloria’s story heartbreaking, like so many others he’s seen.
And his attention goes to one part of Gloria’s story beyond denial-by-algorithm.
Because: It’s not just one denial. It’s that series of denials. You can appeal, but as Gloria testified, the denials speed up. And you have to win every single time. The company only has to win once.
I mean, unless you’re ready to get a lawyer and take your chances in court– which, in addition to being a major undertaking, also means racking up nursing home bills and legal bills you may never get reimbursed for, while the court process plays out.
Bob Herman: This appeal system is designed in such a way that people will give up. If you have a job, you know, even if you don’t, and you’re, and you’re also trying to take care of a family member, um, it’s a rigorous monotonous process that will chew people up and spit them out and then the people are inevitably going to give up. And I think in some ways insurers know that.
Dan: Going out on a limb to say: I think so too. So Bob and Casey’s first story on NaviHealth came out in March of 2023. They were the characters in the movie who go, “HEY, I THINK THERE’S SOMETHING REALLY BAD HAPPENING HERE.”
And people started paying attention. Like the U.S. Senate. which held that hearing where Gloria Bent told her story.
And like the federal agency that runs Medicare — the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, CMS.
CMS finalized a rule that told insurers: You can’t deny care to people just from using an algorithm.
And something else happened too: Bob and Casey started suddenly getting a lot MORE information.
Bob Herman: We received so many responses from people and it just opened the floodgates for former employees, just patients and family members, just everyone across the board.
Dan: And not just former employees. Current employees. And what they learned was: There was absolutely a strategy at work in how this algorithm was being used. It was strategy some people on the inside didn’t feel good about.
And this strategy got developed after United HealthGroup — and its subsidiary, Optum– bought NaviHealth in 2020. And here’s what NaviHealth employees started telling Casey and Bob about that strategy.
Bob Herman: For some of us, it’s creating this moral crisis. Like we know that we are having to listen to an algorithm to essentially kick someone out of a nursing home, even though we know that they can barely walk 20 feet.
Dan: What Bob and Casey learned from insiders– and how it connects to United’s role as a health care behemoth– that’s next.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News. That’s a nonprofit newsroom covering healthcare in America. Their reporters do amazing work, and I’m honored to work with them. We’ll have a little more about KFF Health News at the end of this episode.
So, NaviHealth — the company with the algorithm — got started in 2015.. And the idea behind it was to use data to get people home faster from nursing homes if they didn’t actually need to be there.
Because there was a lot of evidence that some people were being kept longer than they needed.
Bob Herman: There is some validity to the idea that there’s, there’s wasteful care in Medicare, like, you know, there’s been cases in the past proving that people stay in a nursing home for way longer than is necessary. And obviously there’s financial incentives for nursing homes to keep people as long as possible.
Dan: Traditional Medicare does have limits on nursing home care — but if you need “post-acute care” — help getting back on your feet after leaving a hospital traditional Medicare pays in full for 20 days– pretty much no questions asked. One of the selling points of Medicare Advantage — like selling points to policy nerds and politicians — was that it could cut waste, by asking those kinds of questions. NaviHealth and its algorithm were designed to help Medicare Advantage plans ask those questions in a smart way.
Bob Herman: There were… a lot of believers within NaviHealth that were like, okay, I think we’re doing the right thing. We’re trying to make sure people get home sooner because who doesn’t want to be at home.
Dan: And as those employees told Bob and Casey: Before United and Optum came in, the algorithm had been there as a guide — a kind of first guess — but not the final word.
NaviHealth has staff people who interact directly with patients. And back in the day, the pre-United day, Bob and Casey learned that those staff could make their own judgments.
Which made sense, because the algorithm doesn’t know everything about any individual case. It’s just making predictions based on the data it has.
Bob Herman: And there was just, just this noticeable change after United and OptiMentor that it felt more rigid. There’s no more variation.
Dan: If the algorithm says you go, you are pretty much going.
Bob Herman: United has said, no, that’s not the case, but obviously these documents and other communications that we’ve gotten kind of say otherwise.
Dan: Because these employees weren’t just talking. They were sharing. Internal memos. Emails. Training materials. All making clear: The company wanted people shipped out on the algorithm’s timetable.
Bob Herman: Documents came in showing that like this was a pretty explicit strategy. You know, UnitedHealth was telling its employees. Listen, we have this algorithm. We think it’s really good. So when it tells you how many, how many days someone should be in a nursing home, stick to it.
Dan: Stick to it or maybe be fired. Bob and Casey got documents — employee performance goals– saying: How close you stick to the algorithm’s recommendations? That’s part of how we’re evaluating your job performance.
Bob Herman: It’s okay. Algorithm said 17 days, you better not really go outside of that because your job is on the line.
Dan: Here’s how closely people were expected to stick to it. In 2022, employee performance goals shared with STAT showed that workers were expected to keep actual time in nursing homes to within three percent of what the algorithm said it should be. Across the board.
So, say you had 10 patients, and the algorithm said they each should get 10 days. That’s 100 days. Your job was to make sure that the total actual days for those patients didn’t go past 103 days.
Then, in 2023, the expectations got more stringent: Stay within one percent of the algorithm’s predictions. 10 patients, the algorithm says 100 days total? Don’t let it get past a hundred and one.
Bob Herman: Like that is, almost nothing. Like what, what, your hands are tied. If you’re that employee, what are you going to do? Are you going to get fired? Are you going to do what you’re told?
Dan: And one person who ended up talking, to did get fired.
Bob Herman: Correct. Yes. Uh, Amber Lynch did get fired And what she said was what we had also heard just more broadly was it, it created this internal conflict, like, Oh my God, what I’m doing doesn’t feel right.
Dan: Amber Lynch was a case manager. She told Bob and Casey about onepatient who couldn’t climb the stairs in his home after knee surgery. But the algorithm said he was ready. Amber’s supervisor said, “Have you asked the nursing home staff if they’ve tried to teach him butt bumping?” Amber grit her teeth and made the suggestion to the rehab director.
Amber Lynch: And she looked at me like I had two heads. She’s like, he is 78 years old. He’s not going to do that. He’s not safe to climb the stairs yet. He’s not doing it. We’re not going to have it butt bump the stairs.
Dan: Amber told Bob and Casey that when she got fired, it was partly for failing to hit the one percent target and partly for being late with paperwork– which she told Bob and Casey she fell behind because her caseload was so heavy.
She wasn’t the only one with that complaint.
Bob and Casey’s story shows another NaviHealth case manager– not named in the story because they’re still on the job — in their home office, struggling to keep up.
That week, they were supposed to work with 27 patients and their families. Gather documents, hold meetings. Another week, shortly before, they’d had 40 patients.
“Do you think I was able to process everything correctly and call everyone correctly the way I was supposed to?” the case manager asked. “No. It’s impossible. No one can be that fast and that effective and capture all of the information that’s needed.”
Bob and Casey watched this case manager fill out a digital form, feeding the algorithm the information it asked for on a man in his 80s with heart failure, kidney disease, diabetes and trouble swallowing, who was recovering from a broken shoulder.
A few minutes later, the computer spat out a number: 17 days.
The case manager didn’t have a lot of time or leeway to argue, but they were skeptical that the algorithm could get that number exactly right based on only the data it had.
And what data is the algorithm working with? What’s it comparing the data on any given patient TO? Bob Herman says that’s a big question.
