What I Learned From the World’s Last Smallpox Patient
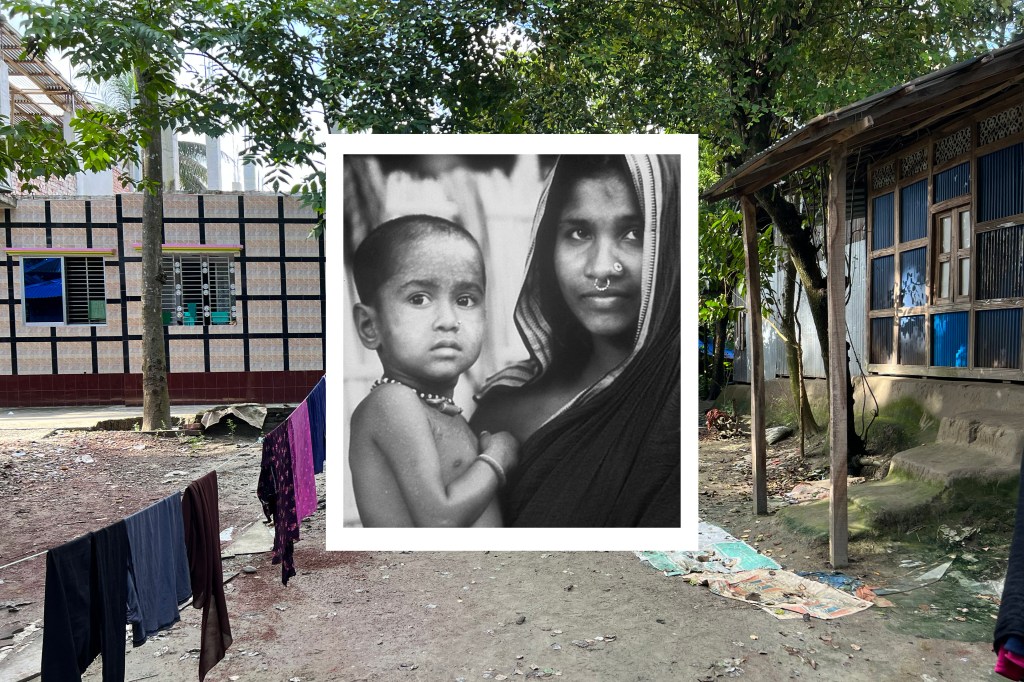
Rahima Banu, a toddler in rural Bangladesh, was the last person in the world known to contract variola major, the deadly form of smallpox, through natural infection. In October 1975, after World Health Organization epidemiologists learned of her infection, health workers vaccinated those around her, putting an end to variola major transmission around the world.
The WHO officially declared smallpox eradicated in 1980, and it remains the only human infectious disease ever to have been eradicated.
Among infectious-disease doctors like me, Banu is famous as a symbol of the power of science and modern medicine.
And yet, beyond that distinction, Banu has largely been forgotten by the public. That fate is a reminder that, well after a global pandemic recedes from headlines in wealthy countries, its survivors have needs that go unmet. Although Banu survived smallpox, she’s been sickly her whole life. She was once bedridden for three months with fevers and vomiting, but she couldn’t afford to see a good doctor. The doctor she could afford, she recalled, prescribed her cooked fish heads. Banu also complains of poor vision: “I cannot thread a needle, because I cannot see clearly,” she told me, via a translator, during an interview in Digholdi, the village where she lives.
“I cannot examine the lice on my son’s head and cannot read the Quran well because of my vision,” she said.
In the years following smallpox eradication, journalists from all over the world traveled to interview Banu, but they petered out years ago. “Mother is so famous, but they do not take any follow-up of Mom to know whether she is in a good or bad state,” her middle daughter, Nazma Begum, told me.
Banu and her family are proud of her place in history, but their role in the eradication of smallpox speaks to the limits of merely fighting diseases. In his biography of the doctor and philanthropist Paul Farmer, author Tracy Kidder recorded a Haitian saying: “Giving people medicine for TB and not giving them food is like washing your hands and drying them in the dirt.”
After Banu and her family survived smallpox, the rest of the world dried its hands in the dirt — just as it did for the poorest victims of covid-19 and later the most marginalized people with mpox, formerly known as monkeypox.
I traveled to South Asia to speak with aging public health workers and smallpox survivors in South Asia for the audio-documentary podcast “Epidemic: Eradicating Smallpox.”
To meet Banu, I flew 14 hours to Delhi and another two hours the next day to Dhaka, then took a five-hour drive to Barishal, followed the next day by a 90-minute ferry ride and a two-hour drive to arrive in Digholdi. Banu and her family — her husband, their three daughters, and their son — share a one-room bamboo-and-corrugated-metal home with a mud floor. The home, which lacks indoor plumbing, is divided down the middle by a screen and a curtain. Water leaks in through the roof, soaking their beds. A bare bulb hangs from a wire overhead. Her in-laws used to live with them, too, but they have passed away.
Women in rural Bangladesh rarely work outside the home. Banu’s husband, Rafiqul Islam, pedals a rickshaw. Some days he earns nothing. On a good day, he might make 500 taka (not quite $5). Although the World Health Organization arranged for a plot of land in her name, Banu said, the family has nowhere to cultivate. “They gave me the land, but the river consumes that. Some of it is in the river,” she said. Cyclones and rising sea levels have led to coastal erosion and saltwater intrusion, and there have also been land disputes.
Begum, now 23, completed a year of college but then dropped out. Banu and her husband couldn’t afford the fees. Instead, they arranged for her to marry. Her mother’s fame “did not help me in any way in my studies or financially,” Begum told me.
The family’s financial life is precarious. Five hundred taka used to buy a 10-kilogram bag of rice and vegetables. During my visit in 2022, the instability of the Russia-Ukraine war created fluctuating oil prices, and Banu said that amount was enough to pay only for the rice.
Banu is well aware that thanks to vaccination, millions of people no longer die of smallpox and other infectious diseases. By one estimate, the eradication of smallpox has prevented at least 5 million deaths around the world each year. Vaccines remain one of the most cost-effective and lifesaving gifts of modern medicine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that the U.S. saves 10 times what it spends on childhood vaccination. But all this is cold comfort to Banu when she and her family are struggling to survive.
Every public health crisis leaves people behind. When I worked as an Ebola aid worker in Guinea in 2015, residents asked why I cared so much about Ebola when local women were hemorrhaging in childbirth and didn’t have enough to eat. They were right not to trust our efforts. Why should they upend their lives to help us defeat Ebola? They knew their lives wouldn’t be materially better when we declared victory and left, as we had done so many times before as soon as our own interests were protected. Their prediction was correct.
As the coronavirus pandemic winds down in the United States, Banu’s life is a reminder that illness has a long tail of consequences and doesn’t end with a single shot. The world’s most powerful nation hasn’t ensured equitable access for its own citizens to health care and lifesaving tools such as covid vaccines, Paxlovid, and monoclonal antibodies. The resulting disparities will get worse as the federal government finishes turning America’s emergency covid response over to the routine health care system. Many Americans can’t afford to stay home when they or their children are sick. Families lack support to care for young or elder family members or people with medical illnesses or disabilities. Many say their biggest worry is paying for groceries or gas to get to work.
Their plight is less extreme than Banu’s, but their suffering is real — and it is magnified worldwide. As long as vulnerable communities are deprived of holistic, comprehensive responses to mpox, covid, Ebola, or other public health emergencies to come, these people will have a reason to be suspicious, and enlisting their help to fight the next crisis will be that much harder.
A version of this article first appeared in The Atlantic in August 2022.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 11 months ago
Public Health, Race and Health, Epidemic
A New Era of Vaccines Leaves Old Questions About Prices Unanswered
The world is entering a new era of vaccines. Following the success of covid-19 mRNA shots, scientists have a far greater capacity to tailor shots to a virus’s structure, putting a host of new vaccines on the horizon.
The world is entering a new era of vaccines. Following the success of covid-19 mRNA shots, scientists have a far greater capacity to tailor shots to a virus’s structure, putting a host of new vaccines on the horizon.
The most recent arrivals — as anyone on the airwaves or social media knows — are several new immunizations against respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV.
These shots are welcome since RSV can be dangerous, even deadly, in the very old and very young. But the shots are also expensive — about $300 for those directed at adults, and up to $1,000 for one of the shots, a monoclonal antibody rather than a traditional vaccine, intended for babies. Many older vaccines cost pennies.
So their advent is forcing the United States to face anew questions it has long sidestepped: How much should an immunization that will possibly be given — maybe yearly — to millions of Americans cost to be truly valuable? Also, given the U.S. is one of two countries that permit direct advertising to consumers: How can we ensure the shots get into the arms of people who will truly benefit and not be given, at great expense, to those who will not?
Already, ads on televisions and social media show active retirees playing pickleball or going to art galleries whose lives are “cut short by RSV.” This explains the lines for the shot at my local pharmacy.
But indiscriminate use of expensive shots could strain both public and private insurers’ already tight budgets.
Other developed countries have deliberate strategies for deciding which vulnerable groups need a particular vaccine and how much to pay for it. The U.S. does not, and as specialized vaccines proliferate, public programs and private insurers will need to grapple with how to use and finance shots that can be hugely beneficial for some but will waste precious health dollars if taken by all.
A seasonal viral illness, RSV can cause hospitalization or, in rare cases, death in babies and in people age 75 or older, as well as those with serious underlying medical conditions such as heart disease or cancer. For most people who get RSV, it plays out as a cold; you’ve likely had RSV without knowing it.
But RSV puts about 2% of babies under age 1 in the hospital and kills between 100 and 300 of those under 6 months, because their immune systems are immature and their airways too narrow to tolerate the inflammation. Merely having a bad case of RSV in young childhood increases the risk of long-term asthma.
That’s why Barney Graham, the scientist who spent decades at the government’s National Institutes for Health perfecting the basic science that led to the current shots, said: “The most obvious use is in infants,” not adults.
That’s also why European countries trying to figure out how best to use these vaccines without breaking the bank focused first on babies and determining a sensible price. Though more of the very old may die of RSV, the years of life lost are much greater for the very young. (Babies can get the monoclonal antibody shot or gain protection through a traditional vaccine given to the mother near the end of pregnancy, conferring immunity through the womb.)
A consortium of European experts led by Philippe Beutels, a professor in health economics at the University of Antwerp in Belgium, calculated that the shots would only be “worth it” in terms of the lives saved and hospitalizations averted in infants if the price were under about $80, he said in a phone interview. That’s because almost all babies make it through RSV with supportive care.
The calculation will be used by countries such as Belgium, England, Denmark, Finland, and the Netherlands to negotiate a set price for the two infant shots, followed by decisions on which version should be offered, depending partly on which is more affordable.
They have not yet considered how to distribute the vaccines to adults — considered less pressing — because studies show that RSV rarely causes severe disease in adults who live outside of care settings, such as a nursing home.
Why did the United States and Europe approach the problem from opposite directions?
In the U.S., there was a financial incentive: Roughly 3.7 million babies are born each year, while there are about 75 million Americans age 60 and older — the group for whom the two adult vaccines were approved. And about half of children get their vaccines through the Vaccines for Children program, which negotiates discounted prices.
Also, babies can get vaccinated only by their clinicians. Adults can walk into pharmacies for vaccinations, and pharmacies are only too happy to have the business.
But which older adults truly benefit from the shot? The two manufacturers of the adult vaccines, GSK and Pfizer, conducted their studies presented to the FDA for approval in a population of generally healthy people 60 and older, so that’s the group to whom they may be marketed. And marketed they are, even though the studies didn’t show the shots staved off hospitalization or death in people ages 60 to 75.
That led to what some have called a “narrow” endorsement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for people 60 to 75: Patients in that age range could get the shot after “shared clinical decision-making” with a health provider.
It is likely that because of this fuzzy recommendation, some Americans 60 and over with commercial insurance are finding that their insurers won’t cover it. Under Obamacare, insurers are generally required to cover at no cost vaccines that are recommended by the ACIP; however, if a provider recommends vaccination, then it must be covered by insurance.
(In late September, the ACIP recommended immunization of all babies with either the antibody or the maternal vaccine. Insurers have a year to commence coverage and many have been dragging their feet because of the high price.)
There are better and more equitable ways to steer the shots into the arms of those who need it, rather than simply administering it to those who have the “right” insurance or, swayed by advertising, can pay. For example, insurers, including Medicare, could be required to cover only those ages 60 to 75 who have a prescription from a doctor, indicating shared decision-making has occurred.
Finally, during the pandemic emergency, the federal government purchased all covid-19 vaccines in bulk at a negotiated price, initially below $20 a shot, and distributed them nationally. If, to protect public health, we want vaccines to get into the arms of all who benefit, that’s a more cohesive strategy than the patchwork one used now.
Vaccines are miraculous, and it’s great news that they now exist to prevent serious illness and death from RSV. But using such novel vaccines wisely — directing them to the people who need them at a price they can afford — will be key. Otherwise, the cost to the health system, and to patients, could undermine this big medical win.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 12 months ago
Aging, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Pharmaceuticals, Public Health, CDC, Children's Health, Drug Costs, vaccines
Epidemic: What Good Is a Vaccine When There Is No Rice?
The 1970s was the deadliest decade in the “entire history of Bangladesh,” said environmental historian Iftekhar Iqbal. A deadly cyclone, a bloody liberation war, and famine triggered waves of migration. As people moved throughout the country, smallpox spread with them.
In Episode 7 of “Eradicating Smallpox,” Shohrab, a man who was displaced by the 1970 Bhola cyclone, shares his story. After fleeing the storm, he and his family settled in a makeshift community in Dhaka known as the Bhola basti. Smallpox was circulating there, but the deadly virus was not top of mind for Shohrab. “I wasn’t thinking about that. I was more focused on issues like where would I work, what would I eat,” he said in Bengali.
When people’s basic needs — like food and housing — aren’t met, it’s harder to reach public health goals, said Bangladeshi smallpox eradication worker Shahidul Haq Khan.
He encountered that obstacle frequently as he traveled from community to community in southern Bangladesh.
He said people asked him: “There’s no rice in people’s stomachs, so what is a vaccine going to do?”
To conclude this episode, host Céline Gounder speaks with Sam Tsemberis, president and CEO of Pathways Housing First Institute.
He said when public health meets people’s basic needs first, it gives them the best shot at health.
The Host:
Céline Gounder
Senior Fellow & Editor-at-Large for Public Health, KFF Health News
Céline is senior fellow and editor-at-large for public health with KFF Health News. She is an infectious diseases physician and epidemiologist. She was an assistant commissioner of health in New York City. Between 1998 and 2012, she studied tuberculosis and HIV in South Africa, Lesotho, Malawi, Ethiopia, and Brazil. Gounder also served on the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board.
In Conversation With Céline Gounder:
Sam Tsemberis
Founder, president, and CEO of Pathways Housing First Institute
Voices From the Episode:
Shohrab
Resident of the Bhola basti in Dhaka
Iftekhar Iqbal
Associate professor of history at the Universiti Brunei Darussalam
Shahidul Haq Khan
Former World Health Organization smallpox eradication program worker in Bangladesh
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: What Good Is a Vaccine When There Is No Rice?
Podcast Transcript
Epidemic: “Eradicating Smallpox”
Season 2, Episode 7: What Good Is a Vaccine When There Is No Rice?
Air date: Oct 24, 2023
Editor’s note: If you are able, we encourage you to listen to the audio of “Epidemic,” which includes emotion and emphasis not found in the transcript. This transcript, generated using transcription software, has been edited for style and clarity. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
[Ambient sounds from a ferry play softly.]
Céline Gounder: I’m on a boat in southern Bangladesh, headed toward Bhola, the country’s largest island.
We’re traveling by ferry on calm waters. But my head spins — and my stomach roils just a bit — as I imagine how these same waters nearly destroyed Bhola Island.
[Tense instrumental music begins playing.]
It was 1970.
In November, under an almost-full moon and unusually high tides.
The island was hit by one of the most destructive tropical storms in modern history: the Bhola cyclone.
[Shohrab speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shohrab: There were floods. Back then there weren’t any embankments to stop the water from rising.
Céline Gounder: Counterclockwise winds, torrential rains, and treacherous waves swept entire villages into the sea. People held onto whatever they could to keep their heads above water.
[Shohrab speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shohrab: I remember at that time the water level rose so high that people ended up on top of trees. The water had so much force. Many people died.
Céline Gounder: The Bhola cyclone killed some 300,000 people. And for those who survived, there wasn’t much left to return to. Hundreds of thousands of people lost their homes, their farms, and their access to food.
The man whose voice you’ve been hearing was one of the survivors.
[Shohrab speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shohrab: My name is Shohrab. I am 70 years old.
Céline Gounder: Shohrab was a teenager when the cyclone hit. And in the days and weeks after the storm, he and his family joined a mass migration of people who fled southern Bangladesh.
They traveled about a hundred miles north from Bhola Island to the streets of Dhaka, the busy capital of Bangladesh.
There, they settled in a makeshift community, a kind of unsanctioned encampment dubbed the Bhola basti.
In Bengali that word,“basti,” means settlement — or “slum,” in some translations.
The residents forged a community, but soon, the poor people there — and what they built — would be seen as a threat to the effort to keep smallpox in check.
Not just in South Asia — but around the world.
I’m Dr. Céline Gounder. This is “Epidemic.”
[“Epidemic” theme music plays.]
[Ambient sounds from the Bhola basti, including voices of people speaking Bengali, play softly.]
