A $229,000 Medical Bill Goes to Court
In 2014, Lisa French had spinal surgery. Before the operation, she was told she would have to pay $1,337 in out-of-pocket costs and that her insurance would cover the rest. However, the hospital ended up sending French a bill for $229,000. When she didn’t pay, it sued her.
In 2014, Lisa French had spinal surgery. Before the operation, she was told she would have to pay $1,337 in out-of-pocket costs and that her insurance would cover the rest. However, the hospital ended up sending French a bill for $229,000. When she didn’t pay, it sued her.
The case went all the way to the Colorado Supreme Court. In this episode of “An Arm and a Leg,” host Dan Weissmann finds out how the court ruled and how the decision is reshaping the fine print on hospital bills in ways that could cost patients a lot of money.
Dan Weissmann
Host and producer of "An Arm and a Leg." Previously, Dan was a staff reporter for Marketplace and Chicago's WBEZ. His work also appears on All Things Considered, Marketplace, the BBC, 99 Percent Invisible, and Reveal, from the Center for Investigative Reporting.
Credits
Emily Pisacreta
Producer
Adam Raymonda
Audio Wizard
Afi Yellow-Duke
Editor
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: A $229,000 Medical Bill Goes to Court
Note: “An Arm and a Leg” uses speech-recognition software to generate transcripts, which may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
Dan: Hey there–
Lisa French was a clerk for a trucking company in Denver. She’d been in a car crash, and her doctor told her that to keep her spine stable, she ought to get surgery.
She asked the folks at the hospital what it was gonna cost her, out of pocket. They ran her insurance and told her: Your end is going to be one thousand, three hundred thirty-six dollars, and ninety cents.
She said, thanks.
Then, she and her husband sat down at their kitchen table and talked it over: They had a rainy-day fund. A thousand dollars they’d socked away, they kept it at home, in cash. Were they ready to spend it all for this?
They decided they were, and Lisa went to the hospital with a thousand dollars cash.
She had the surgery, it went fine. The hospital had been expecting about 55 thousand dollars from Lisa’s insurance. They actually got more like 74 thousand.
But they decided that wasn’t enough. They decided they wanted their full sticker price: 303 thousand dollars. So they billed Lisa French for the rest: 229 thousand dollars.
And when they didn’t get it, they sued her.
Lisa French had her surgery in 2014. The court case finally got resolved last year, in 2022, by the Colorado Supreme Court.
If you’ve been listening to this show for a while, you probably remember: We have gotten VERY interested in understanding, when we get a wild medical bill, what legal rights do we have? How can we use those rights to fight back? Even on a small scale, like in small claims court?
And even though Lisa French’s case is a LONG way from small claims court, it has a LOT to teach us about these questions.
This is An Arm and a Leg, a show about why health care costs so freaking much, and what we can maybe do about it. I’m Dan Weissmann. I’m a reporter, and I like a challenge. So our job on this show is to take one of the most enraging, terrifying, depressing parts of American life, and bring you something entertaining, empowering, and useful.
And I should say upfront: We won’t be hearing from Lisa French directly.
Her case made a lot of headlines– in 2018, when a jury heard it, in YEAR when an appeals court overturned the trial court, and last year when the state supreme court made its ruling.
Not in the kind of detail that we’re gonna go into, but come on: Who can resist the headline?
Male Anchor: Well, tonight we have a story of David versus Goliath. David being a woman who needed spinal surgery in 2014 Goliath, the hospital that charged her more than $200,000 to do it.
Dan: So over the years, a lot of reporters wanted a sound bite from Lisa French. Her attorney used to let her know when there was an inquiry, and she’d say yes or no.
Eventually, she told her lawyer: Don’t even tell me when they call anymore. I just want to live my life.
Fair enough.
So here’s who we’ve got.
Ted Lavender: I’m Ted Lavender. I’m an attorney in Atlanta, Georgia. I’ve been practicing law for 26 years,
Dan: And he spent several of those years representing Lisa French.
It’s probably worth answering one question up front: If Lisa French had to empty her family’s rainy-day fund to pay the hospital a thousand bucks, who’s paying the lawyer from Atlanta?
The insurance from her job. Which had played a role in starting the whole mess.
Ted Lavender: the company that she worked for had a health benefits plan that was slightly different than what you might call run of the mill health insurance.
Dan: It worked this way: They weren’t in-network with any hospitals. Instead, they’d just take whatever bill any hospital sent, make their own evaluation of what a fair price would be, and send the hospital a check.
It’s a somewhat unusual model– one survey says about 2 percent of employers use a plan like this– but Ted Lavender says it often works.
Ted Lavender: a very large percentage of the time , the hospital would accept the check and no one would hear anything more from the hospital, which in legal parlance would mean acceptance
Dan: And as a backstop, in case there was any trouble, the health plan would send a lawyer. That’s Ted.
And here’s what happened that led to all the trouble in Lisa French’s case: Whoever ran her insurance card at the hospital, they didn’t read it very carefully.
If they had, they would’ve seen a little logo under the insurance-company name that said, “provider only” — that is: This plan only has doctors and nurses and other PROVIDERS in network.
With hospitals, there’s no network, no “in-network rate.” We’ll just send a check for what we think is right.
The same health-benefits company has a different plan, one that does have a hospital network. You know how it is. Insurance companies, a million different plans, every one its own snowflake.
The hospital mistook Lisa French’s snowflake for another one, and that’s how they came up with that estimate.
Ted Lavender: based on their calculation, they expected to collect a total of
$56,000, the 1,336 from Ms. French and the remainder from her health plan.
Dan: And they presumably would’ve been happy with 56 thousand. But they got more. They got about 75 thousand dollars.
But once they got it, they wised up to the mistake they had made about Lisa French’s insurance. They had no agreement with the insurance plan to accept 56 thousand.
So, they decided: There’s no reason for us not to charge our full sticker price here.Three hundred and three thousand dollars.
So Lisa French had been expecting a bill for three hundred thirty-six dollars and ninety cents. That’s the difference between what she’d been quoted and the thousand dollars she’d paid in advance. But the bill she got wasn’t what she expected.
Ted Lavender: it turned out to be a whopper of a bill. We ended up with an itemized bill that showed every line item for every charge that totaled this
$303,000
And then at the bottom was, you know, subtracting the thousand she paid, subtracting the money the insurance paid, leaving a balance of 229,000 and change
Dan: Of course, Lisa French did not have 229 thousand dollars, or anything like it.
Ted Lavender: Eventually she got a visit from the sheriff who served her with a lawsuit and she was sued for that $229,000.
Dan: And that’s where Ted Lavender entered the scene.
The jury trial in 2018 took six days. As Ted Lavender says, it wasn’t exactly a splashy murder trial, in terms of drama.
Ted Lavender: this was a six day trial involving hospital billing. So, you know, there was no murder weapon. There was no aha, big, gotcha moment that was really exciting.
Dan: But Ted Lavender did his best. Like one time, when he got a hospital executive on the witness stand.
To stabilize Lisa French’s spine, surgeons had implanted 13 pieces of metal into her body. So Ted Lavender had the hospital executive walk the jury through the price for each of those bits of metal. Or actually, the prices..
Ted Lavender: And I first showed him the itemized bill and asked him to identify what they charged for these 13 pieces of hardware .
I had given him sort of an oversized calculator that was sitting there in front of him on the witness stand, admittedly, for some dramatic effect
And through adding these up on the itemized bill, he arrived at the number which was $197,000.
Dan: A hundred and ninety-seven thousand dollars. So that’s about two-thirds of the three hundred and three thousand dollars the hospital is trying to charge Lisa French.
And then the next thing I did was I handed in the 13 invoices that we had received from the hospital,
Dan: That is, Ted handed the guy the invoices the hospital had received — and paid — when it bought those bits of metal..
Ted Lavender: and I asked him to add up and tell this jury what did the hospital pay for these 13 pieces of hardware.
He’s adding, and he’s adding and he’s punching in numbers, and he’s turning pages and he’s adding, and he’s adding with each addition, with each plus the jury seemed to ease a little closer up to the front of their chair, and ultimately he arrived at the total, which was $31,000 and change.
Dan: So the hospital’s charging like six and a half times what they paid. And that’s two thirds of this 300 thousand dollar bill.
Ted Lavender: It just, you know, the jury seemingly did not like that.
Dan: So that was a good moment for Lisa French’s side. I mean getting the jury mad at the other side, that’s a win.
And the big calculator wasn’t Ted Lavender’s only visual: He also had a giant post-it note, where he wrote down, in magic marker, all the different prices the hospital accepted for the surgery, depending on who was paying.
Ted Lavender: and we got these numbers from the hospital, they would’ve accepted $146,000 from private insurance.
Dan: That’s less than half of what they were trying to charge Lisa French. And they accepted less than that — a LOT less — from government-funded insurance, like Medicare, Medicaid, or Tricare, which covers folks in the military.
Ted Lavender: The average of what they would’ve accepted for these. Procedures that Ms. French had were $63,199. Again, Ms. French and her insurance company combined paid almost $75,000.
Dan: You can hear that post-it rustling around. It was a good prop, he’s held onto it. So, he’d shown the jury that the hospital charged a HUGE markup, and that what they were suing Lisa French for was way, way more than they charged anybody else.
On the hospital’s side, they were like, Yeah, but this is our actual sticker price. And Lisa French signed a piece of paper that said she would pay “all charges of the hospital.”
So the hospital was like, yep, and these are our charges. That 303 thousand dollars, it comes from a list we keep. It’s called the chargemaster. That’s what Lisa French was signing up for.
And this became something the jury had to decide:
When Lisa French signed a piece of paper saying she’d pay “all charges of the hospital” — was she specifically agreeing to pay what was on the chargemaster?
And here’s one thing that might’ve made jurors a little skeptical on that score: The hospital never showed that chargemaster list to Lisa French. Not before her surgery, not after it. They said it was a trade secret.
Ted Lavender: they went all the way through trial. Never producing it though. We, we, we asked at the very beginning, once the lawsuit was filed, , basically you get to ask questions. Give me this information, give me information that supports your case or helps my case.
And we ask specifically for the charge master and they refuse to produce it on the basis that it was confidential and proprietary.
Dan: By withholding that list, the hospital may have helped Ted Lavender make his argument: How could Lisa French have known what she was signing up for, if she couldn’t see the prices?
Ted Lavender: if we can’t get it through our subpoena power, how in the world would Lisa Friendship been able to use it by, had she asked?
And admittedly she didn’t ask for it, but if she had, surely they wouldn’t have given it to her either.
Dan: In the end, the jury agreed: Lisa French had not specifically agreed to pay the hospital’s chargemaster prices.
And the only other alternative was: She agreed to pay something reasonable.
The jury decided she owed the hospital seven hundred seventy six dollars and 74 cents
Basically, that’s the three hundred and some left over from the original estimate, plus some extra — because she wound up staying in the hospital one night more than expected: She owed a fee for late check-out.
Of course the hospital did not take that lying down. They appealed the outcome– and won! Ted Lavender appealed that decision, which is how the case ended up in front of the Colorado Supreme Court.
We’ve actually got tape of those proceedings. They’re kinda juicy. Plus the outcome, and why it matters for the rest of us. That’s right after this.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News–formerly known as Kaiser Health News.
They’re a national newsroom producing in-depth journalism about health care in America. We’ll have more information about KFF Health News at the end of this episode.
OK, so Lisa French’s case was headed to the Colorado Supreme Court.
And here’s the big issue. Remember how the jury found that Lisa French hadn’t actually agreed to pay the hospital’s chargemaster price, the three hundred and three thousand dollars?
The hospital argued: The jury never should’ve been asked to consider that question.
The law — legal precedent — makes it open and shut: The appeals court had agreed. And it had cited other cases from courts around the country.
So when the hospital’s lawyer, Mike McConnell, got up to address the Supreme Court, he led with those citations.
Mike McConnell: All of the questions that you have raised have been addressed in more than a dozen cases around the country. carefully and thoroughly.
Justice Richard L. Gabriel: Well, let me push back on you. Good morning to you, Mr. McConnell.
Mike McConnell: Good morning.
Dan: This is Justice Richard L Gabriel, stepping right in. He notes that these dozen other decisions all rest on one original case, from 2008, where a court had said: We can’t intervene in health care pricing. Courts shouldn’t try. Health care is too complicated.
Justice Gabriel wasn’t convinced.
Justice Richard L. Gabriel: I guess the question I have is why, you know? I, you know, we may not be the smartest people in the world, but this is a contract and why should the hospital industry— different than any other industry on the planet —have different rules for contract principles?
Dan: The hospital lawyer argued that hospitals couldn’t predict everything that would happen in a patient’s care. In fact, the hospital can’t even control it: Only physicians can decide what treatment to order.
Mike McConnell: You can, uh, I guess imagine that hospitals ought to be able to predict in advance what a particular physician is going to order for a particular patient. Um, and, uh, perhaps, you know, obviously you feel that is the way it ought to be. It is not the way it is, but now
Justice Melissa Hart: Mr. Mr. McConnell, I’m sorry, to interrupt…
Dan: Here’s justice Melissa Hart breaking in
Justice Melissa Hart: …the hospital did provide an estimate in this case. They did calculate what they thought this was going to cost and tell her that. So it is, it seems false to me that they can’t do it. Of course, they can’t predict with absolute certainty. In this case, she had the extra night stay in the hospital and she paid for that. But they can predict in a case like this, and they do.
Dan: The justices didn’t seem super-persuaded by McConnell’s response to that. And that left one more big question in front of the justices.
When Lisa French signed a document promising to pay “all charges,” was she definitely agreeing to pay three hundred and three thousand dollars? Or 229 after insurance.
The appeals court found that the chargemaster rate — the 303 thousand — had been “incorporated by reference” to the document she’d signed, officially called the “hospital services agreement.”
The supreme court wasn’t convinced. Here’s Justice Richard Gabriel again.
Justice Richard L. Gabriel: There’s no reference to the charge master on the face of the hospital services agreement.
How could she have assented to something she never even knew existed?
Dan: And here’s how the hospital’s lawyer responded.
Mike McConnell: When she read the provision, all charges not otherwise paid by insurance. She understood that the hospital charges would, she was responsible for paying the hospital charges that her insurance company did it,
Justice Richard L. Gabriel: Whatever it was. They could have charged her a billion dollars and she’s your position to be she’s bound because she agreed. All charges means all charges.
Dan: Huh! There wasn’t a real comeback to that.
The Supreme Court ruled against the hospital, unanimously. Specifically, they ruled that the chargemaster– the 303 thousand dollars– had not been “incorporated by reference” to the piece of paper Lisa French had signed.
She didn’t know those chargemaster list prices even existed. How could she agree to pay them?
So that meant, the court ruled that, quote, “the hospital services agreements left the price term open.”
Which is language that may ring a bell, if you’ve been listening to this show. It’s a legal principle — a bedrock of contract law:
How the law treats an open-price contract — a contract that doesn’t specify a price term.
Here’s a refresher on that principle from Ted Lavender.
Ted Lavender: if you go to McDonald’s and order a, a quarter pounder with cheese and you know, value meal number three, they tell you the price and that is the price that you have to pay. And then they give you your meal.
You enter that contract with an actual price term
Dan: But you can also enter an open-price contract — a contract without a price term.
Ted Lavender: if you have a contract without a price term, without a specific price in it, then the law infer into that contract a reasonable price.
Dan: In other words, a contract with the price term OPEN is not a blank check. I don’t have to pay whatever number the other side makes up.
And that’s what the Colorado Supreme Court found here.
They ruled that, quote, “principles of contract law can certainly be applied to hospital-patient contracts.” They say, a court may have ruled otherwise in 2008, and other courts may have cited that opinion. We disagree.
The Colorado Supreme Court is saying, even in health care, when no price is specified– when the price term is open– you have the right to a reasonable price.
Yes!
And that’s why Lisa French’s case is so interesting to us, here on this show.
Because we’ve talked here about using this legal principle to fight back against outrageous bills.
We’ve heard from one guy, Jeffrey Fox, who actually took a hospital to small claims court to enforce his right to a reasonable price. And won.
We’ve heard from a listener who tried and failed, but said, more of us should try this.
And this Colorado decision seems like good news for anybody interested in doing something like that.
But honestly, it also raises a few concerns that I had not known about before. First:
Well, there ARE all those other cases out there, in other states, that follow the 2008 case, the one that says health care is too complicated for courts to get into.
And yeah, here’s Colorado saying, “No it isn’t.”
But courts in other states aren’t bound by Colorado’s decision. Hm. And second: there’s also something the Colorado court DIDN’T decide:
What if the paper Lisa French signed had specified, “I agree to pay the hospital’s CHARGEMASTER rates?” Could she be required to pay them then? Even if they were a billion dollars?
In their decision, The Colorado court wrote that the chargemaster rates are “increasingly arbitrary” and “inflated” and “have lost any direct connection to hospitals actual cost.”
So Ted Lavender thinks they might’ve said, No, we can’t be held to a billion dollars, just by adding the word “chargemaster.”
Ted Lavender: I think they would’ve answered that. No, but they did not come right out and actually answer that.
Dan: Because they didn’t HAVE to answer that question.
Ted Lavender: Courts routinely, in fact, it’s almost an objective of appeals courts. They answer as few a number of questions as possible to get to an answer. ,
Dan: So the Colorado court simpley ruled that in Lisa French’s case, the chargemaster rates weren’t “incorporated by reference” into papers she signed.
Those papers didn’t didn’t mention the chargemaster at all– and the hospital kept that chargemaster as a trade secret. Open, shut.
But… hospitals aren’t supposed to keep those rates secret anymore. For the last couple of years, thanks to an executive order from the Trump administration, federal rules have required them to post their chargemaster to the internet.
And so I had all that in mind when I heard from a listener in Atlanta.
Cindi Gatton: my name is Cindy Gatton and I’ve been an independent patient advocate for 11 years now.
Dan: Cindi’s job is helping people deal with medical bills, but she had actually written to me about her experience as a patient.
Before a medical appointment, she got the usual forms online, including one for “Patient Financial Agreement and Responsibilities”
Cindi Gatton: so I thought, you know what? I’m gonna print it and just see exactly what it says. And I’m reading through the thing it says, patient understands and agrees that he, she will be charge. The Piedmont Healthcare Standard charge master rates for all services not covered by a payer or that are self-pay.
I’ve never seen that before, and it shocked me that there was a reference to charge master rates in the financial disclosure.
Dan: And Cindi has been dealing with medical bills full-time for a decade. She’s seen a lot. So when she says it’s new, and that it’s shocking, that seems worth noting.
Cindi Gatton: it just feels wrong to me. It feels really wrong because it, it reminds me of, you know, you, you go to a website and they give you their terms and conditions. Nobody reads those. I don’t read them. You click yes so that you can move on with what it is you wanna do, which is to get care, to be seen by the doctor to, you know, have your procedure.
And I don’t know this, this feels, um, it feels manipulative to me
Dan: Yeah, and to me, it feels ominous. Like lawyers who work for hospitals have been paying attention to the Lisa French decision and thinking:
There’s a wedge here maybe we could exploit. Like, if we get you to sign a document that says “chargemaster” on it, we’re getting you to sign away your right to a reasonable price. After all, the court in Colorado didn’t come out and say that wouldn’t be kosher.
So, where I’m landing at the end of this story is: I’ve got a couple big homework assignments:
First, if I’m interested in seeing how we can use our legal rights to fight back against outrageous, unreasonable bills — and I am —
I need to learn more about which states recognize our rights to a reasonable price in health care, and which ones … maybe don’t. I’m on it, and if you’ve got any tips, please bring them.
That’s the first assignment, and for the second, I’d love your help: How many hospitals are using this “chargemaster” language these days in those financial responsbility documents they ask us to sign?
Do me a favor: See if you can get a copy of that document from any hospital system or doctor group where you get seen. And send me a copy of it?
Redact anything you need to. And also know: we’re not aiming to share this with anybody outside our reporting team.
Here’s what happened when I tried this.
A hospital where I get seen uses a portal called MyChart– a lot of hospitals use it. I just logged on to MyChart there, and I did a little digging around. I found a link to something called “My Documents.” And I found a form there called Universal Consent.”
It has stuff about financial responsibility.
It doesn’t mention chargemaster rates. But it’s a year old. It also says it’s expired.
And here’s an idea I got from Cindi, which I’m gonna try– and which seems worth passing around.
When Cindi found that chargemaster language in the document from her Hospital, here’s what she did. She printed it out and changed it:
Cindi Gatton: what I did is instead of the standard charge master rates, I drew a line through it and I wrote in two x Medicare rates.
Dan: In other words, instead of saying “I’ll pay the chargemaster rates,” it says, “I’ll pay two times the Medicare rate.”
We’ve heard about this strategy before, from former ProPublica reporter Marshall Allen, who wrote about it in his book, “Never Pay the First Bill.”
Here’s the rationale. Medicare pays less than most commercial insurance; hospitals say that at least sometimes they lose money on Medicare. Doubling it seems … generous enough. But it also sets a limit.
So that’s what Cindi wrote on her printout.
Cindi Gatton: I have been taking it with me when I go to be seen that if they ask me for the document that I can say, you know, here it is.
Dan: So far, she says, nobody’s asked for it.
And, I don’t think anybody will be confused, but just to make sure, I’ll say: This isn’t legal advice. I’m not a lawyer. Cindi’s not a lawyer.
She’s just a person going to the doctor, doing her best not to leave too many openings where she could get really screwed. And I’m gonna try following her example.
And I’ve got another request for you: If you try this trick of printing the thing out, exxing out the chargemaster language and writing 2 x medicare rates– LET ME KNOW WHAT HAPPENS, OK?
The place to do all this is on our website at arm and a leg show dot com, slash contact. That’s arm and a leg show dot com, slash, contact.
You are this show’s secret weapon. You’re our eyes and ears. Cindi Gatton’s a listener who got in touch.
How did I first learn about Lisa French’s case? Email from a listener. [Thank you, Terry N, for that note last year! Took us a minute, but we got to this.]
Thank you for listening. You absolutely rule. I’ll catch you soon.
Till then, take care of yourself.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg was produced by me, Dan Weissmann, with help from Emily Pisacreta, and edited by Afi Yellow-Duke.
Daisy Rosario is our consulting managing producer. Adam Raymonda is our audio wizard. Our music is by Dave Winer and Blue Dot Sessions.
Gabrielle Healy is our managing editor for audience. She edits the First Aid Kit Newsletter.
Bea Bosco is our consulting director of operations. Sarah Ballema is our operations manager.
An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News–formerly known as Kaiser Health News.
That’s a national newsroom producing in-depth journalism about health care in America, and a core program at KFF — an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism.
And yes, you did hear the name Kaiser in there, and no: KFF isn’t affiliated with the health care giant Kaiser Permanente. You can learn more about KFF Health News at arm and a leg show dot com, slash KFF.
Zach Dyer is senior audio producer at KFF Health News. He is editorial liaison to this show.
Thanks to Public Narrative — That’s a Chicago-based group that helps journalists and nonprofits tell better stories– for serving as our fiscal sponsor, allowing us to accept tax-exempt donations. You can learn more about Public Narrative at www dot public narrative dot org.
And thanks to everybody who supports this show financially.
If you haven’t yet, we’d love for you to join us. The place for that is arm and a leg show dot com, slash support.
Thank you!
“An Arm and a Leg” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Public Road Productions.
To keep in touch with “An Arm and a Leg,” subscribe to the newsletter. You can also follow the show on Facebook and Twitter. And if you’ve got stories to tell about the health care system, the producers would love to hear from you.
To hear all KFF Health News podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to “An Arm and a Leg” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 6 months ago
Courts, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Multimedia, An Arm and a Leg, Colorado, Hospitals, Out-Of-Pocket Costs, Podcasts
Para pacientes de cáncer sin seguro, conseguir atención médica es una lotería
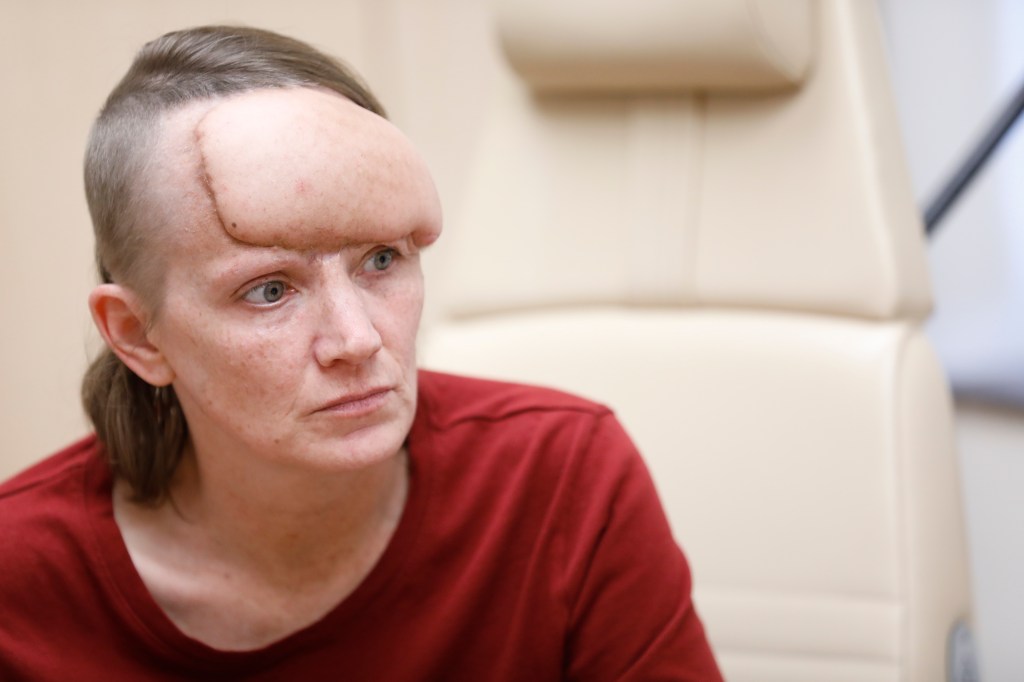
Dieciocho meses después de que April Adcox se enterara de que tenía cáncer de piel, el pasado mes de mayo, regresó por fin a la Universidad Médica de Carolina del Sur en Charleston para recibir tratamiento.