Bob Herman: It’s something that for sure, like Casey and I, it’s been bothering us. Like, what, how is this whole system? Like, what is it based on? And we were never really given straight answers on that. NaviHealth and Optum and United have said it’s based on millions of patient records over time. The sources of that, it’s, it’s a little unclear, where all that’s coming from.
Dan: Bob and Casey talked with an expert named Ziad Obermeyer, a professor at the University of California Berkeley School of Public Health, who is not anti-algorithm. He actually builds algorithmic tools for decision making in public health.
AND he’s done research showing that some widely-used algorithms just scale up and automate things like racial bias.
He told Bob and Casey: Using an algorithm based on how long other, earlier patients have stayed in a nursing home — that’s not a great idea.
Because people get forced out of nursing homes, in his words, “because they can’t pay or because their insurance sucks.” He said, “So the algorightm is basically learning all the inequalities of our current system.”
And leaving aside that kind of bias, it seems unlikely to Bob that any algorithm could predict exactly what every single patient will need every single time.
No matter how much data it’s got, it’s predicting from averages.
Bob Herman: It reminds me of, like, a basketball game where let’s say someone averages 27 points per game. They don’t have 27 points every single, the game they go out there. It just varies from time to time.
Dan: But the NaviHealth algorithm doesn’t have to be right every time for United to make money using it.
Using it to make decisions can allow United to boost profits coming and going.
Bob Herman: United health and the other insurance companies that use Navi health. Are using this technology to more or less kick people out of nursing homes before they’re ready. And that is the claims denial side where it’s like, okay, let’s save as much money as we can instead of having to pay it to a nursing home.
Dan: And that’s just one side of it. The insurance side. Claims denial. But United isn’t just in the insurance business.
United’s Optum side is in every other part of health care.
Including — in the years since United took over NaviHealth — home health services. The kind of services you’re likely to need when you leave a nursing home.
In 2022, Optum bought one top home health company in what one trade publication called a “monster, jaw-dropping mega-deal” — more than 5 billion dollars. In 2023, Optum made a deal to buy a second mega-provider.
Bob and Casey’s story says NaviHealth’s shortening nursing home stays is integral to United’s strategy for these acquisitions. It does seem to open up new opportunities.
Bob Herman: You’re out of the nursing home because our algorithm said so. Now we’re going to send you to a home health agency or we’re going to send some home health aides into your home. And by the way, we own them.
Dan: Oh, right, because: If you’re in a Medicare Advantage plan, your insurer can tell you which providers are covered.
Bob Herman: So the real question becomes, how much is United potentially paying itself?
Dan: That is: How much might United end up taking money out of one pocket — the health insurance side — and paying itself into another pocket, Optum’s home-health services?
We don’t know the answer to how much United is paying itself in this way, or hoping to. And United has said its insurance arm doesn’t favor its in-house businesses.
But it seems like a reasonable question to ask. Actually, it’s a question the feds seem to be asking.
Optum hasn’t wrapped up its purchase of that second home-health company yet, and in February 2024, the Wall Street Journal and other outlets reported that the U.S. Department of Justice had opened an anti-trust investigation.
And you don’t have to be in a Medicare Advantage plan run by United to get kicked out of a nursing home on an algorithm’s say-so.
Bob Herman says NaviHealth sells its algorithm-driven services to other big insurance companies
He says, put together, the companies that use NaviHealth cover as many as 15 million people — about half of everybody in Medicare Advantage.
Bob Herman: Odds are, if you’re in a Medicare Advantage plan, there’s a, there’s a really good shot that your coverage policies, if you get really sick and need nursing home care, for example, or any kind of post acute care, an algorithm could be at play at some point.
Dan: This is the dark side of Medicare Advantage.
Bob Herman: Everyone loves their Medicare Advantage plan when they first sign up, right? Because it’s offering all these bells and whistles. It’s, here’s a gym membership. It’s got dental and vision, which regular Medicare doesn’t have. And it’s also just, it’s, it’s cheaper. Like, if it’s just from a financial point of view, if, if you’re a low income senior, How do you turn it down? There’s, there’s so many plans that offer like free, there’s no monthly premiums in addition to all the bells and whistles. But Nobody understands the trade offs , When you’re signing up for Medicare and Medicare Advantage, you’re on the healthier side of, of being a senior, right?
Dan: And none of us can count on staying healthy forever. When you sign up for Medicare you’re signing up your future self — whether that’s ten or twenty or more years out. That future you, might really need good medical care.
And at that point, as we explained in our last episode, if Medicare Advantage isn’t working for you, you may not be able to get out of it.
Bob Herman: You could potentially not fully get the care that you need. We shouldn’t assume that, that this couldn’t happen to us because it can.
Dan: So, yeah. Kind of a horror story. But: Unlike some horror movies, when Bob and Casey started publishing their stories, they started getting people’s attention.
We mentioned the new rules from the feds and the senate hearings after Bob and Casey’s first story in March 2023
Later in the year, when Bob and Casey published their story with documents and stories from inside NaviHealth, a class-action lawsuit got filed.
Since then, CMS has said it will step up audits under its new rules.
Bob Herman: There was a memo that CMS sent out to Medicare advantage plans that said, Hey, listen, we’re telling you again, do not deny care solely on any AI or algorithms. Like just don’t do it.
Dan: And in February 2024, the Senate held another hearing.
Here’s Senator Elizabeth Warren at that hearing, saying these CMS rules aren’t enough. We need stronger guardrails.
Elizabeth Warren: Until CMS can verify that AI algorithms reliably adhere to Medicare coverage standards by law, then my view on this is CMS should prohibit insurance companies from using them in their MA plans for coverage decisions. They’ve got to prove they work before they put them in place.
Dan: So people — people with at least some power– are paying some attention.
Bob Herman: I don’t think this is necessarily going to escape. Political scrutiny for a while.
Dan: So, basically, the story isn’t over.
This isn’t one of those horror movies where the monster’s been safely defeated at the end, and everybody just starts cleaning up the mess. And it’s not one where the monster is just on the loose, unleashing the apocalypse.
Because it’s not a movie. There’s no ending. There’s just all of us trying to figure out what’s going on, and what we can maybe do about it.
One last thing: I got a lot of emails after our last episode, where we laid out a lot of information about Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare. Most of it was along the lines of, Thank you! That was really helpful! Which made me feel really good.
And we got a couple notes about things we could have done better. Especially this: We said Traditional Medicare leaves you on the hook for 20 percent of everything, without an out of pocket limit.
Which is true — but only for Medicare Part B: Doctor visits, outpatient surgeries and tests. Which can add up, for sure.
Medicare Part A — if you’re actually hospitalized — covers most services at 100 percent, after you meet the deductible. In 2024 that’s one thousand, six hundred thirty-two dollars.
Thanks to Clarke Lancina for pointing that out.
There have been a bunch of other, amazing notes in my inbox recently, and I want to say: Please keep them coming.
If you go to arm and a leg show dot com, slash, contact, whatever you type there goes straight to my inbox. You can attach stuff too: documents… voice memos.
Please let me hear from you. That’s arm and a leg show dot com, slash contact.
I’ll catch you in a few weeks.
Till then, take care of yourself.
This episode of an arm and a leg was produced by me, Dan Weissmann, with help from Emily Pisacreta, and edited by Ellen Weiss.
Adam Raymonda is our audio wizard. Our music is by Dave Weiner and blue dot sessions. Extra music in this episode from Epidemic Sound.
Gabrielle Healy is our managing editor for audience. She edits the first aid kit newsletter.