Céline Gounder: More than 50 years after the cyclone, Shohrab lives in the same area in Dhaka.
I interviewed him at a tea stall near his home. It’s the kind of place where men gather to gossip and share stories over hot drinks.
Inside there’s a colorful display of snacks and sweets hanging from the ceiling. Just outside we sat on well-worn wooden benches.
And as we sip our tea, he tells me about life in the encampment in the 1970s …
[Sparse music plays softly.]
[Shohrab speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shohrab: I used to rent a place there. Five or six of us used to live in one room. Sometimes it was eight people in a room.
Céline Gounder: To cover his portion of the rent he worked as a day laborer, doing odd jobs here and there. Over time the basti became home.
But Shohrab’s new home was likely seen as an eyesore by outsiders — and by the Bangladeshi government.
Such settlements often lack running water, or electricity, or access to proper sanitation. Those conditions spotlight suffering — and for local leaders that spotlight can be uncomfortable.
But, public health experts had a different concern: that the settlement of Bhola migrants in Dhaka would become a deadly stronghold for smallopox. Cramped and unsanitary living conditions put the residents at high risk.
I ask Shohrab if he remembers seeing or hearing about people with smallpox when he first arrived.
[Shohrab speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shohrab: I wasn’t thinking about that. I was more focused on issues like where would I work, what would I eat, etc.
Céline Gounder: As he tried to rebuild his life, other things — like food and shelter — were more urgent.
[Music fades to silence.]
Widening beyond that one migrant encampment in Dhaka, researchers say the picture was similar in cities and villages all across the country.
Bangladesh was hit with a series of crises. Environmental historian Iftekhar Iqbal says each brought human suffering — and that each was a blow to the smallpox eradication effort.
Iftekhar Iqbal: Seventies was really a time when, the coming of the smallpox couldn’t come at a, at a more unfortunate time.
Céline Gounder: In 1970 the Bhola cyclone hit. In 1971, just four months later, the country fought a bloody liberation war. Then, in 1974, heavy rain and flooding triggered a famine. And in 1975 there was a military coup.
Iftekhar Iqbal: The 1970s was the deadliest decade in the history of Bangladesh.
Céline Gounder: This period is when the country became Bangladesh — winning its independence from Pakistan in the liberation war. But residents of the young nation faced cascading upheaval and turmoil. And too much death.
[Instrumental music plays softly.]
On the global stage stopping smallpox was important, but many in Bangladesh were just trying to make it to the next day.
Daniel Tarantola: No. 1 priority is food and food and food. And the second priority is food and food and food.
This was an area where survival was always in question.
Céline Gounder: That’s Daniel Tarantola.
He’s from France and arrived in the region with the mission of helping to eradicate smallpox, but he says the people in front of him needed help with many other things.
Besides hunger, some of the villages he visited were dealing with two epidemics: smallpox and cholera.
Daniel Tarantola: And we were not equipped to do anything but smallpox containment and smallpox eradication. By design or by necessity, we didn’t have the means to do anything much more than that.
Céline Gounder: Over the course of this season we’ve talked about big, complicated issues — like stigma and bias, distrust, or First World arrogance — that threatened to derail the smallpox eradication campaign. We’ve documented the public health workers who found a way around those roadblocks.
But sometimes the need is so big, so entrenched, that your inability to meet it can be demoralizing. I sometimes felt that during my own fieldwork: battling HIV and tuberculosis in Brazil and southern Africa, and during an Ebola outbreak in Guinea, West Africa.
Daniel Tarantola says in South Asia the best he could do was focus on the task at hand.
Daniel Tarantola: Meaning that you had to set up a program to eradicate smallpox or at least eliminate it from Bangladesh and at the same time not get … if I can use the word distracted, um, by other issues that prevailed in Bangladesh.
[Music fades out.]
Céline Gounder: Those were tough emotional realities for health workers and the people they wanted to care for.
But …
Daniel Tarantola: The level of resilience of this population is absolutely incredible given the number of challenges that they have had to survive.
Céline Gounder: One of the main ways people survived the upheaval in Bangladesh was by picking up and moving away from the things trying to kill them.
Remember how Shohrab fled to Dhaka after the cyclone?
Well, mass migration is a survival strategy — but one that can worsen disease.
When the cyclone refugees from Bhola landed in that under-resourced basti in Dhaka, all smallpox needed was an opportunity to spread.
[Solemn music begins playing.]
That opportunity came in 1975 when the Bangladeshi government decided to bulldoze the Bhola basti.
Daniel Tarantola says it was a bad idea.
Daniel Tarantola: We knew there was smallpox transmission in this particular area and therefore they should wait until the outbreak subsides before dismantling the shanties.
Céline Gounder: Government officials did not wait for the outbreak to subside. They bulldozed the basti anyway.
Daniel Tarantola: That resulted in a wide spread of smallpox.
Céline Gounder: Here’s environmental historian Iftekhar Iqbal again.
Iftekhar Iqbal: This eviction is considered one of the policy errors that led to the second wave of postwar smallpox.
Céline Gounder: In the wake of that eviction in 1975, thousands of people scattered. Some surely returned back home to Bhola.
[Music fades out.]
Céline Gounder: Public health’s failure — the government’s failure — to meet the basic need for safety, for food and housing, delayed the goal to stop the virus.
Shahidul Haq Khan, the Bangladeshi public health worker and granddad we met in Episode 4, says he learned that lesson over and over as he urged people to accept the smallpox vaccination.
Their frustration with him — and by extension public health — was clear.
[Shahidul speaking in Bengali fades under English translation.]
Shahidul Haq Khan: There was no rice in people’s stomachs, so what is a vaccine going to do? “You couldn’t bring rice? Why did you bring all this stuff?” That was the type of situation we had to deal with.
[Atmospheric music begins playing.]
Céline Gounder: What good is a vaccine when there is no rice?
Next up, I speak with Sam Tsemberis, founder of Pathways Housing First Institute. It’s an organization that advocates for meeting people’s basic needs first, so they’ll have the best shot at health.
But in the beginning, he found out convincing institutions was easier said than done:
Sam Tsemberis: I try to explain this rationale that I’m telling you, like people need housing first and then services. The hospital is like, “No, no, we’re in the hospital business. We’re not in the housing business.”
Céline Gounder: That’s after the break.
[Music fades to silence.]
Céline Gounder: One of my mentors was Dr. Paul Farmer, the legendary doctor and anthropologist whose work in Haiti was documented by Tracy Kidder in the book “Mountains Beyond Mountains.” Paul always pushed us to look beyond the symptoms to root causes. It’s a lesson we keep having to learn in public health again and again.
Sam Tsemberis is one of the first to apply it to homelessness. He’s the CEO of a nonprofit called the Pathways Housing First Institute. The organization promotes a model of addressing homelessness that begins with putting people into housing.
That idea seems pretty obvious. But back when Sam first started working on homelessness — in New York City in the 1980s — the prevailing model was more like a staircase. People had to work their way up to show they were ready for, or even worthy of, housing.
Sam Tsemberis: If you showed up applying for housing, you had to acknowledge you had a mental illness, you had to demonstrate that you were taking medication, and that you understood why you were taking medication. And you also had to have — if you had any history of alcohol or substance use, you also had to demonstrate a period of sobriety.
It was a very tough regimen to get into housing.
Céline Gounder: Sam said he quickly realized that wasn’t working, even though it was the only approach at the time.
Sam Tsemberis: I was working very hard to help people navigate that. I was doing street outreach. So, “Come come to the shelter, come to the hospital, come to a treatment program, a drop-in center,” hoping that they would engage and successfully make it up the stairs and get housing eventually.
And what began to emerge was that even if people were willing to take the first step — let’s say go to detox or go to the hospital — far too many people ended up returning to the street, which was, which was a signal that, you know, something was wrong with this system. It’s like, why are people falling back?
And the stories on the street were compelling. You know, people would say, “No, I don’t need to go to detox. What I need is a safe place to stay.”
Or, “Yeah, I’ve been diagnosed with schizophrenia, but … you know, and I still hear voices, but I don’t pay attention to them. Right now, I’m just cold, I’m tired, I’m hungry, I need a place to be safe. I need to go inside. That’s what I need first.”
And the repeated pleas for safety, security, a place to call home, from people that had tried and failed and tried and failed that staircase system is what compelled me to, you know, try something different, because what we were doing wasn’t working. And that’s when we started this housing-first approach.
Céline Gounder: Can you explain: What is that, and what’s its impact?
Sam Tsemberis: Housing-first is the answer to a question that we ask people. “OK, what is it that you want?” And people would inevitably say, “I want a place to live, isn’t it obvious?”
So our job as providers, then, was to figure out a way to have a program that we can get money for rent, and money for case management services, and give people who had previously no opportunity to get into housing on their own terms, and also offer the kind of clinical or social or emotional support that’s needed after people get housed.
Céline Gounder: So how did you pilot or how did you jump-start this effort? What did that look like?
Sam Tsemberis: So we ended up having to start our own nonprofit agency, apply for a grant, and we, with fingers crossed, we started to take people that were actively using and in some cases actively symptomatic and put them into apartments of their own and visit them a lot, not knowing how it would turn out.
What we found, much to our shock and surprise, very pleasant surprise, is that 85% of the people we housed, even in that first year, remained housed. And we thought, well, you know, we’re onto something here.
Céline Gounder: So instead of insisting that people be treated for addiction and mental health issues before they got into housing, you gave them housing first. And that was really sort of the measure of success.
Sam Tsemberis: Yes.
Céline Gounder: How successful was the program in treating addiction and mental health?
Sam Tsemberis: The addiction and mental health treatment outcomes were modestly better for the housing-first group that didn’t require to be in treatment. But you know, their treatment was no worse and a little better than the group that required treatment and sobriety.
And there, a measure called the overall quality of life, you know, like, how happy are you with living in the community, with your contacts with relatives, and so on. The group that went into housing first had a significantly higher quality of life than the treatment-first group.
Céline Gounder: So I know there are people out there who will say, Well, you didn’t solve their addiction issue or their mental health issue; how is that a success? How would you respond to that criticism?
Sam Tsemberis: This was never advertised as a program that cures addiction or cures mental illness. Recovery, in some ways, is not abstinence. Recovery, at least in the mental health business, is having a life in spite of your diagnosis.
The main thing is you’re no longer homeless. You know, you don’t have to be on the street until you’ve cured your illness. Because if that was the case, people would likely die on the street before they cured their illness because we don’t have cures for some of these illnesses.
Céline Gounder: So, Sam, Dr. Paul Farmer was a mentor of mine, actually, over the course of my training. And in Tracy Kidder’s biography of Paul, there’s a quote of one of Paul’s colleagues, Haitian colleagues, who says that, “Giving people medicine for tuberculosis and not giving them food is like washing your hands and drying them in the dirt.”
Sam Tsemberis: That is so on target for what all of these issues are about. I think of homelessness, actually, as a poorly named term for all of the systemic failures that people have faced in order to end up homeless.
We need to get, you know, take care of the emergency, put everyone in housing, but that’s sort of the beginning of the job. Then the real work starts to address the root causes that contribute and continue to increase the problem as opposed to just dealing with the symptom all the time.
[“Epidemic” theme music begins playing.]
Céline Gounder: Next time, on the series finale of “Epidemic: Eradicating Smallpox” …
Rahima Banu.
Redwan Ahmed: Rahima Banu.
Daniel Tarantola: Rahima Banu.
Iftekhar Iqbal: Rahima Banu.
Larry Brilliant: The last case …
Steve Jones: The last case …
Alan Schnur: The last case of variola major smallpox. I think this time we’ve got it.
Céline Gounder: “Eradicating Smallpox,” our latest season of “Epidemic,” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Just Human Productions.
Additional support provided by the Sloan Foundation.
This episode was produced by Taylor Cook, Zach Dyer, Bram Sable-Smith, and me.
Saidu Tejan-Thomas Jr. was scriptwriter for the episode.
Redwan Ahmed was our translator and local reporting partner in Bangladesh.
Our managing editor is Taunya English.
Oona Tempest is our graphics and photo editor.
The show was engineered by Justin Gerrish.
We had extra editing help from Simone Popperl.
Voice acting by Susheel C. and Pinaki Kar.
Music in this episode is from the Blue Dot Sessions and Soundstripe.
We’re powered and distributed by Simplecast.
If you enjoyed the show, please tell a friend. And leave us a review on Apple Podcasts. It helps more people find the show.
Follow KFF Health News on X (formerly known as Twitter), Instagram, and TikTok.
And find me on X @celinegounder. On our socials, there’s more about the ideas we’re exploring on our podcasts.
And subscribe to our newsletters at kffhealthnews.org so you’ll never miss what’s new and important in American health care, health policy, and public health news.
I’m Dr. Céline Gounder. Thanks for listening to “Epidemic.”
[“Epidemic” theme fades out.]
Credits
Taunya English
Managing Editor
Taunya is senior editor for broadcast innovation with KFF Health News, where she leads enterprise audio projects.
Zach Dyer
Senior Producer
Zach is senior producer for audio with KFF Health News, where he supervises all levels of podcast production.
Taylor Cook
Associate Producer
Taylor is associate audio producer for Season 2 of Epidemic. She researches, writes, and fact-checks scripts for the podcast.
Oona Tempest
Photo Editing, Design, Logo Art
Oona is a digital producer and illustrator with KFF Health News. She researched, sourced, and curated the images for the season.
Additional Newsroom Support
Lydia Zuraw, digital producer Tarena Lofton, audience engagement producer Hannah Norman, visual producer and visual reporter Simone Popperl, broadcast editor Chaseedaw Giles, social media manager Mary Agnes Carey, partnerships editor Damon Darlin, executive editor Terry Byrne, copy chief Chris Lee, senior communications officer
Additional Reporting Support
Swagata Yadavar, translator and local reporting partner in IndiaRedwan Ahmed, translator and local reporting partner in Bangladesh
Epidemic is a co-production of KFF Health News and Just Human Productions.
To hear other KFF Health News podcasts, click here. Subscribe to Epidemic on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Google, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 1 day ago
Multimedia, Public Health, Environmental Health, Epidemic, Podcasts, vaccines
An Arm and a Leg: John Green vs. Johnson & Johnson (Part 1)
Why is treating drug-resistant tuberculosis so expensive?
Pharmaceutical giant Johnson & Johnson’s patents on a drug called bedaquiline have a lot to do with it.
Why is treating drug-resistant tuberculosis so expensive?
Pharmaceutical giant Johnson & Johnson’s patents on a drug called bedaquiline have a lot to do with it.
In this episode of “An Arm and a Leg,” host Dan Weissmann speaks with writer and YouTube star John Green about how he mobilized his massive online community of “nerdfighters” to change the company’s policy and help make the drug more accessible.
But not every lifesaving drug has a champion with a platform as big as Green’s. Drug companies’ patents limit access to affordable treatments as well.
Weissmann also speaks with drug-patent expert Tahir Amin about how companies keep their drugs under patent for so long and the legal challenges that have been made to these policies around the world.
Dan Weissmann
Host and producer of "An Arm and a Leg." Previously, Dan was a staff reporter for Marketplace and Chicago's WBEZ. His work also appears on All Things Considered, Marketplace, the BBC, 99 Percent Invisible, and Reveal, from the Center for Investigative Reporting.
Credits
Emily Pisacreta
Producer
Adam Raymonda
Audio wizard
Ellen Weiss
Editor
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: John Green vs. Johnson & Johnson (Part 1)
Note: “An Arm and a Leg” uses speech-recognition software to generate transcripts, which may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the podcast.
Dan: Hey there — A little while ago, I got to talk with this widely-beloved dude.
John Green: My name is John Green, and I’m a writer and YouTuber.
Dan: John Green, writer, may be the most likely to ring a bell. His best-known book, “The Fault in Our Stars,” sold millions of copies and became a movie.
But before he was such a big deal as a writer, he and his brother Hank were a big deal on YouTube. And they still are. We’ll get into the details a little bit later.
But for now the thing to know is: Pretty recently, John Green got on the main YouTube channel he and his brother share, and started talking to hundreds of thousands of people about how the drug-maker Johnson & Johnson was using legalistic drug patent games to deny access to life saving tuberculosis medicine to millions of people in poor countries. And John Green wanted anybody listening to stand up and do something about it.
John Green: Tell your friends about this injustice, tell your family, tell the internet, because the only reason Johnson Johnson executives think they can get away with this is that they think we aren’t paying attention in the part of the world where they sell most of their products, their Band Aids, their Tylenol, their Listerine.
Dan: And a lot of the people who watch John Green’s videos– the community calls themselves “nerdfighters” — made a fair amount of noise.
And a few days later, Johnson & Johnson seemed to blink. The company issued a statement saying it would allow a cheaper generic version of that TB drug to be more widely distributed. Here’s John’s brother Hank from their next YouTube video.
Hank Green: And this happened in a week, John, you made a video on Tuesday, “it’s Friday right now! I’m really proud to be a part of this community I’m really proud to be your brother…”
Dan: I mean, that’s a super-fun story that we’re gonna get into: How a self-proclaimed nerd raised an internet posse to influence a global pharma giant to do something pretty decent-sounding.
We are definitely going to tell that story.
… But that story is just a first impression, because the whole thing is bigger and way more complicated.
As John Green would tell you –as he told me – he was adding his bit to a global movement — to advocates and lawyers in places like India, for instance, that have been doing the heavy, heavy lifting, for years.
And, of course, to understand any of this, we are going to have to get into how pharma companies use drug patents. And what it means.
And that is part of where this story comes home.
