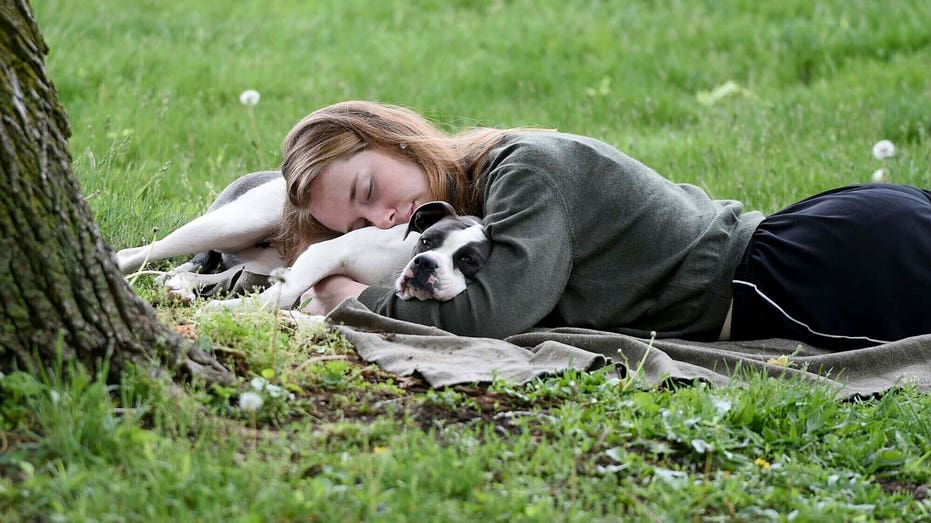
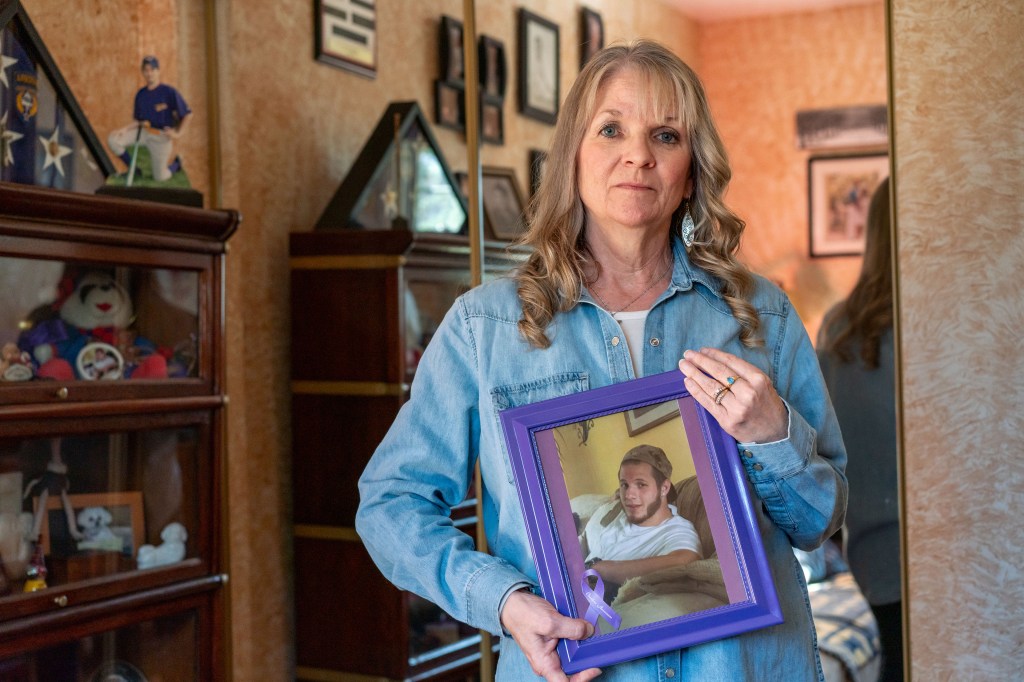
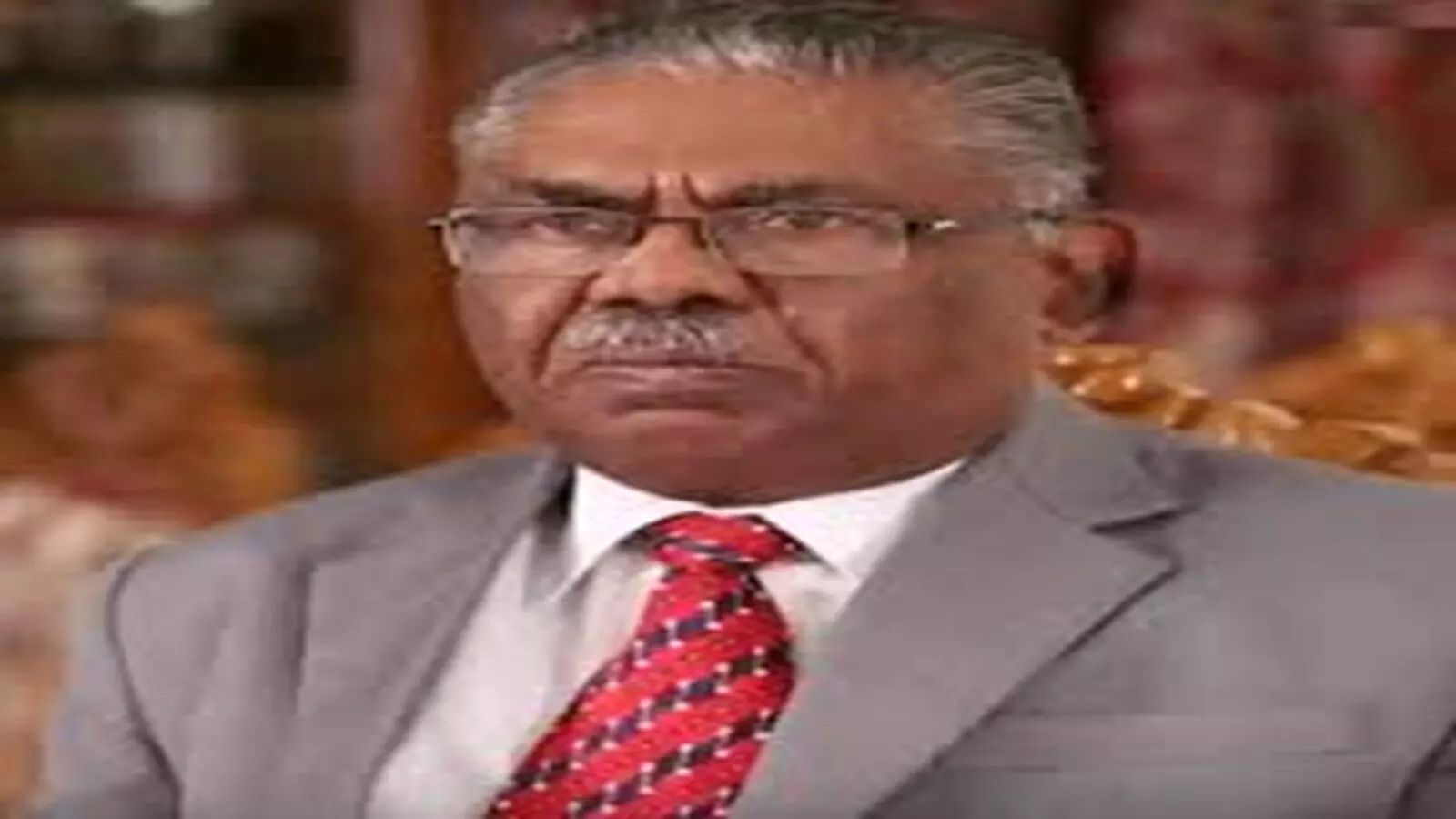
Trial to correlate food allergy prevention with lower health care costs
The Early Allergen System Experience trial will use real-world infant health care data to assess how the early introduction of allergens via supplements will impact the development of allergies and associated health care costs.“We are excited to help show that preventing food allergies can create significant savings for insurance companies, which should encourage them to invest in food allergy
prevention,” Daniel Zakowski, CEO and cofounder of Ready. Set. Food!, told Healio.Ready. Set. Food! is partnering with ObvioHealth to conduct the study with the goal of showing insurance
1 year 6 months ago
Cyber attack exposes Covid-19 vaccination records in Dominican Republic
Santo Domingo.- Over the weekend, the Ministry of Public Health and Social Assistance fell victim to a cyber attack, resulting in the theft of over 8,000 files containing Covid-19 vaccination records.
Santo Domingo.- Over the weekend, the Ministry of Public Health and Social Assistance fell victim to a cyber attack, resulting in the theft of over 8,000 files containing Covid-19 vaccination records. The breach, perpetrated by unidentified individuals, compromised sensitive information including names, phone numbers, and addresses of vaccinated individuals from various sessions organized by the Dominican State.
Sources familiar with the incident revealed that the stolen data is likely to be traded on the Dark Web for prices ranging from 1 to 3 euros (approximately RD$190). This unauthorized access was facilitated by the absence of updated antivirus protection on the Ministry’s computers, leaving them vulnerable to malware and malicious software.