Bea Bosco is our consulting director of operations. Sarah Ballama is our operations manager.
And Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News. That’s a national newsroom producing in depth journalism about healthcare in America and a core program at KFF, an independent source of health policy research, polling and journalism.
Zach Dyer is senior audio producer at KFF Health News. He’s editorial liaison to this show.
And thanks to the Institute for Nonprofit News for serving as our fiscal sponsor, allowing us to accept tax exempt donations. You can learn more about INN at INN. org.
Finally, thanks to everybody who supports this show financially– you can join in any time at arm and a leg show dot com, slash, support — and thanks for listening.
“An Arm and a Leg” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Public Road Productions.
To keep in touch with “An Arm and a Leg,” subscribe to the newsletter. You can also follow the show on Facebook and the social platform X. And if you’ve got stories to tell about the health care system, the producers would love to hear from you.
To hear all KFF Health News podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to “An Arm and a Leg” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 3 months ago
Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, An Arm and a Leg, Podcasts
Adultos mayores, agotados por tener que organizar tanta atención médica
En enero, Susanne Gilliam, de 67 años, estaba yendo a recoger el correo afuera de su casa cuando se cayó al resbalar sobre una capa de hielo negro.
Sintió una punzada de dolor en la rodilla y el tobillo de la pierna izquierda. Después de llamar a su marido por teléfono, logró regresar a su casa con dificultad.
En enero, Susanne Gilliam, de 67 años, estaba yendo a recoger el correo afuera de su casa cuando se cayó al resbalar sobre una capa de hielo negro.
Sintió una punzada de dolor en la rodilla y el tobillo de la pierna izquierda. Después de llamar a su marido por teléfono, logró regresar a su casa con dificultad.
Y así comenzó el vaivén interminable que tantas personas enfrentan cuando tienen que navegar el desorganizado sistema de salud de Estados Unidos.
El cirujano ortopédico de Gilliam, que la había tratado antes por problemas en la misma rodilla, la vio esa tarde pero le aclaró: “Yo no me ocupo de tobillos”.
La derivó a un especialista en tobillos que ordenó nuevas radiografías y una resonancia magnética. Gilliam pidió hacerse las pruebas en un hospital cerca de su casa en Sudbury, Massachusetts, que le resultaba más conveniente. Pero cuando llamó para pedir una cita, el hospital no tenía la orden del doctor, que finalmente llegó después de varias llamadas más.
Coordinar la atención que necesita para recuperarse, incluyendo sesiones de fisioterapia, se convirtió en un trabajo de medio tiempo para Gilliam. (Los terapeutas trabajan solo en una parte del cuerpo por sesión, y por lo tanto Gilliam requiere visitas separadas para su rodilla y su tobillo, varias veces a la semana).
“El peso de organizar todo lo que necesito es enorme”, dijo Gilliam. “Te queda una sensación de agotamiento físico y mental”.
En algunos casos, las deficiencias del sistema de salud son el precio que se paga por avances extraordinarios en el campo de la medicina. Pero también ponen en evidencia las incoherencias entre las capacidades de los adultos mayores y las demandas del sistema.
“La buena noticia es que sabemos mucho más y podemos hacer mucho más por las personas con distintas afecciones”, dijo Thomas H. Lee, director médico de Press Ganey, una consultoría que hace seguimiento de las experiencias de los pacientes con el sistema de salud. “La mala noticia es que el sistema se ha vuelto tremendamente complejo”.
Esto se agrava por las múltiples guías para tratar afecciones, la super especialización médica, y los incentivos financieros que hacen que los pacientes reciban cada vez más atención, dijo Ishani Ganguli, profesora asociada en la Escuela de Medicina de Harvard.
“No es raro que pacientes mayores tengan tres o más cardiólogos que les programan citas y pruebas regulares”, dijo. Si alguien tiene varios problemas de salud (por ejemplo, enfermedades cardíacas, diabetes y glaucoma), las interacciones con el sistema se multiplican.
Ganguli es la autora de un nuevo estudio que muestra que los pacientes de Medicare dedican aproximadamente tres semanas al año a hacerse pruebas médicas, ver a doctores, someterse a tratamientos o procedimientos médicos, buscar atención en salas de emergencia o pasar tiempo en el hospital o en centros de rehabilitación. (Los datos son de 2019, antes de la pandemia de covid, que alteró los patrones de atención médica. Cada servicio recibido se contó como un día de contacto con el sistema de salud).
El estudio determinó que poco más de 1 de cada 10 personas mayores, incluyendo las que se estaban haciendo controles o recuperándose de enfermedades graves, pasaban más tiempo recibiendo atención médica: al menos 50 días al año.
“Hay aspectos de esto que son muy beneficiosos y valiosos para las personas, pero hay otros que son menos esenciales”, dijo Ganguli. “No hablamos lo suficiente sobre lo que les pedimos a los adultos mayores que hagan, y si tiene sentido”.
Victor Montori, profesor de medicina de la Clínica Mayo en Rochester, Minnesota, lleva muchos años advirtiendo sobre lo que llama la “carga de tratamiento” que enfrentan los pacientes.
Esto incluye el tiempo que dedican a recibir atención médica, programar citas, encontrar transporte para las visitas médicas, obtener y tomar medicamentos, comunicarse con las aseguradoras, pagar facturas médicas, monitorear su salud en casa y seguir consejos como cambios en la dieta.
Hace cuatro años, en un artículo titulado “¿Se siente mi paciente agobiado?”, Montori y sus colegas descubrieron que el 40% de los pacientes con enfermedades crónicas como asma, diabetes y trastornos neurológicos “sentían que su carga de tratamiento era insostenible”.
Cuando la carga de tratamiento es excesiva, las personas dejan de seguir las recomendaciones médicas y dicen que su calidad de vida empeora, según los investigadores. Los adultos mayores con múltiples afecciones médicas y bajo nivel de educación son especialmente vulnerables, ya que experimentan inseguridad económica y aislamiento social.
El uso cada vez más frecuente de sistemas telefónicos digitales y portales electrónicos para pacientes en los consultorios y la falta de tiempo por parte de los doctores profundizan las barreras. “Cada vez es más difícil para los pacientes acceder a doctores que puedan pasar tiempo con ellos, para ayudarlos a resolver problemas y responder sus preguntas”, dijo Montori.
Mientras tanto, los médicos rara vez preguntan a los pacientes sobre su capacidad para realizar las tareas que se les pide. “A menudo tenemos poca idea de qué tan compleja es la vida de nuestros pacientes”, escribieron médicos en un informe de 2022 sobre cómo reducir la carga de tratamiento.
Un ejemplo es lo que vivieron Jean Hartnett, de 53 años de Omaha, Nebraska, y sus ocho hermanos después que su madre de 88 años sufriera un derrame cerebral en febrero de 2021, mientras hacían compras en Walmart.
En ese momento, su madre estaba cuidando al padre de Hartnett, quien sufría de una enfermedad renal y necesitaba ayuda con las tareas diarias, como ducharse o ir al baño.
Durante el año posterior al derrame cerebral, los padres de Hartnett, ambos trabajadores agrícolas extremadamente independientes que vivían en Hubbard, Nebraska, sufrieron varios achaques y las crisis médicas se volvieron comunes.
Cuando un médico cambiaba el plan de atención de su mamá o su papá, eran necesarios nuevos medicamentos, suministros y equipos médicos, y programar nuevas sesiones de terapia ocupacional, física y del habla.
Ninguno de los padres podía quedarse solo si el otro necesitaba atención médica.