As John Green mentioned in his video, the story of this tuberculosis drug wouldn’t normally draw a lot of attention in the U.S. TB isn’t one of our top health issues.
But … the mechanisms at play with this tuberculosis drug – the patent games – are some of the same mechanisms that make so many drugs here so expensive: Drugs like Humira, and insulin, and pretty much everything else.
And here’s what’s actually the most interesting part:
Behind the first impression version of this story – nerds in the U.S. and their online posse for people in what’s called the Global South –
There’s a story about people and ideas from the Global South coming here to save the U.S. from our own messed-up drug patent system.
Because they’ve figured out that unless we save ourselves, they’re screwed too. That’s a LOT! And it’s gonna take us two episodes to connect all the dots.
You ready? Here we go…
This is An Arm and a Leg. A show about why health care costs so freaking much, and what we can maybe do about it. I’m Dan Weissmann. I’m a reporter, and I like a challenge. So our job on this show is to take one of the most enraging, terrifying, depressing parts of American life, and to bring you something entertaining, empowering, and useful.
And so, let’s start with John Green — YouTuber.
John and his brother Hank were among the people who invented the idea of being a professional quote-unquote “creator” on the internet – maybe kind of by accident, at first. But they were hugely successful at it.
In 2007, they started posting video messages to each other on this still-kinda-new website called YouTube. They thought a few hundred people might be interested, if they kept it up for a year.
Then Hank posted a song about waiting for the last Harry Potter book to come out.
Hank Green: [Singing] … I’m getting kind of petrified. What would Ron do if Hermione died or if Voldemort killed Hedwig, Just for yucks? …
Dan: It got a million views– which, early YouTube? That was huge. And they were off. Today, that original YouTube channel has more than three and a half million subscribers. Hank now manages more than a hundred full-time employees and a whole bunch of contractors.
And, you know, it’s impossible to sum up the thousands of videos they’ve shared.
Hank Green: Good morning, John. Today we’re gonna be making cinnamon toast two different ways.
John Green: Good morning, Hank, it’s Tuesday. So I need your help with the thing I’m working on. I need to learn some jokes, but not just any jokes.
Dan: But it’s fair to say digressive, ranty arguments are kind of a staple.
John Green: Good morning Hank, it’s Tuesday. I kind of hate Batman.
Hank Green: Good morning, John, you pretty much got Batman entirely wrong.
John Green: Batman is just a rich guy with an affinity for bats who’s playing out his insane fantasy of single-handedly ridding Gotham of crime. How is that heroic?
Hank Green: Of course, I know that Your video on Tuesday wasn’t really about Batman, it was just using Batman as a tool to say something.
Dan: The arguing may have something to do with why they call their community nerd-fighters.
But the idea is more that this is a community of nerds fighting for something. As they put it: fighting to ‘reduce the amount of suck in the world.’
Partly by producing things that can be amusing and sweet and thoughtful – but also by giving money to worthy causes and encouraging others to do the same.
Every year, since the beginning, they have hosted a kind of online telethon called the Project for Awesome.
John Green: Good morning, Hank. It’s Thursday, December 17th, 2009. Time for the Project for Awesome! Hooray! Oh! [crashing sound] Ow! Whoa! I got too excited about the awesome.
Dan: It is SUPER-interactive: People upload videos pitching their favorite charities, they vote, they give. They’ve raised more than 30 million dollars. And a lot of it has gone to an organization called Partners in Health, which provides incredibly effective health services in places like Haiti and Sierra Leone.
And just to indulge my own tendency to nerdy digression here: A book about Partners in Health and its founder, Paul Farmer, is one of my favorite books of all time.
It’s called Mountains Beyond Mountains, and when we finally do start a book club – and I haven’t forgotten making that suggestion here – I want to nominate it as one of our first picks.
Anyway, the Green brothers are huge supporters of Partners in Health. And then, three years ago, John started one of his weekly videos this way.
John Green: Good morning, Hank, it’s Tuesday. So over the next five years, our families are donating six and a half million dollars to Partners in Health Sierra Leone. Also we need your help…
Dan: And here’s where we get to tuberculosis. In the run up to that commitment, John Green visited Sierra Leone with his wife Sarah, and met some of the folks there from Partners in Health.
Here’s how he told the story to me. I’m not gonna interrupt:
John Green: On the last day, two of the physicians from Partners in Health, who we were visiting with said, “Hey, if it’s not a big deal to you, we’d really like to stop by this TB hospital on the way back to the capitol because we have a case we’re really concerned about.” And I said, “Yeah, of course, I’m not going to get in the way of actual doctoring.” So … But I, you know, I didn’t think much of it at the time.
So we get to this TB hospital. And immediately upon arriving, the doctors go off to do doctor stuff. And Sarah and I are just sort of sitting there in this little nine year old boy who tells me his name is Henry, which is my son’s name, at the time, my son was nine, kind of grabs me by the shirt and starts walking me around. And he takes me to the lab, shows me how to look into the microscope to see if a specimen has tuberculosis, introduces me to the lab technician, he takes me to the patient wards, he takes me to the kitchen where they make the food, he takes me all over the hospital, and then eventually I end up in the room with where the doctors are, and, uh, and the, and the kid has departed and I said, you know, “I just spent 30 minutes with an extraordinary child named Henry and he gave me a tour of the whole facility and I have no idea who he is. Is he somebody’s kid? Is he a doctor’s kid?” And one of the doctors said, “you know, that’s what I thought when I first got here, uh, about Henry because he does seem like that. And actually he’s the case that we’re so concerned about that we, um, needed to come here.” And he wasn’t nine. He was 16. He was just really stunted and emaciated by tuberculosis.
And, um, even though he was feeling pretty good at the time, the doctors knew that his treatment for multidrug resistant TB was failing, and that he needed access to a new cocktail that included bedaquiline, this drug that’s been around in the U.S. since 2013, but was, was at the time totally unavailable in Sierra Leone. And so, that was my introduction to TB and we were on our way to the airport and I said, “what’s gonna, what’s gonna happen to that kid?” And they were like, “it’s going to be a difficult path for him um, if we can’t get, if we can’t get the new treatment cocktail to him, he has a very low chance of survival.”
So that’s the beginning of the story for me, is meeting Henry.
Dan: I’m going to skip to the end of this part of the story: Henry’s OK. He’s alive, because he did get the drug cocktail that included Bedaquiline.
But, after that visit, John Green did not know that, and he started obsessing a bit about tuberculosis. Reading about it, thinking about it. And over the last year or so, he started occasionally sharing, making videos about TB. Some of them were fun, short, nerdy explainers.
John Green: What if I told you that tuberculosis gave us the cowboy hat?
John Green: How did TB reinvigorate women’s shoe fashions?
John Green: How did tuberculosis help New Mexico become a state? I’m so glad you asked.
Dan: But he also dug into the deeper reason he’d become obsessed with TB. Because it’s a surprisingly big deal, still.
John Green: It’s almost certain that in the last 2, 000 years, more people died just from tuberculosis than died from all wars combined.
And before you think like, oh, but that’s ancient history. No, more people died last year from tuberculosis than died in war, and every year going back to World War II
Dan: We fact checked that. He’s actually understating things. By a lot.
TB is a growing problem. In the middle of the 20th Century, new medicines took TB off the list of diseases that most people in the rich parts of the world had to worry about. But it never got wiped out.
And in less-rich parts of the world, where access to the best treatments was spottier, drug-resistant strains of TB developed and developed. But no new drugs came out– no drugs for drug-resistant TB.
Until bedaquiline, produced by Johnson & Johnson. The drug that did eventually help save Henry, the kid that John Green met in Sierra Leone.
But bedaquiline is expensive. So people in less-rich parts of the world often can’t get it. One study estimated that eight out of nine people who needed treatment with a drug like bedaquiline weren’t getting it.
And of course medicines stay expensive when they’re under patent protection: Once the patent on a drug expires, anybody can make and sell a generic version of the drug. Which, you know, competition, usually allows prices to fall.
And in one way, as John Green started making tuberculosis videos in 2022, it might have seemed like there was hope coming up:
Bedaquiline was patented in 2003. Patents last twenty years. By 2023, that patent would expire.
Except, not really. Because it turns out, patents on drugs have ways of living for way more than twenty years.
That’s next.
MIDROLL: This episode of An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News. That’s a nonprofit newsroom that covers health care in America. KFF Health News are amazing journalists – their work wins all kinds of awards every year – and I’m honored to work with them. We’ll have a little more information about KFF at the end of this episode.
Dan: So, let’s talk about drug patents and how they work– and why they don’t just last 20 years. And this is something my colleague Emily Pisacreta has been interested in for a long time.
Emily: It’s true. As I’ve said before on the show, I’m an insulin-dependent diabetic. If I can’t get insulin, I’m literally dead. And, insulin is super expensive. And insulins have became so expensive in part because of the kinds of patents on them – even though those patents are way more than twenty years old! ..
Dan: Right, so you’ve got a big interest in this question: How can a patent last more than twenty years?
Emily: And Dan, my answer to that question is a riddle: When is a patent not a patent?
Dan: OK, I give up. When is a patent not a patent.
Emily: When it’s 74 patents.
Dan: Yeah, this riddle is going to need some explaining.
Emily: Right. So, for a while I used an insulin called Lantus.It’s a once-a-day, long acting insulin made by the French company Sanofi. Sanofi first patented Lantus in 1994. So, that should mean it’s out of patent protection by 2014, right?
Dan: Uh-huh
Emily: Except, according to a report from a few years back, Sanofi actually filed for 74 patents on Lantus. And a lot of those patents were filed WAY after 1994. So, ONE patent from 1994 would’ve lasted till 2014. 74 patents could’ve lasted until 2031.
Dan: Ah, hence the very-specific answer for your riddle. I mean, I knew the principle – these insulin products have multiple patents on them, but 74 is … more than I’d imagined. What are 74 things you even COULD patent?
Emily: I mean, for Lantus, there are patents on formulations to improve stability. Like, all right … But there are also patents on the pen cartridge that Lantus comes in. And inside of that, a whole bunch of patents on the drive mechanisms, like the little plastic piston that lets you pick the right dose. These kinds of things.
Dan: OK. Now, I notice you said, those 74 patents COULD’ve lasted until 2031?
Emily: That’s right. As it turns out, in the case of Lantus, another drug maker actually did fight some of Sanofi’s later patents and won. But more often – and I mean a lot more often — simply filing for a patent is enough to keep generic makers away.
Dan: Sure. Who wants to spend money fighting a patent lawsuit when you could just y’know, manufacture some other drug?
Emily: Right. And of course this is not just insulin.
Tahir Amin: Oh, this is the standard practice. This happens with every drug.
Emily: That’s Tahir Amin – one of the big global experts on drug patents. Tahir the CEO and cofounder of a non-profit called I-MAK, which stands for …
Tahir Amin: The Initiative for Medicines Access and Knowledge. We work on building a more just and equitable access to medicine system.
Emily: The report that documented 74 patents on Lantus, that one insulinI used to use? Tahir’s group wrote it. And Tahir says this is business as usual, because it means big money.
Tahir Amin: Particularly when you’re talking about some of the drugs that you see in the US market, like for rheumatoid arthritis, these are worth billions of dollars.
Emily: Tahir’s group did a study on the 12 best-selling drugs in the U.S. They had an average of 131 patents each. If all the patents stick, that’s an average of 38 years of patent protection.
Dan: So maybe we can update your riddle:
When is a patent not a patent?
When it’s 131 patents.
Emily: Yeah, activists and experts call this kind of thing “patent thicketing” or “evergreening.”
Dan: I’ve been reading up on this too. Drug companies have their own name for this practice. They call it “life-cycle management.”
Emily: What a term of art. And actually bedaquiline, the TB drug,is a great example. In 2014, Tahir did what they call a “patent landscape” on bedaquiline, mapping all the different patents J&J filed around the world.
Tahir Amin: We all knew that with the advent of multiple drug resistance TB, we needed to know how we’re gonna get these drugs to the communities and the countries that need them most.
Emily: He identified a long list of patents J&J filed. And the most important being the original formula for the drug, set to expire in 2023, and the second most important patent was on something called the salt formulation for the drug.
Dan: Salt formulation.
Emily: Yep, and it’s kind of worth getting into the weeds here just for a second. Because this sort of thing is at the absolute heart of these drug patent games. When you develop a drug, the first step is finding a molecule that works in a test tube, that does the thing you want, like kills the germ. That gonna be the first patent, that molecule. But the molecule isn’t medicine.
Tahir Amin: You have to develop it, formulate it so that it’s actually more bioavailable, that it can get into the bloodstream and, and do whatever biological activity that it does. And this is classic organic chemistry stuff that is routine.
Emily: It’s routine. SO what he’s saying here, and other experts agree, by the way, identifying a salt formulation that can work as medicine isn’t where the innovation is. And most importantly, it doesn’t have to take a long time. But J&J didn’t apply for their secondary patent on it until a full four years after their initial patent.
Dan: I’ve started reading about “lifecycle management,” you know, what the pharma industry calls all this. And this is literally the playbook. One lawyer has advice about when to file this kind of secondary patent, here’s what he says, quote:
“You want to do this as late as possible, but before clinical trials. If Company X can hold off filing for two or three years during the drug discovery phase, it will buy more time on the back end of the patent’s term.”
Emily: Yep, and J & J waited four years. A little extra.
Dan: And we asked Johnson & Johnson: Hey, did you put off filing this secondary patent on the salt formulation to stretch out your patent rights? We haven’t heard back.
So: TB advocates kind of had their eye on July 2023. Because in July 2023 the original patent that Johnson & Johnson had on bedaquiline was set to expire. And the secondary patent, this sort of basic add on, was to become the next big obstacle.
So, back to John Green. He’s learning all this stuff about TB – including about how the secondary patent on bedaquiline is gonna keep clamping down access.
And he’s making all these TB videos, but it’s not like he has some kind of big plan:
John Green: But the, for me, You know, this is all I was thinking about. It was the first thing I thought about in the morning and the last thing I thought about before I went to sleep, is how did we end up in a world where the world’s deadliest infectious disease is largely ignored in the richest parts of the world?
Dan: And he was getting kind of discouraged.
John Green: I felt powerless before it. And this is one of the real lessons for me is that I felt like, well, what … what are we going to do? It’s not like Johnson & Johnson is going to abandon the idea of secondary patents, right?
Dan: He knew: secondary patents can be worth billions of dollars.
John Green: And so they’re not going to abandon these attempts to make their patents last longer than they should because they’re a for profit company. And I felt really … Yeah, I just felt powerless.
Dan: And then, earlier this year, something changed. It was not something that John Green, or an army of nerds could have done, or could’ve done anything about.
It was done by India’s patent office – responding to a legal challenge brought by two young women who had survived tuberculosis – one from India and one from South Africa.
It was based on legal work that our new pal Tahir Amin and others did in India almost twenty years ago.
And gave John Green an idea of how an army of nerdfighters could join this battle.
That’s next time, on An Arm and a Leg. Till then, take care of yourself.
This episode of An Arm and a Leg was produced by me, Dan Weissmann, and Emily Pisacreta – with help from Bella Cjazkowski, and edited by Ellen Weiss.
Daisy Rosario is our consulting managing producer.
Adam Raymonda is our audio wizard.
Our music is by Dave Winer and Blue Dot Sessions.
Gabrielle Healy is our managing editor for audience. She edits the First Aid Kit Newsletter.
Bea Bosco is our consulting director of operations.
Sarah Ballema is our operations manager.
An Arm and a Leg is produced in partnership with KFF Health News–formerly known as Kaiser Health News. That’s a national newsroom producing in-depth journalism about health care in America, and a core program at KFF — an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism.
And yes, you did hear the name Kaiser in there, and no: KFF isn’t affiliated with the health care giant Kaiser Permanente. You can learn more about KFF Health News at armandalegshow.com/KFF.
Zach Dyer is senior audio producer at KFF Health News. He is editorial liaison to this show.
Thanks to Public Narrative — that’s a Chicago-based group that helps journalists and nonprofits tell better stories — for serving as our fiscal sponsor, allowing us to accept tax-exempt donations. You can learn more about Public Narrative at www.publicnarrative.org.
And thanks to everybody who supports this show financially.
If you haven’t yet, we’d love for you to join us. The place for that is armandalegshow.com/support. That’s armandalegshow.com/support.
It helps us out a lot, so thanks for pitching in if you can! And thanks for listening!
“An Arm and a Leg” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Public Road Productions.
To keep in touch with “An Arm and a Leg,” subscribe to the newsletter. You can also follow the show on Facebook and Twitter. And if you’ve got stories to tell about the health care system, the producers would love to hear from you.
To hear all KFF Health News podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to “An Arm and a Leg” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts,Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 2 weeks ago
Health Care Costs, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, Public Health, An Arm and a Leg, Drug Costs, Podcasts
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': An Encore: 3 HHS Secretaries Reveal What the Job Is Really Like
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
This week, while KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” takes a break, here’s an encore of a favorite episode this year: Host and chief Washington correspondent Julie Rovner leads a rare conversation with the current and two former secretaries of Health and Human Services. Taped in June before a live audience at Aspen Ideas: Health, part of the Aspen Ideas Festival, in Aspen, Colorado, Secretary Xavier Becerra and two of his predecessors, Kathleen Sebelius and Alex Azar, talk candidly about what it takes to run a department with more than 80,000 employees and a budget larger than those of many countries.
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode, originally aired in June:
- The Department of Health and Human Services is much more than a domestic agency. It also plays a key role in national security, the three HHS secretaries explained, describing the importance of the “soft diplomacy” of building and supporting health systems abroad.