An ongoing investigation, led by the National Police, has traced the breach to a specific Internet Protocol (IP) address. However, apprehending the perpetrators proves challenging, given their potential presence within the Dominican Republic and the sophisticated tools required to access the Dark Web.
Accessing the Dark Web necessitates specialized tools like TOR, a platform known for its anonymity and unindexed nature, making it a hub for illicit activities ranging from drug trafficking to the sale of weapons, counterfeit currency, stolen financial data, and forged documents. Unraveling the network of organizations involved in data theft requires the expertise and resources of agencies like the FBI.
1 year 6 months ago
Health
Less than half of Americans say they get enough sleep, new poll shows
If you're feeling — YAWN — sleepy or tired while you read this and wish you could get some more shut-eye, you're not alone. A majority of Americans say they would feel better if they could have more sleep, according to a new poll.
But in the U.S., the ethos of grinding and pulling yourself up by your own bootstraps is ubiquitous, both in the country's beginnings and our current environment of always-on technology and work hours. And getting enough sleep can seem like a dream.
The Gallup poll, released Monday, found 57% of Americans say they would feel better if they could get more sleep, while only 42% say they are getting as much sleep as they need. That’s a first in Gallup polling since 2001; in 2013, when Americans were last asked, it was just about the reverse — 56% saying they got the needed sleep and 43% saying they didn’t.
IMPROVE YOUR SLEEP BY OPTIMIZING 6 BIOMARKERS: ‘INTEGRAL TO HEALTH’
Younger women, under the age of 50, were especially likely to report they aren't getting enough rest.
The poll also asked respondents to report how many hours of sleep they usually get per night: Only 26% said they got eight or more hours, which is around the amount that sleep experts say is recommended for health and mental well-being. Just over half, 53%, reported getting six to seven hours. And 20% said they got five hours or less, a jump from the 14% who reported getting the least amount of sleep in 2013.
(And just to make you feel even more tired, in 1942, the vast majority of Americans were sleeping more. Some 59% said they slept eight or more hours, while 33% said they slept six to seven hours. What even IS that?)
The poll doesn't get into reasons WHY Americans aren't getting the sleep they need, and since Gallup last asked the question in 2013, there's no data breaking down the particular impact of the last four years and the pandemic era.
But what's notable, says Sarah Fioroni, senior researcher at Gallup, is the shift in the last decade toward more Americans thinking they would benefit from more sleep and particularly the jump in the number of those saying they get five or less hours.
"That five hours or less category ... was almost not really heard of in 1942," Fioroni said. "There’s almost nobody that said they slept five hours or less."
In modern American life, there also has been "this pervasive belief about how sleep was unnecessary — that it was this period of inactivity where little to nothing was actually happening and that took up time that could have been better used," said Joseph Dzierzewski, vice president for research and scientific affairs at the National Sleep Foundation.
It’s only relatively recently that the importance of sleep to physical, mental and emotional health has started to percolate more in the general population, he said.
And there’s still a long way to go. For some Americans, like Justine Broughal, 31, a self-employed event planner with two small children, there simply aren't enough hours in the day. So even though she recognizes the importance of sleep, it often comes in below other priorities like her 4-month-old son, who still wakes up throughout the night, or her 3-year-old daughter.
"I really treasure being able to spend time with (my children)," Broughal says. "Part of the benefit of being self-employed is that I get a more flexible schedule, but it’s definitely often at the expense of my own care."
So why are we awake all the time? One likely reason for Americans' sleeplessness is cultural — a longstanding emphasis on industriousness and productivity.
Some of the context is much older than the shift documented in the poll. It includes the Protestants from European countries who colonized the country, said Claude Fischer, a professor of sociology at the graduate school of the University of California Berkeley. Their belief system included the idea that working hard and being rewarded with success was evidence of divine favor.
"It has been a core part of American culture for centuries," he said. "You could make the argument that it ... in the secularized form over the centuries becomes just a general principle that the morally correct person is somebody who doesn’t waste their time."
Jennifer Sherman has seen that in action. In her research in rural American communities over the years, the sociology professor at Washington State University says a common theme among people she interviewed was the importance of having a solid work ethic. That applied not only to paid labor but unpaid labor as well, like making sure the house was clean.
A through line of American cultural mythology is the idea of being "individually responsible for creating our own destinies," she said. "And that does suggest that if you’re wasting too much of your time ... that you are responsible for your own failure."
"The other side of the coin is a massive amount of disdain for people considered lazy," she added.
Broughal says she thinks that as parents, her generation is able to let go of some of those expectations. "I prioritize ... spending time with my kids, over keeping my house pristine," she said.
But with two little ones to care for, she said, making peace with a messier house doesn't mean more time to rest: "We’re spending family time until, you know, (my 3-year-old) goes to bed at eight and then we’re resetting the house, right?"
While the poll only shows a broad shift over the past decade, living through the COVID-19 pandemic may have affected people's sleep patterns. Also discussed in post-COVID life is "revenge bedtime procrastination," in which people put off sleeping and instead scroll on social media or binge a show as a way of trying to handle stress.
Liz Meshel is familiar with that. The 30-year-old American is temporarily living in Bulgaria on a research grant, but also works a part-time job on U.S. hours to make ends meet.
On the nights when her work schedule stretches to 10 p.m., Meshel finds herself in a "revenge procrastination" cycle. She wants some time to herself to decompress before going to sleep and ends up sacrificing sleeping hours to make it happen.
"That’s applies to bedtime as well, where I’m like, ’Well, I didn’t have any me time during the day, and it is now 10 p.m., so I am going to feel totally fine and justified watching X number of episodes of TV, spending this much time on Instagram, as my way to decompress," she said. "Which obviously will always make the problem worse."
1 year 6 months ago
Polls, associated-press, sleep-disorders, culture-trends, mental-health
Swap Funds or Add Services? Use of Opioid Settlement Cash Sparks Strong Disagreements
State and local governments are receiving billions of dollars in opioid settlements to address the drug crisis that has ravaged America for decades.
State and local governments are receiving billions of dollars in opioid settlements to address the drug crisis that has ravaged America for decades. But instead of spending the money on new addiction treatment and prevention services they couldn’t afford before, some jurisdictions are using it to replace existing funding and stretch tight budgets.
Scott County, Indiana, for example, has spent more than $250,000 of opioid settlement dollars on salaries for its health director and emergency medical services staff. The money usually budgeted for those salaries was freed to buy an ambulance and create a financial cushion for the health department.
In Blair County, Pennsylvania, about $320,000 went to a drug court the county has been operating with other sources of money for more than two decades.
And in New York, some lawmakers and treatment advocates say the governor’s proposed budget substitutes millions of opioid settlement dollars for a portion of the state addiction agency’s normal funding.
The national opioid settlements don’t prohibit the use of money for initiatives already supported by other means. But families affected by addiction, recovery advocates, and legal and public health experts say doing so squanders a rare opportunity to direct additional resources toward saving lives.
“To think that replacing what you’re already spending with settlement funds is going to make things better — it’s not,” said Robert Kent, former general counsel for the Office of National Drug Control Policy. “Certainly, the spirit of the settlements wasn’t to keep doing what you’re doing. It was to do more.”
Settlement money is a new funding stream, separate from tax dollars. It comes from more than a dozen companies that were accused of aggressively marketing and distributing prescription painkillers. States are required to spend at least 85% of the funds on addressing the opioid crisis. Now, with illicit fentanyl flooding the drug market and killing tens of thousands of Americans annually, the need for treatment and social services is more urgent.
Thirteen states and Washington, D.C., have restricted the practice of substituting opioid settlement funds for existing dollars, according to state guides created by OpioidSettlementTracker.com and the public health organization Vital Strategies. A national set of principles created by Johns Hopkins University also advises against the practice, known as supplantation.
Paying Staff Salaries
Scott County, Indiana — a small, rural place known nationally as the site of an HIV outbreak in 2015 sparked by intravenous drug use — received more than $570,000 in opioid settlement funds in 2022.
From August 2022 to July 2023, the county reported using roughly $191,000 for the salaries of its EMS director, deputy director, and training officer/clinical coordinator, as well as about $60,000 for its health administrator. The county also awarded about $151,000 total to three community organizations that address addiction and related issues.
In a public meeting discussing the settlement dollars, county attorney Zachary Stewart voiced concerns. “I don’t know whether or not we’re supposed to be using that money to add, rather than supplement, already existing resources,” he said.
But a couple of months later, the county council approved the allocations.
Council President Lyndi Hughbanks did not respond to repeated requests to explain this decision. But council members and county commissioners said in public meetings that they hoped to compensate county departments for resources expended during the HIV outbreak.
Their conversations echoed the struggles of many rural counties nationwide, which have tight budgets, in part because they poured money into addressing the opioid crisis for years. Now as they receive settlement funds, they want to recoup some of those expenses.
The Scott County Health Department did not respond to questions about how the funds typically allocated for salary were used instead. But at the public meeting, it was suggested they could be used at the department’s discretion.
EMS Chief Nick Oleck told KFF Health News the money saved on salaries was put toward loan payments for a new ambulance, purchased in spring 2023.
Unlike other departments, which are funded from local tax dollars and start each year with a full budget, the county EMS is mostly funded through insurance reimbursements for transporting patients, Oleck said. The opioid settlement funds provided enough cash flow to make payments on the new ambulance while his department waited for reimbursements.