Para entonces, la zona rojiza a lo largo de la línea del cabello había pasado de ser un círculo de 2 pulgadas a cubrirle casi toda la frente. Supuraba líquido y le dolía.
Dieciocho meses después de que April Adcox se enterara de que tenía cáncer de piel, el pasado mes de mayo, regresó por fin a la Universidad Médica de Carolina del Sur en Charleston para recibir tratamiento.
Para entonces, la zona rojiza a lo largo de la línea del cabello había pasado de ser un círculo de 2 pulgadas a cubrirle casi toda la frente. Supuraba líquido y le dolía.
“La verdad es que esperaba morir de esto, porque pensaba que eso era lo que tenía que pasar”, afirmó la mujer de 41 años, madre de tres hijos y residente en Easley, Carolina del Sur.
Adcox se había reunido por primera vez con los especialistas del centro médico a finales de 2020, después de que una biopsia diagnosticara un carcinoma basocelular. La operación para extirpar el cáncer requeriría varios médicos, le dijeron, incluido un neurocirujano, debido a lo cerca que estaba de su cerebro.
Pero Adcox no tenía seguro. Había perdido su trabajo en una fábrica de automóviles en los primeros días de la pandemia y, en el momento del diagnóstico, sentía pánico ante la complejidad de la operación y la perspectiva de una factura elevada. En lugar de seguir el tratamiento, intentó camuflar la zona cancerosa en expansión durante más de un año con sombreros y flequillos largos.
Si hubiera padecido cáncer de mama o de cuello uterino, probablemente habría tenido derecho a cobertura por una ley federal que amplía el Medicaid a los pacientes de bajos ingresos diagnosticados con esos dos tipos de cáncer.
Para las mujeres con otros tipos de cáncer, así como para casi todos los hombres, las opciones son escasas, especialmente en Carolina del Sur y los otros 11 estados que aún no han implementado la expansión de Medicaid, según oncólogos y expertos en política sanitaria que estudian el acceso a la atención.
Los estudios demuestran que, a veces, los adultos sin seguro retrasan la atención, lo que puede perjudicar las probabilidades de supervivencia. Pero que los pacientes obtengan un seguro para cubrir el tratamiento se parece un poco al juego de la ruleta, es decir, depende de dónde vivan y del tipo de cáncer que padezcan.
“Es muy aleatorio; creo que eso es lo más desgarrador”, afirmó el doctor Evan Graboyes, cirujano de cabeza y cuello, y uno de los médicos de Adcox. “Vivir o morir de cáncer no debería depender del estado en el que vives”.
La Ley de Cuidado de Salud a Bajo Precio (ACA) dio a los estados la opción de ampliar Medicaid para cubrir a más personas. Poco después de la aprobación de la ley, sólo el 2,6% de los adultos de 18 a 64 años con un nuevo diagnóstico de cáncer carecían de seguro en los estados de Medicaid ampliado frente al 7,8% en los estados sin expansión, según un estudio publicado en JAMA Oncology en 2018.
Investigadores de la Sociedad Americana del Cáncer, que realizaron el análisis, estiman que unas 30,000 personas sin seguro son diagnosticadas con cáncer cada año.
Pero en todos los estados, los pacientes sin seguro, de bajos ingresos, con cáncer de mama o de cuello uterino pueden obtener cobertura, incluso si no califican para Medicaid.
Los adultos con cáncer detectado a través del Programa Nacional de Detección Temprana de Cáncer de Mama y de Cuello Uterino pueden inscribirse en Medicaid durante la duración de su tratamiento contra el cáncer, gracias al activismo y la legislación federal que comenzó hace más de tres décadas.
En 2019, se inscribieron 43,549 pacientes con estos tipos de cáncer, según un informe de la Oficina de Rendición de Cuentas del Gobierno (GAO) publicado en 2020.
“Si te diagnostican cáncer de mama o de cuello uterino, tienes suerte”, dijo la doctora Fumiko Chino, oncóloga radioterapeuta del Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center de Nueva York, que estudia el acceso y los costos del tratamiento del cáncer. “De no ser así, puedes enfrentar obstáculos importantes”.
El importe total facturado a la aseguradora durante el año siguiente a un diagnóstico de cáncer puede ser abultado. Por ejemplo, los costos en 2016 ascendieron a un promedio de $168,730 por cáncer de pulmón y $137,663 por cáncer colorrectal, según un estudio de 2022 que calculó las reclamaciones a la aseguradora por varias neoplasias malignas comunes diagnosticadas en pacientes con seguro privado.
Dado que los adultos sin seguro pueden tener dificultades para pagar la atención preventiva, su cáncer puede no ser identificado hasta que esté avanzado, por lo que es más costoso para el paciente y el sistema de salud, explicó Robin Yabroff, autor del estudio en JAMA Oncology y vicepresidente científico de la Sociedad Americana del Cáncer.
Los pacientes que no pueden obtener ayuda financiera a través de un centro de la red a veces acumulan deudas médicas, utilizan tarjetas de crédito o lanzan campañas de recaudación de fondos en internet, dijo Yabroff. “Nos cuentan historias de personas que hipotecan sus casas para pagar el tratamiento del cáncer”.
Los pacientes de cáncer pueden adquirir un seguro a través del mercado de seguros de salud de ACA. Pero a menudo deben esperar hasta el período de inscripción regular al final del año, y esos planes de salud no entran en vigor hasta el comienzo del año siguiente.
Esto se debe a que la ley federal fue diseñada para animar a la gente a inscribirse cuando están sanos, lo que ayuda a controlar los costos, señaló MaryBeth Musumeci, profesora de política y gestión de la salud en la Universidad George Washington en Washington, DC. Si un nuevo diagnóstico te calificara para la nueva cobertura, dijo, “entonces se incentivaría a la gente a permanecer sin seguro mientras están sanos y piensan que no van a necesitar cobertura”.
Mientras tanto, el acceso a la cobertura de Medicaid para pacientes de bajos ingresos con cáncer de mama y de cuello uterino, es una historia de éxito que se remonta a una ley de 1990 que creó el programa nacional de cribado de mama y cuello de útero. Las mamografías empezaron a recomendarse de forma generalizada en la década de 1980, y los activistas presionaron para llegar a más personas desfavorecidas, explicó Katie McMahon, directora de políticas de la Red de Acción contra el Cáncer de la Sociedad Americana del Cáncer.
Sin embargo, una investigación demostró que algunos adultos sin seguro tenían dificultades para recibir atención por los cánceres detectados a través de los cribados, dijo McMahon. Una ley del año 2000 permitía a los estados extender Medicaid a estas personas, y en 2008 los 50 estados y el Distrito de Columbia ya lo habían hecho, según el informe de la GAO de 2020.
Para otros enfermos de cáncer, una de las vías de cobertura que les quedan, según Chino, es reunir los requisitos para la discapacidad a través de la Administración de la Seguridad Social, tras lo cual pueden solicitar Medicaid. La agencia federal tiene una larga lista de criterios para los pacientes con cáncer. También cuenta con el programa Compassionate Allowances, (Beneficios por Compasión), que ofrece revisiones más rápidas para pacientes con determinadas afecciones médicas graves, incluidos cánceres avanzados o agresivos.
Aunque las normas varían, muchos pacientes no califican hasta que la enfermedad se ha extendido o el cáncer requiere al menos un año de tratamiento intenso, explicó Chino. Esto supone un dilema para las personas que no tienen seguro pero padecen cánceres curables.
“Para tener derecho a Medicaid, tengo que esperar a que mi cáncer sea incurable”, dijo, “lo cual es muy deprimente”.
Por ejemplo, el programa de Beneficios por Compasión no incluye el carcinoma basocelular, y sólo cubre el cáncer de cabeza y cuello si se ha extendido a otras partes del cuerpo o no puede extirparse quirúrgicamente.
Adcox dijo que antes de su operación de 12 horas, el pasado mes de junio, su solicitud de ayuda económica a la Universidad Médica de Carolina del Sur estaba aún pendiente. Alguien del hospital calculó que su factura ascendería a $176,000 y le preguntó cuánto podía adelantar. Consiguió reunir $700 con la ayuda de sus seres queridos.
Pero pudo optar a una ayuda económica y no ha recibido ninguna factura, salvo de un proveedor externo de servicios de laboratorio. “Se acabó”, exclamó Adcox. Desde entonces ha recibido radioterapia y se someterá a más operaciones reconstructivas. Pero ya no tiene cáncer. “No me ha matado. No me mató”.
Aun así, no todo el mundo encuentra una red de seguridad.
Brian Becker, de El Paso, Texas, no tenía seguro ni trabajo cuando supo que padecía leucemia mielógena crónica en el verano de 2021, según contó Stephanie Gamboa, su ex mujer y madre de su hija pequeña. Su médico oncólogo le exigió un pago por adelantado, dijo, y tardó varios meses en pedir prestado el dinero suficiente.
Empezó la quimioterapia al año siguiente y, con el paso de los meses, perdió peso y se debilitó, volviendo a urgencias con infecciones y un empeoramiento de la función renal, explicó Gamboa. La última vez que su hija vio a su padre, “no podía levantarse de la cama. Era literalmente piel y huesos”, dijo Gamboa.
Becker inició los trámites para solicitar prestaciones por incapacidad. El mensaje de texto que envió a Gamboa, y que ella compartió con KHN, decía que la revisión de su solicitud comenzó en junio de 2022 y se esperaba que durara seis meses.
La carta de denegación, fechada el 4 de febrero de 2023, llegó más de un mes después de la muerte de Becker en diciembre, a los 32 años. Decía en parte: “Basado en una revisión de sus condiciones médicas, usted no califica para beneficios en esta reclamación”.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 6 months ago
Health Care Costs, Insurance, Medicaid, Noticias En Español, Cancer, Latinos
Montana May Require Insurers to Cover Monitoring Devices for Diabetes
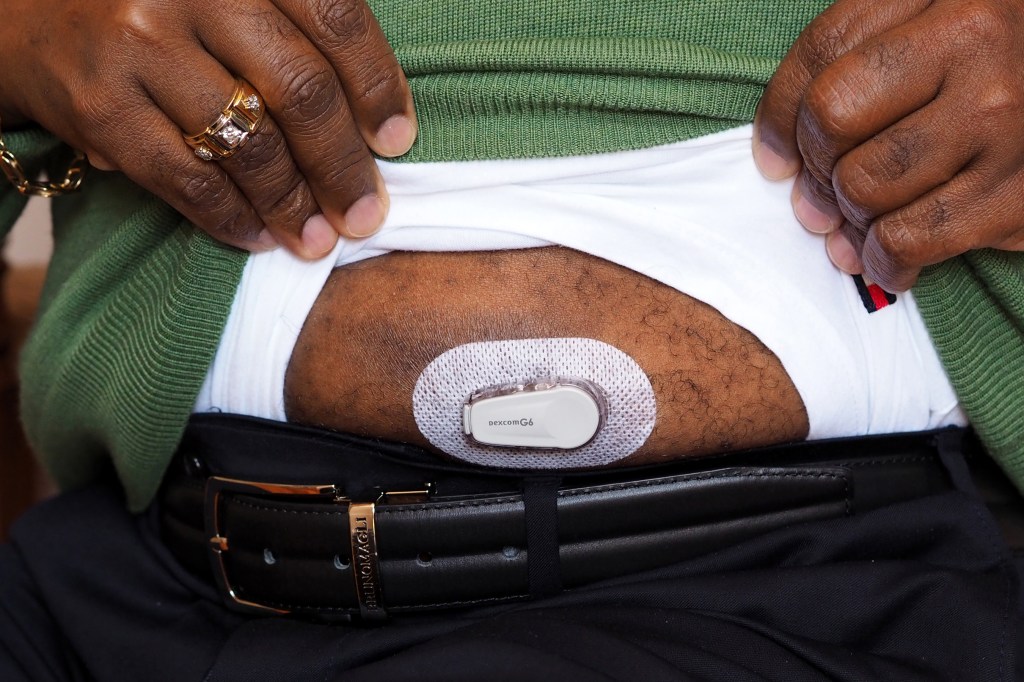
In between sets of tumbling warmups, Adrienne Prashar crossed the gym to where she had stashed her diabetes supplies and tested her blood sugar. Prashar, who was diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes the day before her 13th birthday, said tumbling usually drops her blood sugar levels.
Prashar, now 14, did a finger stick, saw her blood sugar was 127, and went back to the mat. For most people with diabetes, the target range is about 80-130, and up to 180 two hours after meals.
Prashar doesn’t have to check her blood sugar often. She wears a continuous glucose monitor, or CGM, that gives her blood glucose readings on her phone every five minutes. When she’s feeling differently than her CGM is showing, as on that March day at the gym, she checks her level by doing a finger stick.
But most of the time, she simply glances at her phone to see whether her numbers are trending low or high, which beats repeatedly pricking her finger, she said.
“I would hate it so much,” Prashar said. “It’s such a pain and it’s harder to see trends.”
Montana lawmakers are considering a bill that would require insurance companies to cover CGMs for people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Multiple studies and experts back up the effectiveness of the devices, showing better blood test results, fewer long-term complications, and a reduction in health care costs.
Studies show CGMs can greatly benefit people with Type 1 diabetes. There are also promising results for people with Type 2 diabetes, the more prevalent of the two types, but the research is limited compared with that on Type 1.
House Bill 758 has broad support from lawmakers, but it faces opposition from insurance companies and some providers. That opposition focuses on the cost, whether a CGM is medically necessary at all stages of diabetes, and the possibility that CGM manufacturers will raise their prices if there is an insurance mandate.
CGMs can be worn on the legs, stomach, or arms, and they stay in place with an adhesive patch. A thin tube goes under the skin and measures blood glucose levels from tissue fluid. The data is transmitted via Bluetooth to a phone or similar device. Instead of a finger prick, which provides a reading for a single point in time, a CGM gives the wearer a continuous stream of data.
According to GoodRx Health, CGMs can cost between $1,000 and $3,000 each year out-of-pocket.
Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Montana, the state’s largest insurer, estimates the bill, if passed, would cost the organization nearly $5 million a year, spokesperson John Doran said.
CGMs aren’t medically necessary in all circumstances, Doran said, and medical necessity should be determined through a partnership between provider and payer. But Doran said that he understands there are instances in which a CGM may be necessary and that Blue Cross already covers CGMs in those cases.
“These things are a convenience,” Doran said. “They provide you real-time information and there is some benefit to a person’s lifestyle to these monitors.”
Lawmakers in several states are considering bills to regulate coverage of CGMs, and Illinois’ governor signed one such bill into law last year.
A study published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology in 2022 says about 30 million Americans have diabetes, a condition in which a person’s body can’t make enough insulin (as in Type 1) or use it effectively (as in Type 2). By 2030, the study estimated, 55 million people in the U.S. will have diabetes, with total medical and societal costs of more than $622 billion — a 53% increase from 2015. According to the American Diabetes Association, nearly 78,000 Montanans have been diagnosed with diabetes.
Various studies, diabetes educators, and health care providers say that CGMs can help people with diabetes reduce their A1C levels, a common measure of blood sugar levels used in diabetes management. Proper management can reduce complications from diabetes — like retinopathy, heart attack, and nerve damage — that lead to higher costs in the health care system through emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
Dr. Brian Robinson, an endocrinologist at St. Peter’s Health in Helena, said supplies for people with Type 1 diabetes are generally covered by insurance. When he considers recommending a glucose monitor for a patient, he said, the decision is driven by insurance rules that are informed by the American Diabetes Association’s standards of care.
“My patients are better because of CGMs, there’s no doubt about that,” Robinson said. But he noted the science doesn’t yet support his opinion that CGMs should be given to everyone with diabetes, no matter what.
Not all physicians, especially in endocrinology, agree that a person with Type 2 diabetes needs a continuous glucose monitor, Robinson said. But if a person needs a shot each day to manage diabetes, he said, that patient should have access to a CGM.
Lisa Ranes, manager of the diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolism center at Billings Clinic, said the benefits of a CGM are the same for people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Many studies have shown that CGMs are just as effective for patients on lower quantities of insulin, like some people with Type 2 diabetes, as for people with Type 1 diabetes, who rely on insulin throughout the day.
“It gives patients that complete picture to help them make the decisions on what they need to do to keep their blood sugar safe,” Ranes said, giving examples like upping the frequency or dose of insulin, having some food, or exercising.
For people with Type 2 diabetes, Ranes said, CGMs could be helpful in early diagnosis. Type 2 diabetes is progressive, Ranes said, so the sooner it is under control, the better.
When Cass Mitchell, 76, was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes over 30 years ago, her doctor told her that people with Type 2 diabetes don’t live long because they have a hard time managing their care.
Mitchell, who lives in Helena, warmed to finger pricks. But test strips were expensive, about $1 each at the time, she said.
About 10 years ago, she got a CGM. Mitchell went from testing maybe twice a day to looking at her blood sugar on an app 20 to 25 times each day. She said she’s more in tune with her diabetes and uses her device’s time-in-range reports — showing how often blood glucose stays within a set range — to make lifestyle changes.
Mitchell has lowered her A1C from around 11% to 7%. According to the ADA, the target for most adults with diabetes is less than 7%.
Mitchell’s device is covered under Medicare and supplemental insurance and would remain so with the passage of HB 758. She said if she had to pay out-of-pocket she wouldn’t be able to afford her CGM and that she was excited about the potential of the bill to give more people access to CGMs.
Dr. Hayley Miller, medical director of Mountain States Diabetes in Missoula, initially thought HB 758 sounded good, but now she isn’t so sure. She thinks the biggest risk of the bill passing is that prices for CGMs go up.
“It seems like I’m against it, but it really is, when insurance gets involved everything gets tricky,” Miller said.
Emma Peterson, a former diabetes educator for St. Vincent Healthcare in Billings and Providence Endocrinology in Missoula, said most people working in diabetes care think everyone diagnosed should just have a continuous glucose monitor.
“At the end of the day, both forms of diabetes and all the other many forms of diabetes have the same complications and still face the same struggles of trying to keep blood sugars in range,” Peterson said.
Keely Larson is the KHN fellow for the UM Legislative News Service, a partnership of the University of Montana School of Journalism, the Montana Newspaper Association, and Kaiser Health News. Larson is a graduate student in environmental and natural resources journalism at the University of Montana.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 6 months ago
Health Care Costs, Insurance, States, diabetes, Legislation, Montana
A Doctor’s Love Letter to ‘The People’s Hospital’
Could a charity hospital founded by a crusading Dutch playwright, a group of Quakers, and a judge working undercover become a model for the U.S. health care system? In this episode of the podcast “An Arm and a Leg,” host Dan Weissmann speaks with Dr. Ricardo Nuila to find out.
Nuila’s new book, The People’s Hospital: Hope and Peril in American Medicine, uses the innovative model of the Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, where he practices, to argue for a publicly funded health system in the U.S. that’s available to everybody, with or without insurance.
Dan Weissmann
Host and producer of "An Arm and a Leg." Previously, Dan was a staff reporter for Marketplace and Chicago's WBEZ. His work also appears on All Things Considered, Marketplace, the BBC, 99 Percent Invisible, and Reveal, from the Center for Investigative Reporting.
Credits
Emily Pisacreta
Producer
Adam Raymonda
Audio Wizard
Afi Yellow-Duke
Editor
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: A Doctor’s Love Letter to ‘The People’s Hospital’
Note: “An Arm and a Leg” uses speech-recognition software to generate transcripts, which may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
Dan: Ben Taub Hospital is a publicly funded safety net hospital in Houston, Texas. The majority of patients don’t have insurance of any kind.
Dr. Ricardo Nuila has been working at Ben Taub since he was an intern, a medical student. He took me on a tour.
Ricardo Nuila: I started here and, you know, literally I just did not want to leave here cuz I just, just really enjoyed my job here
Dan: He’s just published a book called “The People’s Hospital” that’s not just a love letter to the place, it’s a pitch:
Not only is this place way, way cheaper than what we’re used to, in many ways it’s better. And it’s a model, a real alternative to what-we’re-used-to.
So, I ask him to pick ONE patient’s story from the book to tell, he picks a patient he calls Stephen. A restaurant manager, a Republican. A guy who did not expect to end up here.
But he had a giant lump on the side of his throat, and his insurance didn’t cover much. He paid cash, upfront, to get seen in a local ER.
Ricardo Nuila: finally there was a doctor who had seen a CAT scan and said, you have tonsillar cancer, cancer, however, you don’t have, uh, insurance
Dan: Tonsillar cancer. Cancer of the tonsils. That landed hard. So did the “however.”
Ricardo Nuila: He felt shitty you know, that somebody could tell you cancer, but there’s nothing that we are gonna do about it because of, of how much and…
Dan: It’s like it’s too painful — or too obvious — to finish the sentence: Because of your insurance. Somebody tells Steven to try the public hospital, Ben Taub. He expects the worst. But that’s not what he finds.
Ricardo Nuila: He comes to love this place. He gives, this is like so Steven, but he, he gives gift cards to the people greeting at the door because they’re nice and they do their job well cuz they make his day,
Dan: And it’s not just that he likes the people at the door.
Ricardo Nuila: He feels like he got really good healthcare and that he also, um, thought that the price was extremely reason.
Dan: Stephen lost his insurance when he got too sick to work, and he doesn’t qualify for Medicaid. He owns a house, he’s got savings, Texas has really stringent Medicaid restrictions– so he’s paying out of pocket.
Ricardo Nuila: But his final bill is pennies of what he thought he would pay.
Dan: Stephen’s dad had gotten radiation treatment for cancer, and the sticker price was 700 thousand dollars. Stephen had gotten radiation AND chemo AND surgery — and had been hospitalized for a good while.
His bill was 32 thousand, three hundred and seventy-eight bucks. Real money for sure, but he can pay it. And it’s less than five percent of his dad’s bill for much less extensive treatment.
Ricardo Nuila: And the healthcare is really good. And so he’s almost proud that he’s had this experience
Dan: Steven’s become a convert. And as Ricardo Nuila walks me into a conference room, it’s clear: He hopes his book will create more converts.
Ricardo Nuila: you start to see this model and it makes you think, can things be different in healthcare? I think that that’s an option. But we as a country haven’t thought about that. Seriously. You know?
Dan: And if it seems politically unimaginable that we could have anything like this around the country– an effective, efficient, CHEAP, publicly-funded health system–
Well, the idea that Houston could have one, that was pretty unlikely too.
In fact, the story of how Ben Taub got here may be the most surprising story in Ricardo Nuila’s whole book.
This is An Arm and a Leg, a show about why health care costs so freaking much, and what we can maybe do about it. I’m Dan Weissmann. I’m a reporter, and I like a challenge. So our job on this show is to take one of the most enraging, terrifying, depressing parts of American life and to bring you a show that’s entertaining, empowering and useful.
Ben Taub Hospital sits at the edge of the Texas Medical Center– that’s a giant neighborhood full of hospitals and medical schools, including some of the best in the country, like the M.D. Anderson cancer center.
In his book, Ricardo Nuila writes about how some patients at Ben Taub can see from their rooms the gleaming buildings of Ben Taub’s neighbors.
So when I visit, I make him show me the view. We look out from a stairwell at a glass tower, M.D. Anderson’s Sheikh Zayed building.
Ricardo Nuila: that’s glamorous. Right? you get a glimpse into the rest of the medical center here. Ben Taub sticks out, I feel like, because it’s, it’s brick versus glass.
Dan: But as Ricardo Nuila makes clear in his book: This unglamorous brick building gets the job done.
In addition to Steven, there’s Ebonie, whose complicated pregnancy — there’s a lot of vaginal bleeding– gets tracked more precisely than it would elsewhere:
At other hospitals, nurses eyeball the pads that absorb that blood and note heavy, medium or light bleeding. At Ben Taub, they’ve adopted an innovative approach: weighing each pad to get an exact measurement.
Another patient, Christian, has bounced around other systems without anybody accurately diagnosing the dire kidney problems that have kept him in pain for years. Because he didn’t have good insurance, it wasn’t worth anybody’s time.
At Ben Taub, insurance isn’t an obstacle,
Ricardo Nuila: We organize things, which is basically, okay, we need to focus on your kidneys right now and we need to get you to see a geneticist. And both of those things happened.
Dan: they not only diagnose him, they get him on a form of dialysis that he can manage himself at home.
It’s cheaper, and delivers better quality of life for him.
Everything at Ben Taub is cheaper. The system spends about a third as much per patient as the national average. In part, that may be because nobody earns million-dollar salaries here.
But Ricardo Nuila makes the case over and over again that they take the time– because they have it– to make wise use of resources.
They don’t have as many MRI machines as other hospitals. But guess what? A lot of patients don’t need MRIs.
But Ben Taub can’t meet every need: One patient, Geronimo, needs a liver transplant, and that requires resources the hospital just doesn’t have.
But Ricardo Nuila and his colleagues put a lot of time into wrenching him back onto Medicaid, so he can get the transplant somewhere else. They rope in a Congressman to get it done.
Geronimo tells his mom:”I feel so important. Everyone treats me like I’m rich.”
Ricardo Nuila: That’s what I think a lot of people really want is just the sense that the person who’s responsible for your care is thinking through the problem with you and aware that you are not having a great day and wants to deal with that situation with you. And I just felt like this environment allowed me to like, have those moments.
Dan: So who pays for this environment? It may be cheaper, but it isn’t free.
Some patients are on Medicaid. Some are on Medicare. Some have private insurance. But the majority don’t have any insurance at all.
Some, like Stephen, pay cash. And a lot of the rest — about a third of Ben Taub’s patients — are treated for free.
The bulk of Ben Taub’s funding comes from a special property tax in Harris County, where Houston is located. It funds a whole system called Harris Health– Ben Taub, a second hospital, and a bunch of clinics.
And of course, none of this has always existed.
In fact, it’s only here, like this, because of a really wild story, with two big characters. One of whom wasn’t even from Houston. He was a writer I’d never heard of, a Dutch guy named Jan de Hartog.
Ricardo Nuila: de Hartog was one of the most amazing people that you could read about. He was a Nazi resistance fighter, Dutch ship captain.
Dan: And while he was hiding out in Denmark during the war– in between saving a few Jewish babies and running war missions in his tugboat–
he wrote a romantic dramedy that — later became a broadway hit. And then got adapted into a Broadway musical called I Do, I Do– which, Broadway-musical nerds in the house– starred Mary Martin and Robert Preston– you know, The Music Man– and had a song that your mom might still remember.