- Each HHS secretary — Sebelius, who served under former President Barack Obama; Azar, who served under former President Donald Trump; and Becerra, the current secretary, under President Joe Biden — offered frank, sobering, and even funny stories about interacting with the White House. “Anything you thought you were going to do during the day often got blown up by the White House,” Sebelius said. Asked what he was unprepared for when he started the job, Azar quipped: “The Trump administration.”
- Identifying their proudest accomplishments as the nation’s top health official, Azar and Becerra both cited their work responding to the covid-19 pandemic, specifically Operation Warp Speed, the interagency effort to develop and disseminate vaccines, and H-CORE, which Becerra described as a quiet successor to Warp Speed. They also each touted their respective administrations’ efforts to regulate tobacco.
- Having weathered recent debates over the separation of public policy and politics at the top health agency, the panel discussed how they’ve approached balancing the two in decision-making. For Becerra, the answer was unequivocal: “We use the facts and the science. We don’t do politics.”
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: An Encore: 3 HHS Secretaries on What the Job Is Really Like
[Editor’s note: This transcript, generated using transcription software, has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello “What the Health?” listeners. We’re taking this week off from the news while KFF holds an all-staff retreat. We’ll be back next week, but in the meantime, here’s an encore of one of our favorite episodes of the year — a chat with three Health and Human Services Secretaries. We’ll be back next week with our regular news roundup.
Hello and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, coming to you this week from the Aspen Ideas: Health conference in Aspen, Colorado. We have a cool special for you this week. For the first time, the current secretary of Health and Human Services sat down for a joint interview with two of his predecessors. This was taped before a live audience on Wednesday evening, June 21, in Aspen. So, as we like to say, here we go.
Hello. Good evening. Welcome to Aspen Ideas: Health. I’m Julie Rovner. I’m the chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News and also host of KFF Health News’ health policy podcast, “What the Health?,” which you are now all the audience for, so thank you very much. I’m sure these people with me need no introduction, but I’m going to introduce them anyway because I think that’s required.
Immediately to my left, we are honored to welcome the current U.S. secretary of Health and Human Services, Xavier Becerra. Secretary Becerra is the first Latino to serve in this post. He was previously attorney general of the state of California. And before that, he served in the U.S. House of Representatives for nearly 25 years, where, as a member of the powerful Ways and Means Committee, he helped draft and pass what’s now the Affordable Care Act. Thank you for joining us.
Next to him, we have Kathleen Sebelius, who served as secretary during the Obama administration from 2009 to 2014, where she also helped pass and implement the Affordable Care Act. I first met Secretary Sebelius when she was Kansas’ state insurance commissioner, a post she was elected to twice. She went on to be elected twice as governor of the state, which is no small feat in a very red state for a Democrat. Today, she also consults on health policy and serves on several boards, including — full disclosure — that of my organization, KFF. Thank you so much for being here.
And on the end we have Alex Azar, who served as HHS secretary from 2018 to 2021 and had the decidedly mixed privilege of leading the department through the first two years of the covid pandemic, which I’m sure was not on his to-do list when he took the job. At least Secretary Azar came to the job with plenty of relevant experience. He’d served in the department previously as HHS deputy secretary and as general counsel during the George W. Bush administration and later as a top executive at U.S. drugmaker Eli Lilly. Today, he advises a health investment firm, teaches at the University of Miami Herbert Business School, and sits on several boards, including the Aspen Institute’s. So, thank you.
Former Secretary of Health and Human Services Alex Azar: Thank you.
Rovner: So I know you’re not here to listen to me, so we’re going to jump in with our first question. As I’m sure we will talk about in more detail, HHS is a vast agency that includes, just on the health side, agencies including the Food and Drug Administration, the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The department has more than 80,000 employees around the country and throughout the world and oversees more than one and a half trillion dollars of federal funding each year. I want to ask each of you — I guess we’ll start with you — what is the one thing you wish the public understood about the department that you think they don’t really now?
Secretary of Health and Human Services Xavier Becerra: Given everything you just said, I wish people would understand that the Constitution left health care to the states. And so, as big as we are and as much as we do — Medicare, Medicaid, CHIP [Children’s Health Insurance Program], Obamacare — we still don’t control or drive health care. The only way we get in the game is when we put money into it. And that’s why people do Medicare, because we put money into it. States do Medicaid because we put money into it. And it became very obvious with covid that the federal government doesn’t manage health care. We don’t have a national system of health or public health. We have a nationwide system of public health where 50 different states determine what happens, and so one state may do better than another, and we’re out there trying to make it work evenhandedly for everyone in America. But it’s very tough because we don’t have a national system of public health.
Rovner: Secretary, what’s the thing that you wish people understood about HHS?
Former Secretary of Health and Human Services Kathleen Sebelius: Well, I agree with what Secretary Becerra has said, but it always made me unhappy that people don’t understand fully, I don’t think, the international role that HHS plays, and it is so essential to the safety and security and resilience of the United States. So we have employees across the world. CDC has employees in about 40 other countries, and helping to build health systems in various parts of the world, sharing information about how you stand up a health system, what a great hospital looks like. NIH does experiments and clinical trials all over the globe and is regarded as the gold standard. And we actually, I think, at HHS were able to do what they call soft diplomacy. And a lot of countries aren’t eager to have the State Department involved. They’re certainly not eager to see soldiers. Our trade policies make some people uncomfortable. But they welcome health professionals. They welcome the opportunity to learn from the United States. So it’s really a way often to get into countries and make friendships. And we need to monitor across the globe, as covid showed so well. When an outbreak happens someplace else in the world, we can’t wait for it to arrive on the border of the United States. Safety and security of American citizens really depends on global information exchange, a global surveillance exchange. The CDC has also trained epidemiologists in regions around the world so that they can be faster and share information. And I think too often in Congress, those line items for foreign trips, for offices elsewhere, people say, “Well, we don’t really need that. We should focus all our attention on America.” But I’ve always thought, if folks really understood how integral it is not just to our health security, but really national security, that we have these partnerships — and it’s, as I say, I think the best soft diplomacy and the cheapest soft diplomacy underway is to send health professionals all over the globe and to make those friendships.
Rovner: Do you think people understand that better since covid?
Sebelius: Maybe. You know, but some people reacted, unfortunately, to covid, saying, “Well, we put up bigger walls, and we” — I mean, no disease needs a passport, no wall stops things from coming across our borders. And I’m not sure that still is something that people take to heart.
Rovner: Secretary Azar, you actually have the most — in terms of years — experience at the department. What is it that people don’t know that they should?
Azar: So I probably would have led with what Secretary Becerra said about just how highly decentralized the public health infrastructure and leadership and decision-making is in the United States. I mean, it really — all those calls are made, and it’s not even just the 50 states. It’s actually 62 public health jurisdictions, because we separately fund a whole series of cities. I’ll concur in that. I’d say the other thing that people probably don’t understand, and maybe this is too inside baseball, is the secretary of HHS is, on the one hand, probably the most powerful secretary in the Cabinet and, on the other hand, also quite weak. So literally every authority, almost every authority, in the thousands and thousands of pages of U.S. statute that empower programs at HHS, say, “The secretary shall …” So the FDA, the CDC, CMS, all of these programs really operate purely by delegation of the secretary, because Secretary Becerra allows them to make decisions or to run programs. They are his authorities. And so the media, then, when the secretary acts, will … [unintelligible] … “How dare you,” you know, “how dare you be involved in this issue or that issue?” Well, it is legally and constitutionally Secretary Becerra’s job. And, on the other hand, you are supervising — it’s like a university, because you’re also supervising operating divisions that are global household brands. It is really like being a university president, for all that’s good and evil of that. You have to lead by consensus. You have to lead by bringing people along. You are not a dictator, in spite of what the U.S. statutes say. It’s very, very similar to that — that you, the secretary, is both powerful, but also has to really lead a highly matrixed, consensus-based organization to get things done.
Rovner: You’re actually leading perfectly into my next question, which is, how do you juggle all the moving pieces of this department? Just putting the agency heads in one room could fill a room this size. So tell us what sort of an average day for each of you would look like as secretary, if there’s such a thing as an average day.
Azar: Well, first, not an average administration, so take with a grain of salt my average day. So, interspersed among the two to five phone calls with the president of the United States between 7 a.m. and midnight, you know, other than that, um — I started every day meeting with my — you know, as secretary, you’ve got to have a team around you that’s not just your operating divisions, but I would start every morning — we would have just a huddle with chief of staff, deputy chief of staff, my head of public affairs. Often my general counsel would join that, my legislative leader. Just what’s going to hit us in the face today? Like, what are we trying to do, and what’s going to hit us in the face today? Just a situational awareness, every morning at about 8 a.m., quick huddle on that, and then diving into really the rhythm of the day of — I tried to drive — I use a book that I helped actually do some of the work on called “The 4 Disciplines of Execution,” just a tool of how do you focus and drive change in very complex organizations? So I tried to focus on four key initiatives that I spent as much of my time as secretary on leading and pushing on, and so I tried to make sure as much of my time was doing that. But then it’s reactive. You’re having to go to White House meetings constantly. You have to sign off on every regulation at the department. And so you’re in meetings just getting briefed and deciding approve or disapprove, so that rhythm constantly, and then add travel in, add evening commitments, add speeches. I’d say the biggest challenge you have as a leader in HHS is that first point of, focus, because you could be like a bobber on the water, just going with whatever’s happening, if you don’t have a maniacally focused agenda of, “I’ve got a limited amount of time. I’m going to drive change here. And if I don’t spend time every day pushing the department on this issue, being basically a burr in the saddle to make it happen, it won’t.” And you’ve just got to constantly be on that.
Rovner: Secretary Sebelius, what did your average day look like?
Sebelius: Well, I’m not going to repeat what Alex has just said. A lot of that goes on in the daily routine. First of all, I think all of us would be sent home the night before with a binder of materials — briefings for what you’re going to do the next day. So you may have 10 meetings, but each of those has a 20-page brief behind it. And then what the issues are, what the questions might be. So that’s your homework often that you’re leaving with at 7 or 8 at night. I like to run in the morning, and I would get up, read my schedule, and then go out and run on the [National] Mall because it sort of cleared my head. I’m proud of having — some of the folks may still be here — none of the detail ran before I started running, and my deal with them was, “I’m much older than you are, you know. We’re all going to run.”
Azar: They still —
Sebelius: Oh, here we go.
Azar: They still talk about it.
Sebelius: Well, one of them got to be a great marathon runner, you know. Can’t hurt. One guy started riding a bike, and I was like, “What are you doing?” I mean, if I fall, what are you going to do with the bike? I mean, am I going to carry it, are you going to carry it? I mean, who — anyway, so I started that way. You’d go then into the office. And one of the things that was not mentioned is HHS has an amazing, camera-ready studio, TV studio, that lots of other Cabinet agencies used. It has a setting that looks like “The View.” It has a stool that you can look in cameras, but two or three days a week we would do what they call “Around the Country.” So you would sit in a stool, and I’d be doing updates on the ACA or a pitch to enrollment or something about a disease, and you would literally have a cue card up that would say “Minneapolis, Andrea.” And I would say, “Good morning, Andrea.” And we would do a two-second spot in Minneapolis and they’d have numbers for me and then the camera would switch and it would be Bob in St. Louis. “Hello, Bob. How are you?” So that was a morning start that’s a little bit different. Anything you thought you were going to do during the day often got blown up by the White House: somebody calling, saying, you know, “The president wants this meeting,” “the vice president’s calling this.” So then the day gets kind of rearranged. And I think the description of who the key staff are around, but 12 operating agencies — any one of them could be a much more than full-time job. So just getting to know the NIH or, you know, seeing what CDC in Atlanta does every day, but trying to keep the leadership in touch, in tune, and make sure that — one of the things that, having been a governor and working with Cabinet agencies, that I thought was really important, is everybody has some input on everything. These are the stars, the agency heads. They know much more about health and their agencies than I would ever know. But making sure that I have their input and their lens on every decision that was made. So we had regular meetings where the flatter the organization, the better, as far as I’m concerned. They were all there and they gave input into policy decisions. But it is not a boring job and it’s never done. You just had to say at the end of the day, with this giant book, “OK, that’s enough for today. I’ll start again tomorrow, and there’ll be another giant book and here we go.”
Rovner: And your day, since you’re doing it now?
Becerra: I don’t know if it’s the pleasure or the bane of starting off virtually. Almost everything we did was via Zoom. I didn’t meet many of my team until months into the term because we were in the midst of covid. So we would start the days usually pretty early in the morning with Zooms and it would go one Zoom after the other. Of course, once we started doing more in-person activities, schedulers still thought they could schedule you pretty much one right after the other, and so they pack in as much as they can. I think all of us would say we’re just blessed to have some of the most talented people. I see Commissioner Califf from the FDA over there in the room. I will tell you, it’s just a yes … [applause] … . It’s a blessing to get to serve with these folks. They are the best in their fields. And you’re talking about some pretty critical agencies, FDA, NIH, CDC, CMS. I mean, the breadth, the jurisdiction, of CMS is immense. They do fabulous work. They are so committed. And so it makes it a lot easier. And then, of course, we all — we each have had — I have my group of counselors who are essentially my captains of the different agencies, and they help manage, because without that it would be near-impossible. And these are people who are younger, but my God, they’re the folks that every CEO looks for to sort of help manage an agency, and they’re so committed to the task. And so I feel like a kid in a candy store because I’m doing some of the things that I worked on so long when I was a member of Congress and could never get over the finish line. Now I get to sort of nudge everything over the finish line, and it really is helpful, as Alex said, to remind people that the statute does say, “The secretary shall … ,” not someone else, “the secretary shall … .” And so, at the end of the day, you get to sort of weigh it. And so it’s a pleasure to work with very talented, committed people.
Sebelius: Julie, I want to throw in one more thing, because I think this is back to what people don’t know, but it’s also about our days. There’s an assumption, when administrations change, the whole agency changes, right? Washington all changes. In a department like HHS, 90,000 employees scattered in the country and around the world, there are about 900 total political appointees, and they are split among all the agencies and the secretary’s office there. So you’re really talking about this incredibly talented team of professionals who are running those agencies and have all the health expertise, with the few people across the top that may try to change directions and put — but I think there’s an assumption that sort of the whole group sweeps out and somebody else sweeps in, and that really is not the case.
Rovner: So, as I mentioned, all three of you had relevant government experience before you came to HHS. Secretary Sebelius, you were a governor, so you knew about running a large organization. I want to ask all three of you, did you really understand what you were getting into when you became secretary? And is there some way to grow up to become HHS secretary?
Azar: I mean, yeah, I — yeah, I have no excuse. My first day, right after getting sworn in — the secretary has a private elevator that goes directly up to the sixth floor where the suite is, the deputy secretary’s office to the right, secretary to the left — my first day, I’m up, headed up with my security detail, and I get off and I walk off to the right. “Mr. Secretary, no, no, no. It’s this way.” Literally, it was like — it had been 11 years, but it was like coming home to me. I was literally about to walk into my old office as deputy secretary, and they show me to the secretary’s office. And I think for the first three months, I kept thinking Tommy Thompson or Mike Leavitt was going to walk in and say, “Get the hell out of my office.” And no, so it, and it was the same people, as Secretary Sebelius said. I knew all the top career people. I’d worked with them over the course of — in and out of government — 20 years. So it was very much a “coming home” for me. And it was many of the same issues were still the same issues. Sustainable growth rate — I mean, whatever else, it was all the same things going on again, except the ACA was new. That was a new nice one you gave me to deal with also. So, yeah, thank you.
Sebelius: You’re welcome. We had to have something new.
Rovner: What were you unprepared for when you took on this job?
Azar: Well, for me, the Trump administration.
Rovner: Yeah, that’s fair.
Azar: I, you know, had come out of the Bush administration. You’re at Eli Lilly. I mean, you know, you’re used to certain processes and ways people interact. And, you know, it’s just — it was different.