Oleck said this use of settlement dollars will save lives. His staff needs vehicles to respond to overdose calls, and his department regularly trains area emergency responders on overdose response.
“It can be played that it was just money used to buy an ambulance, but there’s a lot more behind the scenes,” Oleck said.
Still, Jonathan White — the only council member to vote against using settlement funds for EMS salaries — said he felt the expense did not fit the money’s intended purpose.
The settlement “was written to pay for certain things: helping people get off drugs,” White told KFF Health News. “We got drug rehab facilities and stuff like that that I believe could have used that money more.”
Phil Stucky, executive director of a local nonprofit called Thrive, said his organization could have used the money too. Founded in the wake of the HIV outbreak, Thrive employs people in recovery to provide support to peers with mental health and substance use disorders.
Stucky, who is in recovery himself, asked Scott County for $300,000 in opioid settlement funds to hire three peer specialists and purchase a vehicle to transport people to treatment. He ultimately received one-sixth of that amount — enough to hire one person.
In Blair County, Pennsylvania, Marianne Sinisi was frustrated to learn her county used about $322,000 of opioid settlement funds to pay for a drug court that has existed for decades.
“This is an opioid epidemic, which is not being treated enough as it is now,” said Sinisi, who lost her 26-year-old son to an overdose in 2018. The county received extra money to help people, but instead it pulled back its own money, she said. “How do you expect that to change? Isn’t that the definition of insanity?”
Blair County Commissioner Laura Burke told KFF Health News that salaries for drug court probation officers and aides were previously covered by a state grant and parole fees. But in recent years that funding has been inadequate, and the county general fund has picked up the slack. Using opioid settlement funds provides a small reprieve since the general fund is overburdened, she said. The county’s most recent budget faces a $2 million deficit.
Forfeited Federal Dollars
Supplantation can take many forms, said Shelly Weizman, project director of the addiction and public policy initiative at Georgetown University’s O’Neill Institute. Replacing general funds with opioid settlement dollars is an obvious one, but there are subtler approaches.
The federal government pours billions of dollars into addiction-related initiatives annually. But some states forfeit federal grants or decline to expand Medicaid, which is the largest payer of mental health and addiction treatment.
If those jurisdictions then use opioid settlement funds for activities that could have been covered with federal money, Weizman considers it supplantation.
“It’s really letting down the citizens of their state,” she said.
Officials in Bucks County, Pennsylvania, forfeited more than $1 million in federal funds from September 2022 to September 2023, the bulk of which was meant to support the construction of a behavioral health crisis stabilization center.
“We were probably overly optimistic” about spending the money by the grant deadline, said Diane Rosati, executive director of the Bucks County Drug and Alcohol Commission.
Now the county plans to use $3.9 million in local and state opioid settlement funds to support the center.
Susan Ousterman finds these developments difficult to stomach. Her 24-year-old son died of an overdose in 2020, and she later joined the Bucks County Opioid Settlement Advisory Committee, which developed a plan to spend the funds.
In a September 2022 email to other committee members, she expressed disappointment in the suggested uses: “Please keep in mind, the settlement funds are not meant to fund existing programs or programs that can be funded by other sources, such as federal grants.”
But Rosati said the county is maximizing its resources. Settlement funds will create a host of services, including grief groups for families and transportation to treatment facilities.
“We’re determined to utilize every bit of funding that’s available to Bucks County, using every funding source, every stream, and frankly every grant opportunity that comes our way,” Rosati said.
The county’s guiding principles for settlement funds demand as much. They say, “Whenever possible, use existing resources in order that Opioid Settlement funds can be directed to addressing gaps in services.”
Ed Mahon of Spotlight PA contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
Courts, Rural Health, States, Indiana, Investigation, New York, Opioid Settlements, Opioids, Pennsylvania
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Fogging schedule for April 15 – 19
A number of communities in St Michael and Christ Church will be fogged by the Ministry of Health and Wellness’ Vector Control Unit this week.
The Unit will begin its fogging exercise on Monday, April 15, in the following St Michael districts: Brittons New Road, Rolling Road, Taitts Road, Eastmond Road, Gunsite Road, Bonnetts Housing Area, and surrounding districts.
A number of communities in St Michael and Christ Church will be fogged by the Ministry of Health and Wellness’ Vector Control Unit this week.
The Unit will begin its fogging exercise on Monday, April 15, in the following St Michael districts: Brittons New Road, Rolling Road, Taitts Road, Eastmond Road, Gunsite Road, Bonnetts Housing Area, and surrounding districts.
It will then visit Thomas Road, Club Morgan Road with avenues, Plantain Walk, Clapham Drive, Simmons Road, and Rendezvous High Ridge with avenues, on Tuesday, April 16.
On Wednesday, April 17, the team will spray Fordes Road with avenues, Clapham Heights, Clapham Road, Clapham Park, Adam’s Road, Observatory Road, Clapham Ridge, Laynes Road, Clapham Close, and neighbouring districts.
The next day, Thursday, April 18, the Unit will go into Christ Church to fog Rendezvous Road, Rendezvous Ridge, Rendezvous Garden, Amity Lodge, Worthing Main Road, Bamboo Road, Craigg Road, Beckles Road, and Harmony Hall with avenues.
The fogging exercise for the week will conclude on Friday, April 19, in St Michael in Bridge Gap, Upper Goodland, Gills Gap and avenues, Browns Gap, Alkins Road, Wilkinson Road, Richmond Gap, Thomas Gap, and Lower Richmond Gap.
Fogging takes place from 4:30 to 8:30 p.m. daily. Householders are reminded to open their windows and doors to allow the spray to enter. Children should not be allowed to play in the fog.
Members of the public are advised that the completion of scheduled fogging activities may be affected by events beyond the Unit’s control. In such circumstances, the Unit will return to communities affected in the soonest possible time.
The post Fogging schedule for April 15 – 19 appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 6 months ago
Health, Local News, Alerts
PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’ Are Pervasive in Water Worldwide, Study Finds
A global survey found harmful levels even in water samples taken far from any obvious source of contamination.
A global survey found harmful levels even in water samples taken far from any obvious source of contamination.
1 year 6 months ago
Water Pollution, Chemicals, PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances), Research, Nature Geoscience (Journal)
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Dengue outbreak continues despite fall in cases
Dengue fever cases continue to decline but the numbers are still above the outbreak threshold.
In its most recent update, the Ministry of Health and Wellness stated that since the outbreak began in October 2023, four deaths have been recorded. It added that a number of people were referred to hospital with warning signs and some were hospitalised with severe dengue.
The predominant serotype identified has been type 2, followed by type 3.
Up to the week ending April 6, 2024, there were 2 915 clinically suspected, and 1 059 laboratory confirmed cases of dengue fever in Barbados. This compares to the same period in 2023, when there were only 158 suspected cases, and 105 confirmed cases.
The ministry reported that the current outbreak peaked in January, this year, and continued to decline in March. Although lower than February, numbers are still above the outbreak threshold for March.
Health authorities have advised members of the public to implement measures to avoid contracting the illness, such as using repellent and wearing protective clothing; eliminating breeding sites by keeping their surroundings clean; and using protective window and door screens as well as mosquito nets, at home.
Furthermore, the Ministry of Health and Wellness disclosed that there has been an increase in gastroenteritis cases in the past two weeks, in persons five years and older. It stated that this may be due to more people eating food which is prepared outside of the home. However, cases in children under five years old have not surpassed the threshold of the expected number during this time period.
“Persons choosing to purchase ready-prepared food are encouraged to check for cleanliness and tidiness of the establishment, including the presence of handwashing facilities if the vendor is itinerant or at a wayside stall. Patrons are reminded to wash or sanitise their hands prior to eating, after coughing or sneezing into tissues, and after using the toilet facilities,” the health ministry stated.
The public is reminded that hot foods are to be served hot, at 140 degrees Fahrenheit or higher, and cold foods should be at 40 degrees Fahrenheit and below. Additionally, cooked and uncooked foods should always be separated.
As for respiratory cases, reports indicate that there was an increase in cases in persons five years and older up to April 6, this year, but levels in children under five years old continue to be low from the beginning of the year.
Influenza and other cough and cold viruses not confirmed may be contributing to the increase, the ministry said. COVID-19 infections remain very low, with no deaths recorded within the last month.
Health authorities encouraged Barbadians to practise stringent respiratory hygiene with use of hand washing, hand sanitising and mask wearing by those with symptoms or those vulnerable to severe disease. (BGIS)
The post Dengue outbreak continues despite fall in cases appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 6 months ago
Health, Local News
Medical News, Health News Latest, Medical News Today - Medical Dialogues |
Pune Cardiologist Dr Manuel Durairaj passes away
Pune: Dr Manuel Durairaj, an illustrious figure in the realm of cardiology, breathed his last, leaving behind an indelible legacy of excellence in clinical practice, research and academia. Throughout his illustrious career, Dr Durairaj earned global acclaim for his profound expertise and unwavering dedication to advancing the field of cardiology.