(musical sounds)
Dan: Yeah. So, interesting guy. And in the early 1960s he came to Houston to teach playwriting at a local University. It was a big time for him. He’d just gotten married — for the third time, but this one was for keeps- and become a Quaker.
Ricardo Nuila: And when he and his wife Marjorie come to Houston, they find that there’s all these whisperings about this charity hospital in town in Houston about how, how awful the conditions are. That the children in the maternity ward would cry all night for the, for a lack of milk, and so as part of his faith, he decides that he needs to volunteer there
Dan: When de Hartog writes about the hospital later, he describes the experience of walking in for the first time as literally mind-boggling.
He’s like: I know what a hospital smells like. Disinfectant, maybe some fresh laundry. And I know what a slaughterhouse smells like: Blood, and shit. And the smell here is slaughterhouse.
As he looks around, the sights are something else.
Ricardo Nuila: He sees a cockroach crawling into the tracheostomy of like a patient. He sees like people sitting in their own filth.
Dan: He and Marjorie do not up and quit. They stick around. And then they recruit a dozen Quakers and a few society ladies to come volunteer with them, and get the Red Cross to train them.
And it’s nuts. This is a rich city. The ZOO is air conditioned. But not this hospital.
And he starts to catch on: Why it’s so horrible.
Number one is racism.
The hospital serves mostly Black and Brown patients. When Jan and Marjorie start volunteering, the other volunteers are all society ladies, and the whole program is set up so they don’t touch patients. DeHartog later says he asked why, and the volunteer coordinator says, Southern ladies can’t have physical contact with black people.
But she doesn’t say black people. She uses the n-word.
When he asks staff why public officials don’t do something about the rotten conditions, they say: What politician is going to stick up for black people? The n-word comes up again.
And– de Hartog doesn’t make this connection, but it seems pretty on the nose: The hospital itself is named after Jefferson Davis, who led the Confederacy in the Civil War.
But there’s also a political mechanism for institutionalizing this neglect, without ever having to acknowledge the role of racism:
No one particular political entity — no one particular political leader– is responsible for the public hospital, financially. The city of Houston and Harris County are each supposed to kick in HALF. So it doesn’t belong to either of them. Here’s de Hartog describing the city-county dynamic in a lecture he gave many years later.
Jan de Hartog: And they were continuously at each other’s throats. The one said, you don’t pay enough. The other said, but you don’t. And they went back and forth
Dan: The top official for Harris County actually has the title County Judge. At that time, this was a guy named Bill Elliott.
And you’ll hear in this clip from a local newscast, he wasn’t exactly reaching for the bill. Here he is, explaining why the some problem with the hospital is actually the CITY’s fault.
Judge Bill Elliott: it’s absolutely ridiculous, uh, to say that, uh, this is a responsibility and this is the fault of Harris County.
Dan: And the city? At least one.council member is calling for a budget cut.
Which really pisses de Hartog off.
And de Hartog actually loves the city. It’s an exciting place. It’s booming– growing super-fast. And it’s not just an oil town.
Ricardo Nuila: Houston at that time was the home of NASA.
NASA narrator: Future manned space flight missions to the moon and perhaps the planets will be commanded from this control room of the Mission Control Center at NASA’s Manned Spacecraft Center,
Ricardo Nuila: It had built this Astrodome, it was the city of the future.
Dan: The Astrodome– you know, a sports stadium WITH AIR CONDITIONING. .
Astrodome Narrator: A fully enclosed building, large enough for any sport convention show or conclave with constant temperature and humidity independent of outside weather,
Dan: CBS News does a report about the booming city: NASA, the oil wealth, the Astrodome. And de Hartog is a main character– talking about how much he loves the town.
Jan de Hartog: it is a city of, a city of unlimited opportunities. It’s an immensely exciting town, and you feel that anything is possible,
Dan: It wraps up with Walter Cronkite talking about how everybody in town is absolutely nuts about football.
Walter Cronkite: Their brand of football is like their brand of city and brand of life. Play wide open. Take a chance, try anything. Above all, do it with zest and do it big.
Dan: Oh, and there’s this OTHER thing Houston is really becoming known for.
Cutting edge medicine. For twenty years, the city’s been building the Texas Medical Center — that giant campus where more than a dozen hospitals and med schools now operate right on top of each other. Baylor College of Medicine actually moved from Dallas to Houston to be part of it.
Ricardo Nuila: Houston is a really deeply medical city. And at that time they’re all working on extraordinary things
Dan: Yeah, in 1964, while Jan de Hartog is witnessing the suffering at the charity hospital, Dr. Michael deBakey is performing the world’s first coronary artery bypass at a private hospital in town.
But the medical establishment were not allies. Jefferson Davis hospital, on the outskirts of town, was about to be replaced by a new building in the Texas Medical Center.
But the Medical Society– the local doctors’ association — hadn’t wanted the charity hospital as a neighbor. They’d actually put up a ballot initiative to keep the new building at the old site.
Medical Society Voice-Over: you the taxpayer, will pay the extra cost That’s why your doctor recommends you vote for the new hospital to remain at its present site.
Dan: It hadn’t worked, but along with the budget cuts, officials were now talking about DELAYING the charity hospital’s move to the new building, which had just been completed. De Hartog and his friends, smell a rat.
They think the powers that be are actually going to sell the new building in the Medical Center to some other hospital that wants in. This has been a public conversation.
Jan de Hartog: There had been offers to buy it and they wanted to wait for the highest bidder
Ricardo Nuila: He writes a series of op-eds for the Houston Chronicle that start to get press, not just in Houston, but around the country and in fact around the world.
Dan: He describes the awful things he’s seen. And he appeals to Houstonians’ sense of pride in their bustling, futuristic city. A city he loves, too. Here’s how his first op-ed ends…
Jan de Hartog: I cannot believe that it is the will of the citizens of Houston, that our growing medical center rightly becoming famous all over the. Shall be allowed to harbor the cancerous sore of man’s inhumanity to man. It would turn the entire center planned as Houston’s glory into Houston’s shame.
Dan: Even just that first op ed made a lot of noise.
Jan de Hartog: the bomb exploded and the national magazines and newspapers and TV zeroed in on the hospital to find out what was going on,
Dan: … and immediately, the hospital DOES move into its new home in the Medical Center. But the funding issue isn’t solved.
So de Hartog keeps pushing.
Ricardo Nuila: He writes a book called “The Hospital”
Dan: He goes to churches around town, synagogues, everywhere he can, recruiting hundreds of volunteers.
But there’s no political progress — and conditions at the hospital actually get worse. Key nurses get burned out and quit. Things go to hell.
In a harrowing diary entry, he writes about full bedpans left on tables next to trays of food. About a patient crying out for help, and hearing back “Shut up!”
Jan de Hartog: Never before had I realized to this extent, the depth of our damnation, and at that deepest moment of desperation, when we knew nothing could be done, nothing would change for the simple reason that
Jan de Hartog: those who had the fate of the hospital in their hands were not there. Mayor Welsh didn’t work there. Uh, commissioner Bill Elliot Judge, the county judge did not work there.
Dan: But THEN, there’s a turn. Somebody shows up. That’s right after this.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with Kaiser Health News. That’s a non-profit newsroom about health care in America. KHN is not affiliated with the giant health care player Kaiser Permanente. We’ll have more information about KHN at the end of this episode.
So, Jan de Hartog keeps slogging away.
He gives a talk at a Baptist church– he reads that diary entry, the one with the bedpans, and the absence of Judge Elliott and other leaders.
And at first he thinks he didn’t go over so big. Nobody even raises their hand to volunteer.
But then it happens.
Jan de Hartog: When, uh, we were about to leave, a man turned up with a baby on his hip who said, uh, do you train people at night?
Dan: And the guy seems to be looking around, trying to make sure nobody’s listening. De Hartog tells the guy, yeah, we could do that…
Jan de Hartog: He said, I mean, a dead of night without anybody seeing.
Dan: De Hartog’s like, “um, sure, I guess. Why, though?”
Jan de Hartog: He said, well, I am Judge Elliot,
Dan: Judge Elliott. The county judge. Probably the most powerful politician in town. That’s who wants to volunteer. In secret. Without anybody seeing. He says to de Hartog
Jan de Hartog: I cannot do it as a judge, but I must do it as a man. And that was the moment that the whole damn thing changed..
Dan: Because Judge Bill Elliott followed through.
Ricardo Nuila: He trains himself in a clandestine manner to be an orderly, at night, and he verifies everything that de Hartog has said.
Dan: de Hartog actually oversees the judge’s final practical exam, where Bill Elliott tends to an African-American man named Willie Small.
Jan de Hartog: the judge with his thermometer went and put his hand on Willie’s shoulder and said, Mr. Small, sir, I’d like to take your temperature to hear that, to hear a southern judge, , say “Mr. Small, sir”
Dan: It was a symbolic moment. The judge had to touch, had to defer to, a Black man. So not only had the judge now seen everything, he took responsibility for what he had seen.
There’s a proposal for a county-wide property tax, to fund what’s called a Hospital District. Now there’s a referendum, and Elliott backs it all the way.
Jan de Hartog: and we all waited with baited breaths for the outcome. And it was no
Dan: Yeah. The referendum fails. And as de Hartog tells it, once it does, a real backlash starts to build. It gets personal.
Jan de Hartog: those who had resented our presence from the very beginning became vocal. Margie and I, were called communists
Ricardo Nuila: De Hartog just would not flinch. I mean, he and his wife’s lives were threatened.
Dan: Also, somebody threw a bag of excrement at their door.
Eventually, de Hartog says the Red Cross, which was training and supervising volunteers at the hospital, came to him and Marjorie and said, “It might be better for us if you left town for a while.”
They did — went on to all kinds of adventures.
Meanwhile, Bill Elliott kept pushing, and keeps pulling in allies– including, eventually, the Medical Society.
Ricardo Nuila: he rallies them to get behind it.
Dan: He gets the question on the ballot AGAIN later that same year. And it passes in November 1965.
It’s a big moment.
Ricardo Nuila: What’s also interesting is that it’s forgotten. Something that I’ve gleaned from all this is that you know, people will forget and you have to remind them.
Dan: And while we’re remembering: In 1965, the whole country is making some big commitments to health care for a lot of people. President Lyndon Johnson signs Medicare and Medicaid into law in July of that year.
It’s probably also worth noting that Medicare and Medicaid help make Ben Taub possible: About a third of the hospital’s patients are on one or the other. It’s a minority of patients, but it’s many millions of dollars of funding.
The 1960s were a notoriously divisive time. And so is this.
Ricardo Nuila doesn’t ignore today’s political polarization — or how that polarization makes it hard to imagine a national conversation about creating a different health care system.
Or the role that doctors have historically played in resisting that conversation.
It’s part of his story. His family story. And in a book about a place where a lot of sad things do happen, this may be the toughest one.
Ricardo Nuila: I was born into a family of doctors and my dad in many ways was a hero to me. I saw how much pride he took in his work of being a doctor
Dan: But over time– as insurance companies got tougher to deal with– the business side of running a medical practice looked a lot less apealing.
Ricardo Nuila: . He had to hire more and more staff. He hired his mother, my grandmother, who is, uh, the type of person not to back down from Chicago, you know, . And so, her job was to be on the insurance companies to make sure that they wouldn’t, screw him out of money.
Dan: His dad turned away patients who didn’t have insurance. His dad growled and grumbled– about insurance companies, and about patients who didn’t have money to pay.
When Ricardo finished college and got into medical school, he put off starting for two years. What he sees as his dad’s life in the business of health care is not appealing.
Ricardo Nuila: the grind wears on him, you know? The fighting with the insurance companies
Dan: I mean in the book, your dad is a bit of a stand-in for . For doctors as a doctoring, as profession and the, and the way in which doctors get alienated from medicine.
Ricardo Nuila: yeah, he is a stand in a bit for doctors. And it’s gonna be, I think the doctors have a lot to say about how healthcare goes in America,
Ricardo Nuila: And unfortunately, the history shows that they haven’t been a great piece of that, at least as far as universal healthcare is concerned.
Dan: This becomes part of Ricardo’s story with his dad. Dad invites him to form a family practice. Ricardo chooses Ben Taub. And over the years, it becomes clear: They’re on opposite sides of a political divide. There are painful conversations, and then they go months without speaking.
Ricardo Nuila: that’s how deep politics run, you know, it’s really, it’s really difficult when you overlay like politics onto like a family dynamic,
Ricardo Nuila: It just felt like he was like totally on board with this idea that, you know, healthcare is something that is earned and healthcare is something that people, if you can’t afford it, you don’t deserve it. Is what I heard from what he was saying.
Dan: is your dad an ideal reader of the book? Is your dad kind of who the person you wanna make that case to?
Ricardo Nuila: That’s really interesting.
Ricardo Nuila: I would say this, that, I did not write this to preach to the choir for sure.
Dan: But he’s not sure his dad would actually pick up a book like this.
Ricardo Nuila: It’s just because I know my dad, he, my dad’s the type of person who reads John Grisham on a beach, you know? So I’m not a hundred percent sure if he would pick up this book, you know?
Dan: Unless, say, his son wrote it. Ricardo does expect his dad to read The People’s Hospital. And even if he doesn’t agree with everything his son has written, Ricardo thinks his dad will be proud.
Ricardo Nuila: I can tell you now as a, as a father, , it’s not clear that your kids are gonna come out Okay. . You know what I mean? I’m just saying that like he has reason to be proud just because I’m a, a living and breathing person right now, you know?
Ricardo Nuila: And I’m, I’m working in as a doctor. So I, I feel, I feel good for him.
Ricardo Nuila: And I think that he’s probably very happy that I wrote about medicine cuz he loves medicine.
Dan: The last chapter of “The People’s Hospital” is called “faith” And in it, Ricardo Nuila describes a daily ritual that he says keeps him grounded. It starts with passing a plaque on his way in. Of course I have him show it to me.
Ricardo Nuila: I park like right over there, .
Ricardo Nuila: I come in here and I just look at, look at this every time.
Dan: So, and describe what we’re seeing here.
Ricardo Nuila: Well, we’re seeing, a plaque that, talks about when this hospital was founded, and the people who constructed the building. And there’s also the, I forgot this is, this is bad of me, but I forgot the name.
Dan: the snake around the stick?
Ricardo Nuila: I’m in big trouble now because I’m on the Caduceus Caduceus. I, it’s the Cadus. Yeah.
Ricardo Nuila: And it’s just a reminder, you know, that we have this structure in place to help care for people who don’t have, uh, the means and that, and
Dan: that people decided to put this building here. Yeah.
Ricardo Nuila: Exactly. It’s a community effort.
Dan: Ricardo Nuila writes that he sees that community as he walks from that plaque to his desk– all the co-workers, in every kind of job, doing their best.
And this is the faith that he says gets affirmed— reading from the book here:
If someone is suffering and there is the capacity within the community to help, in a way that doesn’t harm anyone else, then we not only owe it to that person, we owe it to ourselves to help.
Whatever your politics are, I think that’s pretty great.
Dr. Ricardo Nuila practices at Ben Taub Hospital. He’s associate professor of Medicine, Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine. His book is called “The People’s Hospital.”
Honestly there’s a lot in this book, — more patient stories, more family stories, a very deft summary of a hundred years of health care economics and politics.
I’ll tell you: reading this book, I was reminded of an idea I’ve had before. That it might be cool someday to convene a kind of “Arm and a Leg” book club. Because I’d like to have someone to talk with about a book like this– like maybe you.
Right now, that’s just an idea. The how would take a LOT of figuring out.
But I’m curious how that idea sounds to you. You can let me know at Arm and a Leg show dot com, slash contact.
I mean, that’s always a good place to send ideas and stories and questions— so many of our best episodes come from you.
And I’m curious what you think about this virtual book club idea. If you’ve taken part in something like this, or helped to organize it, I’d love to hear how it went.
That’s arm and a leg show dot com, slash contact.
Next time on An Arm and a Leg: A woman named Lisa French asked her hospital what her surgery would cost her. They said, with your insurance, about thirteen hundred bucks.
They expected about 55 thousand more from insurance.
They got 75 thousand. But then they wanted more. 229 thousand more. They wanted it from Lisa French, and they sued her for it.
After eight years, the case finally got resolved last June. Lisa French won!
The case has a LOT to teach us about our legal rights.
That’s next time on An Arm and a Leg.
Till then, take care of yourself.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg was produced by me, Dan Weissmann, with help from Emily Pisacreta, and edited by Afi Yellow-Duke.
The recording of Jan de Hartog’s lecture is courtesy of the Baylor College of Medicine Archives.
The audio of Bill Elliott is from a KHOU-TV newscast, thanks to the Texas Archive of the Moving Image.
Big thanks to the archivists who helped us find some of the tape for this episode!
That includes Emily Vinson at the University of Houston library
Matt Richardson and Sandra Yates at the Texas Medical Center Archives
And David Olmos at the Baylor College of Medicine archives.
Daisy Rosario is our consulting managing producer. Adam Raymonda is our audio wizard. Our music is by Dave Winer and Blue Dot Sessions.
Gabrielle Healy is our managing editor for audience. She edits the First Aid Kit Newsletter.
Bea Bosco is our consulting director of operations. Sarah Ballema is our operations manager.
This season of an arm and a leg is a co production with Kaiser health news. That’s a nonprofit news service about healthcare in America, an editorially-independent program of the Kaiser family foundation.
KHN is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente, the big healthcare outfit. They share an ancestor: The 20th century industrialist Henry J Kaiser. When he died, he left half his money to the foundation that later created Kaiser health news.
You can learn more about him and Kaiser health news at arm and a leg show dot com slash Kaiser.
Zach Dyer is senior audio producer at KHN. He is editorial liaison to this show.
Thanks to Public Narrative — That’s a Chicago-based group that helps journalists and non-profits tell better stories– for serving as our fiscal sponsor, allowing us to accept tax-exempt donations. You can learn more about Public Narrative at www dot public narrative dot org.
And thanks to everybody who supports this show financially.
If you haven’t yet, we’d love for you to join us. The place for that is arm and a leg show dot com, slash support.
Thank you!
“An Arm and a Leg” is a co-production of KHN and Public Road Productions.
To keep in touch with “An Arm and a Leg,” subscribe to the newsletter. You can also follow the show on Facebook and Twitter. And if you’ve got stories to tell about the health care system, the producers would love to hear from you.
To hear all KHN podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to “An Arm and a Leg” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 6 months ago
Health Care Costs, Insurance, Multimedia, An Arm and a Leg, Hospitals, Podcasts, texas
In Texas, Medicaid Coverage Ends Soon After Childbirth. Will Lawmakers Allow More Time?
Victoria Ferrell Ortiz learned she was pregnant during summer 2017. The Dallas resident was finishing up an AmeriCorps job with a local nonprofit, which offered her a small stipend to live on but no health coverage. She applied for Medicaid so she could be insured during the pregnancy.
“It was a time of a lot of learning, turnaround, and pivoting for me, because we weren’t necessarily expecting that kind of life change,” she said.
Ferrell Ortiz would have liked a little more guidance to navigate the application process for Medicaid. She was inundated with forms. She spent days on end on the phone trying to figure out what was covered and where she could go to get care.
“Sometimes the representative that I would speak to wouldn’t know the answer,” she said. “I would have to wait for a follow-up and hope that they actually did follow up with me. More than 476,000 pregnant Texans are currently navigating that fragmented, bureaucratic system to find care. Medicaid provides coverage for about half of all births in the state — but many people lose eligibility not long after giving birth.
Many pregnant people rely on Medicaid coverage to get access to anything from prenatal appointments to prenatal vitamins, and then postpartum follow-up. Pregnancy-related Medicaid in Texas is available to individuals who make under $2,243 a month. But that coverage ends two months after childbirth — and advocates and researchers say that strict cutoff contributes to rates of maternal mortality and morbidity in the state that are higher than the national average.
They support a bill moving through the Texas legislature that would extend pregnancy Medicaid coverage for a full 12 months postpartum.
Texas is one of 11 states that has chosen not to expand Medicaid to its population of uninsured adults — a benefit offered under the Affordable Care Act, with 90% of the cost paid for by the federal government. That leaves more than 770,000 Texans in a coverage gap — they don’t have job-based insurance nor do they qualify for subsidized coverage on healthcare.gov, the federal insurance marketplace. In 2021, 23% of women ages 19-64 were uninsured in Texas.
Pregnancy Medicaid helps fill the gap, temporarily. Of the nearly half a million Texans currently enrolled in the program, the majority are Hispanic women ages 19-29.
Texans living in the state without legal permission and lawfully present immigrants are not eligible, though they can get different coverage that ends immediately when a pregnancy does. In states where the Medicaid expansion has been adopted, coverage is available to all adults with incomes below 138% of the federal poverty level. For a family of three, that means an income of about $34,300 a year.
In Texas, childless adults don’t qualify for Medicaid at all. Parents can be eligible for Medicaid if they’re taking care of a child who receives Medicaid, but the income limits are low. To qualify, a three-person household with two parents can’t make more than $251 a month.
For Ferrell Ortiz, the hospitals and clinics that accepted Medicaid near her Dallas neighborhood felt “uncomfortable, uninviting,” she said. “A space that wasn’t meant for me” is how she described those facilities.
Later she learned that Medicaid would pay for her to give birth at an enrolled birthing center.
“I went to Lovers Lane Birth Center in Richardson,” she said. “I’m so grateful that I found them because they were able to connect me to other resources that the Medicaid office wasn’t.”
Ferrell Ortiz found a welcoming and supportive birth team, but the Medicaid coverage ended two months after her daughter arrived. She said losing insurance when her baby was so young was stressful. “The two-months window just puts more pressure on women to wrap up things in a messy and not necessarily beneficial way,” she said.
In the 2021 legislative session, Republican Gov. Greg Abbott signed a bill extending pregnancy Medicaid coverage from two months to six months postpartum, pending federal approval.
Last August, The Texas Tribune reported that extension request had initially failed to get federal approval, but that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had followed up the next day with a statement saying the request was still under review. The Tribune reported at the time that some state legislators believed the initial application was not approved “because of language that could be construed to exclude pregnant women who have abortions, including medically necessary abortions.”The state’s application to extend postpartum coverage to a total of six months is still under review.
The state’s Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Review Committee is tasked with producing statewide data reports on causes of maternal deaths and intervention strategies. Members of that committee, along with advocates and legislators, are hoping this year’s legislative session extends pregnancy Medicaid to 12 months postpartum.
Kari White, an associate professor at the University of Texas-Austin, said the bureaucratic challenges Ferrell Ortiz experienced are common for pregnant Texans on Medicaid.
“People are either having to wait until their condition gets worse, they forgo care, or they may have to pay out-of-pocket,” White said. “There are people who are dying following their pregnancy for reasons that are related to having been pregnant, and almost all of them are preventable.”
In Texas, maternal health care and Pregnancy Medicaid coverage “is a big patchwork with some big missing holes in the quilt,” White said. She is also lead investigator with the Texas Policy Evaluation Project (TxPEP), a group that evaluates the effects of reproductive health policies in the state. A March 2022 TxPEP study surveyed close to 1,500 pregnant Texans on public insurance. It found that “insurance churn” — when people lose health insurance in the months after giving birth — led to worse health outcomes and problems accessing postpartum care.
Chronic disease accounted for almost 20% of pregnancy-related deaths in Texas in 2019, according to a partial cohort review from the Texas Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Review Committee’s report. Chronic disease includes conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. The report determined at least 52 deaths were related to pregnancy in Texas during 2019. Serious bleeding (obstetric hemorrhage) and mental health issues were leading causes of death.
“This is one of the more extreme consequences of the lack of health care,” White said.
Black Texans, who make up close to 20% of pregnancy Medicaid recipients, are also more than twice as likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than their white counterparts, a statistic that has held true for close to 10 years with little change, according to the MMMRC report.
Stark disparities such as that can be traced to systemic issues, including the lack of diversity in medical providers; socioeconomic barriers for Black women such as cost, transportation, lack of child care and poor communication with providers; and shortcomings in medical education and providers’ implicit biases — which can “impact clinicians’ ability to listen to Black people’s experiences and treat them as equal partners in decision-making about their own care and treatment options,” according to a recent survey.
Diana Forester, director of health policy for the statewide organization Texans Care for Children, said Medicaid coverage for pregnant people is a “golden window” to get care.
“It’s the chance to have access to health care to address issues that maybe have been building for a while, those kinds of things that left unaddressed build into something that would need surgery or more intensive intervention later on,” she said. “It just feels like that should be something that’s accessible to everyone when they need it.”
Extending health coverage for pregnant people, she said, is “the difference between having a chance at a healthy pregnancy versus not.”
As of February, 30 states have adopted a 12-month postpartum coverage extension so far, according to a KFF report, with eight states planning to implement an extension.
“We’re behind,” Forester said of Texas. “We’re so behind at this point.”
Many versions of bills that would extend pregnancy Medicaid coverage to 12 months have been filed in the legislature this year, including House Bill 12 and Senate Bill 73. Forester said she feels “cautiously optimistic.”
“I think there’s still going to be a few little legislative issues or land mines that we have to navigate,” she said. “But I feel like the momentum is there.”
Ferrell Ortiz’s daughter turns 5 this year. Amelie is artistic, bright, and vocal in her beliefs. When Ferrell Ortiz thinks back on being pregnant, she remembers how hard a year it was, but also how much she learned about herself.
“Giving birth was the hardest experience that my body has physically ever been through,” she said. “It was a really profound moment in my health history — just knowing that I was able to make it through that time, and that it could even be enjoyable — and so special, obviously, because look what the world has for it.”
She just wishes people, especially people of color giving birth, could get the health support they need during a vulnerable time.
“If I was able to talk to people in the legislature about extending Medicaid coverage, I would say to do that,” she said. “It’s an investment in the people who are raising our future and completely worth it.”