Sebelius: I had a pretty different experience. The rhythm of being a governor and being a Cabinet secretary is pretty similar. Cabinet agencies, working with the legislative process, the budget. So I kind of had that sense. I had no [Capitol] Hill experience. I had not worked on the Hill or served on the Hill, so that was a whole new entity. You’re not by protocol even allowed in the department until you’re confirmed. So I had never even seen the inside of the office. I mean, Alex talked about being confused about which way to turn. I mean, I had no idea [about] anything on the sixth floor. I hadn’t ever been there. My way of entering the department — I was President [Barack] Obama’s second choice. [Former South Dakota Democratic Senator] Tom Daschle had been nominated to be HHS secretary. And that was fine with me. And I said, “I’m a governor. I’ve got two more years in my term. I’ll join you sometime.” And then when Sen. Daschle withdrew, the president came back to me and said, “OK, how about, would you take this job if you’re able to get it?” And I said, “Yes, that’s an agency that’s interesting and challenging.” So I still was a governor, so I was serving as governor, flying in and out of D.C. to get briefings so I could go through hearings on this department that I didn’t know a lot about and had never really worked with, and then would go back and do my day job in Kansas. And the day that the Senate confirmation hearing began, a call came to our office from the White House. And this staffer said, “This governor? “Yes.” “President Obama has a plane in the air. It’s going to land at Forbes Air Force Base at noon. We want you on the plane.” And I said, you know, “That’s really interesting, but I don’t have a job yet. And I actually have a job here in Kansas. And here’s my plan. You know, my plan is I’m going to wait until I get confirmed and then I’ll resign and then I’ll get on the plane and then I’ll come to D.C.” And they said, “The president has a plane in the air, and it will land. He wants you on the plane.” First boss I’d had in 20 years. And I thought, “Oh, oh, OK. That’s a new thing.” So I literally left. Secretary Azar has heard this story earlier, but I left an index card on my desk in Kansas that said, “In the event I am confirmed, I hereby resign as governor.” And it was notarized and left there because I thought, I’m not giving up this job, not knowing if I will have another job. But halfway across the country I was confirmed and they came back and said — so I land and I said, “Where am I going?” I, literally, where — I mean, I’m all by myself, you know, it’s like, where am I going? “You’re going to the White House. The president’s going to swear you in.” “Great.” Except he couldn’t swear me in. He didn’t have the statutory authority, it turns out, so he could hold the Bible and the Cabinet secretary could swear me in. And then I was taken to the Situation Room, with somebody leading the way because I’d never been to the Situation Room. And the head of the World Health Organization was on the phone, the health minister from Canada, the health minister from Mexico, luckily my friend Janet Napolitano, who was Department of Homeland Security secretary — because we were in the middle of the H1N1 outbreak, swine flu, nobody knew what was going on. It was, you know, an initial pandemic. And everybody met and talked for a couple of hours. And then they all got up and left the room and I thought, woo-hoo, I’m the Cabinet secretary, you know, and they left? And somebody said to me later, well, “Does the White House find you a place to live?” I said, “Absolutely not. Nobody even asked if I had a place to stay.” I mean, it was 11 o’clock at night. They were all like, “Good night,” “goodbye,” “see ya.” So I luckily had friends in D.C. who I called and said, “Are you up? Can I come over? I’d like somebody to say, ‘Yay,’ you know, ‘we’re here.’” So that’s how I began.
Rovner: So you are kind of between these two. You have at least a little more idea of what it entailed. But what were you unprepared for in taking on this job?
Becerra: Probably the magnitude. Having served in Congress, I knew most of the agencies within HHS. I had worked very closely with most of the bigger agencies at HHS. As AG — Alex, I apologize — I sued HHS quite a —
Azar: He sued me a lot.
Becerra: Quite a few times.
Azar: Becerra v. Azar, all over the place.
Becerra: But the magnitude. I thought running the largest department of justice in the land other than the U.S. Department of Justice was a pretty big deal. But then you land and you have this agency that just stretches everywhere. And I agree with everything that Kathleen said earlier about the role that we play internationally. We are some of the best ambassadors for this country in the world because everyone wants you to help them save lives. And so it really helps. So the magnitude — it just struck me. When President Biden came in, we lost the equivalent of about — what, 13 9/11 twin tower deaths one day. Every day we were losing 11 twin tower deaths. And it hits you: You’ve got to come up with the answer yesterday. And so the White House is not a patient place, and they want answers quickly. And so you’re just, you’re on task. And it really is — it’s on you. You really — it smothers you, because you can’t let it go. And whether it was covid at the beginning or monkeypox last year, all of a sudden we see monkeypox, mpox, starting to pop up across the country. And it was, could this become the next covid? And so right away you’ve got to smother it. And the intensity is immediate. Probably the thing that I wasn’t prepared for as well, along with the magnitude, was, as I said, the breadth. Came in doing all these Zooms virtually to try to deal with the pandemic. But probably the thing that I had to really zero in on even more, that the president was expecting us to zero in on more, was migrant kids at the border and how you deal with not having a child sleep on a cement floor with an aluminum blanket and just trying to deal with that. It won’t overwhelm you necessarily, but — and again, thank God you’ve got just people who are so committed to this, because at any hour of the day and night, you’re working on these things — but the immensity of the task, because it’s real. And other departments also have very important responsibilities — clearly, Department of Defense, Department of State. But really it truly is life-and-death at HHS. So the gravity, it hits you, and it’s nonstop.
Rovner: All three of you were secretary at a time when health was actually at the top of the national agenda — which is not true. I’ve been covering HHS since 1986, and there have been plenty of secretaries who sort of were in the back of the administration, if you will, but you all really were front and center in all of these things. I want to go to sort of down the line. What was the hardest decision you had to make as secretary?
Becerra: Um …
Rovner: You’re not finished yet. I should say so far.
Becerra: I mean, there have been a lot of tough decisions, but, you know, when your team essentially prepares them up and you have all this discussion, but by the time it gets to me, it really has been baked really, really well. And now it’s sort of, White House is looking at this, we are seeing some of this, we’ve got to make a call. And again, Dr. Califf could speak to this as well. At the end of the day, the decisions aren’t so much difficult. It’s that they’re just very consequential. Do you prepare for a large surge in omicron and therefore spend a lot of money right now getting ready? Or do you sort of wait and see a little bit longer, preserve some of your money so you can use some of that money to do the longer-term work that needs to be done to prepare for the next generation of the viruses that are coming? Because once you spend the dollar, you don’t have it anymore. So you got to make that call. Those are the things that you’re constantly dealing with. But again, it just really helps to have a great team.
Sebelius: So I would say I was totally fortunate that the pandemic we dealt with was relatively short-lived and luckily far, far milder than what consumed both the secretaries to my left and right, and that was fortunate. A lot of our big decision areas were under the rubric of the Affordable Care Act and both trying to get it passed and threading that needle but then implementation. And I — you know, thinking about that question, Julie, I would say one of the toughest decisions — just because it provided a real clash between me and some of the people in the White House; luckily, at the end of the day, not the president, but — was really about the contraception coverage. Reproductive health had been something I’d worked on as a legislator, as governor. I felt very strongly about it. We’d fought a lot of battles in Kansas around it, and part of the Affordable Care Act was a preventive services benefit around contraceptive care. And that was going to be life-changing for a lot of women. And how broad it should be, how many battles we were willing to take on, how that could be implemented became a clash. And I think there were people in the administration who were hopeful that you could avoid clashes. So just make a compromise, you know, eliminate this group or that group, who may get unhappy about it. And at the end of the day, I was helped not just by people in the department, but mobilized some of my women Cabinet friends and senior White House women friends. And we sort of had a little bit of a facedown. And as I say, the president ended up saying, “OK, we’ll go big. We’ll go as big as we possibly can.” But I look back on that as a — I mean, it was a consequential decision, and it was implementation — not passing the rag in the first place, but implementing it. And it had a big impact. A big impact. It’s not one I regret, but it got a little a little tense inside, but what would be friendly meetings.
Azar: I’d use the divide Secretary Becerra talked about, which is that consequential versus hard decisions, that a lot — I think one could have a Hamlet-like character. I don’t. And so making the call when it comes to you wasn’t a terribly difficult thing, even. These are life-and-death decisions, but still yourself, you know your thought processes, you think it through, it’s been baked very well, you’ve heard all sides. You just have to make that call. So I’d maybe pivot to probably it’s more of a process thing. The hardest aspect for me was just deciding when do you fight and when do you not fight with, say, the White House? What hills do you die on? And where do you say, “Yeah, not what I would do, but I just have to live to fight another day.” Those were probably the toughest ones to really wrestle with.
Rovner: Was there one where you really were ready to die on the hill?
Azar: There were a lot. There were a lot. I mean, I’ll give you one example. I mean, I left a lot of blood on the field of battle just to try to outlaw pharmaceutical rebates, to try to push those through to the point of sale. I probably stayed to the end just to get that dag — because I, the opponents had left the administration and I finally got that daggone rule across the finish line right at the end. And that was something that I felt incredibly strongly that you could never actually change. I’ve lived inside that world. You could never change the dynamic of pharmaceutical drug pricing without passing through rebates to the point of sale. And I had so many opponents to get that done. It was a three-year constant daily battle that felt vindicated then to get it done. But that was a fight.
Rovner: And of course, I can’t help but notice that all of the things that you all are talking about are things that are still being debated today. None of them are completely resolved. Let’s turn this around a little bit. I wanted to ask you what you’re most proud of actually getting accomplished. Was it the rebate rule? That was a big deal.
Azar: For me, it has to be Operation Warp Speed. …[applause] … Yeah. Thank you. That was just — I mean, and I don’t want to take the credit. I mean, it was public-private. Mark Esper, this could not have happened without the partnership of the Defense Department, and it could not have happened without Mark Esper as secretary, because — I guarantee you, I’ve dealt with a lot of SecDefs in my career — and when the secretary of defense says to you, “Alex, you have the complete power and support of the Department of Defense. You just tell me what you need.” I haven’t heard those words before. And he was a partner and his whole team a partner throughout. And when you have the muscle of the U.S. military behind you to get something done, it is miraculous what happens. I mean, we were making hundreds of millions of doses of commercial-scale vaccine in June of 2020, when we were still in phase 2 clinical trials. We were just making it at risk. So we’re pumping this stuff out. And in one of the factories, a pump goes down. The pump is on the other side of the country on a train. The U.S. military shoots out a fighter jet, it gets out there, stops the train, pulls the train over, puts it on a helicopter, gets it on the jet, zips it off to the factory. We have colonels at every single manufacturing facility, and they get this installed. We’re up and running within 24 hours. It would have taken six to nine months under normal process. But the U.S. military got that done. So that for me was like just — the other two quick, one was banning flavored e-cigarettes. We got 25% reduction in youth use of tobacco in 12 months as a result of that. And then one of the great public health victories that this country had and the world had got ignored because it got concluded in June of 2020: We had the 11th Ebola outbreak. It was in the war zone in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. This was the pandemic I was really, really worried about. One-hundred seventy-four warring groups in the war zone in the eastern Congo. Got [WHO Director-General] Tedros [Adhanom Ghebreyesus] and [then-Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Anthony] Fauci and [then-CDC Director Robert] Redfield, and we went over and we went on the ground and we got that. And by June of 2020, that one got out, which was a miracle of global public health. I’m with Kathleen on that one; I think global public health is a key instrument of American power projection humanity around the world. Sorry to go so long.
Rovner: It’s OK. Your turn.
Sebelius: I think proudest is the ability to participate in the Affordable Care Act and push that over the finish line. And for me, it was a really personal journey. My father was in Congress and was one of the votes for Medicare and Medicaid to be passed, so that chunk of the puzzle. I was the insurance commissioner in Kansas when the Republican governor asked me to do the implementation of the Children’s Health Insurance Program. So I helped with that piece. I was on President [Bill] Clinton’s patient protection commission and ended up with a lot of that package in the Affordable Care Act. And then finally to work for and support and watch a president who basically said when he announced for president, “This is my priority in my first term: I want to pass a major health care bill.” And a lot of people had made that pledge. But 15 months later, there was a bill on his desk and he signed it, and we got to implement it. So that was thrilling. Yeah. And, I should tell you, then-Congressman Becerra was one of the wingmen in the House who I worked with carefully, who — there was no better vote counter than Nancy Pelosi, but by her side was this guy, part of her delegation, named Xavier Becerra, who was whipping the votes into place. So he played a key role in making sure that crossed the finish line.
Becerra: So I’m still here, so you’re going to have to —
Rovner: You can change your answer later.
Becerra: I need a bit of grace here, because I’m going to start with Warp Speed, because I bet no one here knows there’s no longer a Operation Warp Speed. It’s now called H-CORE. And the reason I’m very proud of that is because you don’t know that it’s now H-CORE. And what makes it such a good thing is that the Department of Defense no longer has any role in the protection of the American people from covid. It’s all done in-house at HHS. Everything used to be done essentially under the auspices of the Department of Defense, because they are just the folks that can get things done in 24 hours. We do that now, and it’s the operations that were begun a while back. Kathleen had them, Alex had them. Our ASPR, that’s our Preparedness and Response team, they’re doing phenomenal work, but you don’t know it, and you don’t know that H-CORE took to flight in the first year of the Biden administration. By December of 2021, Department of Defense had transferred over all those responsibilities to us, and we’ve been doing it since. But if you ask me what am I most proud of, it’s, I mean, there are more Americans today than ever in the history of this country who have the ability to pay for their own health care because they have health insurance, more than 300 million. Part of that is Obamacare; a record number, 16 and a half million Americans, get their insurance through the marketplaces, and we haven’t stopped yet. There are close to 700 million shots of covid vaccine that have gone into the arms of Americans. That’s never been done in the history of this country. Some of you are probably familiar with three digits, 988, at a time when Americans are … [applause] … 9 in 10 Americans would tell you that America is experiencing a mental health crisis, especially with our youth. And Congress got wise and said, instead of having in different parts of the country, based on region, you could call a phone number for a suicide lifeline, if you didn’t know the 10-digit number or what part of the country you were in, you were out of luck — today, all you have to do is dial 988. But as I said before, federal government doesn’t run mental health. It’s all done by the states. But President Biden is very committed to mental health. His budgets have surpassed any type of investments that have been called for by any president in history for mental health. And he was very committed to 988 to make sure it launched right. And so we have, by exponential numbers, put money into 988 to make sure every state was ready to have it launch. And so by July of 2022, we launched 988, and it is working so well that people are actually calling — actually, not just calling. We now have a text feature and a chat feature because surprise, surprise, young people prefer not to call; they actually prefer to text. And we have increased the number of Americans who are reaching out by over 2 million, which is great, but it’s also not great because it shows you how much Americans are hurting. So there’s so many things I can tell you that I feel very good about that we’re doing. We’re not done. We’re moving beyond on tobacco where Alex left. We’re now moving to ban menthol in cigarettes. Menthol cigarettes are the most popular brand of cigarettes in America. They hook you because of the menthol, and we’re moving to extract menthol. We’re moving to ban flavored cigars and cigarillos. And we may be on course to try to see if we can move to extract as much nicotine out of tobacco as possible before it becomes a product on the market for folks to smoke. So we’re doing a whole lot of things there. And obviously on vaping, e-cigarettes as well — and Dr. Califf could mention that. But I’ll say the thing I’m probably most proud of is that, out of all the government agencies in America, federal government agencies, HHS ranks No. 2 as the best place to work. And I will tell you we’re No. 2, because if we had the capacity to tell our workforce, we will fly you to the moon and back the way NASA does, we’d be No. 1. So that’s what I think I’m most proud of, is that people, as hard as we work them, still say, “Come work at HHS.”
Rovner: So all of you have mentioned these things that were really hard to do because of politics. And you’ve all talked about how some of these decisions, when they get to you, have been baked by your staff and, you know, they vetted it with every side. But I think the public feels like politics determine everything. And I think you all would like to think that policy is what helps determine most things. So, what’s the balance? How much does politics determine what gets done, and how much is it just the idea that this would be the right policy for the American public?
Azar: Mike Leavitt, who was the secretary when I was deputy secretary, he had a phrase, and I’ll probably mangle it, but it was essentially, “Facts for science, and politics for policy.” And it’s important to remember this distinction. So, facts are facts. You gather data. We are especially a data-generating agency. But on top of that are policy overlays. And there are choices that are made about how do you use those facts? What do those facts mean? What are the implications? The United States Constitution vests under Article 2 in the president of the United States to make those choices and, as his delegee, the secretary and the other appointed leaders of the department. So there’s often this notion of politicizing science, but it’s, are there facts? Facts are facts. You generate facts. But what are the implications for policymaking? And I don’t think there’s anything illegitimate — I think is completely appropriate, whether a Democratic or Republican president — that you look and you consider all kinds of factors. Because for instance, for me, I’m going to look at things very much from a public health lens as I assess things. The secretary of the treasury, the secretary of commerce, may bring a completely and important different perspective to the table that I don’t bring. And it’s completely legitimate that that gets factored on top of whatever I or other agencies bring in as fact. So I think it takes some nuance and that we often, frankly, in public discourse don’t catch nuance. Interesting. We don’t do nuance well.
Rovner: We don’t do nuance.
Sebelius: Well, I would agree with the description of the facts versus the policy. And policy does often have political flavors. I was fortunate to work for a president who said, meant, and said it over and over and over again that he would follow the science. And he did. And I had interesting political debates with people around him, on his team, about what should be done, “rewrite the guidance on this,” “do that,” “this is going to upset this group of people.” And he was very resilient and very consistent, saying, “What does the science say? What do the scientists say? That’s where we’re going,” on those areas which were really defined as giving advice to the American public on health issues, doing a variety of things. I mean, he was totally focused on listening to the science. The politics came in, as I think Secretary Azar said well, in some decisions that were brought to him, which really involved often battles between Cabinet agencies, and both were very legitimate. Again, we had pretty ferocious battles on food labeling and calorie counts and how much sodium would, should manufacturers be allowed to put in all of our manufactured goods. I’m sure many of you are aware, but, you know, American sodium levels are just skyrocketing. And it doesn’t matter what kind of salt you use at your table; it’s already baked into every loaf of bread, every pat of butter, every can of soup. And a lot of European countries have done a great job just lowering that. So the goods that are manufactured that you pick up in an EU country — Kellogg’s Corn Flakes has a third of the sodium that the Kellogg’s Corn Flakes that you get in Aspen does, just because that was a choice that those governments made. That’s a way to keep people healthy. But we would come at that through a public health perspective and argue strenuously for various kinds of limits. The Department of Agriculture, promoting farm products, supporting goods it exports, you know, not wanting to rile people up, would come in very strongly opposing a lot of those public health measures. And the president would make that call. Now, is that politics? Is it policy? Is it, you know, listening to a different lens? But he made the call and some of those battles we would win and some we would lose. But again, it’s a very legitimate role for the president to make. He’s getting input from leaders who see things through a different lens, and then he’s the ultimate decider and he would make the decision.