A distinguished alumnus of Armed Forces Medical College, Dr Durairaj a Gold Medalist, completed his DM Cardiology in 1974 at CMC Vellore. Following his academic pursuits, he embarked on a remarkable journey in the Army Medical Corp, retiring with the esteemed rank of Lieutenant Colonel. His tenure in the armed forces was marked by exemplary service and a commitment to upholding the highest standards of medical care.
Also Read:Pune: 23 private hospitals get show cause notice for violation of Nursing Home Act
According to Pune Mirror, Dr Durairaj's professional journey took him to prestigious institutions, including CMC Vellore and Poona University, where he played a pivotal role in establishing the DM Cardiology programme. His visionary leadership as Head of Cardiology at MH (CTC), Lullanagar, laid the foundation for groundbreaking advancements in cardiac care. In 1988, Dr Durairaj embarked on a new chapter in his career by founding the Marian Cardiac Centre and Research Foundation, a beacon of hope for countless individuals grappling with cardiac ailments.
His tenure as Professor and inaugural Chairman of the Academic Department of Cardiology at the Grant Medical Foundation in Pune exemplified his unwavering commitment to nurturing the next generation of medical professionals.
A luminary in his field, Dr Durairaj's influence extended far beyond the realms of academia and clinical practice. His transformative work in cardiology revolutionized treatment modalities, saving countless lives and setting new benchmarks for excellence in healthcare delivery. His compassionate approach endeared him to patients from diverse corners of the globe, with many seeking his expertise from the Middle East, United States, West Indies, West Africa, and beyond.
Beyond his professional achievements, Dr Durairaj's altruistic spirit and unwavering commitment to serving humanity were evident in his tireless efforts to provide care and support to the less fortunate. Dr Durairaj's passing leaves a void in the medical fraternity, but his legacy of compassion, dedication, and excellence will continue to inspire generations to come. He is survived by his beloved wife, Mrs Valsamma, children Mrs Manju Durairaj Schwister and Dr Manoj Durairaj, along with grandchildren Joseph-Durai, James, and Maria.
A solemn church service will be held on April 12 at 4:30 pm at St. Patrick's Cathedral, Pune, Prince of Wales Drive, followed by interment at Sepulchre Cemetery, Hadapsar. As the medical community mourns the loss of a stalwart, Dr Manuel Durairaj's enduring impact on healthcare and humanity will be cherished and commemorated by all whose lives he touched, reports the Daily.
Also Read: Renowned plastic surgeon Dr Sam Chandra Bose passes away at 95
1 year 6 months ago
State News,News,Health news,Maharashtra,Doctor News,Latest Health News,Recent Health News
Health – Demerara Waves Online News- Guyana
Guyana rolls out massive fight against cervical cancer
Guyana on Friday launched the Global Strategy for Cervical Cancer Elimination, saying with officials saying that the country has embarked on a countrywide campaign to vaccinate persons against the human papilloma virus (HPV) and screen persons for cancer caused by that virus. With Guyana currently having 40 percent HPV vaccine coverage, Director of the Ministry of ...
Guyana on Friday launched the Global Strategy for Cervical Cancer Elimination, saying with officials saying that the country has embarked on a countrywide campaign to vaccinate persons against the human papilloma virus (HPV) and screen persons for cancer caused by that virus. With Guyana currently having 40 percent HPV vaccine coverage, Director of the Ministry of ...
1 year 6 months ago
Health, News, brachytherapy, cancer screening, Global Strategy for Cervical Cancer Elimination, Health Minister Dr Frank Anthony, human papilloma virus (HPV), Mount Sinai Health System, National Reference Laboratory
What's Going On AbbVie Stock On Friday? - Yahoo Finance
- What's Going On AbbVie Stock On Friday? Yahoo Finance
- Atogepant: New migraine drug recommended for NHS use in England BBC.com
- NICE recommends first oral treatment for chronic and episodic migraines Pavilion Health Today
- AbbVie Announces Late-Breaking Data at AAN Supporting Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Atogepant (QULIPTA®) for Preventive Treatment of Migraine PR Newswire
- AbbVie’s oral therapy Aquipta recommended by NICE for migraine prevention in adults PMLiVE
1 year 6 months ago
CDC investigating fake Botox injections: ‘Serious and sometimes fatal’
Fake Botox is on the CDC’s radar.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced on Friday that it is investigating reports of "a few botulism-like illnesses in several states resulting from botulinum toxin injections (commonly called ‘Botox’) administered in non-medical settings," the agency said in a statement.
"We are coordinating a multi-state outbreak investigation," the agency added.
Illnesses have been reported to the Tennessee and Illinois health departments, which are working with the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on the investigation, the CDC noted.
In Tennessee, four patients sought medical care after experiencing "botulism-like signs and symptoms" after receiving Botox injections for cosmetic purposes, according to an online statement from the Tennessee Department of Health.
Two of the patients were hospitalized.
"Joint investigations have identified concerns about use of counterfeit products or products with unclear origin administered in non-medical settings such as homes or cosmetic spas," the statement said.
The Illinois Department of Public Health issued a similar statement after two patients reported receiving potentially counterfeit Botox injections in LaSalle County.
ARTIFICIAL BEAUTY: WARNING OF THREATS TO GIRLS’ SELF-ESTEEM, DOVE RECOMMITS TO NEVER USING AI IN ADS
The two individuals reported symptoms that included blurred/double vision, droopy face, fatigue, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath and hoarse voice, the statement said.
The patients, both of whom were hospitalized, received the injections from a licensed nurse who was "performing work outside her authority."
Additional cases have been reported in Kentucky, Washington and Colorado.
"The sources of these botulinum toxin products are unknown or unverified at this time," the CDC stated.
"Questions about product regulation and product investigation should be directed to the FDA."
Botulism is a "serious and sometimes fatal" illness that occurs when a toxin attacks the body’s nerves, according to the CDC.
Initial symptoms usually include muscle weakness around the eyes, face, mouth and throat, which could also spread to the neck, arms, torso and legs.
Other symptoms can include blurred or double vision, difficulty breathing, trouble swallowing, drooping eyelids, slurred speech and difficulty moving the eyes.
"What’s particularly concerning are the respiratory problems that some are experiencing," Dr. Salar Hazany, a certified dermatologist and reconstructive surgeon at Scar Healing Institute in Beverly Hills, told Fox News Digital.
"If the wrong patient begins having trouble with their breathing, it could be fatal."
Dr. Craig Lehrman, director of aesthetic surgery at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, noted that fake Botox has been an issue since the early 2000s.
"Unfortunately, I treat several patients a year who have received non-approved injectables of things they are told to be safe, which ends up having serious consequences," he told Fox News Digital.
"It has mostly been linked to injections in settings such as someone's home or a poorly regulated med spa."
Botox is made from a specific type of Clostridium botulinum, a bacteria that produces paralysis in the muscles where it is injected, he said.
"The people receiving the presumed counterfeit Botox are suffering from an illness that is similar to botulism, caused by the same bacteria," he said.
There are strict safety criteria for the use and storage of Botox, and serious risks come with the injection of fraudulent or poorly managed products, Lehrman warned.
"Botulism can carry detrimental effects ranging from infection, to permanent deformity, to serious wound formation."
"Cosmetic injections should be an FDA-approved product, administered by licensed providers and in licensed settings," the CDC stated.
There has been a large increase in the number of people offering these services who are not board-certified in the fields of plastic surgery, dermatology or ENT, according to Lehrman.
PLASTIC SURGERY DEATHS HAVE SPIKED AMONG US PATIENTS WHO TRAVELED TO DOMINICAN REPUBLIC: CDC REPORT
"I would advise potential patients to do their research on the person who will be injecting them — and not just search for the cheapest option," he said.
"I would recommend going to a center that has rigorous standards of education and a track record of safety."
In most cases, Botox injections are safe, according to experts.
"Laboratory-confirmed cases of systemic botulism occurring after cosmetic or therapeutic injections of botulinum toxin are rare," the CDC said in its statement.
Millions of injections are performed each year by licensed medical providers and have been shown to be safe when done in the correct manner, Lehrman added.
"Those considering Botox should research the background of the provider and make sure that the practice has not racked up a number of complaints," added Hazany.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
"Do not go to an unlicensed provider. If the offer seems too good to be true, it probably is."
Anyone who experiences botulism-like symptoms following an injection should seek medical attention, according to health officials.
Fox News Digital reached out to Abbvie (manufacturer of Botox), the FDA, the Tennessee Department of Public Health, and the Illinois Department of Public Health requesting comment.
1 year 6 months ago
Health, cosmetic-surgery, beauty-and-skin, lifestyle, medications, health-care
The Push for a Better Dengue Vaccine Grows More Urgent - The New York Times
- The Push for a Better Dengue Vaccine Grows More Urgent The New York Times
- Dengue passes 1000 deaths mark in Brazil Magnetic Media
- Brazil accounts for nearly 70% of dengue cases in LatAm and Caribbean MercoPress
- Brazil releases anti-dengue mosquitos CGTN America
- An Escalation of Dengue in Brazil Echoes a Global Crisis Medscape
1 year 6 months ago
What you need to know about the latest outbreak of dengue fever - PBS NewsHour
- What you need to know about the latest outbreak of dengue fever PBS NewsHour
- The Push for a Better Dengue Vaccine Grows More Urgent The New York Times
- Vaccine 'Will Not Curb' Dengue Epidemic, Says PAHO Medscape
- Dengue Update – Brace for Potential Worst Dengue Season Magnetic Media
- Dengue Outbreaks Continue in the Caribbean — Precision Vaccinations News Precision Vaccinations
1 year 6 months ago
Amjevita leads Humira biosimilars in clinician comfort as rheumatologists remain wary
Only half of rheumatologists are “extremely comfortable” prescribing the Humira biosimilar Amjevita, while just 16% can say the same for all other adalimumab biosimilars combined, according to a market analysis from Spherix Global Insights.For reference, 83% of rheumatologists included in the analysis reported being “extremely comfortable” prescribing originator Humira (adalimumab, AbbVie).