This story is part of a partnership that includes KERA, NPR, and KHN.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 7 months ago
Health Care Costs, Insurance, Medicaid, Multimedia, States, Audio, Legislation, Pregnancy, texas, Women's Health
A Judicial Body Blow to the ACA
The Host
Julie Rovner
KHN
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KHN’s weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Opponents of the Affordable Care Act may have stopped trying to overturn the entire law in court, but they have not stopped challenging pieces of it — and they have found an ally in Fort Worth, Texas: U.S. District Judge Reed O’Connor. In 2018, O’Connor held that the entire ACA was unconstitutional — a ruling eventually overturned by the Supreme Court. Now the judge has found that part of the law’s requirement for insurers to cover preventive care without copays violates a federal religious freedom law.
In a boost for the health law, though, North Carolina has become the 40th state to expand the Medicaid program to lower-income people who were previously ineligible. Even though the federal government will pay 90% of the cost of expansion, a broad swath of states — mostly in the South — have resisted widening eligibility for the program.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KHN, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Cohrs of Stat, and Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Panelists
Rachel Cohrs
Stat News
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Sandhya Raman
CQ Roll Call
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Thursday’s decision out of Texas affects health plans nationwide and is expected to disrupt the health insurance market, which for years has provided preventive care without cost sharing under the ACA. Even if the decision survives a likely appeal, insurers could continue offering the popular, generally not-so-costly benefits, but they would no longer be required to do so.
- The decision, which found that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force cannot mandate coverage requirements, hinges on religious freedom objections to plans covering PrEP, the HIV medication, alongside other preventive care.
- Speaking of the ACA, this week North Carolina became the latest state to expand Medicaid coverage under the health law, which will render an estimated 600,000 residents newly eligible for the program. The development comes amid reports about hospitals struggling to cover uncompensated care, particularly in the 10 states that have resisted expanding Medicaid.
- Pushback against Medicaid expansion has contributed over the years to a yawning coverage divide between politically “blue” and “red” states, with liberal-leaning states pushing to cover more services and people, while conservative-leaning states home in on policies that limit coverage, like work requirements.
- On the abortion front, state attorneys general are challenging the FDA’s authority on the abortion pill — not only in Texas, but also in Washington state, where Democratic state officials are fighting the FDA’s existing restrictions on prescribing and dispensing the drug. The Biden administration has adopted a similar argument as it has in the Texas case challenging the agency’s original approval of the abortion pill: Let the FDA do its job and impose restrictions it deems appropriate, the administration says.
- The FDA is poised to make a long-awaited decision on an over-the-counter birth control pill, an option already available in other countries. One key unknown, though, is whether the agency would impose age restrictions on access to it.
- And as of this week, 160 Defense Department promotions have stalled over one Republican senator’s objections to a Pentagon policy regarding federal payments to service members traveling to obtain abortions.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: New York Magazine/The Cut’s “Abortion Wins Elections: The Fight to Make Reproductive Rights the Centerpiece of the Democratic Party’s 2024 Agenda,” by Rebecca Traister.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Stat’s “How the Drug Industry Uses Fear of Fentanyl to Extract More Profit From Naloxone,” by Lev Facher.
Rachel Cohrs: The Washington Post’s “These Women Survived Combat. Then They Had to Fight for Health Care,” by Hope Hodge Seck.
Sandhya Raman: Capital B’s “What the Covid-19 Pandemic and Mpox Outbreak Taught Us About Reducing Health Disparities,” by Margo Snipe and Kenya Hunter.
Also mentioned in this week’s podcast:
- The New York Times’ “‘We’re Going Away’: A State’s Choice to Forgo Medicaid Funds Is Killing Hospitals,” by Sharon LaFraniere.
- KHN’s “Fresh Produce Is an Increasingly Popular Prescription for Chronically Ill Patients,” by Carly Graf.
- California Healthline’s “Prescription for Housing? California Wants Medicaid to Cover 6 Months of Rent,” by Angela Hart.
click to open the transcript
Transcript: A Judicial Body Blow to the ACA
KHN’s ‘What the Health?’Episode Title: A Judicial Body Blow to the ACAEpisode Number: 291Published: March 30, 2023
[Editor’s note: This transcript, generated using transcription software, has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to KHN’s “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent at Kaiser Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, March 30, at 11 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go. Today we are joined via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Good morning.
Rovner: Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Sandhya Raman: Good morning.
Rovner: And happy birthday to you.
Raman: Thank you.
Rovner: And Rachel Cohrs of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: We’ve got breaking news, so we will get right to it. In Texas, we’ve got a major decision from a federal judge with national implications. No, not the abortion pill case — that is still out there. This time, Judge Reed O’Connor has ruled that the Affordable Care Act can’t require coverage of preventive services recommended by the [U.S.] Preventive Services Task Force because the PSTF, as an independent advisory board, can’t legally mandate anything. This case was specifically — although it was about a lot of things — but it was mostly about employers who didn’t want to cover preexposure prophylaxis [PrEP] for people at high risk of HIV because it violated their religious beliefs. And if the name Reed O’Connor sounds familiar, that’s because he’s the same judge who ruled in 2018 that the entire Affordable Care Act was unconstitutional, a finding that wasn’t formally overturned until it got to the Supreme Court. Alice, you’ve been following this case. What happens now?
Ollstein: I’m expecting the Biden administration to appeal at lightning speed, although that appeal will go to the 5th Circuit, which is very right-leaning. It’s ruled to chip away at the Affordable Care Act in the past. So who really knows what will happen there? But yeah, this is really huge. This is saying that this board that has decided what services insurance companies have to cover for free, with no cost sharing, going all the way back to 2010 is not constitutional, and thus what they say can’t be enforced. And so this throws the insurance market into a bit of chaos.
Rovner: Yeah, although one would think that it wouldn’t affect this year’s policies — I mean, for people who are going to be worried that all of a sudden, you know, oh my God, I scheduled my mammogram and now my insurer might not pay for it. It’s not going to be that immediate, right?
Ollstein: We’re not expecting that. I mean, we’re expecting the Biden administration to ask for courts to stay the impact of the ruling until further arguments and appeals can be made. But we really don’t know at this point. And I will say, you know, I’ve seen some misinformation out there about how the ruling deals with contraception. They do not block the contraception mandate. That is related to this case, but the court did not accept that part of the challengers’ claims.
Rovner: Yeah, we should say there are a bunch of different claims and the judge only accepted a couple of them. It could have been even broader. But, you know, unlike the previous Affordable Care Act cases, this one doesn’t threaten the entire law, but it does threaten one of the law’s most popular pieces, those requirements that plans cover preventive care that’s been shown to be cost-effective. This could be an uncomfortable case for the Supreme Court, assuming it gets there, couldn’t it?
Cohrs: It could be an uncomfortable case for the Supreme Court, but it’s also uncomfortable for insurers, too, who’ve promised this. People have come to expect it. And if it is cost-effective, I mean, certainly there may be plans that, you know, make choices to restrict coverage or impose some cost sharing. If this stands, if this is applied nationwide — again, very big ifs at this point — but if these really are cost-effective, then it’s kind of an open question what insurers will choose to do, because obviously they want people to enroll in their plans as well.
Rovner: Yeah, I was going to say, I could see insurers sort of deciding as a group that we’re going to keep providing this stuff, as you say, Rachel, because they want, you know, they want to attract customers, because for the most part it’s not that expensive. I mean, obviously, you know, things like colonoscopies can run into the thousands of dollars, but a lot of these things are, if not de minimis, then just not very expensive. And, as I mentioned, they’re very popular. So it’s possible that, even though they may strike down the mandate, there won’t be as much of an impact from this as some people are saying. But, as Alice points out, we don’t really know anything at this point.
Ollstein: And I think some of the concern is the kind of risk-pool sorting we used to see, you know. So the challengers said that their right to purchase insurance that doesn’t cover certain things was being infringed upon. And so if insurers start to create separate plans, some of which cover all kinds of preventive care, including sexual health care, and separate ones that don’t, and people who don’t think they need a lot of stuff, you know, sort themselves into some plans and not others, you can see that reflected in premiums that could lead to some of the major pre-ACA problems we used to see.
Rovner: If the idea that somebody doesn’t like something and therefore can’t buy something without it, you can see that leading to all kinds of problems down the line about people saying, well, “I don’t like that drugstores sell condoms, so therefore I should be able to go to a drugstore that doesn’t sell condoms,” although that’s not a mandate. But you can see that this could stretch very far with people’s religious beliefs. And indeed, the basis of this claim is that this violated the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. That’s one of the things that Judge O’Connor found, and that could be taken to quite the extreme, I imagine.
Ollstein: Right. I mean, they weren’t required to actually purchase PrEP. They weren’t required to use it. They weren’t required to prescribe it. Just the insurance company was required to cover it along with everything else they cover. And the folks said even purchasing insurance that had that as one of the things it could conceivably cover violated their religious rights.
Rovner: Yes. And this goes back to the contraceptive cases, where the religious organization said that, you know, by having birth control in their plans, it made them complicit in something that they thought was a sin. And that’s exactly what’s being stressed here, even among the individual plaintiffs: that having to buy insurance that has these benefits, even if they don’t use them, makes them complicit in, basically, sex outside of marriage. I mean, that’s what’s in the decision. It’s quite a reach. I’ll be interested to see, as this goes up, what people think of it. So, before we got Judge O’Connor’s opinion, what I thought would be the biggest news of the week comes from North Carolina, which on Monday became the 40th state to expand Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, to cover people with incomes up to 138% of poverty. That’s about $20,000 in 2023. Well, it’s almost there. The newly eligible 600,000 people won’t be able to sign up until the legislature approves a budget, which is likely later this spring. North Carolina expanding the program leaves only a swath of states across the South, including Florida, Georgia, and Texas, and a couple in the Great Plains as still holding out on a 90% federal match. Is anyone else on the horizon or is this going to be it for a while?
Raman: I think one thing to note about how this is happening is that North Carolina was able to do this finally through the legislature after like a yearslong process. And it has been increasingly rare for this to happen through the legislature. The last time was Virginia, in 2018, but every other state that has done it in recent years has all been through ballot initiative and going that route. And the 10 holdouts that we have, you know, we have Republican-controlled legislatures who’ve been pretty against doing this. So I think if any of those states were to be able to do that at this point that haven’t been tempted by, you know, any of the incentives … [unintelligible] … get a higher match rate or anything like that, it would have to be through the ballot, which is already a difficult process, can take years. There have been various roadblocks to push back and even some of the states in the past that have been able to get it through ballot initiative — some of the legislatures afterwards have tried to like push back on it — when we saw with Utah a few years ago, where even if the voters had voted that they wanted to expand, they wanted to kind of pull it back.
Rovner: We thought in Maine, where the governor blocked it until basically he was out of office.
Raman: Yeah.
Ollstein: And in Missouri, where they just refused to fund it.
Raman: Yeah, so I think that’ll be definitely something to watch with how the budget goes in the next few months. But I guess, at least with North Carolina, this was something that was bipartisan. It was spearheaded in the legislature by Republicans, so I think they might not have the same issues there than Missouri, but it’s a tough haul to get the remaining 10 at this point after this many years.
Rovner: Yeah, I feel like North Carolina is much more like Virginia, which is that, finally, after a lot of wearing down, the Republican legislature and the Democratic governor were able to come to some kind of agreement. That’s what happened in Virginia. And that seems to be what’s happened here in North Carolina. Meanwhile, in those 10 states, hospitals which end up providing free care to people who can’t pay aren’t doing so well. In Florida, the state’s hospital association has been all but begging the state government to expand Medicaid pretty much since it was available to them, which is now going on 13 years. According to the American Hospital Association, 74% of rural hospital closures around the country took place in states that have not expanded Medicaid or where expansion had been in place for less than a year. And the New York Times has a story this week about the toll that that lack of insurance is taking — I’m sorry — and the New York Times has a story this week about the toll that lack of insurance for the working poor is taking there, not just on the state’s hospitals, but on the health of the state’s population. Lawmakers in these states are very happy to take federal money for all manner of things. What is it about this Medicaid expansion that’s making them say, “No, no, no”?
Raman: This was something that came up this week in the House. Appropriations’ Labor, HHS, Education Subcommittee had a hearing this week specifically on rural communities and some of the issues they face. And Medicaid expansion obviously did come up with some of the witnesses and some of the lawmakers as something that would be helpful given the number of hospital closures they’ve seen, and there might only be one health care facility for miles or in a county, and just how it would be helping them to kind of relieve paying for the uncompensated care that they’re already dealing with, you know, highlighted a number of the issues there. So it’s something that comes up, but I think one of the pushbacks that we saw was, you know, again, that it is a) tied to the Affordable Care Act, which has been such a partisan back-and-forth since its inception, and then b) just the messaging has always been about the cost. I mean, even if the general consensus is that it does save money over time for taking care of that care, something that came up was why states get more of a reimbursement for expansion than they do for traditional Medicaid. That was brought up a couple times, things like that. And so I think it’s hard to get some of those folks on board just because of how partisan it has become.
Rovner: Yeah, I remember I watched the hearing in Wyoming on this last year. They didn’t want to do it, it seemed, more for ideology. I mean, a lot of states that are doing this, you know, you can levy a tax on hospitals and nursing homes, who are happy to pay the tax because they’re now getting paid for these patients who couldn’t pay. And the state’s really not out-of-pocket, as it were, at all. But and yet, as we point out, these last 10 states, including some of the really big ones, have yet to actually succumb to this. Well, while we are talking about Medicaid, there have been a couple of interesting stories from my KHN colleagues in the past few weeks about so-called social determinants of health, those not strictly medical interventions that have a big impact on how sick or healthy people are. In California, Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom wants to use Medicaid to pay for six months of rent or temporary housing for homeless people. And in Montana, health professionals can now prescribe vouchers for fruit and vegetables for patients with little access to fresh food. Is this the wave of the future, or will those who want to shrink rather than expand the welfare state and government in general roll programs like these back?
Cohrs: I think there certainly is a trend, a lot of momentum behind the idea of food as medicine and, you know, moving away and exploring some of these non-medication treatments or some of these underlying reasons why people do have health issues. I think certainly support for the Medicaid program is going to be a hot-button issue in D.C. over the next few months, but there is a lot that states can do on their own as well. And I know states have, you know, programs to kind of cover people that fall between the cracks of traditional insurance programs. California has a robust program for that, the local levels as well. So I think there may be ways to get around that, even if we do see some more restrictions. And again, the administration is Democratic at this point, so I think they may be friendlier to some of these innovations than prior ones, and that could change at any time. But this certainly isn’t something that’s going to go away.
Rovner: I wonder if we’re going to end up with blue states having all of these more robust pro — I mean, we already have blue states with more robust programs, but blue states having these more inclusive programs and red states not. Alice, you’re nodding.
Ollstein: Absolutely. And that’s been the trend for a while, but it could even accelerate now, I think, and you’re seeing that on both sides, with blue states looking to cover more and more things; also looking to cover more and more people, including undocumented people. That’s another trend in Medicaid. At the same time, you have red states that have long explored how to cover fewer and fewer, you know, trying to change the income eligibility threshold for expanded Medicaid, trying to do work requirements, trying to do, like, other restrictions. And so I think the patchwork and the divide is only going to continue.
Rovner: Well, moving on to abortion this week, we are still waiting, as I said, for that other decision out of Texas that could impact the future of the abortion pill mifepristone. But Alice, there’s another case at the other end of the country that could have something to say about the Texas case. What’s going on in Washington state?
Ollstein: This one has really flown under the radar. So this is an interesting situation where the same — a lot of the same Democratic attorneys general who were siding with the Biden administration in the Texas case are challenging the Biden administration in a different case in Washington state, basically saying that the remaining federal restrictions on abortion pills — mainly that providers have to get certified in order to prescribe the drugs or dispense them — saying that that should be tossed out, that it’s not supported by medicine and science. And so it’s interesting because you have the Biden administration fighting back against an effort to make the pills more accessible, which is not what a lot of people expect. It goes sort of against their rhetoric in recent months; they’ve talked about wanting to make the pills more accessible and they’re opposing an effort that would do that. But it is somewhat consistent with their position in the Texas case, which is, they’re saying, “Look, this is the FDA’s job. Let the FDA do its job. The FDA has a process, came up with these rules, got rid of some, kept others, and you outside folks don’t have the right to challenge and overturn it.”
Rovner: So what happens if the judges in both of these cases find for the plaintiffs, which would be kind of, but not completely, conflicting?
Ollstein: Yeah, so the Washington state case could just apply to the dozen states that are part of the challenge. And so you could have, again, more of a patchwork in which the abortion pills become even more accessible in those blue states and even less accessible in other states. You could also have these competing rulings that ultimately trigger Supreme Court review.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s not exactly a circuit split because it wouldn’t be opposite decisions on the same case; they’re different cases here. But as you point out, it’s really a case challenging the authority of the FDA to do what the FDA does. So it’s going to be really interesting to watch how this all plays out. While the future of mifepristone remains in doubt, the FDA is going to consider making at least one birth control pill over the counter. We know that morning-after pills, which are high doses of regular birth control pills, are already available without a prescription. So why hasn’t there been an over-the-counter birth control pill until now?
Ollstein: Everything concerning birth control, emergency contraception, abortion, it just — these fights drag on for years and years and years. So finally, we seem to be on the cusp of having a decision on this. It’s expected, from most people I’ve talked to, that they will approve this over-the-counter birth control. There’s a lot of data from around the world. A lot of other countries already have this. And one key unknown is whether the FDA will maintain an age restriction on it. A lot of progressive advocates do not want an age restriction because they think that this is important to help teens prevent unwanted pregnancies. And I think that’s going to be a big piece of the fight that I’m watching.
Rovner: And oh, my goodness, it was that age restriction that held up the over-the-counter morning-after pill for years. That was like a 13-year process to get that over the counter. It went on and on and on, and I covered it. All right. Well, there is abortion-related action on Capitol Hill too this week. We’ve got a potential abortion standoff brewing in the Senate over reproductive health policy at the Department of Defense. Who wants to talk about that one?
Raman: This one has been, I think, really interesting, since we’re all health reporters. And it’s been really something that I think my defense colleagues have been following so closely. But we have Senator Tuberville, who’s been holding up military nominations because the Pentagon has a policy that allows, you know, service members leave for reproductive care and it covers travel to seek an abortion. And so —
Rovner: Although it still doesn’t pay for the abortion.
Raman: It does not pay for the abortions. It’s for the travel. And so I know that my colleagues have looked at this and how this point, like, both sides have been getting a little frustrated, you know, with even some senators saying, “Hey, I agree that I don’t like this policy, but you need to find another way,” because as of earlier this week 160 promotions have been stalled. And so it’s just been kind of ramping up and holding up a lot of folks for kind of an unusual method.
Rovner: Yeah, and the defense secretary saying, I mean, this threatens national security because these are promotions — are important promotions. Flag officers, these are not, you know, just sort of — they’re routine, but they’re, you know, but if they don’t happen, if they get stalled, it’s a problem. In all of my years of seeing anti-abortion senators hold up things, this is not one I have seen before. It’s at least — it’s sort of new and imaginative, and I guess we will see how that plays out. Back in the states, though, it seems that the efforts to restrict reproductive rights are getting very extreme, very fast. Yes, the Oklahoma Supreme Court ruled earlier this month that a pregnant woman does have a right to an abortion when continuing the pregnancy threatens her life. But four of the nine justices there didn’t even want to go that far, suggesting that the legislature has the right to basically require saving the fetus even at the cost of the pregnant person’s life. In Texas, a lawsuit in which the ex-husband is suing the friend of his ex-wife for the wrongful death of his child for helping her get abortion medication is setting the stage for the so-called personhood debate: the idea that a new person with full legal right is created upon fertilization of an egg by sperm. Over the past few decades, several states have rejected personhood ballot measures as a bridge too far. But it feels like all bets are off now. I mean, it’s sort of like a race to see who can be the most extreme state.
Ollstein: I think the trends are revealing some interesting things. I mean, one, anti-abortion folks are well aware that people are still getting abortions, mainly in one of two ways: either traveling out of state or ordering pills online and taking them at home, both of which are very difficult to enforce and stop. And so there’s just a lot of, like, throwing spaghetti against the wall and seeing what sticks, in terms of, can we actually criminalize either of those things? If so, how is it enforced, or does it even need to be enforced? Or is just the fear and the chilling effect enough? I mean, we definitely see that. We definitely see medical providers holding off on doing even perfectly legal things because of fear and the chilling effect. And so there’s just a lot of experimentation at the state level right now.
Rovner: Yeah, I forgot to mention Idaho, where the legislature introduced a bill that would make it a crime — that creates abortion trafficking as a crime — for someone to take a minor, it’s not really across state lines, because the state can’t do that, so it’s like taking the minor to the border in an effort to cross state lines to get an abortion. There was, for many years in the late 1990s and early 2000s, something called the Child Custody Protection Act in Congress, because they needed that for the interstate part of it, that would make it a crime to take a minor across state lines in violation of the home state’s parental involvement laws. It passed both the House and the Senate at various times. It never became law. It’s been introduced recently, but nobody’s tried to take it up recently. I wouldn’t be surprised to see that come back up, too. But it really does seem that every day there’s another bill in another state legislature that says — after all the claims of the anti-abortion movement for decades, that we don’t want to punish the women, we only want to punish the providers — that’s gone out the window, right?
Raman: I guess I would add that, you know, we’re seeing a lot of this activity now. But something that I keep in mind is that a) it’s gotten a lot harder to know what’s going to, you know, using the spaghetti metaphor that Alice did, like what will stick. So there’s just a lot more flurry of action. And then I feel like I see increasingly, you know, people, since they don’t know that, just like fixating a lot on various things, just because you don’t know. I think, you know, even a few years ago, there were a lot of things that would have one sponsor or two sponsors and have no chance of going anywhere, as most bills introduced anywhere do. But now, a) a lot of these things are moving very, very quickly in the legislature, and b) since we don’t know, it’s hard to know where to kind of focus, even to some of the experts that I’ve talked to, where it’s just, “We’re not sure.” So just be aware of all of these things in various places because of kind of that uncertainty.
Rovner: Yeah, I know I’m generally loath to talk about bills that got introduced either in Congress or in state legislatures, because I think it unnecessarily creates expectations that for the most part don’t happen. But as both of you say, some of these things are happening so fast that, if you mention them one week, they’re law by the next week. So we will see as this continues to move quickly. All right. That’s the news for this week. Now it is time for our extra credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at khn.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Rachel, why don’t you go first this week?
Cohrs: All right. So my story is from the Washington Post, and the headline is “These Women Survived Combat. Then They Had to Fight for Health Care,” by Hope Hodge Seck. And I thought it was just a really great feature on this very niche issue. And I think veterans’ kind of health care overall just doesn’t get as much coverage as it should, and —
Rovner: Particularly women’s veteran’s health care.
Cohrs: Exactly. Yes. And so these women were essentially going into combat situations to help relations with women in very conservative cultures, and they were exposed to the grenade blasts and a lot of these combat situations. But then their health care coverage upon returning wasn’t covered. And there is kind of a new bill with some momentum behind it that is trying to plug that loophole. So, yeah, I thought it was a very great feature on an issue that’s undercovered.
Rovner: Yeah, this was something I knew nothing about until I read this story. Alice?
Ollstein: I chose a piece by Rachel’s colleague at Stat, Lev Facher, called “How the Drug Industry Uses Fear of Fentanyl to Extract More Profit From Naloxone.” And this is really timely, with the approval this week of over-the-counter opioid-overdose-reverse medication. And basically it’s about how these drug companies are coming up with new forms of the drug, really huge doses, new delivery forms, injectables, and nasal sprays, and stuff that are not really justified by science and are sort of just an opportunity for more profit because the basic form of the drug that works extremely well and is very affordable, they are basically hyping the fear of fentanyl to try to push these stronger products they’re coming up with. And the fear is that municipal governments that have limited resources are going to spend their money on those not really justified new forms and get fewer medication for everyone than just using the basic stuff that we know works.
Rovner: Indeed. Sandhya?
Raman: My extra credit is from Margo Snipe and Kenya Hunter at Capital B, and it’s called “What the Covid-19 Pandemic and Mpox Outbreak Taught Us About Reducing Health Disparities.” And I thought this was an interesting look that they did, highlighting how, you know, there’s been a lot more talk about the various health inequities among, you know, racial and ethnic and sexual minority communities after these two pandemics have started. And they look at how some of the targeted efforts have narrowed some of the gaps in things like vaccines, but just how some of these lessons can be used to address other health disparities, you know, things like community outreach and expanding types of screenings and how many languages public health information is translated into and things like that. So, it’s a good read.
Rovner: Well, my extra credit this week is a long read, a very long read, by Rebecca Traister in New York Magazine, called “Abortion Wins Elections: The Fight to Make Reproductive Rights the Centerpiece of the Democratic Party’s 2024 Agenda.” And while I’m not sure I’m buying everything that she’s selling here, this is an incredibly thorough and interesting look at the past, present, and possibly future of the abortion rights movement at the national, state, and local levels. If you are truly interested in this subject, it’s well worth the half hour or so of your time that it takes to get through the entire thing. It’s a really, really good piece. OK, that is our show for this week. As always, if you enjoyed the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us too. Special thanks, as always, to our ever-patient producer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can tweet me still. I’m @jrovner. Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein.
Rovner: Rachel?
Cohrs: @rachelcohrs.
Rovner: Sandhya?
Raman: @SandhyaWrites.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KHN’s What the Health? on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 7 months ago
Health Care Costs, Insurance, Medicaid, Multimedia, Public Health, States, Abortion, Contraception, FDA, KHN's 'What The Health?', North Carolina, Obamacare Plans, Podcasts, texas, Women's Health
STAT+: Drugmakers push back on a clever tactic employers use to avoid paying for specialty medicines
In the face of rising drug prices, health plan sponsors have quietly used a clever, but questionable tactic over the past few years to deflect costs. And now, some pharmaceutical companies are pushing back.
The maneuver goes by different names — it’s sometimes called a specialty carve out, or alternative funding – but relies on exploiting charitable programs. It works like this: a health plan sponsor excludes certain expensive specialty medicines from coverage and taps an outside vendor to help patients obtain the drugs for free from patient assistance programs run by drugmakers or foundations.
2 years 7 months ago
Pharma, Pharmalot, drug pricing, Insurance, Pharmaceuticals, STAT+
March Medicaid Madness
The Host
Julie Rovner
KHN
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KHN’s weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
With Medicare and Social Security apparently off the table for federal budget cuts, the focus has turned to Medicaid, the federal-state health program for those with low incomes. President Joe Biden has made it clear he wants to protect the program, along with the Affordable Care Act, but Republicans will likely propose cuts to both when they present a proposed budget in the next several weeks.