Becerra: So um, I’ve done politics and policy much longer than I’ve done the secretary role. And I will tell you that there is a big difference. We do do some policy, but for the most part we execute. The policy has been given to us by Congress, and to some degree the White House will help shape that policy. We have some role in policymaking because we put out guidances, and the guidance may look like it’s political or policy-driven, or we decide how much sodium might be allowed in a particular product and so forth. But for the most part, we’re executing on a policy that’s been dictated to the agencies by Congress. And I love that, because when I became AG in California, it really hit you how important it is to be able to marshal facts. And in HHS, it’s not just facts; it’s scientific facts. It is such a treat, as an attorney, to get to rely on scientific facts to push things like masking policy in the face of some hostility that went throughout the country to the point that our CDC director had to have security detail because she was getting death threats for having policies that would urge society to have masking policies for adults, for children. We do rely principally on science and the facts at HHS. Maybe folks don’t believe it, but I can put those on the table for you to take a look at. And perhaps the best example I can give you, and I don’t know if I’ll have time to connect the dots for you, because it’s a little esoteric: Title 42, which many of you got to hear about all the time in the news. Title 42 was a policy that was put in place under the Trump administration when we were in the height of the covid pandemic. We didn’t know what was causing covid, so we were trying to make sure that we protected ourselves and our borders. And so therefore, for public health reasons, we sort of closed our borders to the degree that we could, except for those who proved that they had gone through steps and so forth to be able to come in. Title 42 was used under the Trump administration, under the Biden administration to stop people from coming through our southern border. And there reached a point where, as things got better, our team said Title 42, which is health-based — it’s to stop the spread of contagion — was no longer the appropriate tool to use at the border, because we were letting people in the northern border, by plane, and all the rest. You just had to go through protocols. And so they were saying for health care reasons you go through protocols. But Title 42 is probably not the blanket way to deal with this issue, because it’s no longer simply a health care issue. We pushed really hard on that within the administration to the point where, finally, the administration said, “We’re pulling down Title 42.” Then the politics and the policy came in, from Congress saying, “Oh, how dare you take down Title 42? How dare you do that and let the flood of people come into this country?” Well, look, if you want to deal with people coming into the country, whatever way, then deal with our country’s borders through our immigration laws, not through our health care laws. Don’t try to make health care experts be the reason why you’re stopping someone from coming into this country. Stop hiding behind their skirt. And that’s where we went. And the administration took that policy as well. They took the policy. We then got sued and a court said, “No, you will not take down Title 42.” Ultimately, we think we were going to prevail in court, but ultimately, because we pulled down the public health emergency, things got better under covid, we no longer needed Title 42. But just again, to be clear, the women and men at HHS, we execute; we use the facts and the science. We don’t do politics.
Rovner: So we’ve been very serious.
Becerra: Not everybody believed me on that one.
Rovner: I know, I know. We’ve been very serious here for 50-some minutes. I want to go down the line. What’s the most fun thing you got to do as secretary or the coolest thing that you got to do as secretary?
Azar: Probably for me, it was the trip to the Congo, you know, being in the DRC, going to Uganda, going to Rwanda, flying on MONUSCO [United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo] U.N. peacekeeping forces; there was a Russian gunboat taking Tedros and Fauci and Redfield and me there into this war zone. I mean, it’s a once-in-a-lifetime — it’s sort of crazy — but once-in-a-lifetime thing that had impact.
Rovner: I don’t know that most people would call that fun.
Azar: I mean, it’ll be one of those great memories for life. Yeah. Yeah.
Sebelius: There were certainly some great trips and memorable experiences around health results in various parts of the world. Some martinis on the presidential balcony and looking at the Washington Monument — that’s pretty cool at night. But my, I think, personally kind of fun thing. I raised my children on “Sesame Street,” and they loved “Sesame Street” and the characters, and that was sort of part of the family routine. And so I got to go to “Sesame Street” and make a public service commercial with Elmo. I got to see Oscar’s garbage can. I met Snuffleupagus. But the Elmo commercial was to teach kids how to sneeze because, again, we were trying to spread good health habits. And so the script said — I mean, Elmo is right here and I’m here — and the script said, “OK, Elmo, we need to practice how to sneeze. So put your arm up and bend your elbow and sneeze into your arm.” And the puppet answered, “Elmo has no elbow.” That wasn’t part of the script. It was like, really? “And if Elmo does that, it will go like this: Achoo!” OK, so we flipped the script and Elmo taught me to sneeze. But that was a very memorable day to finally be on “Sesame Street.” It was very cool.
Rovner: OK, beat that.
Becerra: My team has not yet scheduled me to go on “Sesame Street,” so it’s going to be tough.
Sebelius: But just remember, Elmo has no elbows, if you get to go.
Becerra: I think probably what I will think of most is that I had had a chance to be in the White House and meet with the president in the Oval Office and the rest as a of member of Congress and so forth. When I went in, and it was because things were kind of dire with the kids at the border, and I knew I was going to get a whiplash after the meeting — it wasn’t fun at the time, but walking out, you know, it’s the kind of thing you think of, you know, “West Wing” kind of thing. You actually got the — president sat at the table, I was the guy that sat across from him. Everybody else was to the sides. You know, for a kid who was the first in his family to go to college, Dad didn’t get past the sixth grade, Mom didn’t come here till she was 18, when she came from Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico. It was pretty cool.
Rovner: So I could go on all night, but I think we’re not supposed to. So I want to ask you all one last question, which is, regardless of party affiliation, what is one piece of advice you would give to a successor as HHS secretary? Why don’t you start?
Becerra: Gosh, don’t start with me because I’m still there, so —
Rovner: All right.
Azar: I’m going to plagiarize and I’m going to give you the advice I wish Donna Shalala had given me before I took the job. But I would give it to any successor, which: She told me, “Do not take the job unless you have authority over personnel. Refuse to take the job unless you have control over who’s working, because people is policy and you have to be able to control the ethics, the tone, the culture of the organization. And people are that, and you need to have that authority.” And ever really since the Reagan administration, the Office of Presidential Personnel has just been this vortex of power that controls all political appointees at Cabinet departments. And I think if the president really wants you, you need to strike a deal that says, at a minimum, I’ve got veto or firing rights.
Sebelius: I think my advice would be the advice you give to a lot of employees who work in the private sector or public sector is, Make sure you’re aligned with the mission of the CEO, so in this case the president. I mean, don’t take the job because it’s cool and you’ll be a Cabinet member, because then it will be miserable. And with HHS, recognize the incredible assets across this agency. It is the most dazzling workforce I’ve ever had an opportunity to be with — the brightest people of all shapes, sizes, backgrounds, who taught me so much every day — and just cherish and relish your opportunity to be there, even for a short period of time. It’s miraculous.
Becerra: So I’d agree with Alex: Assemble your team. And it really is, because Kathleen mentioned it, it’s a very small group that actually you get to bring in, or even the administration gets to bring in, because most of the folks are civil service, so it’s only a fraction of the people that are going to be new. But your inner circle, the team that’s going to sort of be there and guide you and tell you what’s truth, they’ve got to be your team, because someone’s got to have your back. But I’d also say, know your reach, because as Kathleen said, this is not the Azar administration or the Sebelius administration, the Becerra administration. It’s the administration of the guy who got elected. And at the end of the day, the president gets to make the call. So as much as you may want to do something, you’ve got to know your reach.
Rovner: Well, I want to thank you all. I hope the audience had half as much fun as I did doing this. Let’s do it again next year. Thank you, all. OK, that’s our show for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, and particularly this week, to our producer, Francis Ying. Also as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can tweet me. I’m @jrovner. We’ll be back in your feed from Washington next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 2 weeks ago
COVID-19, Elections, Multimedia, Public Health, HHS, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Podcasts, vaccines
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': More Medicaid Messiness
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Federal officials have instructed at least 30 states to reinstate Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program coverage for half a million people, including children, after an errant computer program wrongly determined they were no longer eligible. It’s just the latest hiccup in the yearlong effort to redetermine the eligibility of beneficiaries now that the program’s pandemic-era expansion has expired.
Meanwhile, the federal government is on the verge of a shutdown, as a small band of House Republicans resists even a short-term spending measure to keep the lights on starting Oct. 1. Most of the largest federal health programs, including Medicare, have other sources of funding and would not be dramatically impacted — at least at first. But nearly half of all employees at the Department of Health and Human Services would be furloughed, compromising how just about everything runs there.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post, Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call, and Sarah Karlin-Smith of Pink Sheet.
Panelists
Sarah Karlin-Smith
Pink Sheet
Sandhya Raman
CQ Roll Call
Rachel Roubein
The Washington Post
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Officials in North Carolina announced the state will expand its Medicaid program starting on Dec. 1, granting thousands of low-income residents access to health coverage. With North Carolina’s change, just 10 states remain that have not expanded the program — yet, considering those states have resisted even as the federal government has offered pandemic-era and other incentives, it is unlikely more will follow for the foreseeable future.
- The federal government revealed that nearly half a million individuals — including children — in at least 30 states were wrongly stripped of their health coverage under the Medicaid unwinding. The announcement emphasizes the tight-lipped approach state and federal officials have taken to discussing the in-progress effort, though some Democrats in Congress have not been so hesitant to criticize.
- The White House is pointing to the possible effects of a government shutdown on health programs, including problems enrolling new patients in clinical trials at the National Institutes of Health and conducting food safety inspections at the FDA.
- Americans are grappling with an uptick in covid cases, as the Biden administration announced a new round of free test kits available by mail. But trouble accessing the updated vaccine and questions about masking are illuminating the challenges of responding in the absence of a more organized government effort.
- And the Biden administration is angling to address health costs at the executive level. The White House took its first step last week toward banning medical debt from credit scores, as the Federal Trade Commission filed a lawsuit to target private equity’s involvement in health care.
- Plus, the White House announced the creation of its first Office of Gun Violence Prevention, headed by Vice President Kamala Harris.
Also this week, Rovner interviews KFF Health News’ Samantha Liss, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month,” about a hospital bill that followed a deceased patient’s family for more than a year. If you have an outrageous or infuriating medical bill you’d like to send us, you can do that here.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: JAMA Internal Medicine’s “Comparison of Hospital Online Price and Telephone Price for Shoppable Services,” by Merina Thomas, James Flaherty, Jiefei Wang, et al.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: The Los Angeles Times’ “California Workers Who Cut Countertops Are Dying of an Incurable Disease,” by Emily Alpert Reyes and Cindy Carcamo.
Rachel Roubein: KFF Health News’ “A Decades-Long Drop in Teen Births Is Slowing, and Advocates Worry a Reversal Is Coming,” by Catherine Sweeney.
Sandhya Raman: NPR’s “1 in 4 Inmate Deaths Happen in the Same Federal Prison. Why?” by Meg Anderson.
Also mentioned in this week’s episode:
- KFF Health News’ “Diagnosis: Debt,” by Noam N. Levey and KFF Health News, NPR, and CBS staff.
- The New York Times’ “In Hospitals, Viruses Are Everywhere. Masks Are Not,” by Apoorva Mandavilli.
click to open the transcript
Transcript: More Medicaid Messiness
KFF Health News’ ‘What the Health?’Episode Title: More Medicaid MessinessEpisode Number: 316Published: Sept. 27, 2023
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping early this week, on Wednesday, Sept. 27, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might’ve changed by the time you hear this, so here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post.
Rachel Roubein: Good morning. Thanks for having me.
Rovner: Sandhya Raman of CQ Roll Call.
Sandhya Raman: Good morning.
Rovner: And Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: Later in this episode we’ll have my KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month” interview with Samantha Liss. This month’s bill is literally one that followed a patient to his family after his death. But first, the news. I want to start with Medicaid this week. North Carolina, which approved but didn’t fund its Medicaid expansion earlier this year, approved a budget this week that will launch the expansion starting Dec. 1. That leaves just 10 states that have still not expanded the program to, mostly, low-income adults, since the Affordable Care Act made it possible in, checks notes, 2014. Any other holdout states on the horizon? Florida is a possibility, right, Rachel?
Roubein: Yes. There’s only technically three states that can do ballot measures. Now North Carolina, I believe, was the first state to actually pass through the legislature since Virginia in 2018. A lot of the most recent states, seven conservative-leaning states, instead pursued the ballot measure path. In Florida, advocates have been eyeing a 2026 ballot measure. But the one issue in Florida is that they need a 60% threshold to pass any constitutional amendment, so that is pretty, pretty high and would take a lot of voter support.
Rovner: And they would need a constitutional amendment to expand Medicaid?
Roubein: A lot of the states have been going the constitutional amendment route in terms of Medicaid in recent years. Because what they found was some legislatures would come back and try and change it, but if it’s a constitutional amendment, they weren’t able to do that. But a lot of the holdout states don’t have ballot measure processes, where they could do this — like Alabama, Georgia, etc.
Raman: Kind of just echoing Rachel that this one has been interesting just because it had come through the legislature. And even with North Carolina, it’s been something that we’ve been eyeing for a few years, and that they’d gone a little bit of the way, a little bit of the way a few times. And it was kind of the kind of gettable one within the ones that hadn’t expanded. And the ones we have left, there’s just really not been much progress at all.
Rovner: I would say North Carolina, like Virginia, had a Democratic governor that ran on this and a Republican legislature, or a largely Republican legislature, hence the continuing standoff. It took both states a long time to get to where they had been trying to go. And you’re saying the rest of the states are not split like that?
Raman: Yeah, I think it’ll be a much more difficult hill to climb, especially when, in the past, we had more incentives to expand with some of the previous covid relief laws, and they still didn’t bite. So it’s going to be more difficult to get those.
Rovner: No one’s holding their breath for Texas to expand. Anyway, while North Carolina will soon start adding people to its Medicaid rolls, the rest of the states are shedding enrollees who gained coverage during the pandemic but may no longer be eligible. And that unwinding has been bumpy to say the least. The latest bump came last week when the Department of Health and Human Services revealed that more than half a million people, mostly children, had their coverage wrongly terminated by as many as 30 states. It seems a computer program failed to note that even if a parent’s income was now too high to qualify, that same income could still leave their children eligible. Yet the entire family was being kicked off because of the way the structure of the program worked. I think the big question here is not that this happened, but that it wasn’t noticed sooner. It should have been obvious — children’s eligibility for Medicaid has been higher than adults since at least the 1980s. This unwinding has been going on since this spring. How is this only being discovered now? It’s September. It’s the end of September.
Roubein: Yeah. I mean, this was something advocates who have been closely watching this have been ringing the alarm bells for a while, and then it took time. CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] had put something out, I believe it was roughly two weeks before they actually then had the roughly half a million children regain coverage — they had put out a, “OK, well, we’re exploring which states.” And lots of reporters were like, “OK, well which state is this an issue?” So yeah, the process seemed like it took some time here.
Rovner: I know CMS has been super careful. I mean, I think they’re trying not to politicize this, because they’ve been very careful not to name states, and in many cases who they know have been wrongly dropping people. I guess they’re trying to keep it as apolitical as possible, but I think there are now some advocates who worry that maybe CMS is being a little too cautious.
Karlin-Smith: Yeah, I think from the other side too, if you’ve talked to state officials, they’re also trying to be really cautious and not criticize CMS. So it seems like both sides are not wanting to go there. But I mean some Democrats in Congress have been critical of how the effort has gone.
Rovner: Yeah. And of course, if the government shuts down, as seems likely at the end of this week, that’s not going to make this whole process any easier, right? The states will still get to do what the states are doing. Their shutdown efforts, or their re-qualification efforts, are not federally funded, but the people at CMS are.
Karlin-Smith: Yeah, that’ll just throw another thorn in this as we’re getting very, very likely headed towards a shutdown at this point on the 27th. So I think that’ll be another barrier for them regardless. And I mean, most CMS money isn’t even affected by the yearly budget anyways because it’s mandatory funding, but that’ll be a barrier for sure.
Rovner: So, speaking of the government shutdown, it still seems more likely than not that Congress will fail to pass either any of the 12 regular spending bills or a temporary measure to keep the lights on when the fiscal year ends at midnight Sunday. That would lead to the biggest federal shutdown since 2013 when, fun fact, the shutdown was an attempt to delay the rollout of the Affordable Care Act. What happens to health programs if the government closes? It’s kind of a big confusing mess, isn’t it?
Roubein: Yeah, well, what we know that would definitely continue and in the short term is Medicare and Medicaid, Obamacare’s federal insurance marketplace. Medicaid has funding for at least the next three months, and there’s research developing vaccines and therapeutics that HHS, they put out their kind of contingency “What happens if there’s a shutdown?” plan. But there’s some things that the White House and others are kind of trying to point to that would be impacted, like the National Institutes of Health may not be able to enroll new patients in clinical trials, the FDA may need to delay some food safety inspections, etc.
Rovner: Sarah, I actually forgot because, also fun fact, the FDA is not funded through the rest of the spending bill that includes the Department of Health and Human Services. It’s funded through the agriculture bill. So even though HHS wasn’t part of the last shutdown in 2018 and 2019, because the HHS funding bill had already gone through, the FDA was sort of involved, right?
Karlin-Smith: Right. So FDA is lumped with the USDA, the Agriculture Department, for the purposes of congressional funding, which is always fun for a health reporter who has to follow both of those bills. But FDA is always kind of a unique one with shutdown, because so much of their funding now is user fees, particularly for specific sections. So the tobacco part of FDA is almost 100% funded by user fees, so they’re not really impacted by a shutdown. Similarly, a lot of drug, medical device applications, and so forth also are totally funded by user fees, so their reviews keep going. That said, the way user fees are, they’re really designated to specific activities.