This yawning gap underscores how rheumatologists, who have grown comfortable with an increasing array of biologic medications, now face the challenge of navigating a complicated
1 year 6 months ago
Alarmin molecule identified as therapeutic target for allergic respiratory diseases
One of the molecules responsible for triggering the inflammation that causes allergic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis, has just been discovered by scientists from the CNRS, Inserm and the Université Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier.
One of the molecules responsible for triggering the inflammation that causes allergic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis, has just been discovered by scientists from the CNRS, Inserm and the Université Toulouse III – Paul Sabatier.
1 year 6 months ago
Health – Demerara Waves Online News- Guyana
GPHC-Gift of Life Int’l first paediatric heart mission for 2024 starts
The Georgetown Public Hospital Corporation (GPHC), in collaboration with Gift of Life International (GOLI) an international non-profit organization that provides lifesaving cardiac treatment to children in need from developing countries, on Thursday announced the start of the first of three Paediatric Cardiac Missions scheduled for 2024.
This groundbreaking initiative kicked off on Sunday, April 6, ...
1 year 6 months ago
Health, News, congenital heart defects, corrective surgeries, Georgetown Public Hospital Corporation (GPHC), Gift of Life International (GOLI), Paediatric Cardiac Missions
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Arizona Turns Back the Clock on Abortion Access
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
The Arizona Supreme Court shook up the national abortion debate this week, ruling that a ban originally passed in 1864 — before the end of the Civil War and decades before Arizona became a state — could be enforced. As in some other states, including Florida, voters will likely have the chance to decide whether to enshrine abortion rights in the state constitution in November.
The Arizona ruling came just one day after former President Donald Trump declared that abortion should remain a state issue, although he then criticized the ruling as having gone “too far.”
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post, and Rachel Cohrs Zhang of Stat.
Panelists
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Rachel Roubein
The Washington Post
Rachel Cohrs Zhang
Stat News
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Former President Donald Trump’s remarks this week reflect only the latest public shift in his views on abortion access. During an appearance on NBC’s “Meet the Press” in 1999, he described himself as “very pro-choice,” but by the 2016 presidential campaign, he had committed to nominating conservative Supreme Court justices likely to overturn the constitutional right to an abortion. Trump later blamed Republican losses in the 2022 elections on the overturning of that right.
- Arizona officials, as well as doctors and patients, are untangling the ramifications of a state Supreme Court ruling this week allowing the enforcement of a near-total abortion ban dating to the Civil War. Yet any ban — even one that doesn’t last long — can have lasting effects. Abortion clinics may not survive such restrictions, and doctors and residents may factor them into their decisions about where to practice medicine.
- Also in abortion news, an appeals court panel in Indiana unanimously ruled that the state cannot enforce its abortion ban against a group of non-Christians who sued, siding with mostly Jewish plaintiffs who charged that the ban violates their religious freedom rights.
- A discouraging new study finds that paying off an individual’s medical debt once it has reached collections doesn’t offer them much financial — or mental health — benefit. One factor could be that the failure to pay medical debt is only a symptom of larger financial difficulties.
Also this week, Rovner interviews KFF Health News’ Molly Castle Work, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month” feature about an air-ambulance ride for an infant with RSV that his insurer deemed not to be medically necessary. If you have an outrageous or baffling medical bill you’d like to send us, you can do that here.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: Stat’s “Your Dog Is Probably on Prozac. Experts Say That Says More About the American Mental Health Crisis Than Pets,” by Sarah Owermohle.
Rachel Cohrs Zhang: KFF Health News’ “Ten Doctors on FDA Panel Reviewing Abbott Heart Device Had Financial Ties With Company,” by David Hilzenrath and Holly K. Hacker.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: The Texas Tribune’s “How Texas Teens Lost the One Program That Allowed Birth Control Without Parental Consent,” by Eleanor Klibanoff.
Rachel Roubein: The Washington Post’s “As Obesity Rises, Big Food and Dietitians Push ‘Anti-Diet’ Advice,” by Sasha Chavkin, Caitlin Gilbert, Anjali Tsui, and Anahad O’Connor.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- Live Action’s “Hi, My Name’s Olivia” video.
- The New York Times’ “Insurers Reap Hidden Fees by Slashing Payment. You May Get the Bill,” by Chris Hamby.
- The Nation Bureau of Economic Research’s “The Effects of Medical Debt Relief: Evidence From Two Randomized Experiments,” by Raymond Kluender, Neale Mahoney, Francis Wong, and Wesley Yin.
- USA Today’s “The Database You Don’t Want to Need: Check to See if Your Health Data Was Hacked,” by Cecilia Garzella.
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: Arizona Turns Back the Clock on Abortion Access
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, April 11, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Rachel Cohrs Zhang of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs Zhang: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And we welcome back from her leave Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post.
Rachel Roubein: Hi, happy to be here.
Rovner: Later in this episode we’ll have my interview with my KFF Health News colleague Molly Work about the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month,” about yet another very expensive air-ambulance ride that an insurer deemed “unnecessary.” As you will hear, that is hardly the case.
But first, this week’s news, and there is lots of it. We start again this week with abortion because, again, that’s where the biggest news is. I want to do this chronologically because there were a lot of things that happened and they all built on each piece before them. So on Monday, former President [Donald] Trump, as promised, issued his long-awaited statement on abortion, a four-minute video posted on his platform Truth Social, in which he took credit for appointing the justices who overturned Roe v. Wade, but then kind of declared the job done because abortion is now up to the individual states. And while he didn’t say so directly, that strongly suggested he would not be supporting efforts by anti-abortion groups to try to pass a federal 15-week ban, should Republicans retake the presidency and both houses of Congress. That alone was a big step away from some of his strongest anti-abortion supporters like the SBA List [Susan B. Anthony Pro-Life America], which helped got him elected in 2016, right, Alice? I see you nodding.
Ollstein: Yes. He kind of left himself some wiggle room. He made a statement that, at first, people could sort of read into it what they wanted. And so you had several anti-abortion groups going, “Well, he didn’t advocate for a national ban, but he also didn’t rule it out.” But then, as I’m sure we’ll get to, he was asked follow-up questions and he kind of did rule it out. He kind of did say, “No, I wouldn’t sign a national ban if it were presented to me.” And so the little crumbs of hope anti-abortion groups were picking up on may or may not be there. But it was both notable for what he did say and what he didn’t say. There are still a lot of unanswered questions about what he would do in office, both in terms of legislation, which is really a remote possibility that no one thinks is real, but he didn’t say anything.
Rovner: It would need 60 votes in the Senate.
Ollstein: Exactly.
Rovner: Legislation.
Ollstein: Exactly. And no one really on the right or left thinks that is going to happen, but he didn’t say anything about what he would do with executive powers, which, as we’ve discussed, could go a long, long way towards banning abortion nationwide.
Rovner: One of the things that sort of fascinates me, I’ve been covering abortion for a long time, longer than some of you have been alive, and I have seen lots of politicians switch sides on this. I mean, Joe Biden started out as very anti-abortion, now very in favor of abortion rights. So I’ve seen politicians go both ways, but the general rule has always been you get to switch once. You get to either go from being pro-life to pro-choice or being pro-choice to pro-life. You don’t get to go back and forth and yet that seems to be very much what Trump has done. He seems to have taken every conceivable position there is on this extraordinarily binary issue and gotten away with it.
Ollstein: One last thing I wanted to flag in the statement was that he kind of said the quiet part out loud and that he directly said that this is about winning elections. So he’s saying, “This is what we need to say in order to win,” which leaves open what he really believes or what he really would do.
Roubein: Yeah, I mean, going back to Trump’s shifting view on abortion, because that’s really important and that’s something that the anti-abortion movement is sort of looking towards. I mean, in 1999 in an interview in “Meet the Press,” he called himself “very pro-choice,” and then we kind of saw by 2016, he had committed to naming justices who had anti-abortion views. And as Alice mentioned then, after the midterms in 2022, he blamed Republican losses on that.
Rovner: Yeah, I assume that makes it hard for people who try to follow him. I know [Sen.] Lindsey Graham came out, Lindsey Graham, who’s been sort of the major backer of the 15-week abortion ban in Congress for some time now, and suddenly Lindsey Graham, who has been nothing but loyal to Trump, finds himself on the other side of a big, important issue. I mean, Trump seems to get away with it. The question is, are his followers going to get away with having different positions on this?