Meanwhile, confusion over abortion restrictions continues, particularly at the FDA. One lawsuit in Texas calls for a federal judge to temporarily halt distribution of the abortion pill mifepristone. A separate suit, though, asks a different federal judge to temporarily make the drug easier to get, by removing some of the FDA’s safety restrictions.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of Kaiser Health News, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Cohrs of STAT News, and Lauren Weber of The Washington Post.
Panelists
Rachel Cohrs
Stat News
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Lauren Weber
The Washington Post
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- States are working to review Medicaid eligibility for millions of people as pandemic-era coverage rules lapse at the end of March, amid fears that many Americans kicked off Medicaid who are eligible for free or near-free coverage under the ACA won’t know their options and will go uninsured.
- Biden promised this week to stop Republicans from “gutting” Medicaid and the ACA. But not all Republicans are on board with cuts to Medicaid. Between the party’s narrow majority in the House and the fact that Medicaid pays for nursing homes for many seniors, cutting the program is a politically dicey move.
- A national group that pushed the use of ivermectin to treat covid-19 is now hyping the drug as a treatment for flu and RSV — despite a lack of clinical evidence to support their claims that it is effective against any of those illnesses. Nonetheless, there is a movement of people, many of them doctors, who believe ivermectin works.
- In reproductive health news, a federal judge recently ruled that a Texas law cannot be used to prosecute groups that help women travel out of state to obtain abortions. And the abortion issue has highlighted the role of attorneys general around the country — politicizing a formerly nonpartisan state post. –And Eli Lilly announced plans to cut the price of some insulin products and cap out-of-pocket costs, though their reasons may not be completely altruistic: An expert pointed out that a change to Medicaid rebates next year means drugmakers soon will have to pay the government every time a patient fills a prescription for insulin, meaning Eli Lilly’s plan could save the company money.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The New York Times’ “A Drug Company Exploited a Safety Requirement to Make Money,” by Rebecca Robbins.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: The New York Times’ “Alone and Exploited, Migrant Children Work Brutal Jobs Across the U.S.,” by Hannah Dreier.
Rachel Cohrs: STAT News’ “Nonprofit Hospitals Are Failing Americans. Their Boards May Be a Reason Why,” by Sanjay Kishore and Suhas Gondi.
Lauren Weber: KHN and CBS News’ “This Dental Device Was Sold to Fix Patients’ Jaws. Lawsuits Claim It Wrecked Their Teeth,” by Brett Kelman and Anna Werner.
Also mentioned in this week’s podcast:
- Politico’s “Why One State’s Plan to Unwind a Covid-Era Medicaid Rule Is Raising Red Flags,” by Megan Messerly.
- The Washington Post’s “Doctors Who Touted Ivermectin as Covid Fix Now Pushing It for Flu, RSV,” by Lauren Weber.
- NPR’s “To Safeguard Healthy Twins in Utero, She Had to ‘Escape’ Texas for Abortion Procedure,” by Selena Simmons-Duffin.
- The Daily Beast’s “Tennessee Abortion Ban a ‘Nightmare’ for Woman With Doomed Pregnancy,” by Michael Daly.
click to open the transcript
Transcript: March Medicaid Madness
KHN’s ‘What the Health?’Episode Title: Medicaid March MadnessEpisode Number: 287Published: March 2, 2023
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to KHN’s “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent at Kaiser Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We are taping this week on Thursday, March 2, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So, here we go. We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Good morning.
Rovner: Rachel Cohrs of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And we officially welcome to the podcast panel this week Lauren Weber, ex of KHN and now at The Washington Post covering a cool new beat on health and science disinformation. Lauren, welcome back to the podcast.
Lauren Weber: Thanks for having me.
Rovner: So we’re going to get right to this week’s news. We’ve talked a lot about the political fight swirling around Medicare the past couple of weeks. So this week, I want to talk more about Medicaid. Our regular listeners will know, or should know, that states are beginning to re-determine eligibility for people who got on Medicaid during the covid pandemic and were allowed to stay on until now. In fact, Arkansas is vowing to re-determine eligibility for half a million people over the next six months. Alice, the last time Arkansas tried to do something bureaucratically complicated with Medicaid, it didn’t turn out so well, did it?
Ollstein: No. It was so much of a cautionary tale that no other state until now has gone down that path, although now at least a couple are attempting to. So Arkansas was the only state to actually move forward under the Trump administration with implementing Medicaid work requirements. And we covered it at the time, and just thousands and thousands of people lost coverage who should have qualified. They were working. They just couldn’t navigate the reporting system. Part of the problem was that you had to report your working hours online and a lot of people who are poor don’t have access to the internet. And, you know, the system was buggy and clunky and it was just a huge mess. But that is not stopping the state from trying again on several fronts. One, they want to do Medicaid work requirements again. The governor, Sarah Huckabee Sanders, has said that they plan to do that and also they plan to do their redeterminations for the end of the public health emergency in half the time the federal government would like states to take to do it. The federal government has incentives for states to go slow and take a full year to make sure people know how to prove whether or not they qualify for Medicaid and to learn what other insurance coverage options might be available to them. For instance, you know, Obamacare plans that are free or almost free.
Rovner: Yeah. Presumably most of the people who are no longer eligible for Medicaid but are still low-income will be eligible for Obamacare with hefty subsidies.
Ollstein: That’s right. So the fear is that history will repeat itself. A lot of people who should be covered will be dropped from coverage and won’t even know it because the state didn’t take the time to contact people and seek them out.
Rovner: This is something that we will certainly follow as it plays out over the next year. More broadly, though, there have been whispers — well, more than whispers, whines — over the past couple of weeks that President [Joe] Biden’s challenge to Republicans not to cut Social Security and Medicare, and Republicans’ apparent acceptance of that challenge, specifically leaves out Medicaid. Now, I never thought that was true, at least for the Democrats. But earlier this week, President Biden extended his promises to Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act. How much of a threat is there really to Medicaid in the coming budget battles? Rachel, you wrote about that today.
Cohrs: There is a lot of anxiety swirling around this on the Hill. I know there’s a former Trump White House official who’s circulated some documents that are making people a little bit nervous about Republicans’ position. But it is useful to look at existing documents out there. It is not reflective necessarily of the consensus Republican position. And it’s a very diverse party right now in the House. They have an incredibly narrow majority and Kevin McCarthy is really going to have to walk a tightrope here. And I think it is important to remember that when Medicaid has come up on steep ballot initiatives in red states, so many times it has passed overwhelmingly. So I think there is an argument to be made that Medicaid enjoys more political support among the GOP voting populace than maybe it does among members of Congress. So I think I am viewing it with caution. You know, obviously, it’s something that we’re going to have to be tracking and watching as these negotiations develop. But Democrats still hold the Senate and they still hold the presidency. So Republicans have more leverage than they did last Congress, but they’re still … Democrats still have a lot of sway here.
Rovner: Although I’ll just point out, as I think I pointed out before, that in 2017, when the Republicans tried to repeal the Affordable Care Act, one of the things they discovered is that Medicaid is actually kind of popular. I think … much to their surprise, they discovered that Medicaid is also kind of popular, maybe not as much as Medicare, but more than I think they thought. So I guess the budget wars really get started next week: We get President Biden’s budget, right?
Ollstein: And House Republicans are allegedly working on something. We don’t know when it will come or how much detail it will have, but it will be some sort of counter to Biden’s budget. But, you know, the real work will come later, in hashing it out in negotiations. And, really, a small number of people will be involved in that. And so just like Rachel said, you know, you’re going to see a lot of proposals thrown out over the next several months. Not all of them should necessarily be taken seriously or taken as determinative. Just one last interesting thing: This has been a really interesting education time, both for lawmakers and the public on just who is covered under these programs. I mean, the idea is that Medicare is so untouchable, is this third rail, because it is primarily seniors, and seniors vote. And seniors are more politically important to conservatives and Republicans. But people forget a lot of seniors are also on Medicaid. They get their nursing home coverage through there. And so I’ve heard a lot of Democratic lawmakers really hammering that argument lately and saying, look, you know, the stereotype for Medicaid is that it’s just poor adults, but …
Rovner: Yeah, moms and kids. That was how it started out.
Ollstein: Exactly.
Rovner: It was poor moms and kids.
Ollstein: Exactly. But it’s a lot more than that now. And it is more politically dicey to go after it than maybe people think.
Rovner: Yeah, I think Nancy Pelosi … in 2017 when, you know, if the threat with Medicare is throwing Granny off the cliff in her wheelchair, the threat of Medicaid is throwing Granny out of her nursing home, both of which have their political perils. All right. Well, we’ll definitely see this one play out for a while. I want to move to the public health beat. Lauren, you had a really cool story on the front page of The Washington Post this week about how the promise of ivermectin to treat infectious diseases in humans. And for those who forget, ivermectin is an anti-wormer drug that I give to my horse and both of my dogs. But the idea of using it for various infectious diseases just won’t die. What is the latest ivermectin craze?
Weber: Yes, and to be clear, there is an ivermectin that is a pill that can be given to humans, which is what these folks are talking about. But there’s this group called the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance that really pushed ivermectin in the height of covid. As we all know on this podcast, scientific study after scientific study after clinical trial has disproved that there is any efficacy for that. But this group has continued to push it. And I discovered, looking at their website back this winter, that they’re now pushing it for the flu and RSV. And as I asked the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and medical experts, there’s no clinical data to support pushing that for the flu or RSV. And, you know, as one scientist said to me, they had data that … had antiviral properties in a test tube. But as one scientist said to me, well, if you put Coca-Cola in a test tube, it would show it had antiviral properties as well. So there’s a lot of pushback to these folks. But, that said, they told me that they have had their protocols downloaded over a million times. You know, they’re … absolutely have some prominence and have, you know, converted a share of the American population to the belief that this is a useful medical treatment for them. And one of the doctors that has left their group over their support of ivermectin said to me, “Look, I’m not surprised that they’re continuing to push this for something else. This is what they do now. They push this for other things.” And so it’s quite interesting to see this continue to play out as we continue into covid, to see them kind of expand, as these folks said to me, into other diseases.
Rovner: I know I mean, usually when we see these kinds of things, it’s because the people who are pushing them are also selling them and making money off of them. And I know that’s the case in some of this, but a lot of these are just doctors who are writing prescriptions for ivermectin. Right? I mean, this is an actual belief that they have.
Weber: Yeah, some of them do make money off of telehealth appointments. They can charge up to a couple hundred dollars for telehealth appointments. And one of the couple of co-founders had a lucrative Substack and book deal that talks about ivermectin and do get paid by this alliance. One of them made almost a quarter of a million dollars in salary from the alliance. But yeah, I mean, the average doctor that’s prescribing ivermectin, I mean — there were over 400,000 ivermectin prescriptions in, I think, it was August of 2021. So that’s a lot of prescriptions.
Rovner: They’re not all making money off of it.
Weber: They’re not all making money. And I mean, what’s wild to me is Merck has come out and said, which, in a very rare statement for a pharmaceutical company, you know, don’t prescribe our drug for this. And when I asked them about RSV and the flu, they said, yeah, our statement would still stand on that. So it’s a movement, to some extent. And the folks I talked to about it, they really believe …
Rovner: And I will say, for a while in 2021, you couldn’t get horse wormer, which is a very nasty-tasting paste, even the horses don’t really like it. Because it was hard to get ivermectin at all. So we’ll see where this goes next. Here’s one of those “in case you missed It” stories. The Tulsa World this week has an interview with former Republican Sen. James Inhofe, who said, in his blunt Inhofe way, that he retired last year not only because he’s 88, but because he’s still suffering the effects of long covid. And he’s not the only one — quote, “five or six others have [long covid], but I’m the only one who admits it,” he told the paper, referring to other members of the Senate, presumably other Republican members of the Senate. Now, mind you, the very conservative Inhofe voted against just about every covid funding bill. And my impression from not going to the Hill regularly in 2021 and 2022 is that while covid seemed to be floating around in the air, lots of people were getting it, very few people seemed to be getting very sick. But now we’re thinking that’s not really the case, right?
Ollstein: When I saw this, I immediately went back to a story I wrote about a year ago on Tim Kaine’s long covid diagnosis and his attempts to convince his colleagues to put more research funding or treatment funding, more basic covid prevention funding … you know, fewer people will get long covid if fewer people get covid in the first place. And there was just zero appetite on the Republican side for that. And that’s why a lot of it didn’t end up passing. Inhofe was one of the Republicans I talked to, and I said, you know, do you think you should do more about long covid? What do you think about this? And this is what he told me: “I have other priorities. We’re handling all we can right now.” And then he added that long covid is not that well defined. And he argued there’s no way to determine how many people are affected. Well.
Rovner: OK.
Ollstein: So that … in “Quotes That Aged Poorly Hall of Fame.”
Rovner: You know, obviously Tim Kaine came forward and talked about it. But now I’m wondering if there are people who are slowing down or looking like they’re not well, maybe they have long covid and don’t want to say.
Ollstein: Well, I mean, something that Tim Kaine’s case shows is that there’s no one thing it can look like and somebody can look completely healthy and normal on the outside and be suffering symptoms. And Tim Kaine has also said that members of Congress have quietly disclosed to him and thanked him for speaking up, but said they weren’t willing to do it themselves. And he, Tim Kaine, told me that he felt more comfortable speaking up because the kind of symptoms he had were less stigmatized. They weren’t anything in terms of impeding his mental capacity and function. And there’s just a lot of stigma and fear of people coming forward and admitting they’re having a problem.
Rovner: I find it kind of ironic that last week we talked about how, you know, members of Congress and politicians with mental health, you know, normally stigmatizing problems are more willing to talk about it. And yet here are people with long covid not willing to talk about it. So maybe we’ll see a little bit more after this or maybe not. I want to talk a little bit about artificial intelligence and health care. I’ve been wanting to talk about this for a while, but this week seems to be everyone is talking about AI. There have been a spate of stories about how different types of artificial intelligence are aiding in medical care, but also some cautionary tales, particularly about chat engines. They get all their information from the internet, good or bad. Now, we already have robots that do intricate surgeries and lots and lots of treatment algorithms. On the other hand, the little bit of AI that I already have that’s medical-oriented, my Fitbit, that sometimes accurately tracks my exercise and sometimes doesn’t, and the chat bot from my favorite chain drugstore that honestly cannot keep my medication straight. None of that makes me terribly optimistic about launching into health AI. Is this, like most tech, going to roll out a little before it’s ready and then we’ll work the bugs out? Or maybe are we going to be a little bit more careful with some of this stuff?
Cohrs: I think we’ve already seen some examples of things rolling out before they’re exactly ready. And I just thought of my colleague Casey Ross’ reporting on Epic’s algorithm that was supposed to help …
Rovner: Epic, the electronic medical records company.
Cohrs: Yes, yes. They had this algorithm that was supposed to help doctors treat sepsis patients, and it didn’t work. The problem with using AI in health care is that there are life-and-death consequences for some of these things. If you’re misdiagnosing someone, if you’re giving them medicine they don’t need, there are, like, those big consequences. But there are also the smaller ones too. And my colleague Brittany Trang wrote about how with doctor’s notes or transcripts of conversations between a physician and a patient sometimes AI has difficulty differentiating between an “mm-hm” or an “uh-huh” and telling whether that’s a yes or a no. And so I think that there’s just all of these really fascinating issues that we’re going to have to work through. And I think there is enormous potential, certainly, and I think there’s getting more experimentation. But like you said, I think in health care it’s just a very different beast when you’re rolling things out and making sure that they work.
Weber: Yeah, I wanted to add, I mean, one of the things that I found really interesting is that doctors’ offices are using some of it to reduce some of the administrative burden. As we all know, prior authorizations suck up a lot of time for doctors’ offices. And it seems like this has actually been really helpful for them. That said, I mean, that comes with the caveat of — my colleagues and I and much reporting has shown that — sometimes these things just make up references for studies. They just make it up. That level of “Is this just a made-up study that supports what I’m saying?” I think is really jarring. This isn’t quite like using Google. It cannot be trusted to the level … and I think people do have caution with it and they will have to continue to have caution with it. But I think we’re really only at the forefront of figuring out how this all plays out.
Rovner: I was talking before we started taping about how I got a text from my favorite chain drugstore saying that I was out of refills and that they would call my doctor, which is fine. And then they said, “Text ‘Yes’ if you would like us to call” … some other doctor. I’m like, “Who the heck is this other doctor?” And then I realize he’s the doctor I saw at urgent care last September when I burned myself. I’m like, “Why on earth would you even have him in your system?” So, you know, that’s the sort of thing … it’s like, we’re going to be really helpful and do something really stupid. I worry that Congress, in trying to regulate tech, and failing so far — I mean, we’ve seen how much they do and don’t know about, you know, Facebook and Instagram and the hand-wringing over TikTok because it’s owned by the Chinese — I can’t imagine any kind of serious, thoughtful regulation on this. We’re going to have to basically rely on the medical industry to decide how to roll this out, right? Or might somebody step in?
Ollstein: I mean, there could be agency, you know, rulemaking, potentially. But, yes, it’s the classic conundrum of technology evolving way faster than government can act to regulate it. I mean, we see that on so many fronts. I mean, look how long has gone without any kind of update. And, you know, the kinds of ways health information is shared are completely different from when that law was written, so …
Rovner: Indeed.
Weber: And as Rachel said, I mean, this is life-or-death consequences in some places. So the slowness with which the government regulates things could really have a problem here, because this is not something that is just little …
Rovner: Of the things that keep me awake at night, this is one of the things that keeps me awake at night. All right. Well, one of these weeks, we will not have a ton of reproductive health news. But this week isn’t it. As of this taping, we still have not gotten a decision in that Texas case challenging the FDA approval of the abortion pill, mifepristone, back in the year 2000. But there’s plenty of other abortion news happening in the Lone Star State. First, a federal judge in Texas who was not handpicked by the anti-abortion groups ruled that Texas officials cannot enforce the state’s abortion ban against groups who help women get abortion out of state, including abortion funds that help women get the money to go out of state to get an abortion. The judge also questioned whether the state’s pre-Roe ban is even in effect or has actually been repealed, although there are overlapping bans in the state that … so that wouldn’t make abortion legal. But still, this is a win for the abortion rights side, right, Alice?
Ollstein: Yeah, I think the right knows that there are two main ways that people are still getting abortions who live in ban states. They’re traveling out of state or they are ordering pills in the mail. And so they are moving to try to cut off both of those avenues. And, you know, running into some difficulty in doing so, both in the courts and just practically in terms of enforcing. This is part of that bigger battle to try to cut off, you know, people’s remaining avenues to access the procedure.
Rovner: Well, speaking exactly of that, Texas being Texas, this week, we saw a bill introduced in the state legislature that would ban the websites that include information about how to get abortion pills and would punish internet providers that fail to block those sites. It would also overturn the court ruling we just talked about by allowing criminal prosecution of anyone who helps someone get an abortion. Even a year ago, I would have said this is an obvious legislative overreach, but this is Texas. So now maybe not so much.
Ollstein: I mean, I think lots of states are just throwing things at the wall to see what sticks and to see what gets through the courts. You had states test the waters on banning certain kinds of out-of-state travel, and that hasn’t gone anywhere yet. But even things that don’t end up passing and being implemented can have a chilling effect. You have a lot of confusion right now. You have a lot of people not sure what’s legal, what’s not. And if you create this atmosphere of fear where people might be afraid to go out of state, might be afraid to ask for funding to go out of state, afraid to Google around and see what their options are that serves the intended impacts of these proposals, in terms of preventing people from exploring their options and seeing what they can do to terminate a pregnancy.
Rovner: Yeah. Well, meanwhile, a dozen states that are not named Texas are suing the FDA, trying to get it to roll back some of the prescribing requirements around the abortion pill. The states are arguing that not only are the risk-mitigation rules unnecessary, given the proven safety of mifepristone, but that some of the certification requirements could invade the privacy of patients and prescribers and subject them to harassment or worse. They’re asking the judge to halt enforcement of the restrictions while the case is being litigated. That could run right into [U.S. District] Judge [Matthew] Kacsmaryk’s possible injunction in Texas banning mifepristone nationwide. Then what happens? If you’ve got one judge saying, “OK, you can’t sell this nationwide,” and another judge saying … “Of course you can sell it, and you can’t use these safety restrictions that the FDA has put around it.” Then the FDA has two conflicting decisions in front of it.
Weber: Yeah, and I find the battles of the AGs and the abortion wars are really fascinating because, I mean, this is a lawsuit brought by states, which is attorneys general, Democratic attorneys general. And you’re seeing that play out. I mean, you see that in Texas, too, with [Ken] Paxton. You see it in Michigan with [Dana] Nessel. I mean, I would argue one of the things that attorney generals have been the most prominent on in the last several decades of American history and have actually had immediate effects on due to the fall of Roe v. Wade. So we’ll see what happens. But it is fascinating to see in real time this proxy battle, so to speak, between the two sides play out across the states and across the country.
Rovner: No, it’s funny. State AGs did do the tobacco settlement.
Weber: Yes.
Rovner: I mean, that would not have happened. But what was interesting about that is that it was very bipartisan.
Weber: Well, they were on the same side.
Rovner: And this is not.
Weber: Yeah, I mean, yeah, they were on the same side. This is a different deal. And I think to some extent, and I did some reporting on this last year, it speaks to the politicization of that office and what that office has become and how it’s become, frankly, a huge launching pad for people’s political careers. And the rhetoric there often is really notched up to the highest levels on both sides. So, you know, as we continue to see that play out, I think a lot of these folks will end up being folks you see on the national stage for quite some time.
Ollstein: I’ve been really interested in the states where the attorney general has clashed with other parts of their own state government. And so in North Carolina, for example, right now you have the current Democratic attorney general who is planning to run for governor. And he said, I’m not going to defend our state restrictions on abortion pills in court because I agree with the people challenging them. And then you have the Republican state legislatures saying, well, if he’s not going to defend these laws, we will. So that kind of clash has happened in Kentucky and other states where the attorney general is not always on the same side with other state officials.
Rovner: If that’s not confusing enough, we have a story out of Mississippi this week, one of the few states where voters technically have the ability to put a question on the ballot, except that process has been blocked for the moment by a technicality. Now, Republican legislators are proposing to restart the ballot initiative process. They would fix the technicality, but not for abortion questions. Reading from the AP story here, quote, “If the proposed new initiative process is adopted, state legislators would be the only people in Mississippi with the power to change abortion laws.” Really? I mean, it’s hard to conceive that they could say you can have a ballot question, but not on this.
Ollstein: This is, again, part of a national trend. There are several Republican-controlled states that are moving right now to attempt to limit the ability of people to put a measure on the ballot. And this, you know, comes as a direct result of last year. Six states had abortion-related referendums on their ballot. And in all six, the pro-abortion rights side won. Each one was a little different. We don’t need to get into it, but that’s the important thing. And so people voted pretty overwhelmingly, even in really red states like Kentucky and Montana. And so other states that fear that could happen there are now moving to make that process harder in different ways. You have Mississippi trying to do, like, a carve-out where nothing on abortion can make it through. Other states are just trying to raise, like, the signature threshold or the vote threshold people need to get these passed. There are a lot of different ways they’re going about it.
Rovner: I covered the Mississippi “personhood” amendment back in 2011. It was the first statewide vote on, you know, granting personhood to fetuses. And everybody assumed it was going to win, and it didn’t, even in Mississippi. So I think there’s reason for the legislators who are trying to re-stand up this ballot initiative process to worry about what might come up and how the voters might vote on it. Well, because I continue to hear people say that women trying to have babies are not being affected by state abortion bans and restrictions, this week we have not one but two stories of pregnant women who were very much impacted by abortion bans. One from NPR is the story of a Texas woman pregnant with twins — except one twin had genetic defects not only incompatible with life, but that threatened the life of both the other twin and the pregnant woman. She not only had to leave the state for a procedure to preserve her own life and that of the surviving twin, but doctors in Texas couldn’t even tell her explicitly what was going on for fear of being brought up on charges of violating the state’s ban. I think, Alice, you were the one talking about how, you know, women are afraid to Google. Doctors are afraid to say anything.
Ollstein: Yeah, absolutely. I mean, it’s a really chilling and litigious environment right now. And I think, as more and more of these stories start to come forward, I think that is spurring the debates you’re seeing in a lot of states right now about adding or clarifying or expanding the kind of exceptions that exist on these bans. So you have very heated debates going on right now in Utah and Tennessee and in several states around, you know, should we add more exceptions because there are some Republican lawmakers who are looking at these really tragic stories that are trickling out and saying, “This isn’t what we intended when we voted for this ban. Let’s go back and revisit.” Whether exceptions even work when they are on the books is another question that we can discuss. I mean, we have seen them not be effective in other states and people not able to navigate them.
Rovner: We’ve seen a lot of these stories about women whose water broke early and at what point is it threatening her life? How close to death does she have to be before doctors can step in? I mean, we’ve seen four or five of these. It’s not like they’re one-offs. The other story this week is from the Daily Beast. It’s about a 28-year-old Tennessee woman whose fetus had anomalies with its heart, brain, and kidneys. That woman also had to leave the state at her own expense to protect her own health. Is there a point where anti-abortion forces might realize they are actually deterring women who want babies from getting pregnant for fear of complications that they won’t be able to get treated?
Ollstein: Most of the pushback I’ve seen from anti-abortion groups, they claim that the state laws are fine and that doctors are misinterpreting them. And there is a semantic tug of war going on right now where anti-abortion groups are trying to argue that intervening in a medical emergency shouldn’t even count as an abortion. Doctors argue, no, it is an abortion. It’s the same procedure medically, and thus we are afraid to do it under the current law. And the anti-abortion groups are saying, “Oh, no, you’re saying that in bad faith; that doesn’t count as an abortion. An abortion is when it’s intended to kill the fetus.” So you’re having this challenging tug of war, and it’s not really clear what states are going to do. There’s a lot of state bills on this making their way through legislatures right now.