“No era inusual para mí estar llevando a uno de mis padres a su casa después del hospital o de la visita al médico y pasar una ambulancia o un familiar transportando al otro al doctor”, explicó Hartnett. “Se necesitaba muchísima coordinación”.
Hartnett se mudó a la casa de sus padres durante las últimas seis semanas de vida de su padre, cuando los médicos decidieron que estaba demasiado débil como para someterse a diálisis. Falleció en marzo de 2022. Su madre murió meses después, en julio.
Entonces, ¿qué pueden hacer los adultos mayores y sus cuidadores y familiares para aliviar la carga de la atención médica?
Para empezar, es importante sincerarse con el médico si el plan de tratamiento que recomienda no resulta factible, y explicarle por qué, dijo Elizabeth Rogers, profesora asistente de medicina interna en la Escuela de Medicina de la Universidad de Minnesota.
Recomendó preguntar sobre cuáles intervenciones serían las más importantes para mantenerse saludable y cuáles podrían ser prescindibles.
Los médicos pueden ajustar los planes, suspender los medicamentos que no producen beneficios significativos y programar visitas virtuales, en caso de que las personas puedan manejar la tecnología necesaria (muchos adultos mayores no pueden).
Pregunte también si un asistente de pacientes (también llamados navegadores) puede ayudarle a programar varias citas y exámenes en el mismo día, para minimizar la carga de ir y venir de los centros médicos. Estos profesionales también pueden ayudarlo a conectarse con recursos comunitarios, como servicios de transporte. (La mayoría de los centros médicos tienen personal de este tipo, pero los consultorios médicos no).
Si no entiende cómo hacer lo que su médico pide, pregunte: ¿Qué implicaría esto de mi parte? ¿Cuánto tiempo llevaría? ¿Qué necesitaré? Y pida materiales escritos, como guías de autocontrol del asma o la diabetes, que puedan ayudarle a comprender mejor los requisitos.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 3 months ago
Aging, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicare, Navigating Aging, Noticias En Español, Massachusetts, Nebraska
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': The ACA Turns 14
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
The Affordable Care Act was signed into law 14 years ago this week, and Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra joined KFF Health News’ Julie Rovner on this week’s “What the Health?” podcast to discuss its accomplishments so far — and the challenges that remain for the health law.
Meanwhile, Congress appears on its way to, finally, finishing the fiscal 2024 spending bills, including funding for HHS — without many of the reproductive or gender-affirming health care restrictions Republicans had sought.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Mary Agnes Carey of KFF Health News, Tami Luhby of CNN, and Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Panelists
Mary Agnes Carey
KFF Health News
Tami Luhby
CNN
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- The Supreme Court will hear oral arguments next week in a case that could decide whether the abortion pill mifepristone will remain easily accessible. The case itself deals with national restrictions rather than an outright ban. But, depending on how the court rules, it could have far-reaching results — for instance, preventing people from getting the pills in the mail and limiting how far into pregnancy the treatment can be used.
- The case is about more than abortion. Drug companies and medical groups are concerned about the precedent it would set for courts to substitute their judgment for that of the FDA regarding drug approvals.
- Abortion-related ballot questions are in play in several states. The total number ultimately depends on the success of citizen-led efforts to collect signatures to gain a spot. Such efforts face opposition from anti-abortion groups and elected officials who don’t want the questions to reach the ballot box. Their fear, based on precedents, is that abortion protections tend to pass.
- The Biden administration issued an executive order this week to improve research on women’s health across the federal government. It has multiple components, including provisions intended to increase research on illnesses and diseases associated with postmenopausal women. It also aims to increase the number of women participating in clinical trials.
- This Week in Medical Misinformation: The Supreme Court heard oral arguments in the case Murthy v. Missouri. At issue is whether Biden administration officials overstepped their authority when asking companies like Meta, Google, and X to remove or downgrade content flagged as covid-19 misinformation.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The Washington Post’s “Arizona Lawmaker Tells Her Abortion Story to Show ‘Reality’ of Restrictions,” by Praveena Somasundaram. (Full speech here.)
Alice Miranda Ollstein: CNN’s “Why Your Doctor’s Office Is Spamming You With Appointment Reminders,” by Nathaniel Meyersohn.
Tami Luhby: KFF Health News’ “Georgia’s Medicaid Work Requirement Costing Taxpayers Millions Despite Low Enrollment,” by Andy Miller and Renuka Rayasam.
Mary Agnes Carey: The New York Times’ “When Medicaid Comes After the Family Home,” by Paula Span, and The AP’s “State Medicaid Offices Target Dead People’s Homes to Recoup Their Health Care Costs,” by Amanda Seitz.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- NPR’s “Standard Pregnancy Care Is Now Dangerously Disrupted in Louisiana, Report Reveals,” by Rosemary Westwood.
- The Washington Post’s “As the Cost of Storing Frozen Eggs Rises, Some Families Opt to Destroy Them,” by Amber Ferguson.
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: The ACA Turns 14
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, March 21, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Tami Luhby of CNN.
Tami Luhby: Hello.
Rovner: And my KFF Health News colleague Mary Agnes Carey.
Mary Agnes Carey: It’s great to be here.
Rovner: Later in this episode to mark the 14th anniversary of the Affordable Care Act, we’ll have my interview with Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra, but first, this week’s news. So it appears our long national nightmare following the progress of the fiscal 2024 spending bill for the Department of Health and Human Services is nearly over, nearly halfway through the fiscal year. The White House, House, and Senate have, as far as we can tell, reached a compromise on the last tranche of spending bills, which is a good thing because the latest temporary spending bill runs out at midnight Friday. Funding for the Department of Health and Human Services, from what I’ve seen so far, is basically flat, which is a win for the Democrats because the Republicans had fought for a cut of something in the neighborhood of 22%.
Now, assuming this all happens, the House is scheduled to vote, as we speak now, on Friday at 11 a.m., leaving the Senate not very much time to avert a possible partial shutdown. Democrats seem also to have avoided adding all manner of new restrictions on reproductive and gender-affirming health care to the HHS part of the bill. It’s the last big train leaving the station likely until after the election. So Alice, we’ll get to the add-ons in a minute, but have you seen anything in the HHS funding worthy of note or did they manage to fend off everything that would’ve been significantly newsworthy?
Ollstein: Like you said, it is basically flat. It’s a small increase, less than 1% overall for HHS, and then a lot of individual programs are just completely flat, which advocacy groups argue is really a cut when you factor in inflation. The cost of providing services and buying medications and running programs and whatnot goes up. So flat funding is a cut in practice. I’m hearing that particularly from the Title X family planning folks that have had flat funding for a decade now even as demand for services and costs have gone up.
So I think that in the current environment, Democrats are ready to vote for this. They don’t want to see a shutdown. And in the House, the bill passage will depend on those Democratic votes because they are likely to lose a lot of Republicans. Republicans are mad that there weren’t deeper cuts to spending and, as you alluded to, they’re mad that they didn’t get these policy rider wins they were banking on.
Rovner: As I’ve mentioned, since this is a must-pass bill, there are always the efforts to add non-spending things to it. And on health care, apparently, the effort to add the PBM, pharmacy benefit regulation bill we’ve talked about so much failed, but lawmakers did finally get a one-year deal to extend PEPFAR, the international AIDS/HIV program. Alice, you’ve been dutifully following this since it expired last year. Remind us why it got held up and what they finally get.