Cohrs Zhang: Oh, I also just wanted to say that I think it’ll be interesting to see who Trump chooses as his running mate on this because obviously his opinion and his position is very important, but I think we saw kind of last time around with him leaning on Mike Pence a little bit for credibility with the anti-abortion movement. So I think it’ll be interesting to see whether he chooses someone again who can mend some of these relationships or whether he’s just going to carry on and make those decisions himself and lean less on his VP.
Rovner: Well, let’s move on to Tuesday because on Tuesday the Trump abortion doctrine got a pretty severe test from the Arizona Supreme Court, which ruled that an almost absolute abortion ban that was passed in 1864, before Arizona was a state, before the end of the Civil War, can be enforced. Alice, what’s this law and when might it take effect?
Ollstein: So the Supreme Court kicked some of those issues back down to the lower court and so it’s still being worked out. Currently, abortion is banned after 15 weeks of pregnancy. The total ban could go into effect in a little over a month, but it’s really uncertain. And so you’re seeing a lot of the same fear and confusion that we saw in the immediate aftermath of Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization], where providers and patients don’t know what’s legal and whether they can provide or receive care and are, in some instances, over-complying and holding off on doing things that are still legal.
And so just a great example of how Trump and these national political figures, they can take whatever position they want, but that often gets overtaken by events. And so you saw Trump come out and say, “States should decide.” This is arguably an instance of states deciding, although the Supreme Court upholding a law from when no one was currently alive, was part of that, the law was implemented when women couldn’t vote, when Arizona wasn’t even a state yet. So whether this is an example of “will of the people,” that can be debated. But this is an example of “leave it to states.” And then Trump was asked about the Arizona decision, whether it went too far, and he said “Yes, it did go too far.” So it’s like should states be allowed to decide or not?
Rovner: It’s like, “Leave it to states unless they go too far.”
Roubein: And who decides what too far is, because a lot of anti-abortion groups were very complimentary of the Arizona ruling and said it was the right thing to do. So depends who you ask.
Rovner: So this obviously scrambles politics beyond just the presidential race, although I think it’s pretty clear to say that it puts Arizona, which had been teetering as being sort of purple state-ish, right back in play, but it’s going to affect things down the ballot and in other states, right?
Ollstein: I mean just looking at Arizona, I mean abortion rights and Democrats have really been pushing ballot measures here, and, I think as Julie was alluding to, there’s a ballot measure effort in Arizona, and I believe the organizers have said that they have enough signatures to qualify, then there’s steps to actually qualifying. So that’s going to really put a spotlight on Arizona. But, we’ve seen ballot measures in other states, Florida. Democrats really want Florida to be in play now that there’s been a Florida state Supreme Court ruling and there’s a ballot measure there. The threshold’s higher, it’s 60%, but all around the country it’s going to be putting increasing emphasis on this ballot measure effort.
Rovner: So the Republicans now really have no place to hide. I saw there was a Senate candidate in Wisconsin who had been very completely anti-abortion, now seems to be a lot less anti-abortion. I mean Republicans have spent a lot of time putting Democrats on the spot about not wanting to be specific on their abortion position, and that’s what leads to the, “You support abortion up until the ninth month,” which isn’t a thing. But now I feel like it’s a chance for Democrats to turn this on Republicans saying, “Now you have to say exactly what your position is rather than just you are ‘anti-abortion’ or ‘100% pro-life,’ which for many, many elections was plenty and all the candidates needed to say.
Cohrs Zhang: Just as we talk about all of these different, how this is playing out, certainly I think the instance you brought up was an example of a position on the larger issue of what a candidate is going to support generally, but I think there are these kind of tangential local issues too that candidates are going to have to take positions on. I think if we look back, like IVF, that’s something that candidates have never really had to weigh in on, and I think it is going to become local in a new way, which just seeing all these offshoot rulings and court decisions. And I think that it was an excellent catch, and, certainly, it’ll be interesting to see how candidates move across the spectrum as we see some more and more extreme local cases coming up even beyond the national standard.
Rovner: And as Alice points out, this is more than just political. This affects health care on the ground. Doctors either not wanting to train in states that have strict bans or doctors in some cases picking up and leaving states, not wanting to be threatened with jail or loss of license. So that affects what other kinds of women’s health care is available. Alice, you wanted to add something?
Ollstein: Yeah, I’ve been seeing a lot of people saying, both with the Florida ruling and with the Arizona ruling, so in both of these instances, a very sweeping abortion ban is expected to go into effect, but then there’s going to be a ballot referendum in the fall where voters will have the opportunity to get rid of those bans. And so you’re seeing a lot of people saying, “OK, well this is only temporary. Voters will be so outraged over this that they’ll vote to support these ballot measures to overturn it.” But I think it’s important to remember that a lot of the impacts will linger for a long time if these clinics can’t hang on even a few months under a near-total ban and shut their doors. You can’t just flip a switch and turn that back on. It’s incredibly hard to open a new abortion clinic.
Rovner: Or even to reopen one that you’ve closed down “temporarily.”
Ollstein: Exactly. And like you said, medical students and residents and doctors are making decisions about where to live and where to practice that could have impacts that last for years and years. And so people saying, “Oh, well, it’s not that important if these bans go into effect now because in November voters will have their say.” Even a few months can have a very long effect in a state.
Rovner: Yeah. I just want to continue to reiterate this is about more than politics. This is actually about health care on the ground.
Well, in other abortion news, a three-judge panel of the Indiana Court of Appeals ruled last week that the state cannot enforce its abortion ban against a group of plaintiffs who are non-Christians and charge that the ban violates their freedom of religion because some religions, notably Judaism but others too, include tenets that prioritize the life and health of the pregnant woman over that of the fetus. This is obviously not the last word on this case. It could still go to the Indiana Supreme Court or even the U.S. Supreme Court, but it does seem significant. I think it’s the first decision we’ve seen on one of these cases, and it was unanimous. And interestingly, it turns a lot of the recent decisions protecting religious freedom for Christians right back on those who would ban abortion. Alice, there are more of these … awaiting hearing, right?
Ollstein: Yes. There’s ones going on really around the country that are testing these legal theories, and part of it is that state-level religious freedom laws are often more expansive and protective than federal religious freedom laws. And so they’re leaning on that. And yeah, it’s a really fascinating test case of, were these religious freedom laws intended to only protect one particular religion that has hegemonic power in the United States right now or were they designed to protect every one of every religion? And I think Judeo-Christian values is a term that’s thrown out a lot, and this really shows that there are very different beliefs when it comes to pregnancy and abortion and which life to prioritize between the mother and the child. And when it even counts as an abortion, when it even counts as life beginning, that is a lot more muddled.
And look, in this case it was led by Jewish plaintiffs challenging, but I’ve been tracking cases that draw from many different religions, and these protections even apply to avowed atheists in some instances. And so I think this is definitely something to keep an eye on. In addition to Indiana, the other case I’ve been following most closely is in Missouri, so it’ll be really fascinating to see what happens.
Rovner: There was one in Kentucky, too. Did anything ever happen with that one? I think that was the first one we talked about.
Ollstein: They’re still waiting.
Rovner: Like two years ago.
Ollstein: Yeah. The wheels of justice turn slowly.
Rovner: Indeed, they do. Well, finally, Tennessee is on the verge of enacting a bill that would require students to be shown a three-minute video on fetal development and strongly recommends one made by the anti-abortion group Live Action. Not surprisingly, medical experts say the video is inaccurate and manipulative. I will post a link to it so you can watch it and judge for yourself. What jumped out to me in this story is that one Tennessee lawmaker, himself a physician, said, and I quote, “Whether all of the exact details are correct, I don’t think that is important.” Is that where we have come with this debate these days, that facts are no longer important?
Cohrs Zhang: I mean, I thought it was interesting that there was an amendment rejected that would’ve allowed parents to opt out of it. And I just feel like there’s so many permission slips in schools these days for any book or movie that something like this would be mandated is just kind of like an interesting twist on that. So again, we’ll be interested to see if it actually takes effect, but …
Rovner: I mean, it’s a pretty benign video. It’s basically purporting to show fetal development from the moment of fertilization up to birth. The big complaint about it is it’s misleading on the timing because it’s counting from a different place than doctors count from. It’s counting from the moment of fertilization. Doctors generally count pregnancy from the last missed period because it’s hard to tell. You don’t know when the moment of fertilization was. But when we talk about first trimester or however many weeks, medically you’re talking about weeks since last missed period. So this makes everything look like it happened earlier than it actually does in common parlance. Have I explained that right, Alice?
Ollstein: Yes. And we are seeing efforts on this front both to make these educational mandates for students, but we’re also seeing them mandated for doctors’ education in some states as well. Part of this is to address what everyone on all sides acknowledges is a problem, which is that doctors don’t understand when the exemptions to these abortion bans apply in terms of life and health of the parent coming into play. Oftentimes these bans are written with nonmedical language talking about serious threats. What’s serious? Talking about harm to a major bodily function. What’s major? So, you are seeing doctors holding off from providing abortions even in cases that they think should be exempt, these emergency situations, and so anti-abortion groups are pushing these bills mandating certain curricula for doctors to try to address this confusion. The medical groups I’ve spoken to don’t think this is a solution, but it’s interesting as an attempt.