Rovner: And doctors and patients are caught in the middle. Well, finally this week, Eli Lilly announced it would lower, in some cases dramatically, the list prices for some of its insulin products. You may remember that, last year, Democrats in Congress passed a $35-per-month cap for Medicare beneficiaries but couldn’t get those last few votes to apply the cap to the rest of the population. Lilly is getting very good press. Its stock price went up, even though it’s not really capping all the out-of-pocket costs for insulin for everybody. But I’m guessing they’re not doing this out of the goodness of their drugmaking heart, right, Rachel?
Cohrs: Probably not. Even though there’s a quote from their CEO that implied that that was the case. I think there was one drug pricing expert at West Health Policy Center, Sean Dickson, who is very sharp on these issues, knows the programs well. And he pointed out that there’s a new policy going into effect in Medicaid next year, and it’s really, really wonky and complicated. But I’ll do my best to try to explain that, generally, in the Medicare program, rebates are capped, or they have been historically, at the price of the drug. So you can’t charge a drugmaker a rebate that’s higher than the cost. But …
Rovner: That would make sense.
Cohrs: Right. But that math can get kind of wonky when there are really high drug price increases and then that math gets really messed up. But Congress, I want to say it was in 2021, tweaked this policy to discourage those big price increases. And they said, you know what? We’re going to raise the rebate cap in Medicaid, which means that, drugmakers, if you are taking really big price increases, you may have to pay us every time someone on Medicaid fills those prescriptions. And I think people thought about insulin right away as a drug that has these really high rebates already and could be a candidate disproportionately impacted by this policy. So I thought that was an interesting point that Sean made about the timing of this. That change is supposed to go into effect early next year. So this could, in theory, save Lilly a lot of money in the Medicaid program because we don’t know exactly what their net prices were before.
Rovner: But this is very convenient.
Cohrs: It’s convenient. And there’s a chance that they’re not really losing any money right now, depending on how their contracts work with insurers. So I think, yeah, there is definitely a possibility for some ulterior motives here.
Rovner: And plus, the thing that I learned this week that I hadn’t known before is that there are starting to be some generic competition. The three big insulin makers, which are Lilly, Sanofi, and Novo Nordisk, may actually not become the, almost, the only insulin maker. So it’s probably in Lilly’s interest to step forward now. And, you know, they’re reducing the prices on their most popular insulins, but not necessarily their most expensive insulin. So I think there’s still money to be made in this segment. But they sure did get, you know, I watched all the stories come across. It’s, like, it’s all, oh, look at this great thing that Lilly has done and that everything’s going to be cheap. And it’s, like, not quite. But …
Cohrs: But it is different. It’s a big step. And I think …
Rovner: It is. It is.
Cohrs: Somebody has to go first in breaking this cycle. And I think it will be interesting to see how that plays out for them and whether the other two companies do follow suit. Sen. Bernie Sanders asked them to and said, you know, why don’t you just all do the same thing and lower prices on more products? So, yeah, we’ll see how it plays out.
Weber: Day to day, I mean, that’s a huge difference for people. I mean, that is a lot of money. That is a big deal. So, I mean, you know, no matter what the motivation, at the end of the day, I think the American public will be much happier with having to pay a lot less for insulin.
Rovner: Yeah, I’m just saying that not everybody who takes insulin is going to pay a lot less for insulin.
Weber: Right. Which is very fair, very fair.
Rovner: But many more people than before, which is, I think, why it got lauded by everybody. Although I will … I wrote in my notes, please, someone mention Josh Hawley taking credit and calling for legislation. Sen. Hawley from Missouri, who voted against extending the $35 cap, as all Republicans did, to the rest of the population, put out a tweet yesterday that was, like, this is a great thing and now we should have, you know, legislation to follow up. And I’m like: OK.
Cohrs: You’ll have to check on that. I actually think Hawley may have voted for it.
Rovner: Oh, a-ha. All right.
Cohrs: There were a few Republicans.
Rovner: Thank you.
Cohrs: It’s not enough, though.
Rovner: Yeah, I remember that they couldn’t get those last few votes. Yes, I think [Sen. Joe] Manchin voted against. He was the one, the last Democrat they couldn’t get right. That’s why they ended up dropping …
Cohrs: Uh, it had to be a 60-vote threshold, so …
Rovner: Oh, that’s right.
Cohrs: Yeah.
Rovner: All right. Good. Thank you. Good point, Rachel. All right. Well, that is the news for this week. Now it is time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at khn.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Alice, why don’t you go first this week?
Ollstein: Yeah. So I did the incredible New York Times investigation by Hannah Dreier on child labor. This is about undocumented, unaccompanied migrant children who are coming to the U.S. And the reason I’m bringing it up on our podcast is there is a health angle. So HHS [the Department of Health and Human Services], their Office of Refugee Resettlement has jurisdiction over these kids’ welfare and making sure they are safe. And that is not happening right now. The system is so overwhelmed that they have been cutting corners in how they vet the sponsors that they release the kids to. Of course, we remember that there were tons of problems with these kids being detained and kept for way too long and that being a huge threat to their physical and mental health. But this is sort of the pendulum has swung too far in the opposite direction, and they’re being released to people who in some cases straight up trafficking them and in other cases just forcing them to work and drop out of school, even if it’s not a trafficking situation. And so this reporting has already had an impact. The HHS has announced all these new initiatives to try to stop this. So we’ll see if they are effective. But really moving, incredible reporting.
Rovner: Yeah, it was an incredible story. Lauren.
Weber: I’m going to shout out my former KHN colleague Brett Kelman. I loved his piece on, I guess you can’t call it a medical device because it wasn’t approved by the FDA, which is the point of the story. But this device that was supposed to fix your jaw so you didn’t have to have expensive jaw surgery. Well, what it ended up doing is it messed up all these people’s teeth and totally destroyed their mouths and left them with a bunch more medical and dental bills. And, you know, what I find interesting about the story, what I find interesting about the trend in general is the problem is, they never applied for anything with the FDA. So people were using this device, but they didn’t check, they didn’t know. And I think that speaks to the American public’s perception that devices and medical devices and things like this are safe to use. But a lot of times the FDA regulations are outdated or are not on top of this or the agency is so understaffed and not investigating that things like this slipped through the cracks. And then you have people — and it’s 10,000 patients, I believe, that have used this tool — that did not do what it is supposed to do and, in fact, injured them along the way. And I think that the FDA piece of that is really interesting. It’s something I’ve run into before looking at air cleaners and how they fit the gaps of that. And I think it’s something we’re going to continue to see as we examine how these agencies are really stacking up to the evolution of technology today.
Rovner: Yeah, capitalism is going to push everything. Rachel.
Cohrs: So my extra credit this week is actually an opinion piece, in Stat, and the headline is “Nonprofit Hospitals Are Failing Americans. Their Boards May Be a Reason Why.” It was written by Sanjay Kishore and Suhas Gondi. I think the part that really stood out to me is they analyzed the backgrounds and makeups of hospital boards, especially nonprofit hospitals. I think they analyzed like 20 large facilities. And the statistic that really surprised me was that, I think, 44% of those board members came from the financial sector representing investment funds, real estate, and other entities. Less than 15% were health care workers, 13% were physicians, and less than 1% were nurses. And, you know, I’ve spent a lot of time and we’ve spent a lot of time thinking about just how nonprofit hospitals are operating as businesses. And I think a lot of other publications have done great work as well making that point. But I think this is just a stark statistic that shows these boards that are supposed to be holding these organizations accountable are thinking about the bottom line, because that’s what the financial services sector is all about, and that there’s so much disproportionately less clinical representation. So obviously hospitals need admin sides to run, and they are businesses, and a lot of them don’t have very large margins. But the statistics just really surprised me as to the balance there.
Rovner: Yeah, I felt like this is one, you know, we’ve all been sort of enmeshed in this, you know, what are we going to do about the nonprofit hospitals that are not actually acting as charitable institutions? But I think the boards had been something that I had not seen anybody else look at until now. So it’s a really interesting piece. All right. Well, my story this week is the other big investigation from The New York Times. It’s called “A Drug Company Exploited a Safety Requirement to Make Money,” by Rebecca Robbins. And it’s about those same risk-mitigation rules from the FDA that are at the heart of those abortion drug lawsuits we talked about a few minutes ago. Except in this case, the drug company in question, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, somehow patented its risk-mitigation strategy as the distribution center — it’s actually called the REMS [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies] — which is managed to fend off generic competition for the company’s narcolepsy drug. It had also had a response already. It has produced a bipartisan bill in the Senate to close the loophole — but [I’ll] never underestimate the creativity of drugmakers when it comes to protecting their profit. It’s quite a story. OK. That’s our show for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, to our ever-patient producer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth — all one word — at kff.org. Or you can tweet me. I’m @jrovner. Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein
Rovner: Rachel.
Cohrs: @rachelcohrs
Rovner: Lauren.
Weber: @LaurenWeberHP
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. In the meantime, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KHN’s What the Health? on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 7 months ago
COVID-19, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Abortion, Biden Administration, Drug Costs, FDA, KHN's 'What The Health?', Obamacare Plans, Podcasts, Prescription Drugs, texas, Women's Health
A Health-Heavy State of the Union
The Host
Julie Rovner
KHN
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KHN’s weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Health care was a recurring theme throughout President Joe Biden’s 2023 State of the Union address on Capitol Hill this week. He took a victory lap on recent accomplishments like capping prescription drug costs for seniors on Medicare. He urged Congress to do more, including making permanent the boosted insurance premium subsidies added to the Affordable Care Act during the pandemic. And he sparred with Republicans in the audience — who jeered and called him a liar — over GOP proposals that would cut Medicare and Social Security.
Meanwhile, abortion rights advocates and opponents are anxiously awaiting a federal court decision out of Texas that could result in a nationwide ban on mifepristone, one of two drugs used in medication abortion.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KHN, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Cohrs of Stat, and Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet.
Panelists
Rachel Cohrs
Stat News
Sarah Karlin-Smith
Pink Sheet
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- President Joe Biden’s State of the Union address emphasized recent victories against high health care costs, like Medicare coverage caps on insulin and out-of-pocket caps on prescription drug spending. Biden’s lively, informal exchange with lawmakers over potential cuts to Medicare and Social Security seemed to steal the show, though the political fight over cutting costs in those entitlement programs is rooted in a key question: What constitutes a “cut”?
- Biden’s calls for bipartisanship to extend health programs like pandemic-era subsidies for Affordable Care Act health plans are expected to clash with conservative demands to slash federal government spending. And last year’s Senate fights demonstrate that sometimes the opposition comes from within the Democratic Party.
- While some abortion advocates praised Biden for vowing to veto a federal abortion ban, others felt he did not talk enough about the looming challenges to abortion access in the courts. A decision is expected soon in a Texas court case challenging the future use of mifepristone. The Trump-appointed judge’s decision could ban the drug nationwide, meaning it would be barred even in states where abortion continues to be legal.
- The FDA is at the center of the abortion pill case, which challenges its approval of the drug decades ago and could set a precedent for legal challenges to the approval of other drugs. In other FDA news, the agency recently changed policy to allow gay men to donate blood; announced new food safety leadership in response to the baby formula crisis; and kicked back to Congress a question of how to regulate CBD, or cannabidiol, products.
- In drug pricing, the top-selling pharmaceutical, Humira, will soon reach the end of its patent, which will offer a telling look at how competition influences the price of biosimilars — and the problems that remain for lawmakers to resolve.
Also this week, Rovner interviews Kate Baicker of the University of Chicago about a new paper providing a possible middle ground in the effort to establish universal health insurance coverage in the U.S.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The New York Times’ “Don’t Let Republican ‘Judge Shoppers’ Thwart the Will of Voters,” by Stephen I. Vladeck
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Politico’s “Mpox Is Simmering South of the Border, Threatening a Resurgence,” by Carmen Paun
Sarah Karlin-Smith: KHN’s “Decisions by CVS and Optum Panicked Thousands of Their Sickest Patients,” by Arthur Allen
Rachel Cohrs: ProPublica’s “UnitedHealthcare Tried to Deny Coverage to a Chronically Ill Patient. He Fought Back, Exposing the Insurer’s Inner Workings,” by David Armstrong, Patrick Rucker, and Maya Miller
Also mentioned in this week’s podcast:
- The Associated Press’ “20 Attorneys General Warn Walgreens, CVS Over Abortion Pills,” by Jim Salter
- NPR’s “A Trump-Appointed Texas Judge Could Force a Major Abortion Pill off the Market,” by Sarah McCammon
- Politico’s “Federal Judge Says Constitutional Right to Abortion May Still Exist, Despite Dobbs,” by Kyle Cheney and Josh Gerstein
- The Becker Friedman Institute’s “Achieving Universal Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: Addressing Market Failures or Providing a Social Floor?” by Katherine Baicker, Amitabh Chandra, and Mark Shepard
click to open the transcript
Transcript: A Health-Heavy State of the Union
KHN’s ‘What the Health?’Episode Title: A Health-Heavy State of the UnionEpisode Number: 284Published: Feb. 9, 2023
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to KHN’s “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent at Kaiser Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, Feb. 9, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go. We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Good morning.
Rovner: Rachel Cohrs of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: Hi, Julie.
Rovner: Later in this episode, we’ll play my interview with Kate Baicker of the University of Chicago. She’s one of the authors of a new paper outlining a new proposal for the U.S. to achieve universal health insurance coverage, something every other developing nation already has, but we have not yet been able to achieve. But first, this week’s health news. We’re going to start, of course, with the State of the Union, which was livelier than usual, with way more back and forth than I’ve ever seen at one of these, and also more health-heavy than usual. I’m going to start with entitlements, notably the president threatening Republican proposals to hold the debt ceiling hostage for cuts in Social Security and Medicare. I’m still trying to decide whether this was intended or not, but Biden nevertheless ended up getting Republicans to vow not to demand cuts in Social Security and Medicare in exchange for raising the debt ceiling later this year. Here is the tape.
President Joe Biden: So, folks, as we all apparently agree, Social Security and Medicare is off the books now, right? And they’re not going to strike … [prolonged applause] All right. We got unanimity!
Rovner: So was this very clever or very lucky or both?
Ollstein: Well, it’s a little not quite what it seems. Republicans have been swearing up and down more recently that they never intended to cut Medicare and Social Security. But when they say “We want to reform it, we want to shore it up,” they’re talking about things that could limit benefits for beneficiaries. So it’s a semantics game, in part. I also want to point out that neither Republicans nor Biden have yet said that they consider Medicaid in that same untouchable category. So that really jumped out at me in the speech as well.
Rovner: Yeah, I mean, if you don’t touch Social Security or Medicare — and the Republicans are trying to say that because this has been used as a weapon for so many years — then basically that leaves Medicaid. And as we discovered in 2017, when they were trying to repeal the Affordable Care Act, Medicaid is actually pretty popular, too, because it takes care of a lot of people’s grandparents in nursing homes. I’m wondering when somebody is going to bring that up. Obviously, over the years, many, quote-unquote, “cuts” have been made to both Social Security and Medicare, mainly to slow the growth of the programs so that we can continue to afford them. Many more, quote-unquote, “cuts” will have to be made going forward. Every time you reduce payment to a drugmaker or a hospital or any other health care provider, that’s a cut, but it helps beneficiaries. So, you know, you say “cuts,” [and] beneficiaries say “they’re going to cut our benefits.” Not necessarily. They may just be making the program more affordable, including for the beneficiaries. I mean, this is just the continuous back and forth of each side, weaponizing Medicare in particular, right?
Ollstein: Well, and until we see actual proposals on paper, like you’re indicating, it is a semantics game — what some people consider a cut might not be what other people consider a cut. And there’s going to be all sorts of rhetorical games over the next several months along these lines. So, I’m waiting till we see an actual black-and-white proposal that we can all pick at and analyze together.
Rovner: Well, as we have seen, there’s danger in putting things on paper, as Rick Scott discovered this week. For those who don’t remember, it was his rather infamous proposal — was it last summer, I think? It was before the election — suggesting that all federal programs be sunsetted every five years and then have to be reauthorized, which would include Social Security and Medicare and Medicaid. And that’s not playing well at this point, as I think was predicted at the time, including by us. So moving on, I was also impressed at how the speechwriters managed to combine the, quote, “victory lap” stuff, record Affordable Care [Act] enrollment, Medicare drug price changes, limits on insulin, and surprise bills with the agenda ahead: expanding insulin price caps to the non-Medicare population, Medicaid expansion in the states that haven’t done it, making the Affordable Care Act subsidies expansions permanent. But none of these things — popular, though they may be — are likely to happen in this Congress, are they? … These are the things that fell out of the bill that passed last year.
Cohrs: Right. A lot of those cost money, which is going to cause even more problems this Congress than it did in the last one. And I thought it was pretty informative that the chair of the Energy and Commerce Committee in the House threw cold water on the insulin price-cap idea because it did gain some Republican support in the Senate when it came up for a vote. That was complicated. We won’t go into it. But yeah, it wasn’t a straight up-and-down vote on that policy, really. So I think there was some hope that maybe Republicans could get on board with it. But I think, because it applies to private market insurers, [it was called] a socialist policy, like, they just don’t want government in private plans, even though it’s a wildly popular policy. So, yeah, I think that doesn’t seem like a good signal for that policy in particular and for Medicaid expansion and a lot of these things. Democrats couldn’t even do it when they all agreed or had power in both the House and the Senate. So it’s definitely not a good indication for a lot of these things.
Ollstein: Let’s not forget that [Sen. Joe] Manchin [D-W.Va.] was the one who put the kibosh on the federal Medicaid expansion. He thought it wasn’t fair to states like his that expanded a long time ago and have been paying in a little bit. He thought it wasn’t right that states that were holdouts get a free ride. And the other Democrats argued back that it’s not fair for the residents in those states to be left out in the cold uninsured either. So this will continue. But like Rachel said, not going anywhere soon.
Rovner: So the things that in theory could happen, and these didn’t mostly come up in the speech or didn’t come up very much. But earlier in the day, Biden officials were floating a quote-unquote, “unity agenda” that included a long list of potentially bipartisan health issues, starting with the “cancer moonshot,” mental health and opioid treatment, strengthening the mental health parity rules. Some of these things actually could happen, right?
Cohrs: Yeah, I think especially on the mental health package, I think there was some unfinished business from last Congress, from the Senate Finance Committee. I think that all of these are issues that have been talked about this Congress already. And the leaders have signaled that they might be interested in. But I think there is some daylight here, and we’re still in very much the agenda-setting, throwing ideas out there that are a very vague part of this Congress. And I think actually getting things down on paper and going through hearings and that kind of thing will signal which areas there might actually be some agreement on. But again, spending is going to be a big challenge and there’s just not going to be time to get to everything.
Rovner: I think one of my frustrations is that normally the State of the Union comes right before the president’s budget comes out, usually within a week or two. And this year, the president’s budget isn’t coming out until March 9. So we have this, you know, talk about agenda-setting. We’re going to have a lot of time for people to just yap at each other without any specifics. But speaking of things that didn’t and aren’t likely to happen, the president didn’t talk very much about abortion. And what he did say — like threatening to veto any abortion ban Congress might pass, which won’t happen either with Democrats in charge of the Senate — that disappointed abortion rights supporters. They’re not happy, right, Alice?
Ollstein: Some were not. To be fair, some praised the speech, praised the president for saying the word “abortion.” This was a big thing over much of his career, including the beginning of his presidency. He would talk around it and not actually say the word “abortion,” which the groups felt contributed to stigma around it. And so the big mainstream groups, Planned Parenthood, NARAL, put out statements praising the speech, praising him for saying he would veto a ban, although, again, like you said, that’s a hypothetical. It’s not going to happen. But some other groups were critical that, one, he didn’t talk about some of the very looming direct threats to abortion access in the courts that we’re probably going to get to later.
Rovner: In a minute.
Ollstein: Just in a minute! But they were frustrated that he didn’t lay out more specifics that his administration will actually do to respond to the current loss of access in a lot of the country. They felt that we’re in a crisis moment and he spent less of the speech on abortion than he did on resort fees. That was a sore point for some advocates who I talked to.
Rovner: There was a lot of emphasis on junk fees. And I get why: These are the things that drive people crazy, and, particularly, in times of high inflation. But yes, abortion came very late in the speech — almost after a lot of people had tuned out and stopped paying attention, which I think also made some people unhappy. Well, speaking of abortion, here we are waiting for another make-or-break court decision out of Texas. Alice, this time it’s the future of the “abortion pill,” not just in Texas, but around the nation that’s at stake. How did we get here? And could we really see the abortion pill banned nationwide?
Ollstein: We really could. People have really been sleeping on this case, including some elected officials who were slow to realize the impact it could have. And mainly what people don’t understand is a bunch of states already ban all methods of abortion, including the pill, and then some additional states besides that have restrictions just on the pill. So this will mainly hit blue states and states where abortion access still exists. And so it could really have a huge impact because those states are now serving more than just their own populations. And in a lot of places, losing access to medication abortion means losing access to all abortion because there aren’t clinical services available. And so my colleague and I did some reporting on how the Biden administration is preparing or not for this ruling. They rebuffed calls from activists to declare a public health emergency for abortion. They said they don’t think that would help. While they do plan to appeal the ruling should the FDA lose, the upheaval that could happen in the meantime can’t really be overstated. And not to mention that an appeal would go to the 5th Circuit, which is very conservative, and then to the Supreme Court, which just overturned Roe v. Wade. And so while most experts we’ve talked to don’t think the legal arguments are that sound, you just can’t really …
Rovner: And remind us, this is the lawsuit that’s challenging the 22-year-old approval of the drug in the first place.
Ollstein: Exactly. And so health care legal experts also say that besides the absolute upheaval in the abortion space that this could cause, this would just completely destroy any certainty around drug approvals for the FDA. If anybody could come back decades later and challenge the approval of a drug, how can drugmakers feel comfortable developing and submitting things for approval and making their plans around that? It’s very chaotic.
Rovner: Sarah, is the FDA worried about this case? Has it not been on their radar either?
Karlin-Smith: I mean, they’re involved in the defense.
Rovner: They’re being sued.
Karlin-Smith: Right. I think it is a concern if this is used, right? If the folks who want this drug pulled would win, does it become precedent-setting in a way that you can get other products pulled? Perhaps. Again, the sentiments would not be there for a lot of other products in the way to use it. But it is a bit concerning when you think about judges having this power to overrule the scientific decisions we’ve left to civil servants, not politicians or judges, because they have expertise in science and medicine and clinical trial design and all these things we just would not expect judges to be able to rule on.
Rovner: Well, speaking of more politics, this week — actually, last week — a group of 20 state attorneys general from states with abortion restrictions wrote to CVS and Walgreens, which had already announced that they would apply to become providers of the abortion pill, warning them not to rely on the Justice Department’s interpretation of a 19th-century law that banned the use of the U.S. mail to send abortifacients. The letter doesn’t outright threaten the companies. It merely says that, quote, “We offer you these thoughts on the current legal landscape.” Has anybody sued over this yet? And what do we expect to happen here? I mean, are CVS and Walgreens going to back off their plans to become providers?
Ollstein: Well, the anti-abortion elected officials and advocacy groups are hoping that’s the case. But I think this could play out in so many ways. I mean, one, we have this national ruling that could come down, but we also have a few state rulings that could flip things the other way and force states that have put restrictions on the abortion pill to lift those restrictions and allow it. So now we have cases pending in North Carolina and West Virginia. One of them is by the manufacturer of the abortion pill, saying that states don’t have the right to put the FDA’s hat on their own heads and make those decisions. And the other is by an abortion provider, a doctor who says that these state restrictions hurt her ability to practice and hurt her patients. And so it’s just wild that we can swing anywhere from a national ban to forcing states with bans to lift those bans. I mean, it’s just all up in the air right now. I wanted to quickly point out two other things. A lot of activist groups say they are not counting on the Biden administration to adequately respond to this crisis. And so they’re doing a couple things. One, they’re encouraging people to do something known as “advance provision,” which is order abortion pills before they’re pregnant, before you need them, and just have them on hand just in case. And so they’re advising people do that in advance of the ruling. Interestingly, the FDA does not support that practice, but activist groups are encouraging it anyways. And then the other thing is the abortion pill regimen is actually two pills. And the big FDA lawsuit only goes after the first one. And so people are saying, you know, you can terminate a pregnancy just by taking a few of the second pill, even though that has a higher rate of not working and needing a follow-up procedure. And so …
Rovner: Although it’s still like, 95%, right?
Ollstein: It’s still very effective, but not quite as effective as using the two pills together.
Rovner: And I think it used to be when people would go to Mexico, that’s what they would get. They would get misoprostol, not mifepristone, which is what we think of as “the abortion pill” — and also methotrexate, which we talked about in the context of people with diseases for which methotrexate is indicated not being able to get it because it can cause abortions. But that’s another option there, right? And … it would be hard for FDA to pull those drugs because those drugs do have a lot of uses for other diseases.
Karlin-Smith: Or FDA could, I guess, be forced to take off the formal indication for use for abortion, but the drug would be out there and then could be subject to off-label prescribing, which then could potentially, I guess, impact insurance coverage if you’re using it for abortion. Pivot to if you had to go back to this one-drug regimen while, yes, it would still exist and be possible, I think a lot of providers are worried about the added burden that would create on folks that help people obtain abortion. And this system is just not set up to have enough workers to deal with that more complicated regimen. And it seems like it could end up leading to more need for surgical abortions, depending on how well it works and so forth. So I think logistically it creates a lot more challenges.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s a mess. Well, meanwhile, last issue here, we have a curious story out of a lawsuit in federal district court here in Washington, D.C., in which a judge proffered the notion that while the Supreme Court may have found no right to abortion in the 14th Amendment, that doesn’t mean there isn’t a federal right under the 13th Amendment. That’s the one barring slavery, specifically the restriction on the pregnant person’s personal liberty. As the judge correctly pointed out, the majority in last year’s Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] ruling may well believe there’s no right to abortion anywhere in the Constitution. But that’s not the question that they litigated. Is this potentially an avenue that abortion rights advocates are going to explore?
Ollstein: I am not hearing a lot of hope being placed on this. If it goes anywhere, it would go back to the same Supreme Court that just ruled last year. And so abortion rights advocates are not optimistic about this strategy, but I think it’s a good indication of really both sides right now just trying to get as creative as possible and explore every legal avenue in the U.S. Constitution, in state constitutions, things where it never says the word abortion, but you could interpret it a certain way. I think that’s what we’re seeing right now. And so it’s really interesting to see where it goes.