Ollstein: What happened in the end is it is a one-year reauthorization that’s a so-called clean reauthorization, meaning they are not adding new anti-abortion restrictions and provisions that the Republicans wanted. So what we reported this week is, like any compromise, no one’s happy. So Republicans are upset that they didn’t get the anti-abortion restrictions they wanted, and I’ll explain more on that in a second, and Democrats are upset that this is just a one-year reauthorization. It’s the first reauthorization that’s this sort of short-term stopgap length. In the program’s decades of history, it’s always been a full five-year reauthorization up until now. But the fight over abortion and accusations that program funds were flowing to abortion providers really split Congress on this.
Even though you had mainstream leadership Republicans who were saying, “Look, we just want to reauthorize this as-is,” you had a small but very vocal contingent of hard-line anti-abortion lawmakers backed by some really influential groups like the Heritage Foundation and SBA [Susan B. Anthony Pro-Life America] who were saying, “No, we have to insist on a shorter-term reauthorization,” so that they hope Trump will be in office next year and can impose these exact same anti-abortion restrictions through executive action. So they’re basically trying to punt control of the program into what they hope is a more favorable environment, where either they’ll have the votes in Congress to make these changes and restrictions to the program or they can do it through the White House.
Rovner: So basically, the fight over PEPFAR, not over. So as I already mentioned, Saturday is the 14th anniversary of the Affordable Care Act, which you’ll hear more about in my interview with HHS Secretary Becerra, but I wanted to pose to you guys one of the questions that I posed to him. As Nancy Pelosi famously predicted, at least according to public opinion polls, the more people learned about the health law, indeed, the more they are liking it. But it still lacks the popularity and branding of big government health programs, like Medicare and Medicaid, and I think lots of people still don’t know that lots of the provisions that they like, things like letting your adult children stay on your health plan until they’re 26 or banning preexisting condition exclusions, those were things that came from the Affordable Care Act. Any theories as to why it is still so polarizing? Republicans didn’t love Medicare and Medicaid at the beginning either, so I don’t think it’s just that Republicans still talk about it.
Luhby: Part of it I think is because there are so many provisions and they’re not labeled the Affordable Care Act like Medicare is. Actually to some extent, Medicaid may not be as well known in some states because states have different Medicaid programs and different names and so do the ACA exchanges. So that’s part of it, but also, things like why do you get a free mammogram and why you get to go for a routine checkup every year; that’s not labeled as an Affordable Care Act provision, that’s just the preventive services. So I think that it would be difficult now after 14 years to bring all of that into the everyday branding by doctors and health providers. But that’s certainly what the administration and advocates are trying to do by sending out a lot of messages that list all of the benefits of the ACA.
Rovner: I will say this is the biggest full-court press I’ve seen an administration do on the ACA in quite a while. Obviously, it’s a presidential election year and it’s something that the Biden administration is proud of, but at least I would think that maybe just all the publicity might be part of their strategy. Mac, you wanted to say something.
Carey: No, absolutely. It’s going to be part of the Biden reelection campaign. They’re going to be pushing it, talking a lot about it. We have to remember we’ve had this ringside seat to all the Republican opposition to the Affordable Care Act. All the conversation about we’re going to repeal it and put something better in, former President Trump is still sending that message out to the electorate. I don’t know how much confusion, if any confusion, it creates, but to Tami’s point, you’ve got millions of people that have gotten coverage under the Affordable Care Act but millions more have benefited by all these provisions we’re talking about: the preventive care provisions, leaving adult kids up to 26 on your health insurance plan, that kind of thing.
Also, give it time. Fourteen years is a long time, but it’s not the time of Medicare, which was created in 1965, and Medicaid. So I think over time, the Affordable Care Act is part of the fabric and it will continue to be. But absolutely, for sure, President Biden is going to run on this, like you said, Julie, full-court press, talk extensively about it in the reelection campaign.
Ollstein: It makes sense that they’re leaning really hard on Obamacare as a message because, even if everyone isn’t familiar with it, a lot more people are familiar with it and like it than, polling shows, on the Biden administration’s other big health care accomplishment, which is drug price negotiation, which polling shows that most people, and even most seniors, who are the ones who are set to benefit the most, aren’t aware that it exists. And that makes sense because they’re not feeling the impact of the lower prices yet because this whole thing just started and it won’t be until 2026 that they’ll really actually experience cheaper medications. But people are already feeling the direct impact of Obamacare on their lives, and so it does make sense that they’re going to lean really hard on this.
Rovner: Of course, we went through the same thing with Obamacare, which also didn’t take full effect until, really, this is really the 10th anniversary of the full effect of the Affordable Care Act because it didn’t take effect until 2014. Tami, you wanted to add something.
Luhby: No, I was going to say it’s also the seventh anniversary of the Trump administration and congressional Republicans trying to tear apart the Affordable Care Act and repeal and replace it, which is the messaging that you’re seeing now is very similar to what you saw in 2017. It’s just surprising to me that with very intensive messaging on both sides at that time about what the Republicans saying what the problems are and the Democrats saying what all of the benefits are, — including the protections for people with preexisting conditions and the other things we’ve mentioned — that more people don’t associate those provisions with the ACA now. But the Biden administration is trying to revive all of that and remind people, as they did in 2018 in the successful midterm elections for the Democrats, that the ACA does provide a lot of the benefits that they are taking advantage of and appreciate.
Rovner: I think, in some ways, the 2017 fight was one of the best things that ever happened to the ACA in terms of helping people understand what actually was in it, because the Democrats managed to frighten people about things that they liked being taken away. Here we go again. All right, let us turn to abortion. There’s a new report out from the Guttmacher Institute that finds a dramatic jump in the use of medication abortion in 2023, the first full year since the Supreme Court reversed the nationwide right to abortion in the Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] case, more than 60% of abortions use medication rather than a procedure last year. This news comes as the Supreme Court next week prepares to hear oral arguments in a case that could dramatically restrict availability of the abortion pill mifepristone. Alice, remind us what’s at stake in this case. It’s no longer whether they’re going to just outright cancel the approval.
Ollstein: That’s right. So the Supreme Court is taking up the narrowed version of this from the 5th Circuit. So what’s at stake are national restrictions on abortion pills, but not a national outright ban like you mentioned. But those restrictions could be really sweeping and really impactful. It would prevent people from getting the pills through the mail like they currently do. It would prevent people from potentially getting them in any other way other than directly from a doctor. So this would apply to red states and blue states alike. It would override abortion rights provisions in blue states that have done a lot to increase access to the pills. And it would also restrict their use back to the first seven weeks of pregnancy instead of 10, which is a big deal because people don’t often find out they’re pregnant until getting close to that line or beyond.
So this is a really big deal, and I think you can really see, especially from the flurry of amicus briefs have been filed, that anxiety about this case in the medical community and the pharmaceutical community, the scientific community, it goes way beyond the impact just on abortion. People are really worried about setting a precedent where the FDA’s scientific judgment is second-guessed by courts, and they worry that a win for the anti-abortion groups in this case would open the door to people challenging all kinds of other medications that they have an issue with: contraception, covid vaccines, HIV drugs, the list goes on and on, gender-affirming care medications, all sorts of things. So there are the bucket of potential impacts on abortion specifically, which are certainly significant, and then there’s the bigger slippery slope fears as well.
Rovner: Also, this is obviously still way political. More than just the abortion pill. It’s been a while since we’ve talked about state ballot measures. We, I think, feel like we spent all of last year talking about abortion state ballot measures. Alice, catch us up real quick on where we are. How many states have them? And what is this campaign against, by the anti-abortion people, to try to prevent them from getting on the ballot?