Rovner: In some states, it has to be an affirmative defense. So as you, a doctor, consider an emergency, you perform the abortion and then instead of not getting charged, you get charged and you have to go hire a lawyer and go to court and say, “I decided that this was an emergency.” And that’s not something that’s very attractive to doctors either. And Rachel, you wanted to add …
Roubein: Oh yeah, I was just going to say I think one of the things that stuck out to me about this particular video, one of my colleagues, Dan Rosen, so I [inaudible 00:16: 52] in February, and he said that this is Live Action, which is the group that came under the spotlight in 2011 for releasing undercover videos seeking to discredit Planned Parenthood, but Live Action had been playing the Baby Olivia to legislative audiences, including at an influential conservative group, American Legislative Exchange Council. So just kind of looking at who’s kind of seeking to get this video into classrooms.
Rovner: All right, well now it is time for our weekly dive into why health care costs so darn much. We begin with a fascinating and infuriating investigation from The New York Times about another one of those third-party contractors most of us had never heard of, kind of like Change Healthcare before it got hacked. This one is called MultiPlan, and its job is to recommend how much insurers and/or employers, in self-insured plans, should pay providers. Except it turns out that MultiPlan has an incentive to pay providers less than they charge. It pockets part of the “savings.” And in most of the cases, these out-of-network charges are not covered by the surprise-billing law. I think because patients know they are going out-of-network, that part is not entirely clear to me. And of course, often patients have no other available providers, so they have no choice but to go out-of-network.
Sometimes indeed providers do overcharge outrageously. We’ve talked about that a lot. But in this case, it seems that a lot of these recommendations are to underpay outrageously. The firm told one therapist that her fair payment should be half of what Medicaid pays. Medicaid, traditionally the lowest payer of everyone. I feel like this story’s going to have legs, as they say. Apparently, the American Hospital Association has already asked the U.S. Department of Labor to investigate MultiPlan. Why do I feel like we’re all pawns in this huge competition between health care providers and insurers about who can pay who less or more and pocket the differences?
Cohrs Zhang: Yeah, I think we first heard about MultiPlan, kind of in the conversation around surprise billing, because that was just a different category of these out-of-network bills where patients were getting stuck in the middle. And I think over time we’ve seen more stories come out about loopholes in those protections. And this is another example where MultiPlan is … they have to fix their business model. And the arbitration process for these surprise bills is so backed up, in these certain cases, which are more emergency care, I think, and if patients don’t necessarily have control or knowledge of their provider being out-of-network.
But certainly, people, if you’re looking for a certain specialist or want to go to a certain place to have a procedure done, then you may just elect an out-of-network provider. And I think the part I found really interesting about this reporting, that I think we’ve seen reflected in larger trends on business reporting, is really understanding these business models better and the incentives. And I love the graphics, I think, where you’re showing that if MultiPlan can lowball these providers and manage to squeeze a little bit more of a discount for payers, then they’re taking a cut of that discount, and patients can be left on the hook for these too.
So I think, as with anything, these surprise-billing protections are going to be an iterative process. And certainly I think there’s more to be done in so many different individual cases to protect patients from some of these games that providers and insurers are engaged in and the firms that kind of specialize in brokering these negotiations.
Rovner: It feels very whack-a-mole, every time they sort of put a band-aid on one problem, another one pops up, that it’s just sort of this is what happens when a fifth of your economy goes to health care is that everybody says, “Oh, I can make money doing X.” And then, there’s an awful lot of people making money doing X, which is not necessarily having anything to do with providing or receiving medical care.
Cohrs Zhang: Absolutely. And correct me if I’m wrong, I think MultiPlan, it may be publicly traded as well. So if you look at some of these incentives here to kind of meet those quarterly targets and how that aligns with patients, I think that’s also just something we keep in mind.
Rovner: And there was private equity involved on both sides, too, which I didn’t even want to try to explain. You should really read the story, which is really very complicated and very well explained. Because this is how it works: They make it complicated so you can’t figure out what’s going on.
Well, meanwhile, in a sad payment story of the week, a new study has found that paying off people’s medical debt doesn’t actually fix their financial problems. According to a National Bureau of Economic Research working paper, paying off debts that have already gone to collection did not improve the financial status of the people who owed the money, nor their mental health, nor did it make it more likely that they would be able to pay future medical bills. One thing it did do was help their credit ratings. The researchers said that they hope maybe paying off debt before it reaches the collection status might be more helpful, but that would also be more expensive. What makes it easy to pay off medical debt after it’s gone to collections is they sell it for pennies on the dollar. And of course, the U.S. is already moving towards taking medical debt off of people’s credit report. So obviously we’re talking about patients getting stuck with these huge bills and they end up with this medical debt and now we can’t seem to figure out how to fix the medical debt problem either.
Cohrs Zhang: When I first saw the study, obviously I trust that Sarah Kliff edited her studies, but I scrolled right down to the conflict-of-interest section to see who funded this. And yeah, it was a very depressing study. But I think it’s important to keep in mind that a failure to pay medical debt is a symptom of larger economic problems. Certainly there may be cases where medical debt is the only outstanding debt somebody has or is a shocking surprise or is a lien on their home, something like that that might have just these massive consequences.
But I think one of the points that was brought up in the story was that when you have medical debt, sure, you have collections calls, you have bad impact on your credit, but you’re not getting evicted from your home. And we’ve heard about cases where providers have held outstanding balances against patients, but I don’t think that’s a general practice. You’re supposed to be seen if you go in for medical care. So I think just like the day-to-day challenges of poverty, of debt, are so overwhelming that it is a little discouraging to hear that these individual payments may not have changed someone’s life. But I think there may be anecdotal cases that would be different from that larger trend, but it was not an encouraging study.
Rovner: No. And speaking of conflict of interest, there was the opposite of conflict of interest. It was conducted in part by the group RIP Medical Debt, which was created to help pay off people’s medical debt. And they did say, obviously there are cases in this does make huge differences in individual people’s lives. It was just that, overall, apparently the model by which they are paying off people’s debt is not helping them as much as I guess they had hoped to. So they have to look on to other things.
Moving on to this week in health data security, or lack thereof, it seems that another cyberattack group is trying to get Change Healthcare to pay ransom. This is after the company reportedly paid $22 million. So it seems that after paying, the company didn’t get all of its stolen records back. Meanwhile, it seems that even though we’re not hearing as much about this as we were, there are still lots of providers that aren’t getting paid. I mean, Rachel, this thing as we predicted, has a really long tail.
Roubein: Absolutely does. Yeah, I think we’re seeing these multiple ransomware groups trying to extort money out of UnitedHealthcare. I mean, they have deep pockets. It’s such a mess. I think, who’s to say what’s true about what data they have as well. So it’s kind of hard to report on these kind of things. And I think only UnitedHealthcare has the answers to those questions. But I think we are going to see some more congressional oversight on this issue. I know providers, hospitals, and physician groups were absolutely using these arguments on Capitol Hill during the appropriations negotiations. They’re saying, “We’re in such financial distress.” Going to their lawmakers talking about how it wouldn’t be a good idea to cut provider payments or implement site-neutral payments for hospitals, all these long-term things that lawmakers have been thinking about. There were other political problems, too, but I think it’s definitely seeped into Washington how difficult this has been, how cumbersome some of the workarounds are for providers, large and small, I think who are trying to work around this fiasco.
Rovner: Yeah, I read one story, I mean it really does feel like a spy movie that they’re assuming that maybe the company that got the ransom that was supposed to split it with the company that actually did the hacking didn’t and made off with the money. And now the company that actually did the hacking is trying to get its own ransom and oh my goodness. I mean, again, this is what happens when a fifth of the economy goes through the health care system. But I mean, I want to keep on this story because this story really does keep on impacting the back-room goings-on, which keep the health care system functioning in some ways.
And while we are on the subject of health care data breaches, USA Today has now a searchable tool for you to find out if you’re one of the 144 million Americans whose medical information was stolen or exposed in the last year. Yay? I think? I suppose this is a necessary evil. It’s hard for me to imagine 10 years ago. It’s like, “Wow, you can take some time and find out if your medical information’s been exposed.”
Roubein: It’s better than not knowing because you can change your passwords, you can do some credit monitoring, you could protect your information in some ways. But it’s not the same as better protections for the breaches happening in the first place.
Rovner: I know Congress is talking about a privacy bill, but apparently it is in truly embryonic stages at this point because I don’t think Congress really knows what to do about this either. They just know that they probably should do something.
All right, that is the news for this week. Now we will play my bill of the month interview with Molly [Castle] Work. Then we will come back and do our extra credits.
I am pleased to welcome to the podcast my colleague Molly Work, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month” installment. Molly, thanks for joining us.
Molly Castle Work: Thanks so much, Julie.
Rovner: So this month’s bill, like last month’s bill, is for an air-ambulance ride, a bill that should have been prevented by the federal No Surprises Act. But we’ll get to that in a minute. First, who is our patient this month?
Work: So our patient is Amari Vaca. He was a 3-month-old baby at the time from Salinas, California.
Rovner: And what happened to him?
Work: When Amari was a 3-month-old baby, he had issues with his breathing. His mother took him to a local ER and pretty quickly his team of doctors decided that he needed more specialized care at a larger hospital in San Francisco. So they organized an emergency transport.
Rovner: Via helicopter, yes?
Work: It was actually by air ambulance. So like a small airplane.