So, where there isn’t user fees and it’s not considered a critical kind of public health threat, things do shut down, like Rachel mentioned: a lot of food work and inspections, and even on the drug and medical device side, some activities that are related that you might think would continue don’t get funded.
Rovner: Sandhya, is there any possibility that this won’t happen? And that if it does happen, that it will get resolved anytime soon?
Raman: At this point, I don’t think that we can navigate it. So last night, the Senate put out their bipartisan proposal for a continuing resolution that you would attach as an amendment to the FAA, the Federal Aviation [Administration] reauthorization. And so that would temporarily extend a lot of the health programs through Nov. 17. The issue is that it’s not something that if they are able to pass that this week, they’d still have to go to the House. And the House has been pretty adamant that they want their own plan and that the CR that they were interested in had a lot more immigration measures, and things there.
And the House right now has been busy attempting to pass this week four of the 12 appropriations bills. And even if they finished the four that they did, that they have on their plate, that would still mean going to the Senate. And Biden has said he would veto those, and it’s still not the 12. So at this point, it is almost impossible for us to not at least see something short-term. But whether or not that’s long-term is I think a question mark in all the folks that I have been talking to about this right now.
Rovner: Yeah, we will know soon enough what’s going to happen. Well, meanwhile, because there’s not enough already going on, covid is back. Well, that depends how you define back. But there’s a lot more covid going around than there was, enough so that the federal government has announced a new round of free tests by mail. And there’s an updated covid vaccine — I think we’re not supposed to call it a booster — but its rollout has been bumpy. And this time it’s not the government’s fault. That’s because this year the vaccine is being distributed and paid for by mostly private insurance. And while lots of people probably won’t bother to get vaccinated this fall, the people who do want the vaccine are having trouble getting it. What’s happening? And how were insurers and providers not ready for this? We’d been hearing the updated vaccines would be available in mid-September for months, Sarah. I mean they really literally weren’t ready.
Karlin-Smith: Yeah. I mean, it’s not really clear why they weren’t ready, other than perhaps they felt they didn’t need to be, to some degree. I mean, normally, I know I was reading actually because we’ve also recently gotten RSV [respiratory syncytial virus] vaccine approvals — normally they actually have almost like a year, I think, to kind of add vaccines to plans and schedules and so forth, and pandemic covid-related laws really shortened the time for covid. So they should have been prepared and ready. They knew this was coming. And people are going to pharmacies, or going to a doctor’s appointment, and they’re being told, “Well, we can give you the vaccine, but your insurance plan isn’t set up to cover it yet, even though technically you should be.” There seems like there’s also been lots of distribution issues where again, people are going to sites where they booked appointments, and they’re saying, “Oh, actually we ran out.” They’re trying another site. They’ve run out.
So, it’s sort of giving people a sense of the difference of what happens when sort of the government shepherds an effort and everybody — things are a bit simplified, because you don’t have to think about which site does your insurance cover. There is a program for people who don’t have insurance now who can get the vaccine for free, but again, you’re more limited in where you can go. There’s not these big free clinics; that’s really impacting childhood vaccinations, because, again, a lot of children can’t get vaccinated at the pharmacy. So I think people are being reminded of what normal looked like pre-covid, and they’re realizing maybe we didn’t like this so much after all.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s not so efficient either. All the people who said, “Oh, the private sector could do this so much more efficiently than the government.” And it’s like, we’re ending up with pretty much the same issues, which is the people who really want the vaccine are chasing around and not finding it. And I know HHS Secretary Becerra went and had this event at a D.C. pharmacy where he was going to get his vaccine. And I think the event was intended to encourage people to go get vaccinated, but it happened right at the time when the big front surge of people who wanted to get vaccinated couldn’t find the vaccine.
Karlin-Smith: I think that’s a big concern because we’ve had such low uptake of booster or additional covid shots over the past couple of years. So the people who are sort of the most go-getters, the ones who really want the shots, are having trouble and feeling a bit defeated. What does that mean for the people that are less motivated to get it, who may not make a second or third attempt if it’s not easy? We sort of know, and I think public health folks kind of beat the drum, that sort of just meeting people where they are, making it easy, easy, easy, is really how you get these things done. So it’s hard to see how we can improve uptake this year when it’s become more complicated, which I think is going to be a big problem moving forward.
Rovner: Yeah. Right. And clearly these are issues that will be ironed out probably in the next couple of weeks. But I think what people are going to remember, who are less motivated to go get their vaccines, is, “Oh my God, these people I know tried to get it and it took them weeks. And they showed up for their appointment and they couldn’t get it.” And it’s like, “It was just too much trouble and I can’t deal with it.” And there’s also, I think you mentioned that there’s an issue with kids who are too young to get the vaccine too, right?
Karlin-Smith: Right. Still, I think people forget that you have to be 6 months to get the vaccine. If you’re under 3, you basically cannot get it in a pharmacy, so you have to get it in a doctor’s office. But a lot of people are reporting online their doctor’s office sort of stopped providing covid vaccines. So they’re having trouble just finding where to go. It seems like the distribution of shots for younger children has also been a bit slower as well. And again, this is a population where just even primary series uptake has been a problem. And people are in this weird gap now where, if you can’t get access to the new covid vaccine but your kid is eligible, the old vaccine isn’t available.
So you’re sort of in this gap where your kid might not have had any opportunity yet to get a covid vaccine, and there’s nothing for them. I think we forget sometimes that there are lots of groups of people that are still very vulnerable to this virus — including newborn babies who haven’t been exposed at all, and haven’t gotten a chance to get vaccinated.
Rovner: Yeah. So this is obviously still something that we need to continue to look at. Well, meanwhile, mask mandates are making a comeback, albeit a very small one. And they are not going over well. I’ve personally been wearing a mask lately because I’m traveling later this week and next, and don’t want to get sick, at least not in advance. But masks are, if anything, even more controversial and political than they were during the height of the pandemic. Does public health have any ideas that could help reverse that trend? Or are there any other things we could do? I’ve seen some plaintiff complaints that we’ve not done enough about ventilation. That could be something where it could help, even if people won’t or don’t want to wear masks. I mean, I’m surprised that vaccination is still pretty much our only defense.
Karlin-Smith: I think with masks, one thing that’s made it hard for different parts of the health system and lower-level kind of state public health departments to deal with masks is that the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] recommendations around masking are pretty loose at this point. So The New York Times had a good article about hospitals and masking, and the kind of guidance around triggers they’ve given them are so vague. They kind of are left to make their own decisions. The CDC actually still really hasn’t emphasized the value of KN95 and N95 respirators over surgical masks. So I think it becomes really hard for those lower-level institutions to sort of push for something that is kind of controversial politically. And a lot of people are just tired of it when they don’t have the support of those bigger institutions saying it. And some of just even figuring out levels of the virus and when that should trigger masking.
It’s much harder to track nowadays because so much of our systems and data reporting is off. So, we have this sense we’re in somewhat of a surge now. Hospitalizations are up and so forth. But again, it’s a lot easier for people to make these decisions and figure out when to pull triggers when you have clear data that says, “This is what’s going on now.” And to some extent we’re … again, there’s a lot of evidence that points to a lot of covid going around now, but we don’t have that sort of hard data that makes it a lot easier for people to justify policy choices.
Raman: You just brought up ventilation and it took time, one, for some scientists to realize that covid is also spread through ultra-tiny particles. But it also took, after that, a while for the White House to pivot its strategy to stress ventilation measures in addition to masks, and face covering. So a lot of places are still kind of behind on having better ventilation in an office, or kind of wherever you’re going.
Rovner: Yeah, I mean, one would think that improving ventilation in schools would improve, not only not spreading covid, but not spreading all of the respiratory viruses that keep kids out of school and that make everybody sick during the winter, during the school year.
Roubein: I was going to piggyback on something Sarah said, which was about how the CDC doesn’t have clear benchmarks on when there should be a guideline for what is high transmission in the hospital for them to reinstate a mask mandate or whatever. But there’s also nuance to consider there. Within that there’s, is there a partial masking rule? Which is like: Does the health care staff have to wear them versus the patients? And does that have enough benefit on its own if it’s only required to one versus the other? I mean, I know that a lot of folks have called for more strict rules with that, but then there’s also the folks that are worried about the backlashes. This has gotten so politicized, how many different medical providers have talked about angst at them, attacks at them, over the polarization of covid? So there’s so many things that are intertwined there that it’s tough to institute something.
Karlin-Smith: I think the other thing is we keep forgetting this is not all about covid. We’ve learned a lot of lessons about public health that could be applicable, like you mentioned in schools, beyond covid. So if you’re in the emergency room, because you have cancer and you need to see a doctor right away. And you’re sitting next to somebody with RSV or the flu, it would also be beneficial to have that patient wearing a mask because if you have cancer, you do not need to add one of these infectious diseases on top of it. So it’s just been interesting, I think, for me to watch because it seemed like at different points in this crisis, we were sort of learning things beyond covid for how it could improve our health care system and public health. But for the most part, it seems like we’ve just kind of gone back to the old ways without really thinking about what we could incorporate from this crisis that would be beneficial in the future.
Rovner: I feel like we’ve lost the “public” in public health. That everybody is sort of, it’s every individual for him or herself and the heck with everybody else. Which is exactly the opposite of how public health is supposed to work. But perhaps we will bounce back. Well, moving on. The Biden administration, via the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the CFPB, took the first steps last week to ban medical debt from credit scores, which would be a huge step for potentially tens of millions of Americans whose credit scores are currently affected by medical debt. Last year, the three major credit bureaus, Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion, agreed not to include medical debt that had been paid off, or was under $500 on their credit reports. But that still leaves lots and lots of people with depressed scores that make it more expensive for them to buy houses, or rent an apartment, or even in some cases to get a job. This is a really big deal if medical debt is going to be removed from people’s credit reports, isn’t it?
Roubein: Yeah. I think that was an interesting move when they announced that this week. Because the CFPB had mentioned that in a report they did last year, 20% of Americans have said that they had medical debt. And it doesn’t necessarily appear on all credit reports, but like you said, it can. And having that financial stress while going through a health crisis, or someone in your family going through a health crisis, is layers upon layers of difficulty. And they had also said in their report that medical billing data is not an accurate indicator of whether or not you’ll repay that debt compared to other types of credit. And it also has the layers of insurance disputes, and medical billing errors, and all that sort of thing. So this proposal that they have ends up being finalized as a rule, it could be a big deal. Because some states have been trying to do this on a state-by-state level, but still in pretty early stages in terms of a lot of states being on board. So this can be a big thing for a fifth of people.
Rovner: Yeah, many people. I’m going to give a shout-out here to my KFF Health News colleague Noam Levey, who’s done an amazing project on all of this, and I think helped sort of push this along. Well, while we are on the subject of the Biden administration and money in health care, the Federal Trade Commission is suing a private equity-backed doctors group, U.S. Anesthesia Partners, charging anti-competitive behavior, that it’s driving up the price of anesthesia services by consolidating all the big anesthesiology practices in Texas, among other things. FTC Chair Lina Khan said the agency “will continue to scrutinize and challenge serial acquisitions roll-ups and other stealth consolidation schemes that unlawfully undermine fair competition and harm the American public.” This case is also significant because the FTC is suing not just the anesthesia company, but the private equity firm that backs it, Welsh, Carson, Anderson & Stowe, which is one of the big private equity firms in health care. Is this the shot across the bow for private equity and health care that a lot of people have been waiting for? I mean, we’ve been talking about private equity and health care for three or four years now.
Karlin-Smith: I think that’s what the FTC is hoping for. They’re saying not just that we’re going after anti-competitive practices in health care, that, I think, they’re making a clear statement that they’re going after this particular type of funder, which we’ve seen has proliferated around the system. And I think this week there was a report from the government showing that CMS can’t even track all of the private equity ownership of nursing homes. So we know this isn’t the only place where doctors’ practices being bought up by private equity has been seen as potentially problematic. So this has been a very sort of activist, I think, aggressive FTC in health care in general, and in a number of different sectors. So I think they’re ready to deliberate, with their actions and warnings.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s interesting. I mean, we mostly think, those of us who have followed the FTC in healthcare, which gets pretty nerdy right there, usually think of big hospital groups trying to consolidate, or insurers trying to consolidate these huge mega-mergers. But what’s been happening a lot is these private equity companies have come in and bought up physician practices. And therefore they become the only providers of anesthesia, or the only providers of emergency care, or the only providers of kidney dialysis, or the only providers of nursing homes, and therefore they can set the prices. And those are not the level of deals that tend to come before the FTC. So I feel like this is the FTC saying, “See you little people that are doing big things, we’re coming for you too.” Do we think this might dampen private equity’s enthusiasm? Or is this just going to be a long-drawn-out struggle?
Roubein: I could see it being more of a long-drawn-out struggle because even if they’re showing it as an example, there’s just so many ways that this has been done in so many kind of sectors as you’ve seen. So I think it remains to be seen further down the line as this might happen in a few different ways to a few different folks, and how that kind of plays out there. But it might take some time to get to that stage.
Karlin-Smith: I was going to say it’s always worth also thinking about just the size and budget of the FTC in comparison to the amount of private actors like this throughout the health system. So I mean, I think that’s one reason sometimes why they do try and kind of use that grandstanding symbolic messaging, because they can’t go after every bad actor through that formal process. So they have to do the signaling in different ways.
Raman: I think probably as we’ve all learned as health reporters, it takes a really long time for there to be change in the health care system.
Rovner: And I was just going to say, one thing we know about people who are in health care to make money is that they are very creative in finding ways to do it. So whatever the rules are, they’re going to find ways around them and we will just sort of keep playing this cat and mouse for a while. All right, well finally this week, a story that probably should have gotten more attention. The White House last week announced creation of the first-ever Office of Gun Violence Prevention to be headed by Vice President Kamala Harris. Its role will be to help implement the very limited gun regulation passed by Congress in 2022, and to coordinate other administration efforts to curb gun violence. I know that this is mostly for show, but sometimes don’t you really have to elevate an issue like this to get people to pay attention, to point out that maybe you’re trying to do something? Talk about things that have been hard for the government to do over the last couple of decades.
Raman: It took Congress a long time to then pass a new gun package, which the shooting in Uvalde last year ended up catalyzing. And Congress actually got something done, which was more limited than some gun safety advocates wanted. But it does take a lot to get gun safety reform across the finish line.
Rovner: I know. I mean, it’s one of those issues that the public really, really seems to care about, and that the government really, really, really has trouble doing. I’ve been covering this so long, I remember when they first banned gun violence research at HHS back in the mid-1990s. That’s how far back I go, that they were actually doing it. And the gun lobby said, “No, no, no, no, no. We don’t really want these studies that say that if you have a gun in the house, it’s more likely to injure somebody, and not necessarily the bad guy.” They were very unhappy, and it took until three or four years ago for that to be allowed to be funded. So maybe the idea that they’re elevating this somewhat, to at least wave to the public and say, “We’re trying. We’re fighting hard. We’re not getting very far, but we’re definitely trying.” So I guess we will see how that comes out.
All right, well that is this week’s news. Now, we will play my “Bill of the Month” interview with Sam Liss, and then we’ll come back with our extra credits. I am pleased to welcome to the podcast my KFF Health News colleague Samantha Liss, who reported and wrote the latest KFF Health News-NPR “Bill of the Month” installment. Welcome.
Liss: Hi.
Rovner: This month’s bill involves a patient who died in the hospital, right? Tell them who he was, what he was sick with, and about his family.
Liss: Yeah. So Kent Reynolds died after a lengthy hospital stay in February of 2022. He was actually discharged after complications from colon cancer, and died in his home. And his widow, Eloise Reynolds, was left with a series of complicated hospital bills, and she reached out to us seeking help after she couldn’t figure them out. And her and Kent were married for just shy of 34 years. They lived outside of St. Louis and they have two adult kids.
Rovner: So Eloise Reynolds received what she assumed was the final hospital bill after her husband died, which she paid, right?
Liss: Yeah, she did. She paid what she thought was the final bill for $823, but a year later she received another bill for $1,100. And she was confused as to why she owed it. And no one could really give her a sufficient answer when she reached out to the hospital system, or the insurance company.
Rovner: Can a hospital even send you a bill a year after you’ve already paid them?
Liss: You know what, after looking into this, we learned that yeah, they actually can. There’s not much in the way that stops them from coming after you, demanding more money, months, or even years later.
Rovner: So this was obviously part of a dispute between the insurance company and the hospital. What became of the second bill, the year-later bill?
Liss: Yeah. After Eloise Reynolds took out a yardstick and went line by line through each charge and she couldn’t find a discrepancy or anything that had changed, she reached out to KFF Health News for help. And she was still skeptical about the bill and didn’t want to pay it. And so when we reached out to the health system, they said, “Actually, you know what? This is a clerical error. She does not owe this money.” And it sort of left her even more frustrated, because as she explained to us, she says, “I think a lot of people would’ve ended up paying this additional amount.”
Rovner: So what’s the takeaway here? What do you do if you suddenly get a bill that comes, what seems, out of nowhere?
Liss: The experts we talked to said Eloise did everything right. She was skeptical. She compared, most importantly, the bills that she was getting from the hospital system against the EOBs that she was getting from her insurance company.
Rovner: The explanation of benefits form.
Liss: That’s right. The explanation of benefits. And she was comparing those two against one another, to help guide her on what she should be doing. And because those were different between the two of them, she was left even more confused. I think folks that we spoke to said, “Yeah, she did the right thing by pushing back and demanding some explanations.”
Rovner: So I guess the ultimate lesson here is, if you can’t get satisfaction, you can always write to us.