Ollstein: Check me if I’m wrong, but I don’t believe we know for sure about, especially the states that have citizen-led ballot initiatives where people are gathering signatures. So Florida had one of the earliest deadlines and they did meet their signature threshold. But they are now waiting on the state Supreme Court to say whether or not they have a green light to go forward this fall. A lot of other states are still collecting signatures. I think the only states we know for sure are the ones where the state legislature is the one that is ordering it to be put on the ballot, not regular citizens gathering signatures.
We still don’t know, but things are moving forward. I was just in Arizona reporting on their efforts. Things are moving forward there. Things are moving forward in Montana. They just got a court ruling in their favor to put something on the ballot. And things are moving forward in Missouri, a lot of places. So this could be really huge. Of course, like you mentioned, anti-abortion groups and anti-abortion elected officials are doing a lot of different things to try to prevent this from going on the ballot.
It’s interesting, you heard arguments over the last couple years against this being more along the lines of, “Oh, this is allowing these out-of-state big-money groups to swoop in and mislead and tell us what to do,” and those were the anti-abortion arguments against allowing people to vote on this directly. Now, you’re hearing, I’m hearing, more arguments along the lines of, “This shouldn’t be something subject to a popular vote at all. We shouldn’t put this up for a vote at all.” They consider this a human rights issue, and so I think that’s a really interesting evolution as well, particularly when the fall of Roe [v. Wade] was celebrated for returning the question of abortion access to the people, but maybe not these people specifically.
Rovner: I’ve been interested in seeing some of these anti-abortion groups trying to launch campaigns to get people not to put signatures on petitions. That’s moving it back a step I don’t think I’d ever seen. I don’t think I’ve ever seen a campaign to say, “Don’t sign the petition that would put this on the ballot to let people vote on it.” But that’s what we’re seeing, right?
Ollstein: Well, that’s what I went to Arizona to see firsthand is how that’s working, and it’s fascinating. They really worry that if it gets on the ballot, it’ll pass. It has in every state so far, so it’s reasonable for them to assume that. So they’re trying to prevent it from getting on the ballot. The way they’re doing that is they’re tracking the locations of signature gatherers and trying to go where they are and trying to intervene and hold up signs. I saw this firsthand. I saw it at a street fair. People were gathering signatures and several anti-abortion demonstrators were standing right in front of them with big signs and trying to argue with people and deter them from signing. It was not working, from what I observed. And from the overall signature count statewide, it was not working in Arizona. But it’s fascinating that they’re trying this.
Carey: I was going to say just our reporting from our KFF Health News colleagues found that 13 states are weighing abortion-related ballot measures, most of which would protect abortion rights. To your point, the scope is pretty extensive. And for all the reasons Alice just discussed, it’s quite the issue.
Rovner: Yeah, and we will obviously talk more about this as the election gets closer. I know we talk about Texas a lot on this podcast, but this week, I want to highlight a study from next door in Louisiana, also a very strong anti-abortion state. A new report from three groups, all of which support abortion rights, charges that, as in Texas, women with pregnancy complications are being forced to wait for care until their conditions become critical. And in some cases, women with nonviable pregnancies are being forced to have C-section surgery because their doctors don’t dare use medication or other less-risky procedures in case they could be accused of performing an abortion.
At some point, you have to think that somebody is going to have a malpractice case. Having a C-section because your doctor is afraid to terminate a nonviable pregnancy seems like pretty dangerous and rather aggressive way to go. This is the first I’ve ever heard of this. Alice, have you heard anything about this?
Ollstein: Not the C-section statistics specifically, but definitely the delays in care and some of the other impacts described in that report have absolutely been reported in other states and in legal challenges that have come up in Texas, in Oklahoma, in Tennessee, in Idaho by people who were denied abortions and experienced medical harms because of it. So I think that fits into the broader pattern. And it’s just more evidence about how this is having a chilling effect on doctors. And the exact letter of the law may be one thing, and you have elected officials pointing to exemptions and provisions in the law, but the chilling effect, the fear and the confusion in the medical community, is something in addition to that.
Rovner: As we put it out before, doctors have legitimate fears even if they don’t want to get dragged into court and have to hire lawyers and take time off — even if they’re innocent, even if they have what they consider to be pretty strong evidence that whatever it was that they did was legitimate under the law in terms of taking care of pregnant women. A lot of them, they don’t want to come under scrutiny, let’s put it that way, and it is hard to blame them about that.
Meanwhile, the backlash over the Alabama Supreme Court decision that fertilized embryos for IVF have legal rights is continuing as blue states that made themselves safe spaces for those seeking abortion are now trying to welcome those seeking IVF. Anybody think this is going to be as big a voting issue as abortion this fall? It’s certainly looking like those who support IVF, including some Republicans, are trying to push it.
Carey: I would think yes, it absolutely will be because it has been brought into the abortion debate. The actual Alabama issue is about an Alabama law and whether or not this particular, the litigants who sued were … it was germane and covered by the law, but it’s been brought into the abortion issue. The whole IVF thing is so compelling, about storage of the embryos and what people have to pay and all the restrictions around it and some of the choices they’re making. I guess that you could say more people have been touched by IVF perhaps than the actual abortion issue. So now, it’s very personal to them and it’s been elevated, and Republicans have tried to get around it by saying they support it, but then there’s arguments that whether or not that’s a toothless protection of IVF. It came out of nowhere I think for a lot of politicians and they’ve been scrambling and trying to figure it out. But to your point, Julie, I do wonder if it will be elevated in the election. And it was something they didn’t think they’d have to contend with, rather, and now they do.
Rovner: Obviously, it’s an issue that splits the anti-abortion community because now we’ve had all these very strong pro-lifers like Mike Pence saying, “I created my family using IVF.” Nikki Haley. There are a lot of very strong anti-abortion Republicans who have used IVF. So you’ve got some on the far … saying, “No, no, no, you can’t create embryos and then destroy them,” and then you’ve got those who are saying, “But we need to make sure that IVF is still available to people. If we’re going to call ourselves pro-life, we should be in favor of people getting pregnant and having babies, which is what IVF is for.” Alice, I see you nodding your head.
Ollstein: Yeah. So we’re having sort of a frustrating discourse around this right now because Democrats are saying, “Republicans want to ban IVF.” And Republicans are saying, “No, we don’t. We support IVF. We love IVF. IVF is awesome.” And neither is totally accurate. It’s just missing a lot of nuance. Republicans who say they support IVF also support a lot of different kinds of restrictions on the way it’s currently practiced. So they might correctly argue that they don’t want to ban it entirely, but they do want it practiced in a different way than it is now, such as the production of many embryos, some of which are discarded. So I think people are just not being asked the right questions right now. I think you got to get beyond, “Do you support IVF?” That gives people a way to dodge. I think you really have to drill into, “OK. How specifically do you want this regulated and what would that mean for people?”
Carey: Right, and the whole debate with some of the abortion rights opponents, some of them want the federal government to regulate it. Mike Johnson, speaker of the House, has come out and said, “No, no, that can be done at the state level.” So they’ve got this whole split internally in the party that is, again, a fight they didn’t anticipate.