Rovner: Ah. OK. And before we get too far, he’s OK now, right?
Work: Yes, he is OK. Unfortunately, he was transported to the hospital. He was there for three weeks. They diagnosed him with RSV, but he’s fortunately doing well, now.
Rovner: Well, and then as we say, the bill came. And how much was it?
Work: It was $97,599.
Rovner: Of which the insurance paid how much?
Work: Zero.
Rovner: Now, as I mentioned at the top, the federal surprise-billing law should have prevented the patient from getting a big bill like this, except it didn’t in this case. So why not?
Work: Yeah, so this was really interesting. Cigna, which was Amari’s health plan at the time, decided that the care was not medically necessary. Their argument was that he could have taken a ground ambulance. There was nothing to prove that he had to take this emergency airplane. And so, because of this, Cigna was able to avoid No Surprises Act and they didn’t pay for any of the bill.
Rovner: And, therefore, the patient was left on the hook.
Work: Yes. Amari and his family were left on the hook for the entire bill.
Rovner: So this feels like something that should have been taken care of with a phone call. The insurer calls the doctor and says, “Hey, why’d you order an air ambulance when the hospital’s only 100 miles away?” And the doctor says, “Because it was an infant on a ventilator.” But that would’ve been too easy, right?
Work: Yeah, exactly. There’s a lot of issues with this. First off, one of the best things about No Surprises Act is it’s supposed to take patients out of this. It’s supposed to make it so health plans and providers deal with all these negotiations before it even goes to a patient. But because of how this was handled, instead, Amari’s family is having to do all these negotiations. They’re the ones who are writing letters, using his medical records, to Cigna, and doing multiple appeals.
Rovner: And so far, has there been any progress or is the bill still outstanding?
Work: It’s still outstanding. His mother, Sara, has done two internal appeals. So that means she applied to have the bill changed within Cigna. They denied her both times. Right now she’s working on an external appeal, where an outside provider helps evaluate, and she’s still waiting to hear back on that.
Rovner: So what’s the takeaway here? I mean, obviously you take your critically ill child to a hospital, and they say he has to go, he needs a higher level of care, and recommends an air ambulance. Are you supposed to say, “Wait, I have to call my insurer first to make sure they’re not going to deem this medically unnecessary?”
Work: Yeah, that’s what’s so frustrating because obviously if any of us were in that situation, we would’ve done the same thing. If our baby was sick, we would do the emergency air ambulance, or what we would do what the doctors told us to do. I think what I’ve been hearing from people is that, first off, hospitals should become better acquainted with what plans cover. Of course, we can only hope. But the hospital, for example, should have checked which air-ambulance providers are covered by Cigna before they made the call, because the one they did call was out-of-network for Amari’s family. As patients, what you can really do is you just need to advocate for yourself. It’s easy to be intimidated, but there are lots of times that hospitals just get the medical bill wrong or insurance companies. So do what Sara is doing and appeal. If internal appeals don’t work, go push for that external appeal as well.
Rovner: Yes, these days it helps to know your rights and to try to exercise them when you have them. Molly Work, thank you so much.
Work: Thank you so much, Julie.
Rovner: OK, we are back. It’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Rachel, Rachel Zhang. Why don’t you go first this week? Yep. We have both Rachels.
Cohrs Zhang: Yes. Confusing. So I chose a story in KFF Health News actually, and the headline is “Ten Doctors on FDA Panel Reviewing Abbott Heart Device Had Financial Ties With Company.” And I think this was just a really illuminating explanation of some of the loopholes in conflict-of-interest disclosures with FDA advisory committees. There’s a lot of controversy over what role these committees should play, when they should meet. But we’re seeing them play some very high-profile roles in drug approvals as well. But we have a medical device reporter on our team, and we just think it’s such an important coverage area as we’re looking at the money that the medical device industry spends. And I mean, you’re looking at some of these advisory board members who’ve received, on Open Payments, $200,000 from this company, and they’re not disclosing it because it’s not directly related to this individual device.
And I think it’s fair to say that some of them argued, “It was for a clinical study. The university got the money. I wasn’t spending it on a fancy car or something.” But nonetheless, I think there’s a good argument in this piece for some more stringent requirements for conflict of interest, especially if this data is publicly available.
Rovner: Yes, I was kind of taken this week about how very many good stories there were about investigations into conflicts of interest. Speaking of which, Rachel, other Rachel, why don’t you go next?
Roubein: My extra credit this week is titled “As Obesity Rises, Big Food and Dietitians Push ‘Anti-Diet’ Advice” and it’s a joint investigation by The Washington Post and The Examination, which is a new nonprofit newsroom that’s specializing in global health. And I thought it was a really fascinating window into the food industry and its practices at a time when the FDA and its commissioner wants to crack down, make front-of-package labeling more prevalent. And so basically the story dives into this anti-diet movement, which began as an effort to combat weight stigma and unhealthy obsession with thinness. And the movement has now become kind of a behemoth on social media, and basically food marketers are kind of trying to cash in here. The story kind of focused on one company in particular, General Mills, and its cereal, and the investigation found that the company launched a multipronged campaign to capitalize on the anti-diet movement and giveaways to registered dietitians who promote the cereals online. And I just thought it was kind of a fascinating exploration of all of these dynamics.
Rovner: Yes. Good journalism at work. Alice.
Ollstein: Yeah, I have a story from the Texas Tribune [“How Texas Teens Lost the One Program That Allowed Birth Control Without Parental Consent“] by Eleanor Klibanoff about the impact of the court ruling that said that Title X federal family planning clinics that all across the country have a policy of dispensing contraception, prescribing contraception to teens, whether or not they have parental consent, and doing that in a … advancing privacy and protecting them in that way. There was just a recent court ruling that said, just in Texas, the state’s parental consent laws override that. And they found that at a lot of these clinics, instances of teens coming in and seeking contraception have really fallen off. These are teens, the story documents, who don’t feel comfortable going to their parents. There’s instances of parents even getting violent with their kids when they find out about this. And so it really shows the effect of this, and this is something we should be continuing to track because it went to the 5th Circuit and it could go to the Supreme Court. We don’t know yet.
Rovner: Yeah, we talked about this case a couple of weeks ago. It was another of those cases that was very much aimed at a particular judge that they were confident would rule in their favor, who indeed did rule in their favor.
All right, well, my extra credit this week is not an investigation, it’s just a story I really liked from Stat News from Rachel’s colleague Sarah Owermohle, and it’s called “Your Dog Is Probably on Prozac. Experts Say That Says More About the American Mental Health Crisis Than Pets.” And full disclosure, that is one of my dogs in the background messing with a bone. My dogs are not on Prozac, but I am, and we are all three the better for it. It’s a serious story, though, about how our mental health impacts that of our pets, not just vice versa, and about how so few new medicines there are for anxiety and depression. And as an officer of a dog training club, I will say that it’s more than humans’ projections. We are definitely seeing more dogs with behavioral issues than at any time that I can remember, and I’ve owned dogs all my life.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. You can still find me mostly at X. Alice, where are you these days?
Ollstein: I’m at @AliceOllstein on X, and @alicemiranda on Bluesky.
Rovner: Rachel Zhang?
Cohrs Zhang: I’m at @rachelcohrs on X and also spending more time on LinkedIn these days.
Rovner: Rachel Roubein?
Roubein: @rachel_roubein on X.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
Courts, Elections, Health Care Costs, Multimedia, States, Abortion, Arizona, Bill Of The Month, Children's Health, Emergency Medicine, Florida, Indiana, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Podcasts, Pregnancy, reproductive health, Women's Health
PAHO/WHO | Pan American Health Organization
PAHO Director meets with Minister of Health of Canada to discuss ongoing collaboration with the country
PAHO Director meets with Minister of Health of Canada to discuss ongoing collaboration with the country
Cristina Mitchell
11 Apr 2024
PAHO Director meets with Minister of Health of Canada to discuss ongoing collaboration with the country
Cristina Mitchell
11 Apr 2024
1 year 6 months ago
Atogepant: New migraine drug recommended for NHS use in England - BBC.com
- Atogepant: New migraine drug recommended for NHS use in England BBC.com
- Patients in England to be offered daily pill that can halve migraine frequency The Guardian
- Must-know guide to treating - and preventing - a migraine Daily Mail
- AbbVie’s oral therapy Aquipta recommended by NICE for migraine prevention in adults PMLiVE
- NICE recommends first oral treatment for chronic and episodic migraines Pavilion Health Today
1 year 6 months ago
With 3 Confirmed Cases of Dengue Fever, V.I. Health Officials Urge Public Awareness and Prevention Measures - VI Consortium
- With 3 Confirmed Cases of Dengue Fever, V.I. Health Officials Urge Public Awareness and Prevention Measures VI Consortium
- Government leaders declare new epidemic after over 500 reported cases of mosquito-borne illness: 'A warning sign' The Cool Down
- With 3 Confirmed Cases, V.I. Health Officials Urge Public Awareness and Prevention Measures VI Consortium
- Seminole County uses chickens to identify the diseases that mosquitoes may be carrying Yahoo! Voices
- Central Florida officials prepare for mosquito season amid Dengue Fever outbreak in Puerto Rico WESH 2 Orlando
1 year 6 months ago