Rovner: We are literally at the point where everybody is throwing whatever they can against the wall and seeing what sticks. All right. Well, let us turn to the federal research establishment. Late last month, a panel of advisers recommended a set of policies to strengthen oversight of so-called gain-of-function research that could inadvertently cause new pandemics. This was also one of the subjects of the first House hearing that called leading federal public health officials up on the carpet. What do we learn from the hearing? And has the federal government actually been funding gain-of-function research, or do we even know for sure?
Cohrs: So there has been a moratorium on this sort of research. And the interim director of the NIH [National Institutes of Health] quibbled over the term “gain-of-function research.” And he said we’re talking about a very select part of all of the research that could technically fall under that umbrella term. But he did say that there is a moratorium on funding that right now; there’s not current funding because they are reviewing their practices. And an advisory board did pass proposals and he laid out the process forward for that. So once those are finalized, he’ll write a memo to [Department of Health and Human Services] HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra, then it will get to the White House. So there is this bureaucratic progression that these new guidelines are going to go under, and it’s been pretty transparent and public so far. But we’ll see how things ultimately turn out. But I think they are very sensitive to this politically and they are trying to create guidelines that offer some lessons learned from some of the criticism they’ve gotten recently.
Rovner: And I think, I mean, this has become one of the major lines of argument about Republicans trying to figure out where covid came from. Perhaps it came from U.S.-funded gain-of-function research in China, which we don’t know, I don’t think. But there’s been a lot of “Yes, you did”-“No, you didn’t” going on. I mean, Sarah, does this go back to the, you know, politicians playing scientists?
Karlin-Smith: A little bit. And I think at the hearing, a lot of the Republicans who are pressuring NIH in particular on this are not super interested in listening to the subtleties and nuance of the argument. They just really want to make the point and bring up in people’s minds the possibility of, you know, covid being a lab leak, which I think … which hasn’t 100% been ruled out, but it’s kind of on the 98%, probably 99% ruled out by a lot of scientists. And so it was very hard for NIH and those lawmakers to have a reasonable discussion about the nuances and where this research might possibly benefit us in future pandemic prep. What type of precautions do need to be put in place? And I think NIH was trying to strive to communicate that actually a lot of what was recommended in this oversight report is things they’ve been working on and have put in place. But the hearing was designed by Republicans more to land those political punches and sound bites and not really delve into “Are there policy improvements that could be made here?”
Rovner: Well, speaking of civil servants trying to do their science policy jobs, the FDA’s been busy the last couple of weeks, including lifting a ban on men who have sex with other men donating blood. That’s a ban that’s been in effect in one way or another since the 1980s, when AIDS was first discovered. And in the wake of baby formula shortages, there’s now going to be a new deputy commissioner for food. And finally, the agency is asking Congress for new authority to regulate CBD [cannabidiol] products, particularly as more states legalize marijuana in all forms for recreational use. Sarah, this is an awful lot of stuff at once. Big policy changes where they try to hide some of them, or did they just all show up at once because that’s when they got finished?
Karlin-Smith: The food changes were sort of driven by events not quite within their control, and the blood policy, the CBD stuff were things in the works for some number of years now. So FDA is busy, and these are different divisions operating under it. I think the CBD stuff is drawing a lot of frustration because FDA had been working on considering how to regulate this aspect of hemp for a while now. And instead of coming up with a policy and taking action, they’ve rewound the circle; we’re back to square one and putting it on Congress’ issues. So that’s like one area where there’s a lot of frustration versus, I think, people are generally happier that the blood donation process was finally gone through and changed.
Rovner: Yes, the wheels of the federal regulatory process move slowly, as we know. All right. Finally this week, drug prices. Humira — which is a biological that treats rheumatoid arthritis and many other serious ailments, and for which you have undoubtedly seen TV commercials if you have ever turned on your television, because it’s the top-selling pharmaceutical in the world — is reaching the end of its patent life. That will soon provide the first real test of where the Affordable Care Act’s pathway to allow biosimilar competitors — effectively biologics version of generic drugs — whether that will actually bring down prices. Because there’s a chance here that there’s going to be a bunch of competitors to Humira and the price isn’t going to come down, right?
Karlin-Smith: Yeah, I mean, that’s a major concern for a number of reasons that get us back to the broader U.S. drug pricing debate and — including the role of pharmacy benefit managers in figuring out how people get coverage of their drugs. So Humira is one of the first biologics to lose patent protection, where patients actually fill the prescriptions themselves and give themselves the medicine, which is a very different payment system than if you’re getting a biologic medicine at a doctor’s office or a hospital. And so the way that most of the insurers are covering the drug for this year, they’re actually going to charge patients the same out-of-pocket cost in most instances, as if you’ve got the brand drug or the biosimilar. And because, unlike traditional generic medicines, a lot of these, at least initially, they’re not what is called auto-substitutable. So if your doctor writes you Humira, the pharmacist doesn’t automatically give you that generic. So you’d actually have to request a new prescription from your doctor, and they’d have to write it. And if you’re not going to pay less, why are you motivated to do that?
Rovner: When you’re not even positive how much whether the drug works the same way, whether the biosimilar works the same way.
Karlin-Smith: Right. And they think people are a little bit more hesitant. They don’t understand how biosimilars work compared to generic drugs, where it took — again, when the generic drug industry first started, it took people a while to get comfortable. So there are those issues. So, basically, what has happened is AbbVie has given insurance plans and payers’ discounts on their brand drug to keep it in a good place on their formularies. So there will be savings to the broader health system, for sure. The problem is if that doesn’t get passed on to the patients, and AbbVie can continue their market monopoly, my worry is, down the line, what happens to this biosimilar industry overall? Humira is not the only top-selling, big-selling biologic medicine where we want to bring down the cost. So if these biosimilar competitors don’t eventually gain market share and make money off of doing this, why are they going to go back and develop a biosimilar and try and lower the cost of the next big drug? And that’s what people are watching. I think there’s cautious optimism that, as more biosimilars for Humira launch, there will be some pressure for insurance companies to cut deals and lower prices and not just rely on making money off high rebates. But we don’t really know how it’s going to play out. And AbbVie was pretty creative over the years. In some ways that helped patients and others questionable — how much of … like, you know, there’s high concentration of the drug, low concentration. There is citrate-free, non-citrate-free. And that means that not all the competitors are going to be exactly the same in a way that creates as much competition as it seems at first. So yeah, it’s going to be messy.
Rovner: This is the famous evergreening that we saw with drugs. I mean, where they would change something small and get a whole new patent life.
Karlin-Smith: Right. So usually with generic research, you need three direct competitors to help bring the price down a lot. But in the case of Humira, while there’s going to be, probably at least six competitors this summer, maybe more, they’re not all direct competitors for the same version of Humira. So it sort of bifurcates the space a bit more and makes it harder to, you know, figure out the economics of all of that.
Rovner: Well, if you thought that drug pricing was confusing, now we’re adding a whole new level to it. So, I’m sure we will be talking about this more as we go forward. OK. That’s the news for this week. Now, we will play my interview with Kate Baicker of the University of Chicago. Then we will come back and do our extra credits.
I am excited to welcome to the podcast Katherine Baicker, currently the dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy and soon to be provost of the university. Congratulations.
Katherine Baicker: Thank you so much.
Rovner: So, Kate is a health economist who is well known to health policy students for a lot of things, but most notably as the co-lead author of the Oregon Medicaid health experiment, which was able to follow a randomized population of people who got Medicaid coverage and a population that didn’t to help determine the actual impact of having Medicaid health insurance. Today, she’s here as lead author of a paper with a new way to possibly provide health coverage to all Americans. Kate, thank you so much for joining us.
Baicker: It’s a pleasure.
Rovner: So your new paper is called “Achieving Universal Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: Addressing Market Failures or Providing a Social Safety Net.” And in that single sentence, you’ve pretty much summed up the entire health insurance debate for, like, the last half-century. For those who don’t know, why is it that the U.S. doesn’t have universal insurance when literally all of our economic competitors do?
Baicker: Well, like so many things about our health care system, it goes back to the history of how it evolved, as well as some things that are different about the U.S. from other countries. If you look at how big the U.S. is geographically, how diverse our country is, how heterogeneous the health needs are. A lot of the solutions you see in other countries might not work so well in the U.S.
Rovner: So … and we’ve basically just not ever gotten over the hump here.
Baicker: Well, I also think we haven’t been asking the right questions necessarily. There is a real debate about whether health care is a “right” or not. And, of course, your listeners can’t see my “air quotes,” but I put that in air quotes because I think that’s the wrong question. Health care is not just one thing. Health care is a continuum of things. And if we just boil it down to should people have access to care or not, that doesn’t let us engage with the hard question of how much care we want to provide to everyone and how we’re going to pay for it.
Rovner: So I know a lot of people assume that the Affordable Care Act would — I’ll use my air quotes — “fix” the U.S. health insurance problem. And it has gone a long way to cover a lot of previously uninsured people. But who are the rest of the uninsured and why don’t they have coverage? It’s not necessarily who you think, right?
Baicker: That’s right. And, you know, the ACA, or Obamacare, actually made a lot of headway in covering big swaths of the uninsured population. There was a lot of discussion about health insurance exchanges, but actually more people were covered by Medicaid expansions than by health insurance exchanges. But both of those, as well as letting young people up to age 26 get on their parents’ policies. All of this chipped away at the ranks of the uninsured, but it left, for example, undocumented immigrants uninsured and also the vast majority of the uninsured people in the U.S. are already eligible for either a public program or heavily subsidized private insurance. And we have a problem of takeup and availability, not just affordability.
Rovner: So let’s get to your proposal. It’s not really that different from things that either we’ve tried in some parts of our health insurance ecosystem or what other countries do. What would it actually look like if we were to do it?
Baicker: Well, if you go back to what I think is the right question of how much health care do we want to make sure that everyone has access to and how are we going to get them enrolled in those programs? I think one key feature is having that coverage be as low-hassle as possible, automatic if possible, because we know that nonfinancial barriers to insurance are responsible for a lot of the uninsured population we still see today.
Rovner: We’ve seen that with pension plans, right? That automatically enrolling people get more people to actually put money away?
Baicker: That’s right. That’s one of the takeaways from behavioral economics is that defaults matter. Meaning what the baseline is and letting you opt in and out makes a big difference because people tend to stick with where they are. There’s a lot of inertia in saving for retirement, in enrolling in health insurance, in lots of different things. And being sophisticated in how we design the mechanics of those programs is important, as well as making sure that they’re financially affordable to people. So one step is making sure that whatever is available to people is as easy as possible for them to take advantage of. But the other is having a much harder discussion about what we want that basic package to be. And when you say “I want everybody to have all of the care that might possibly be available, no matter what price and no matter how much it impacts their health,” that’s more than 100% of GDP. We just can’t do that and still have any money for anything like food and housing and education and roads and all of the things that we also care about. So if we had that tough discussion as a nation, as a body politic, to say, here is the care that we think is really high-value that we think is a right for everyone and that we want to make sure is available to everyone, then people could be automatically enrolled in that default package and have the option to get more care that is more expensive and maybe a little less effective, but still worth it to them that they purchase on their own. And that opens up a whole host of other questions and ethical dilemmas that I’m sure you’re going to want to ask about.
Rovner: But it also — as a lot of people are concerned, that something like “Medicare for All” would eliminate the incentive to innovate new kinds of care. I mean, obviously, there’s this race to figure out, you know, a drug to treat Alzheimer’s and that if the federal government were to basically set prices for everything, that there would be no more innovation incentive. You actually address that here, right?
Baicker: Yes. And I’m so glad you raised that concern, because there are many challenges to having a monolithic one-size-fits-all Medicare for All type plan. One of them is, you know, affordability for the system and accessibility. But another is the dulled incentive for innovation and the dulled drive towards having new medicines and new treatments available. Medicare is very slow to innovate. It took 40-plus years for Medicare to include prescription drugs at all. And that was because when Medicare was formed in the Sixties, prescription medicine wasn’t a very important part of health care. It wasn’t a very expensive part of health care, there just weren’t that many drugs to treat people. Well, now those medicines are crucial to health and well-being. And Medicare finally added a prescription drug benefit in 2005. But that was a long lag, and that’s just one example. So I think having some fundamental access to care that we know is of high value for everyone could be coupled with having the option to purchase more generous insurance that covers more things. And that private insurance layered on top would really provide the financial incentives for continued innovation. It acknowledges the reality that in a world of scarce resources, higher-income people are going to have more health care than lower-income people. And that is an ugly reality and one that we ought to grapple with ethically, and as a matter of public policy priorities. I would argue we’re already rationing care. It is not possible for public programs to pay for all care for all people, no matter what the price, no matter what the health benefit, and being intentional about defining what it is we’re going to cover with public dollars and then letting people buy more care with private dollars is a way perhaps to make a financially sustainable system that also promotes innovation.
Rovner: And this isn’t really new. I mean, lots of other countries do this. I was in Switzerland a decade ago, and I remember that they … their extra-benefit package includes things like single rooms in hospitals and homeopathic medicine and things that I’m not sure we would end up putting into our top-up plans, but it’s something that’s important to them.
Baicker: Yes. And when people point to our European counterparts and say, look, they all have single-payer. In fact, a lot of them have a hybrid system like the one that we’re describing. And it’s important to differentiate: We’re talking about a basic plan that’s available for everyone. That doesn’t mean that it only covers cheap things. It should only cover high-value things. But some cheap things are incredibly ineffective and low-value, and some expensive things are really important for health and very high-value. So it’s about the value of the dollar spent in terms of producing health, not whether it’s expensive or cheap. And so when you think about having a top-up plan, it shouldn’t be about billing cost sharing that, you know, lower-income people are exposed to in the basic plan. It should be about adding services that are of less health importance but still valuable to the people purchasing them.
Rovner: Obviously, the biggest issue here is going to be who’s going to make that determination? I’m old enough to remember fights over the ACA, death panels, and the independent Medicare advisory board that never happened. In fact, there were a lot of these, you know, we’re going to appoint experts. And it never happened because none of the experts ever wanted to be on these panels. How do you overcome that hurdle of actually grappling with the decision of what should be covered?
Baicker: Yes, the devil is always in the details for these things, and you put your finger on a really important one where we haven’t provided a robust answer, and our analysis is meant to highlight the importance of making these hard decisions and the value of this framework. But we don’t have a magic bullet for this. I would argue that having Congress make this decision every year is a recipe for lobbying and decision-making that doesn’t actually line up with value. There’s an opportunity perhaps to have a panel of experts who, as you note, is just a hop, skip and a jump from being called a “death panel.” But I think we can rely on some clinical guidelines as guardrails on this. And we do have some examples of experimentation in this direction in the U.S. In fact, more than experimentation — if you look at Medicare Advantage, this used to be a small part of the Medicare program. These are private plans for Medicare beneficiaries that are now, I think, pretty soon going to be the majority of plans that people have. And it’s a mechanism for people to choose among plans that have some things that have to be covered, but can then add additional benefits for enrollees, and it can be a little more tailored to what people value in their plans. So I don’t think that’s the answer either. But it’s a proof of concept that we can do something like this in the U.S.
Rovner: So in some ways this would bridge the gap between Republican marketplace ideas and Democratic Medicare for All ideas. But it feels like, since the fight over the Affordable Care Act, Republicans have moved more to the right on health care and Democrats have moved more to the left on health care. You are no stranger to partisan politics nor the ways of Washington, D.C. How could everybody be brought back to what I daresay looks like a political compromise?
Baicker: Well, I’m an economist, as you noted, and that’s notoriously bad at understanding actual human beings. I don’t have any idea for the path forward through the political thicket that we’re in. In some ways, it is a little disheartening to see how difficult it is to do some basic commonsense things. In any complicated system like the U.S. health care system, there are always small technical fixes that need to be made that are just commonsense, that ought not to be political. And it’s hard to do those.
Rovner: We’re lacking in common sense right now in Washington.
Baicker: Yeah. So I can’t say that I’m hugely optimistic about a big change happening right away. On the other hand, I think covid really highlighted to people across the political spectrum how important it is to have continuity of coverage, how disparate our current system is in terms of access to care, how problematic it is to have your main avenue of health insurance be through your employer when a pandemic is coupled with a recession. So I think the challenges and the vast inequities of our health care system were laid bare during covid. So it is perhaps salient enough that people might be willing to consider alternative structures. But I can’t say I’m holding my breath.
Rovner: Well, Kate Baicker, thank you very much for, if anything, a great thought experiment. It’s really wonderful to look your way through … it’s like, oh, we could get there, maybe in another half a century.
Baicker: I hope sooner than that.
Rovner: I do, too. Thank you so much.
Baicker: My pleasure.
Rovner: OK, we’re back. And it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it; we will post the links on the podcast page at khn.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Rachel, why don’t you go first this week?
Cohrs: My extra credit is headlined “UnitedHealthcare Tried to Deny Coverage to a Chronically Ill Patient. He Fought Back, Exposing the Insurer’s Inner Workings,” in ProPublica by David Armstrong, Patrick Rucker, and Maya Miller. And I thought this story was just such a good illustration of the jargon that we use in D.C., of, like, utilization management and prior authorization. And sometimes these terms just feel so impersonal. But I feel like this story did such a good job walking through one patient’s struggle to find something that worked and then just the arbitrary choices that insurers were making, looking at their bottom line to try to prevent him from getting a very expensive treatment that actually did increase his quality of life significantly. So I would definitely recommend, as we’re thinking about insurers’ role in this whole health care cost debate as well.
Rovner: Yeah, it does bring home how the patient is always in the middle of this. Alice.
Ollstein: I chose a piece by my colleague Carmen Paun called “Mpox Is Simmering South of the Border, Threatening a Resurgence,” and it’s about how the U.S. was extremely successful in vaccinating high-risk people against mpox, which for folks who still remember the artist formerly known as monkeypox, the name was changed to reduce stigma and be more accurate. The U.S. vaccination campaign and messaging campaign to the most high-risk populations was really successful and did the trick. But as we learned from covid and every other infectious disease, if you don’t take care of other parts of the world, it could eventually come back. We’re not an island, and even islands aren’t safe. But, you know, this is about a bunch of countries, including Mexico, that really have made no mass vaccination effort at all. You know, some civil society groups are trying on their own, but they just don’t have official government backing. And that’s really dangerous. And it meant that cases are surging in parts of Latin America and parts of Africa. And as we saw from covid, that leads to the development of new variants and things traveling back to the U.S. and other places around the world. So, certainly, something to pay attention to.
Rovner: Public health is important. World public health is important. Sarah.
Karlin-Smith: I looked at a piece called “Decisions by CVS and Optum Panicked Thousands of Their Sickest Patients,” by Arthur Allen for Kaiser Health News. It’s a deep dive into CVS and Optum moving out of, to some degree, business places where they provide home infusion services of perinatal nutrition to people that essentially cannot eat or drink in most cases. And they basically decided that it’s not a great business opportunity for them in many cases. But these are people that really depend on these services to live and survive, and they’re very complex medicines and essential nutrition to get and deliver. And at the same time, I think what really fascinated me about this story is it talks about this dynamic of while companies are getting out of the space where you’re providing this service to people that need these IV treatments to survive and live, there also has been development of these medical spas, as they’re called, where people that actually do not need IV hydration or IV nutrition are essentially being given it for nonmedical purposes. And there’s a lot of money being made there. And it just shows you how some of the profit incentives in our system don’t necessarily align with treating the people that actually need the health care first.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s like the people with diabetes not being able to get their drugs because people in Hollywood want to lose 10 pounds fast. But this obviously is, you know, another life-or-death issue. Well, I chose an op-ed this week in The New York Times by the University of Texas law professor Steven I. Vladeck called “Don’t Let Republican ‘Judge Shoppers’ Thwart the Will of Voters.” And it answered a lot of questions for me. First, how is it that so many suits end up in front of the same judges who the plaintiffs know are likely to rule in their favor, and all in Texas? So it turns out that Texas has distributed its federal judges in a way that in nine districts there is only one judge. And in 10 more, there are only two judges. Obviously, there’s no random draw in those districts where there’s only one judge. That’s what you’re going to get. So we keep seeing some of the same Texas judges, first Judge Reed O’Connor in Fort Worth, and now Matthew Kacsmaryk, a former advocate for a conservative think tank and the only federal judge in Amarillo. Judge O’Connor had the big ACA case, now has a big preventive care case. Judge Kacsmaryk has the abortion pill case that we’ve been talking about. It’s a really interesting piece about how that could really twist justice. But it also includes several ways to fix it. We’ll have to see if any of them actually get taken up.
OK. That is our show for this week. As always, if you enjoyed the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review — that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, to our ever-patient producer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth — all one word — @kff.org. Or you can tweet me as long as Twitter is still up. I’m @jrovner. Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein
Rovner: Rachel
Cohrs: @rachelcohrs
Rovner: Sarah.
Karlin-Smith: @SarahKarlin
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KHN’s What the Health? on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 8 months ago
Aging, Courts, Insurance, Medicare, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, The Health Law, Abortion, Biden Administration, Drug Costs, FDA, KHN's 'What The Health?', Podcasts, Premiums, Prescription Drugs, U.S. Congress, Women's Health
As US Bumps Against Debt Ceiling, Medicare Becomes a Bargaining Chip
The Host
Julie Rovner
KHN
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KHN’s weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
While repealing the Affordable Care Act seems to have fallen off congressional Republicans’ to-do list for 2023, plans to cut Medicare and Medicaid are back. The GOP wants Democrats to agree to cut spending on both programs in exchange for a vote to prevent the government from defaulting on its debts.
Meanwhile, the nation’s health care workers — from nurses to doctors to pharmacists — are feeling the strain of caring not just for the rising number of insured patients seeking care, but also more seriously ill patients who are difficult and sometimes even violent.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KHN, Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico, Tami Luhby of CNN, and Victoria Knight of Axios.
Panelists
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico
Tami Luhby
CNN
Victoria Knight
Axios
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Conservative House Republicans are hoping to capitalize on their new legislative clout to slash government spending, as the fight over raising the debt ceiling offers a preview of possible debates this year over costly federal entitlement programs like Medicare.
- House Speaker Kevin McCarthy said Republicans will protect Medicare and Social Security, but the elevation of conservative firebrands — like the new chair of the powerful House Ways and Means Committee — raises questions about what “protecting” those programs means to Republicans.
- Record numbers of Americans enrolled for insurance coverage this year under the Affordable Care Act. Years after congressional Republicans last attempted to repeal it, the once highly controversial program also known as Obamacare appears to be following the trajectory of other established federal entitlement programs: evolving, growing, and becoming less controversial over time.
- Recent reports show that while Americans had less trouble paying for health care last year, many still delayed care due to costs. The findings highlight that being insured is not enough to keep care affordable for many Americans.
- Health care workers are growing louder in their calls for better staffing, with a nursing strike in New York City and recent reports about pharmacist burnout providing some of the latest arguments for how widespread staffing issues may be harming patient care. There is bipartisan agreement in Congress for addressing the nursing shortage, but what they would do is another question.
Plus, for extra credit, the panelists recommend their favorite health policy stories of the week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: Roll Call’s “NIH Missing Top Leadership at Start of a Divided Congress,” by Ariel Cohen
Tami Luhby: CNN’s “ER on the Field: An Inside Look at How NFL Medical Teams Prepare for a Game Day Emergency,” by Nadia Kounang and Amanda Sealy
Joanne Kenen: The Atlantic’s “Don’t Fear the Handshake,” by Katherine J. Wu
Victoria Knight: The Washington Post’s “‘The Last of Us’ Zombie Fungus Is Real, and It’s Found in Health Supplements,” by Mike Hume
Also mentioned in this week’s podcast:
The New York Times’ “As France Moves to Delay Retirement, Older Workers Are in a Quandary,” by Liz Alderman
Stat’s “Congressional Medicare Advisers Warn of Higher Drug Prices, Despite New Price Negotiation,” by John Wilkerson
Click to Expand
Episode 280 Transcript
KHN’s ‘What the Health?’Episode Title: As US Bumps Against Debt Ceiling, Medicare Becomes a Bargaining ChipEpisode Number: 280Published: Dec. 19, 2023
Tamar Haspel: A lot of us want to eat better for the planet, but we’re not always sure how to do it. I’m Tamar Haspel.
Michael Grunwald: And I’m Michael Grunwald. And this is “Climavores,” a show about eating on a changing planet.
Haspel: We’re here to answer all kinds of questions. Questions like: Is fake meat really a good alternative to beef? Does local food actually matter?
Grunwald: You can follow us or subscribe on Stitcher, Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen.
Julie Rovner: Hello! Welcome back to KHN’s “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent at Kaiser Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, Jan. 19, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go. Today we are joined via video conference by Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico.
Joanne Kenen: Good morning, everybody.
Rovner: Tami Luhby of CNN.
Tami Luhby: Good morning.
Rovner: And Victoria Knight of Axios.
Victoria Knight: Good morning.
Rovner: So Congress is in recess this week, but there is still plenty of news, so we’ll get right to it. The new Congress is taking a breather for the MLK holiday, having worked very hard the first two weeks of the session. But there’s still plenty going on on Capitol Hill. Late last week, House Republicans leaked to The Washington Post a plan to pay only some of the nation’s bills if the standoff over raising the debt ceiling later this year results in the U.S. actually defaulting. Republicans say they won’t agree to raise the debt ceiling, something that’s been done every couple of years for decades, unless Democrats agree to deep spending cuts, including for entitlement programs like Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid — why we are talking about this. Democrats say that a default, even a partial one, could trigger not just a crisis in U.S. financial markets, but possibly a worldwide recession. It’s worth remembering that the last time the U.S. neared a default but didn’t actually get there, in 2011, the U.S. still got its credit rating downgraded. So who blinks in this standoff? And, Tami, what happens if nobody does?