Rovner: Well, Mac, something that you alluded to that I was struck by was a piece in The Washington Post this week about couples facing increasing costs to store their IVF embryos, often hundreds of dollars a year, which is forcing them to choose between letting the embryos go or losing a chance to possibly have another child. It’s obviously a big issue. I’m wondering what the anti-IVF forces think about that. As we’ve seen in Alabama, it’s not like you can just pick your embryos up in a cooler and move them someplace else. Moving them is actually a very big deal.
I don’t wish to minimize this, but I remember you have storage units for things, not obviously for embryos. One of the ways that they make money is that they just keep raising the cost because they think you won’t bother to move your things, so that you’ll just keep paying the increased cost. It feels like that’s a little bit of what’s happening here with these stored embryos, and at some point, it just gets prohibitively expensive for people to keep them in storage. I didn’t realize how expensive it was.
Carey: They’re all over the place. In preparing for this discussion, I’ve read things about people are paying $600 a year, other people are paying $1,200 a year. There’s big jumps from year to year. It can be an extremely expensive proposition. Oh, my goodness.
Rovner: IVF itself, I think as we’ve mentioned, is also extremely expensive and time-consuming, and emotionally expensive. It is not something that people enter into lightly. So I think we will definitely see more as we go. There’s also women’s health news this week that doesn’t have to do with reproduction. That’s new. Earlier this week, President Biden issued an executive order attempting to ensure that women are better represented in medical research. Tami, what does this order do and why was it needed?
Luhby: Well, it’s another attempt by the Biden administration, as we’ve discussed, to focus on reproductive health and reproductive rights. During the State of the Union address earlier this month, Biden asked Congress to invest $12 billion in new funding for women’s health research. And there are actually multiple components to the executive order, but the big ones are that it calls for supporting research into health and diseases that are more likely to occur midlife for women after menopause, such as rheumatoid arthritis, heart attacks, osteoporosis, and as well as ways to improve the management of menopause-related issues.
We are definitely seeing that menopause care is of increasing focus in a multitude of areas including employer health insurance, but the executive order also aims to increase the number of women participating in clinical trials since they’re poorly represented now. We know that certain medications and certain treatments have different effects on women than men, but we don’t really know that that well because they’re not as represented in these clinical trials. Then it also directs agencies to develop and strengthen research and data standards on women’s health across all of the relevant research and funding opportunities in the government.
Rovner: I’ll say that this is an issue I have very strong feelings about because I covered the debate in 1992 about including women in medical research. At the time, doctors didn’t want to have women in clinical trials because they were worried about hormones, and they might get pregnant, and we wouldn’t really know what that meant for whatever it was that we were testing. Someone suggested that “If you’re going to use these treatments and drugs on women, maybe you should test them on women too.” Then I won an award in 2015 for a story about how they still weren’t doing it, even though it was required by laws.
Carey: And here we are, 2024.
Rovner: Yeah, here we are. It just continues, but at least they’re trying. All right, finally, this week in medical misinformation, we travel to the Supreme Court, where the justices heard oral arguments in a case brought by two Republican state attorneys general charging that the Biden administration, quote, “coerced” social media platforms, Google, Meta, and X, into downgrading or taking down what public health officials deemed covid disinformation. I didn’t listen to the arguments, but all the coverage I saw suggested that the justices were not buying what the attorneys general were selling.
Yet another public-health-adjacent case to watch for a decision later this spring, but I think this is really going to be an important one in terms of what public officials can and cannot do using their authority as public health officials. We’re obviously in a bit of a public health trust crisis, so we will see how that goes.
All right, that is the news for this week. Now, we will play my interview with HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra, then we will be back with our extra credits.
I am so pleased to welcome back to the podcast Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra. I’ve asked him to join us to talk about the Affordable Care Act, which was signed into law 14 years ago this weekend. Mr. Secretary, thanks so much for coming back.
Xavier Becerra: Julie, great to be with you on a great week.
Rovner: So the Affordable Care Act has come a long way, not just in the 14 years since President Obama signed it into law, but in the 10 years since the healthcare.gov website so spectacularly failed to launch, but this year’s enrollment setting a record, right?
Becerra: That’s right, and you should have said, “You’ve come a long way, baby.”
Rovner: So what do we know about this year’s enrollment numbers?
Becerra: Another record breaker. Julie, every year that President Biden has been in office, we have broken records. Today, more Americans have health insurance than ever in the history of the country. More than 300 million people can now go to a doctor, leave their child in a hospital and know they won’t go bankrupt because they have their own health insurance. That’s the kind of peace of mind you can’t buy. Some 21.5 million Americans today look to the marketplace on the Affordable Care Act to get their coverage. By the way, the Affordable Care Act overall, some 45 million Americans today count on the ACA for their health care insurance, whether it’s through the marketplace, through Medicaid, or some of these basic plans that were also permitted under the ACA.
Rovner: Obviously, one of the reasons for such a big uptake is the expanded subsidies that were extended by the Inflation Reduction Act in 2022, but those expire at the end of next year, the end of 2025. What do you think would happen to enrollment if they’re not renewed?
Becerra: Well, and that’s the big question. The fact that the president made health care affordable was the big news. Because having the Affordable Care Act was great, but if people still felt it was unaffordable, they wouldn’t sign on. They now know that this is the best deal in town and people are signing up. When you can get health insurance coverage for $10 or less a month in your premiums, that’s a great deal. You can’t even go see a movie at a theater today for under $10. Now, you can get health care coverage for a full month, Julie. Again, as I always tell people, that doesn’t even include the popcorn and the refreshment at the movie theater, and so it’s a big deal. But without the subsidies, some people would still say, “Ah, it’s still too expensive.” So that’s why the president in his budget calls for extending those subsidies permanently.
Rovner: So there are still 10 states that haven’t taken up the federal government’s offer to pay 90% of the costs to expand Medicaid to all low-income adults in their states. I know Mississippi is considering a bill right now. Are there other states that you expect could join them sometime in the near future? Or are any of those 10 states likely to join the other 40?
Becerra: We’re hoping that the other 10 states join the 40 that have come on board where millions of Americans today have coverage. They are forsaking quite a bit of money. I was in North Carolina recently where Gov. [Roy] Cooper successfully navigated the passage of expansion for Medicaid. Not only was he able to help some 600,000-plus North Carolinians get health coverage, but he also got a check for $1.6 billion as a bonus. Not bad.
Rovner: No, not bad at all. So many years into this law, I feel like people now understand a lot of what it did: let adult children stay on their parents’ health plans until the age of 26; banning most preexisting condition exclusions in health coverage. Yet most people still don’t know that those provisions that they support were actually created by Obamacare or even that Obamacare and the Affordable Care Act are the same thing. Medicare has had such great branding success over the years. Why hasn’t the ACA?
Becerra: Actually, Julie, I think that’s changing. Today, about two-thirds of Americans tell you that they support the marketplaces in the Affordable Care Act. I think we’re actually now beginning an era where it’s no longer the big three, where you had Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid and everyone protects those. Today, I think it’s the big four, the cleanup hitter being marketplace. Today, you would find tens of millions of Americans who would say, “Keep your dirty, stinking hands off of my marketplace.”
Rovner: Well, we will see as that goes forward. Obviously, President Biden was heavily involved in the development of the Affordable Care Act as vice president, as were you as a member of the House Ways and Means Committee at the time. What do you hope is this administration’s biggest legacy to leave to the health law?
Becerra: Julie, I think it’s making it affordable. The president made a commitment when he was first running to be president. He said on health care he was going to make it more affordable for more Americans with better benefits, and that’s what he’s done. The ACA is perfect proof. And Americans are signing up and signaling they agree by the millions. To go from 12 million people on the Affordable Care Act marketplace to 21.5 million in three years, that’s big news.
Rovner: So if I may, one question on another topic. Next week, the Supreme Court’s oral arguments occur in the case it could substantially restrict the availability of the abortion pill mifepristone. Obviously, this is something that’s being handled by the Justice Department, but what is it about this case that worries you most as HHS secretary, about the potential impact if the court rolls back FDA approval to the 2016 regulations?
Becerra: Well, Julie, as you well know from your years of covering health care, today there are Americans who have less protection, fewer rights, than many of us growing up. My daughters, my three daughters today, have fewer protections and access to health care than my wife had when she was their age. That’s not the America most of us know. To see another case where, now, medication abortion, which is used by millions of Americans — in fact, it’s the most common form of care that is received by a woman who needs to have abortion services — that is now at stake. But we believe that if the Supreme Court believes in science and it believes in the facts, because mifepristone has been used safely and effectively publicly for more than 20 years, that we’re going to be fine.
The thing that worries me as much, not just in the reduction of access to care for women in America, is the fact that mifepristone went through a process at the FDA similar to scores and scores of other medications that Americans rely on, that have nothing to do with abortion. And if the process is shut down by the Supreme Court for mifepristone, then it’s probably now at risk for all those other drugs, and therefore those other drugs that Americans rely on for diabetes, for cancer, who knows what, might also be challenged as not having gone through the right process.
Rovner: I know the drug industry is very, very worried about this case and watching it closely, and so will we. Mr. Secretary, thank you so much for joining us.
Becerra: Always good to be with you, Julie.
Rovner: OK, we are back. It’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Tami, why don’t you go first this week?
Luhby: OK, my extra credit this week is an article about Georgia’s unique Medicaid program from KFF Health News’ Andy Miller and Renuka Rayasam. It’s titled “Georgia’s Medicaid Work Requirement Costing Taxpayers Millions Despite Low Enrollment.” And I’m really glad they did this story. I and many others wrote about Georgia launching this program initially but haven’t done follow-up. So I was very happy to see this story.
As many of our listeners probably know, the Trump administration allowed multiple states to impose work requirements in Medicaid for the first time in the program’s history in 2018. But the efforts were eventually stopped by the courts in all states except Georgia. Georgia was allowed to proceed with adding its work requirement to Medicaid because it was actually going to expand coverage to allowing adults with incomes up to 100% of the poverty line to qualify. So the Georgia Pathways to Coverage initiative began last June.
Andy and Renuka took a look at how it’s faring, and the answer is actually not so well. Only about 3,500 people have signed up, far short of the 25,000 that the state projected for the first year. What’s more, the program has cost taxpayers at least $26 million so far, with more than 90% of that going towards administrative and consulting costs rather than actual medical care for low-income people.
By contrast, expanding Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act to people with 138% of the poverty line would make at least 359,000 uninsured Georgia residents newly eligible for coverage and reduce state spending by $710 million over two years. That’s what the advocates are pushing. So we’ll see what happens in coming months. One thing that’s also noted in the story is that about 45% of Pathways applications were still waiting to be processed.
Rovner: I will point out that we did talk a couple of weeks ago about the low enrollment in the Georgia program. What we had not seen was how much it’s actually costing the states per enrollee. So it is really good story. Alice, why don’t you go next?
Ollstein: Yeah, so I have some very relatable news from CNN. It’s called “Why Your Doctor’s Office Is Spamming You With Appointment Reminders.” It’s about why we all get so many obnoxious repeat reminders for every medical appointment. It both explains why medical practices that operate on such a tiny profit margin are so anxious about no-shows and last-minute cancellations, and so that’s part of it. But also part of it is that there are all these different systems that don’t communicate with one another. So the prescription drug system and the electronic medical records system and the doctor’s office’s own system are all operating in parallel and not coordinating with one another, and that’s why you get all these annoying multiple reminders. The medical community is becoming aware that it’s backfiring because the more you get, the more you start tuning them out and you don’t pay attention to which ones might be important. So they are working on it. So a somewhat hopeful piece of news.
Rovner: Raise your hand if you have multiple patient portals that you have to deal with for your multiple …
Ollstein: Oh, my God, yes.
Rovner: I will note that everybody’s hands go up. Mac?
Carey: I have not one but two stories on a very important issue: Medicaid estate recovery. The first is from Paula Span at The New York Times. The headline says it all, “When Medicaid Comes After the Family Home.” And the second story is an AP piece by Amanda Seitz, and that’s titled “State Medicaid Offices Target Dead People’s Homes to Recoup Their Health Care Costs.” Now, these stories are both about a program that’s been around since 1993. That’s when Congress mandated Medicaid beneficiaries over the age of 55 that have used long-term care services, and I’m talking about nursing homes or home care, that states must try to recover those expenses from the beneficiaries’ estates after their deaths.
As you can imagine, this might be a problem for the beneficiaries. They might have to sell a family home, try to find other ways to pay a big bill from Medicaid. Rep. Jan Schakowsky, she’s a Democrat of Illinois, has reintroduced her bill. It’s called the Stop Unfair Medicaid Recoveries Act. She’s trying to end the practice. She thinks it’s cruel and harmful, and her argument is, in fact, the federal and state governments spend way more than what they collect, and these collections often go after low-income families that can’t afford the bill anyway.
So even though it’s been around, it’s important to read up on this. A critical point in the stories was do states properly warn people that assets were going to be recovered if they enroll a loved one in Medicaid for long-term care and so on. So great reading, people should bone up on that.
Rovner: This is one of those issues that just keeps resurfacing and doesn’t ever seem to get dealt with. Well, my story this week is from The Washington Post, although I will say it was covered widely in dozens of outlets. It’s called “Arizona Lawmaker Tells Her Abortion Story to Show ‘Reality’ of Restrictions.” On Monday, Arizona State Sen. Eva Birch stood up on the Senate floor and gave a speech unlike anything I have ever seen. She’s a former nurse at a women’s health clinic. She’s also had fertility issues of her own for at least a decade, having both had a miscarriage and an abortion for a nonviable pregnancy in between successfully delivering her two sons.
Now, she’s pregnant again, but with another nonviable pregnancy, which she plans to terminate. Her point in telling her story in public on the Senate floor, she said, was to underscore how cruel — her words — Arizona’s abortion restrictions are. She’s been subject to a waiting period, required to undergo an invasive transvaginal ultrasound to obtain information she and her doctor already knew about her pregnancy, and to listen to a lecture on abortion, quote, “alternatives,” like adoption, which clearly don’t apply in her case.
While she gave the speech on the floor, several of her Democratic colleagues stood in the camera shot behind her, while many of the Republicans reportedly walked out of the chamber. I will link to the story, but I will also link to the entire speech for those who want to hear it.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our fill-in editor for today, Stephanie Stapleton. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org, or you can still find me at X, @jrovner, or @julierovner at Bluesky and @julie.rovner at Threads. Mary Agnes, where are you hanging out these days?
Carey: I’m hanging out on X, @MaryAgnesCarey.
Rovner: Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein on X, and @alicemiranda on Bluesky.
Rovner: Tami?
Luhby: The best place to find me is at cnn.com.
Rovner: There you go. We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Stephanie Stapleton
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 4 months ago
Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, Public Health, States, Abortion, Biden Administration, Drug Costs, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Misinformation, Podcasts, Pregnancy, Prescription Drugs, Women's Health