Luhby: That’s going to be a major problem for a lot of people. I mean, the U.S. economy, potentially the global economy, global financial markets, but also practical things like Social Security recipients getting their payments and federal employees in the military getting paid, and Treasury bond holders getting their interest payments. So it would be a giant mess. [Treasury Secretary Janet] Yellen last week in her letter to [House Speaker Kevin] McCarthy, signaling that we were going to hit the debt ceiling, likely today, urged Congress to act quickly. But instead, of course, what just happened was they dug their heels in on either side. So, you know, we have the Republicans saying that we can’t keep spending like we are. We don’t have just an unlimited credit card. We have to change our behavior to save the country in the future. And the White House and Senate Democrats saying this is not a negotiable subject. You know, we’ve been here before. We haven’t actually crossed the line before. So we’ll see what happens. But one of the differences is, this year, that McCarthy has a very narrow margin in the House. Any one of his members — this is among the negotiations that he did not want to agree to but had to after 15 rounds of voting for his job — any member can make a motion to vacate the speaker’s chair. And if that happens, then we don’t have to worry about the debt ceiling because we have to worry more about who’s going to be leading the House, because we can’t deal with the debt ceiling until we actually have someone leading the House. So this is going to be even more complicated than in the past.
Rovner: Just to be clear, even if we hit the debt ceiling today, that doesn’t mean we’re going to default, right? I mean, that’s not coming for several months.
Luhby: Right. So Social Security, seniors and people with disabilities, and the military and federal employees don’t have to yet worry about their payments. They’re going to be paid. The Treasury secretary and Treasury Department will take what’s called “extraordinary measures.” They’re mainly just behind-the-scenes accounting maneuvers. They won’t actually hurt anybody. Yellen had said that she expects these extraordinary measures in cash to last at least until early June, although she did warn that the forecast has considerable uncertainty, as does everything around the debt ceiling.
Rovner: So, Victoria, obviously, the sides are shaping up. Is this going to be the big major health fight this year?
Knight: I think it’s going to be one of the big topics that we’re definitely talking about this year in Congress. I think it’s going to be a dramatic year, as we’ve already seen in these first two weeks. My colleagues at Axios, we talked to some Republicans last week, asking them about: Do you actually think they will make cuts to entitlement programs, to Medicare, Medicaid? Is that realistic? It’s kind of a mixed bag. Some are like, yeah, we should look at this, and some are like, we don’t really want to touch it. I think they know it’s really a touchy subject. There are a lot of Medicare beneficiaries that don’t want the age increase. You know, there’s some talk of increasing the age to 67 rather than 65. They know that is a touchy subject. Last week in a press conference, McCarthy said, “We’re Republicans; we’ll protect Medicare and Social Security,” so they know people are talking about this. They know people are looking at it. So I think in a divided government, obviously, the Senate is in Democratic control. I think it seems pretty unlikely, but I think they’re going to talk about it. And we have a new Ways and Means chairman, Jason Smith from Missouri. He’s kind of a firebrand. He’s talked about wanting to do reform on the U.S. spending. So I think it’s something they’re going to be talking about. But I don’t know if that much will actually happen. So we’ll see. I have been talking to Republicans on what else they want to work on this year in Congress. I think a big thing will be PBM [pharmacy benefit managers] reform. It’s a big topic that’s actually bipartisan. So I think that’s something that we’ll see. These are the middlemen in regards to between pharmacies and insurers. And they’re negotiating drug prices. And we know there are going to be hearings on that. I think health care costs. There’s some talk about fentanyl, scheduling. But I think in regards to big health care reform, there probably isn’t going to be a lot, because we are in a divided government now.
Kenen: Just one thing about how people talk about protecting Medicare and Social Security, it doesn’t mean they don’t want to make changes to it. We’ve been through this before. Entitlement reform was the driving force for Republicans for quite a few years under … when Paul Ryan was both, I guess it was budget chair before he was speaker. I mean, that was the thing, right? And he wanted to make very dramatic changes to Medicare, but he called it protecting Medicare. So there’s no one like Ryan with a policy really driving what it should look like. I mean, he had a plan, yet the plan never got through anywhere. It died, but it was an animating force for many years. It went away for a minute in the face of the last 10 years that were about the Affordable Care Act. So I don’t think they’re clear on what they want to do. But we do know some conservative Republicans want to make some kind of changes to Medicare. TBD.
Rovner: And Tami, we know the debt ceiling isn’t the only place where House Republicans are setting themselves up for deep cuts that they might not be able to make while still giving themselves the ability to cut taxes. They finessed some of this in their rules package, didn’t they?
Luhby: Yes, they did. And they made it very clear that they, in the rules, they made it harder to raise taxes. They increased it to a supermajority, 3/5 of the House. They made it easier to cut spending in the debt ceiling and elsewhere. And, you know, the debt ceiling isn’t our only issue that we have coming up. It’s going to be right around the same time, generally, maybe, as the fiscal 2024 budget, which will necessitate discussion on spending cuts and may result in spending cuts and changes possibly to some of our favorite health programs. So we will see. But also just getting back to what we were talking about with Medicare. Remember, the trustees estimate that the trust fund is going to run out of money by 2028. So we’ll see in a couple of months what the latest forecast is. But, you know, something needs to be done relatively soon. I mean … the years keep inching out slowly. So we keep being able to put this off. But at some point …
Rovner: Yeah, we keep getting to this sort of brinksmanship, but nobody, as Joanne points out, ever really has a plan because it would be unpopular. Speaking of which, while cutting entitlement programs here is still just a talking point, we have kind of a real-life cautionary tale out of France, where the retirement age may be raised from 62 to 64, which is still younger than the 67, the U.S. retirement age is marching toward. It seems that an unintended consequence of what’s going on in France is that employers don’t want to hire older workers. So now they can’t get retirement and they can’t find a job. And currently, only half of the French population is still employed by age 62, which is way lower than other members of the European Union. France is looking at protests and strikes over this. Could the same thing happen here, if we might get to that point? It’s been a while since we’ve seen the silver-haired set out on the street with picket signs.
Knight: I think it would be pretty contentious, I think, if they decide to actually raise the age. It’ll be interesting to see [if] there are actual protests, but I think people will be very upset, for sure, especially people reaching retirement age having counted on this. So …
Kenen: They probably wouldn’t do it like … if you’re 62, you wouldn’t [go] to 67. When they’ve talked about these kinds of changes in the past, they’ve talked about phasing it in over a number of years or starting it in the …
Rovner: Right, affecting people in the future.
Kenen: Right.
Rovner: But I’m thinking not just raising the retirement age. I’m thinking of making actual big changes to Medicare or even Medicaid.
Kenen: Well, there’s two things since the last debate about this. Well, first of all, Social Security was raised and it didn’t cause … it was raised slowly, a couple of months at a time over, what, a 20-year period. Is that right? Am I remembering that right, Julie?
Rovner: Yeah, my retirement age is 66 and eight months.
Kenen: Right. So … it used to be 65. And they’ve been going, like, 65 and one month, 65 and two months. It’s crept up. And that was done on a bipartisan basis, which, of course, not a whole lot is looking very bipartisan right now. But I mean, that’s the other pathway we could get. We could get a commission. We could move toward some kind of changes after … last time there was a commission that failed, but the Social Security commission did work. The last Medicare commission did not. The two sides are so intractable and so far apart on debt right now that there’s probably going to have to be some kind of saving grace down the road for somebody. So it could be yet another commission. And also in 2011, 2012, which was the last time there was the big debate over Medicare age, was pre-ACA [Affordable Care Act] implementation. And, you know, if you’re 65 and you’re not working, if they do change the Medicare in the out years, it’s complicated what it would do to the risk pools and premiums and all that. But you do have an option. I mean, the Affordable Care Act would … right now you only get it to Medicare. That would have to be changed. So it’s not totally the same … I’m not advocating for this. I’m just saying it is a slightly different world of options and the chessboard’s a little different.
Rovner: Well, clearly, we are not there yet, although we may be there in the next couple of months. Finally, on the new Congress front. Last week, we talked about some of the new committee chairs in the House and Senate. This week, House Republicans are filling out some of those critical subcommittee chairs. Rep. Andy Harris, a Republican from Maryland who’s also an anesthesiologist who bragged about prescribing ivermectin for covid, will chair the Appropriations subcommittee responsible for the FDA’s budget [the Agriculture, Rural Development, Food and Drug Administration subcommittee]. Things could get kind of interesting there, right?
Knight: Yeah. And there is talk that he wanted to chair the Labor [Health and Human Services, Education] subcommittee, which would have been really interesting. He’s not.
Rovner: Which would’ve been the rest of HHS. We should point out that in the world of appropriations, FDA is with Agriculture for reasons I once tried to figure out, but they go back to the late 1940s. But the rest of HHS is the Labor HHS Appropriations subcommittee, which he won’t chair.
Knight: Right, he is not. Rep. Robert Aderholt is chairing Labor HHS. But this is, as we were talking about, they’re going to have to fund the government. Republicans are talking about wanting to pass 12 appropriations bills. If they actually want to try to do that, they’re going to have to do a lot of negotiations on what goes into the Labor HHS bill, what goes into the AG bill with FDA, with these chairs over the subcommittees, they’re going to want certain things in there. They’re going to maybe want oversight of these agencies, especially in regards to what’s happening with covid, what’s going on with the abortion pills. So I think it’ll be really interesting to see what happens. It seems unlikely they’re actually going to be able to pass 12 appropriations bills, but it’s just another thing to watch.
Rovner: I would point out that every single Congress, Republican and Democrat, comes in saying, we’re going to go back to regular order. We’re going to pass the appropriations bills separately, which is what we were supposed to do. I believe the last time that they passed separately, and that wasn’t even all of them, was the year 2000; it was the last year of President [Bill], it might have been. It was definitely right around then. When I started covering Congress, they always did it all separately, but no more.
Luhby: And they want to pass the debt ceiling vote separately.
Rovner: Right, exactly. Not that much going on this year. All right. Well, last week we talked about health insurance coverage. Now it is official. Obamacare enrollment has never been higher and there are still several weeks to go to sign up in some states, even though enrollment through the federal marketplace ended for the year on Sunday. Tami, have we finally gotten to the point that this program is too big to fail or is it always going to hang by a political thread?
Luhby: Well, I think the fact that we’re all not reporting on the weekly or biweekly enrollment numbers, saying “It’s popular, people are still signing up!” or under the Trump years, “Fewer people are signing up and it’s lost interest.” I think that in and of itself is very indicative of the fact that it is becoming part of our health care system. And I mean, I guess one day I’m not going to write the story that says enrollment opens on Nov. 1, then another one that says it’s ending on Jan. 15.
Rovner: I think we’ll always do that because we’re still doing it with Medicare.
Luhby: Well, but I’m not. So … it’s possible, although now with Medicare Advantage, I think it is actually worth a story. So that’s a separate issue.
Rovner: Yes, that is a separate issue.
Luhby: But yeah, no, I mean, you know, I think it’s here to stay. We’ll see what [District Judge Reed] O’Connor does in Texas with the preventive treatment, but …
Rovner: Yes, there will always be another lawsuit.
Luhby: There will be chips around the edges.
Kenen: I mean, this court has done … we all thought that litigation was over, like we thought, OK, it’s done. They’ve … upheld it, you know, however many times, move on. But this Supreme Court has done some pretty dramatic rulings and not just Roe [v. Wade], on many public health measures, about gun control and the environment and vaccine mandates. And, of course, you know, obviously, Roe. Do I think that there’s going to be another huge existential threat to the ACA arising out of this preventive care thing? No, but we didn’t think a lot of the things that the Supreme Court would do. There’s a real ideological shift in how they approach these issues. So politically, no, we’re not going to see more repeal votes. In the wings could there be more legal issues to bite us? I don’t think it’s likely, but I wouldn’t say never.
Rovner: In other words, just because congressional Republicans aren’t still harping on this, it doesn’t mean that nobody is.
Kenen: Right. But it’s also, I mean, I agree with Tami … I wrote a similar story a year ago on the 10th anniversary: It’s here. They spent a lot of political capital trying to repeal it and they could not. People do rely on it and more … Biden has made improvements to it. It’s like every other American entitlement: It evolves over time. It gets bigger over time. And it gets less controversial over time.
Rovner: Well, we still have problems with health care costs. And this week we have two sort of contradictory studies about health care costs. One from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found a three-percentage-point decline in the number of Americans who had trouble paying medical bills in 2021 compared to the pre-pandemic year of 2019. That’s likely a result of extra pandemic payments and more people with health insurance. But in 2022, according to a survey by Gallup, the 38% of patients reported they delayed care because of cost. That was the biggest increase ever since Gallup has been keeping track over the past two decades, up 12 percentage points from 2020 and 2021. This has me scratching my head a little bit. Is it maybe because even though more people have insurance, which we saw from the previous year. Also more have high-deductible health plans. So perhaps they don’t want to go out and spend money or they don’t have the money to spend initially on their health care. Anybody got another theory? Victoria, I see you sort of nodding.
Knight: I mean, that’s kind of my theory is, like, I think they just have high-deductible plans, so they’re still having to pay a lot out-of-pocket. And I know my brother had to get an ACA plan because he is interning for an electrician and — so he doesn’t have insurance on his own, and I know that, like, it’s still pretty high and he just has to pay a lot out-of-pocket. He’s had medical debt before. So even though more people have health insurance, it’s still a huge issue, it doesn’t make that go away.
Rovner: And speaking of high medical prices, we are going to talk about prescription drugs because you can’t really talk about high prices without talking about drugs. Stat News reports this week that some of the members of the Medicare Payment Advisory Committee, or MedPAC, are warning that even with the changes to Medicare that are designed to save money on drugs for both the government and patients — those are ones taking effect this year — we should still expect very high prices on new drugs. Partly that’s due to the new Medicare cap on drug costs for patients. If insurers have to cover even the most expensive drugs, aside from those few whose price will be negotiated, then patients will be more likely to use them and they can set the price higher. Are we ever going to be able to get a handle on what the public says consistently is its biggest health spending headache? Victoria, you kind of previewed this with the talk about doing something about the middlemen, the PBMs.
Knight: Yeah, I think it’s really difficult. I mean, the drug pricing provisions, they only target 20 of the highest-cost drugs. I can’t remember exactly how they determine it, but it’s only 20 drugs and it’s implemented over years. So it’s still leaving out a lot of drugs. We still have years to go before it’s actually going into effect. And I think drugmakers are going to try to find ways around it, raising the prices of other drugs, you’re talking about. And even though they’re hurt by the IRA [Inflation Reduction Act], they’re not completely down and out. So I don’t know what the answer is to rein in drug prices. I think maybe PBM reform, as I said, definitely a bipartisan issue. This Congress … I think will actually have maybe some movement and we’ll see if actually legislation can be passed. But I know they want to talk about it. So, I mean, that could help a little bit. But I think drugmakers are still a huge reason for a lot of these costs. And so it won’t completely go away even if PBMs have some reforms.
Rovner: And certainly the American public sees drug costs as one of the biggest issues just because so many Americans use prescription drugs. So they see every dollar.
Knight: Yes.
Rovner: So the good news is that more people are getting access to medical care. The bad news is that the workforce to take care of them is burned out, angry, and simply not large enough for the task at hand. The people who’ve been most outspoken about that are the nation’s nurses, who’ve given the majority of the care during the pandemic and taken the majority of patient anger and frustration and sometimes even violence. We’re seeing quite a few nurses’ strikes lately, and they’re mostly not striking for higher wages, but for more help. Tami, you talked to some nurses on the picket line in New York last week. What did they tell you?
Luhby: Yeah, I had a fun assignment last week. Since I live in the Bronx, I spent two days with the striking nurses at the Montefiore Medical Center, and there were 7,000 nurses at Mount Sinai Hospital in Manhattan and Montefiore in the Bronx that went on strike for three days. It was a party atmosphere there much of the time, but they did have serious concerns that they wanted to relay and get their word out. There was a lot of media coverage as well. Their main issue was staffing shortages. I mean, the nurses told me about terrible working conditions, particularly in the ER. Some of them had to put babies on towels on the floor of the pediatric ER or tell sick adults that they have to stand because there aren’t even chairs available in the adult ER, much less beds or cots. And every day, they feared for their licenses. One said that she would go to sleep right when she got home because she didn’t want to think about the day because she was concerned she might not want to go back the next day. And she said, heartbreakingly, that she was tired of apologizing to families and patients, that she was stretched too thin to deliver better care, that she was giving patients their medicines late because she had seven other patients she had to give medicine to and probably handle an emergency. So the nurses at Montefiore, interestingly, they’re demanding staffing. But one thing they kept repeating to me, you know, the leaders, was that they wanted enforcement ability of the staffing. They didn’t just want paper staffing ratios, and they wanted to be more involved in recruitment. While the hospitals — interestingly, this is not necessarily over in New York as it probably won’t be elsewhere. These hospitals reached a tentative agreement with the unions, but there’s another battle brewing. The nurses’ contract for the public hospital system expires on March 2, and the union is already warning that will demand better pay and staffing.
Rovner: Yeah. Well, it’s not just the nurses, though. Doctors are burnt out by angry and sometimes ungrateful patients. Doctors in training, too. And I saw one story this week about how pharmacists, who are being asked to do more and more with no more help — a similar story — are getting fried from dealing with short-tempered and sometimes abusive patients. Is there any solution to this, other than people trying to behave better? Is Congress looking at ways to buttress the health care workforce? This is a big problem. You know, they talked about, when they were passing the Affordable Care Act, that if you’re going to give all these people more insurance, you’re going to need more health care professionals to take care of them.
Knight: Yeah.
Rovner: Yet we haven’t seemed to do that.
Knight: Yeah, I know. It’s something that is being talked about. My colleague Peter [Sullivan] at Axios talked to both Sen. [Bernie] Sanders and Sen. [Bill] Cassidy about things they might want to work on on the HELP [Health, Education, Labor & Pensions] Committee. And I know that the nursing workforce shortage is one thing they do actually agree on. So it’s definitely possible. I do think the medical provider workforce shortage is maybe a bipartisan area in this Congress that they could work on. But I mean, they’ve been talking about it forever. And will they actually do something? I’m not sure. So we’ll see. But I know nursing …
Rovner: Yeah, the spirit of bipartisanship does not seem to be alive and well, at least yet, in this Congress.
Knight: Yeah, well, between the House and the Senate. Yeah, well, we’ll see.
Kenen: But the nursing shortage is, I mean, been documented and talked about for many, many years now and hasn’t changed. The doctor shortage is more controversial because there’s some debate about whether it’s numbers of doctors or what specialties they go into. I mean, and, also, do they go to rich neighborhoods or poor neighborhoods? I mean, if you’re in a wealthy suburb, there’s plenty of dermatologists. Right? But in rural areas, certain urban areas … So it’s not just in quantity. It’s also an allocation both by geography and specialty. Some of that Congress could theoretically deal with. I mean, the graduate medical education residency payment … they’ve been talking about reforming that since before half of the people listening to this were born. There’s been no resolution on a path forward. So some of these are things that Congress can nudge or fix with funding. Some of it is just things that have to happen within the medical community, some cultural shift. Also student debt. I mean, one reason people start out saying they’re going to go into primary care and end up being orthopedic surgeons is their debt. So it’s complicated. Some of it is Congress. Not all of it is Congress. But Congress has been talking about this for a very, very, very, very, very long time.
Rovner: I will point out — and Joanne was with me when this happened — when Congress passed the Balanced Budget Act in 1997, they cut the number of residencies that Medicare would pay for with the promise — and I believe this is in the report, if not in the legislation — that they would create an all-payer program to help pay for graduate medical education by the next year, 1998. Well, now it’s 2023, and they never did that.
Kenen: They meant the next century.
Rovner: We’re a fifth — almost a quarter of the way — through the next century, and they still haven’t done it.
Kenen: And if you were on the front lines of covid, the doctors and the nurses, I mean, at the beginning they had no tools. So many people died. They didn’t know how to treat it. There were so many patients, you know, in New York and other places early on. I mean, it was these nurses that were holding iPads so that people could say goodbye to their loved ones. I don’t think any of us can really understand what it was like to be in that situation, not for 10 minutes, but for weeks and over and over …
Rovner: And months and years, in some cases.
Kenen: Right. But I mean, the really bad … it’s years. But these crunches, the really traumatic experiences, I mean, we’ve also talked in the past about the suicide rate among health care providers. It’s been not just physically exhausting, it’s become emotionally unimaginable for those of us who haven’t been in those ICU or ERs.
Rovner: Well, it’s clear that the pandemic experiences have created a mental health crisis for a lot of people. Clearly, people on the front lines of health care, but also lots of other people. This week, finally, a little bit of good news for at least one population. Starting this week, any U.S. military veteran in a mental health crisis can get free emergency care, not just at any VA [Department of Veterans Affairs] facility, but at any private facility as well. They don’t even have to be in the VA health system because many former members of the military are not actually eligible for VA health care. This is for all veterans. It’s actually the result of a law passed in 2020 and signed by then-President [Donald] Trump. How much of difference could this change, at least, make? I mean, veterans in suicidal crises are also, unfortunately, fairly common, aren’t they?
Kenen: Yeah, but I mean, we have a provider shortage, so giving them greater access to a system that doesn’t have enough providers, I mean, will it help? I would assume so. Is it going to fix everything? I would assume not. You know, we don’t have enough providers, period. And there are complicated reasons for that. And that’s also … they’re not all doctors. They’re, you know, psychologists and social workers, etc. But that’s a huge problem for veterans and every human being on Earth right now. I mean, everybody was traumatized. There’s degrees of how much trauma people had, but nobody was untraumatized by the last three years. And the ongoing stresses. You can be well-adjusted traumatized. You could be in-crisis traumatized. But we’re all on that spectrum of having been traumatized.
Knight: Yeah.
Rovner: Well, lots more work to do. OK. That’s the news for this week. Now it is time for our extra-credit segment, where we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. Don’t worry if you miss it; we will post the links on the podcast page at khn.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Victoria, why don’t you go first this week?
Knight: The story that I’m recommending is called “‘The Last of Us’ Zombie Fungus Is Real, and It’s Found in Health Supplements.” It’s in The Washington Post by Mike Hume. “The Last of Us” is a new HBO show everyone’s kind of talking about. And, basically, people become zombies from this fungus. Turns out that fungus is real in real life. It’s spread by insects that basically infect people and then kind of take over their minds and then shoot little spores out. And in the show, they do that as well, except they don’t spread by spores. They spread by bites. But it’s used in health supplements for different things like strength, stamina, immune boost. So it’s kind of just a fun little dive into a real-life fungus.
Rovner: To be clear, it doesn’t turn people into zombies.
Knight: Yes. To be clear, it does not turn people into zombies. If you eat it, that will not happen to you. But it is based on a real-life fungus that does infect insects and make them zombies.
Rovner: Yes. [laughter] It’s definitely creepy. Tami.
Luhby: My story is by my fantastic CNN colleagues this week. It’s called “ER on the Field: An Inside Look at How NFL Medical Teams Prepare for a Game Day Emergency.” It’s by my colleagues Nadia Kounang, Amanda Sealy, and Sanjay Gupta. Listen, I don’t know anything about football, but I happened to be watching TV with my husband when we flipped to the channel with the Bills-Bengals game earlier this month, and we saw the ambulance on the field. So like so many others, I was closely following the story of Damar Hamlin’s progress. What we heard on the news was that the team and the medical experts repeatedly said that it was the care on the field that saved Hamlin’s life. So Nadia, Amanda, and Sanjay provide a rare behind-the-scenes look at how hospital-quality treatment can be given on the field when needed. I learned that — from the story and the video — that there are about 30 medical personnel at every game. All teams have emergency action plans. They run drills an hour before kickoff. The medical staff from both teams review the plan and confirm the details. They station certified athletic trainers to serve as spotters who are positioned around the stadium to catch any injuries. And then they communicate with the medical team on the sidelines. But then — and this is what even my husband, who is a major football fan, didn’t know this — there’s the all-important red hat, which signifies the person who is the emergency physician or the airway physician, who stands along the 30-yard line and takes over if he or she has to come out onto the field. And that doctor said, apparently, they have all the resources available in an emergency room and can essentially do surgery on the field to intubate a player. So I thought it was a fascinating story and video even for non-football fans like me, and I highly recommend them.
Rovner: I thought it was very cool. I read it when Tami recommended it. Although my only question is what happens when there’s a team, one whose color is red and there are lots of people wearing red hats on the sidelines?
Luhby: That’s a good point.
Rovner: I assume they still can find the doctor. OK, Joanne.
Kenen: There was a piece in The Atlantic by Katherine J. Wu called “Covid Couldn’t Kill the Handshake.” It had a separate headline, depending on how you Googled it, saying “Don’t Fear the Handshake.” So, basically, we stopped shaking hands. We had fist bumps and, you know, bows and all sorts of other stuff. And the handshake is pretty much back. And yes, your hands are dirty, unless you’re constantly washing them, your hands are dirty. But they are not quite as dirty as we might think. We’re not quite as dangerous as we may think. So, you know, if you can’t get out of shaking someone’s hand, you probably won’t die.
Rovner: Good. Good to know. All right. My extra credit this week is a story I wish I had written. It’s from Roll Call, and it’s called “NIH Missing Top Leadership at Start of a Divided Congress,” by Ariel Cohen. And it’s not just about not having a replacement for Dr. Tony Fauci, who just retired as the longtime head of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases last month, but about having no nominated replacement for Frances Collins, who stepped down as NIH [National Institutes of Health] director more than a year ago. In a year when pressure on domestic spending is likely to be severe, as we’ve been discussing, and when science in general and NIH in particular are going to be under a microscope in the Republican-led House, it doesn’t help to have no one ready to catch the incoming spears. On the other hand, Collins’ replacement at NIH will have to be vetted by the Senate HELP Committee with a new chairman, Bernie Sanders, and a new ranking member, Bill Cassidy. I am old enough to remember when appointing a new NIH director and getting it through the Senate was a really controversial thing. I imagine we are back to exactly that today.
OK. That’s our show for this week. As always, if you enjoyed the podcast, you could subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, to our ever-patient producer, Francis Ying, and to our KHN webteam, who have given the podcast a spiffy new page. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth — all one word — @kff.org. Or you can tweet me. I’m still at Twitter, for now, where I’m @jrovner. Tami?
Luhby: I’m @Luhby — L-U-H-B-Y
Rovner: Victoria.
Knight: @victoriaregisk
Rovner: Joanne.
Kenen: @JoanneKenen
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KHN’s What the Health? on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Stitcher, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 9 months ago
Capitol Desk, Elections, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Uninsured, Hospitals, KHN's 'What The Health?', Nurses, Obamacare Plans, Podcasts