Liss: Yeah, I hate to say that in a way, because that’s a hard solution to scale for most folks. But yeah, I mean, I think it points to just how confusing our health care system is. Eloise seemed to be a pretty savvy health care consumer, and she even couldn’t figure it out. And she was pretty tenacious in her pursuit of making phone calls to both the insurance company and the hospital system. And I think when she couldn’t figure that out, and she finally turned to us asking for help.
Rovner: So well, another lesson learned. Samantha Liss, thank you very much for joining us.
Liss: Thanks.
Rovner: Hey, “What the Health?” listeners, you already know that few things in health care are ever simple. So, if you like our show, I recommend you also listen to “Tradeoffs,” a podcast that goes even deeper into our costly, complicated, and often counterintuitive health care system. Hosted by longtime health care journalist and friend Dan Gorenstein, “Tradeoffs” digs into the evidence and research data behind health care policies and tells the stories of real people impacted by decisions made in C-suites, doctors’ offices, and even Congress. Subscribe wherever you listen to your podcasts.
OK, we’re back. It’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org, and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Sarah, you were the first to choose this week, so you get to go first.
Karlin-Smith: Sure. I looked at a story in the Los Angeles Times, “California Workers Who Cut Countertops Are Dying of an Incurable Disease,” by Emily Alpert Reyes and Cindy Carcamo. Hopefully I didn’t mispronounce her name. They wrote a really fascinating but sad story about people working in an industry where they’re cutting engineered stone countertops for people’s kitchens and so forth. And because of the materials in this engineered product, they’re inhaling particles that is basically giving people at a very young age incurable and deadly lung disease. And it’s an interesting public health story about sort of the lack of protection in place for some of the most vulnerable workers. It seems like this industry is often comprised of immigrant workers. Some who kind of essentially go to … outside a Home Depot, the story suggests, or something like that and kind of get hired for day labor.
So they just don’t have the kind of power to sort of advocate for protections for themselves. And it’s just also an interesting story to think about, as consumers I think people are not always aware of the costs of the products they’re choosing. And how that then translates back into labor, and the health of the people producing it. So, really fascinating, sad piece.
Rovner: Another product that you have to sort of … I remember when they first were having the stories about the dust in microwave popcorn injuring people. Sandhya, why don’t you go next?
Raman: So my extra credit this week is from NPR and it’s by Meg Anderson. And it’s called “1 in 4 Inmate Deaths Happen in the Same Federal Prison. Why?” This is really interesting. It’s an investigation that looks at the deaths of individuals who died either while serving in federal prison or right after. And they looked at some of the Bureau of Prisons data, and it showed that 4,950 people had died in custody over the past decade. But more than a quarter of them were all in one correctional facility in Butner, North Carolina. And the investigation found out that the patients here and nationwide are dying at a higher rate, and the incarcerated folks are not getting care for serious illnesses — or very delayed care, until it’s too late. And the Butner facility has a medical center, but a lot of times the inmates are being transferred there when it was already too late. And then it’s really sad the number of deaths is just increasing. And just, what can be done to alleviate them?
Rovner: It was a really interesting story. Rachel.
Roubein: My extra credit, the headline is “A Decades-Long Drop in Teen Births Is Slowing, and Advocates Worry a Reversal Is Coming,” by Catherine Sweeney from WPLN, in partnership with KFF Health News. And she writes about the national teen birth rate and how it’s declined dramatically over the past three decades. And that, essentially, it’s still dropping, but preliminary data released in June from the CDC shows that that descent may be slowing. And Catherine had talked to doctors and other service providers and advocates, who essentially expressed concern that the full CDC dataset release later this year can show a rise in teen births, particularly in Southern states. And she talked to experts who pointed to several factors here, including the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade, intensifying political pushback against sex education programs, and the impact of the pandemic on youth mental health.
Rovner: Yeah. There’ve been so many stories about the decline in teen birth, which seemed mostly attributable to them being able to get contraception. To get teens not to have sex was less successful than getting teens to have safer sex. So we’ll see if that tide is turning. Well, I’m still on the subject of health costs this week. My story is a study from JAMA Internal Medicine that was conducted in part by Shark Tank panelist Mark Cuban, for whom health price transparency has become something of a crusade. This study is of a representative sample of 60 hospitals of different types conducted by researchers from the University of Texas. And it assessed whether the online prices posted for two common procedures, vaginal childbirth and a brain MRI, were the same as the prices given when a consumer called to ask what the price would be. And surprise. Mostly they were not. And often the differences were very large. In fact, to quote from the study, “For vaginal childbirth, there were five hospitals with online prices that were greater than $20,000, but telephone prices of less than $10,000. The survey was done in the summer of 2022, which was a year and a half after hospitals were required to post their prices online.” At some point, you have to wonder if anything is going to work to help patients sort out the prices that they are being charged for their health care. Really eye-opening study.
All right, that is our show for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our amazing engineer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can still find me at X, @jrovner. Sarah.
Karlin-Smith: I’m @SarahKarlin, or @sarahkarlin-smith.
Rovner: Sandhya.
Raman: @SandhyaWrites
Rovner: Rachel.
Roubein: @rachel_roubein
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 4 weeks ago
Courts, COVID-19, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Public Health, States, Guns, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Legislation, Podcasts, vaccines
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Countdown to Shutdown
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Health and other federal programs are at risk of shutting down, at least temporarily, as Congress races toward the Oct. 1 start of the fiscal year without having passed any of its 12 annual appropriations bills. A small band of conservative House Republicans are refusing to approve spending bills unless domestic spending is cut beyond levels agreed to in May.
Meanwhile, former President Donald Trump roils the GOP presidential primary field by vowing to please both sides in the divisive abortion debate.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Cohrs of Stat News, and Tami Luhby of CNN.
Panelists
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Rachel Cohrs
Stat News
Tami Luhby
CNN
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- The odds of a government shutdown over spending levels are rising. While entitlement programs like Medicare would be largely spared, past shutdowns have shown that closing the federal government hobbles things Americans rely on, like food safety inspections and air travel.
- In Congress, the discord isn’t limited to spending bills. A House bill to increase price transparency in health care melted down before a vote this week, demonstrating again how hard it is to take on the hospital industry. Legislation on how pharmacy benefit managers operate is also in disarray, though its projected government savings means it could resurface as part of a spending deal before the end of the year.
- On the Senate side, legislation intended to strengthen primary care is teetering under Bernie Sanders’ stewardship — in large part over questions about how to pay for it. Also, this week Democrats broke Alabama Republican Sen. Tommy Tuberville’s abortion-related blockade of military promotions (kind of), going around him procedurally to confirm the new chair of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
- And some Republicans are breaking with abortion opponents and mobilizing in support of legislation to renew the United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief — including the former president who spearheaded the program, George W. Bush. Meanwhile, polling shows President Joe Biden is struggling to claim credit for the new Medicare drug negotiation program.
- And speaking of past presidents, former President Donald Trump gave NBC an interview over the weekend in which he offered a muddled stance on abortion. Vowing to settle the long, inflamed debate over the procedure — among other things — Trump’s comments were strikingly general election-focused for someone who has yet to win his party’s nomination.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The Washington Post’s “Inside the Gold Rush to Sell Cheaper Imitations of Ozempic,” by Daniel Gilbert.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Politico’s “The Anti-Vaccine Movement Is on the Rise. The White House Is at a Loss Over What to Do About It,” by Adam Cancryn.
Rachel Cohrs: KFF Health News’ “Save Billions or Stick With Humira? Drug Brokers Steer Americans to the Costly Choice,” by Arthur Allen.
Tami Luhby: CNN’s “Supply and Insurance Issues Snarl Fall Covid-19 Vaccine Campaign for Some,” by Brenda Goodman.
Also mentioned in this week’s episode:
- The AP’s “Biden’s Medicare Price Negotiation Is Broadly Popular. But He’s Not Getting Much Credit,” by Seung Min Kim and Linley Sanders.
- Roll Call’s “Sanders, Marshall Reach Deal on Health Programs, but Challenges Remain,” by Jessie Hellmann and Lauren Clason.
CLICK TO EXPAND THE TRANSCRIPT
Transcript: Countdown to Shutdown
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, Sept. 21, at 9 a.m. because, well, lots of news this week. And as always, news happens fast, and things might well have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go. We are joined today via video conference by Tami Luhby of CNN.
Tami Luhby: Good morning.
Rovner: Rachel Cohrs of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Let’s get to some of that news. We will begin on Capitol Hill, where I might make a T-shirt from this tweet from Wednesday from longtime congressional reporter Jake Sherman: “I feel like this is not the orderly appropriations process that was promised after the debt ceiling deal passed.” For those of you who might’ve forgotten, many moons ago, actually it was May, Congress managed to avoid defaulting on the national debt, and as part of that debt ceiling deal agreed to a small reduction in annual domestic spending for the fiscal year that starts Oct. 1 (as in nine days from now). But some of the more conservative Republicans in the House want those cuts to go deeper, much deeper, in fact. And now they’re refusing to either vote for spending bills approved by the Republican-led appropriations committee or even for a short-term spending bill that would keep the government open after this year’s funding runs out. So how likely is a shutdown at this point? I would hazard a guess to say pretty likely. And anybody disagree with that?
Ollstein: It’s more likely than it was a week or two ago, for sure. The fact that we’re at the point where the House passing something that they know is dead on arrival in the Senate would be considered a victory for them. And so, if that’s the case, you really have to wonder what the end game is.
Rovner: Yeah, I mean it was notable, I think, that the House couldn’t even pass the rule for the Defense Appropriations Bill, which is the most Republican-backed spending bill, and the House couldn’t get that done. So I mean it does not bode well for the fate of some of these domestic programs that Republicans would, as I say, like to cut a lot deeper. Right?
Cohrs: Democrats are happy, I think, to watch Republicans flail for a while. I think we saw this during the speaker votes. Obviously, a CR [continuing resolution] could pass with wide bipartisan support, but I think there’s a political interest for Democrats going into an election year next year to lean into the idea of the House Republican chaos and blaming them for a shutdown. So I wouldn’t be too optimistic about Democrats billing them out anytime soon.
Rovner: But, bottom line, of course, is that a shutdown is not great for Democrats who support things that the government does. I mean, Tami, you’re watching, what does happen if there’s a shutdown? Not everything shuts down and not all the money stops flowing.
Luhby: No, and the important thing, unlike in the debt ceiling, potentially, was that Social Security will continue, Medicare will continue, but it’ll be very bothersome to a lot of people. There’ll be important things that … potentially chaos at airlines and food safety inspectors. I mean some of them are sometimes considered essential workers, but there’s still issues there. So people will be mad because they can’t go to their national parks potentially. I mean it’s different every time, so it’s a little hard to say exactly what the effects will be and we’ll see also whether this will be a full government shutdown, which will be much more serious than a partial government shutdown, although at this point it doesn’t look like they’re going to get any of the appropriation bills through.
Rovner: I was going to say, yeah, sometimes when they get some of the spending bills done, there’s a partial shutdown because they’ve gotten some of the spending bills done, but I’m pretty sure they’ve gotten zero done now. I think there’s one that managed to pass both the House and the Senate, but basically this would be a full shutdown of everything that’s funded through the appropriations process. Which as Tami points out, the big things are the Smithsonian and the National Zoo close, and national parks close, but also you can’t get an awful lot of government services. Meanwhile, the ill will among House Republicans is apparently rubbing off on other legislation. The House earlier this week was supposed to vote on a relatively noncontroversial package of bills aimed at making hospital insurance and drug prices more transparent, among other things. But even that couldn’t get through. Rachel, what happened to the transparency bill that everybody thought was going to be a slam-dunk?
Cohrs: Well, I don’t think everybody thought it was going to be a slam-dunk given the chaos that we saw, especially in the Democratic Caucus last week, where one out of three chairmen who work on health care in the House endorsed the package, but the other two would not. And they ran into a situation where, with the special rule that they were using to consider the House transparency package, they needed two-thirds vote to pass and they couldn’t get enough Democrats on board to pass it. And I think there were some process concerns from both sides that there was a compromise that came out right after August recess and it hadn’t been socialized properly and they didn’t have their ducks in a row in the Democratic side. But ultimately, I mean, the big picture for me I think was how hard it really is to take on the hospital industry. Because this was the first real effort I think from the House and it melted down before its first vote. That doesn’t mean it’s dead yet, but it was an embarrassment, I think, to everyone who worked on this that they couldn’t get this pretty noncontroversial package through. And when I tried to talk to people about what they actually oppose, it was these tiny little details about a privacy provision or one transparency provision and not with the big idea. It wasn’t ideological necessarily. So I think it was just a reflection on Congress has taken on pharma, they’re working on PBMs this year, but if they really do want to tackle hospital costs, which are a very big part of Medicare spending, it’s going to be a tough road ahead for them.
Rovner: As we like to point out, every single member of Congress has a hospital in their district, and they are quick to let their members of Congress know what they want and how they want them to vote on things. Before we move on, where are we on the PBM legislation? I know there was a whole raft of hearings this week on doing something about PBMs. And my inbox is full of people from both sides. “The PBMs are making drug prices higher.” “No, the PBMs are helping keep drug prices in check.” Where are we with the congressional effort to try and at least figure out what the PBMs do?
Cohrs: Yeah, I think there is still some disarray at this point. I would watch for action in December or whenever we actually have a conversation about government funding because some of these PBM bills do save money, which is the golden ticket in health care because there are a lot of programs that need to be paid for this year. So Congress will continue to debate those over the next couple of weeks, but I think everyone that I talk to is expecting potential passage in a larger package at the end of the year.
Rovner: So speaking of things that need to be paid for, the saga of Sen. Bernie Sanders and the reauthorization of some key primary care programs, including the popular community health center program, continues. When we left off last July, Sen. Sanders, who chairs the Senate Health, Education, Labor & Pensions Committee [HELP], tried to advance a bill to extend and greatly expand primary care programs without negotiating with his ranking Republican on the committee, Louisiana Sen. Bill Cassidy, who had his own bill to renew the programs. Cassidy protested and blocked the bill’s movement and the whole enterprise came to a screeching halt. Last week, Sanders announced he’d negotiated a bipartisan bill, but not with Cassidy, rather with Kansas Republican Roger Marshall, who chairs the relevant subcommittee. Cassidy, however, is still not pleased. Rachel, you’re following this. Sanders has scheduled a markup of the bill for later today. Is it really going to happen?
Cohrs: Well, I think things are on track and the thing to remember about a markup is it passes on a majority. So as long as Sen. Sanders can keep his Democratic members in line and gets Sen. Marshall, then it can pass committee. But I think there are some concerns that other Republicans will share with Sen. Cassidy about how the bill is paid for. There are a lot of ambitious programs to expand workforce training, have debt forgiveness, and address the primary care workforce crisis in a more meaningful way. But the list of pay-fors is a little undisciplined from what I’ve seen, I would say.
Rovner: That’s a good word.
Cohrs: Sen. Sanders is pulling some pay-fors from other committees, which he can’t necessarily do by himself, and they don’t actually have estimates from the Congressional Budget Office for some of the pay-fors that they’re planning to use. They’re just using internal committee math, which I don’t think is going to pass muster with Republicans in the full Senate, even if it gets through committee today. So I think we’ll see some of those concerns flare up. It could get ugly today compared with HELP markups of the past of community health center bills. And there are certainly some concerns about the application of the Hyde Amendment too, and how it would apply to some of this funding as it moves through the appropriations process.
Rovner: That’s the amendment that bans direct government funding of abortion, and there’s always a fight about the Hyde Amendment, which are reauthorizing these health programs. But I mean, we should point out, I mean this is one of the most bipartisanly popular programs, both the community health center program and these programs that basically give federal money to train more primary care doctors, which the country desperately needs. I mean, it’s something that pretty much everybody, or most of Congress, supports, but Cassidy has what, 60 amendments to this bill. I guess he’s really not happy. Cassidy who supports this in general just is unhappy with this process, right?
Cohrs: I think his concern is more that the legislation is half-baked, not that he’s against the idea of it. And Sen. Cassidy did sign on to a more limited House proposal as well, just saying, we need to fund the community health centers, we need to do something. This isn’t ready for prime time. We could see further negotiations, but the time is ticking for this funding to expire.
Rovner: Well, another program whose authorization expires at the end of the month is PEPFAR, the international AIDS/HIV program. It’s being blocked by anti-abortion activists among others, even though it doesn’t have anything to do with the abortion. And this is not just a bipartisan program, it’s a Republican-led program. Former President George W. Bush who signed it into law in 2003, had an op-ed this week pushing for the program in The Washington Post. Alice, you’ve been following this one. Is there any progress on PEPFAR?
Ollstein: Yes and no. There’s not a vote scheduled, there’s not a “Kumbaya” moment, but we are seeing some movement. I call it “Establishment Republican Strike Back.” You have some both on- and off-the-Hill Republicans really mobilizing to say, “Look, we need to reauthorize this program. This is ridiculous.” And they’re going against the anti-abortion groups and their allies on Capitol Hill who say, “No, let’s just extend this program just year by year through appropriations, not a reauthorization.” Which they say would rubber-stamp the Biden administration redirecting money towards abortion, which the Biden administration and everybody else denies is happening. And so we confirmed that Chairman Mike McCaul in the House and Lindsey Graham in the Senate are working with Democrats on some sort of reauthorization bill. It might not be the full five years, it might be three years, we don’t really know yet. But they think that at least a multiyear reauthorization will give the program some stability rather than the one-year funding patch that other House Republicans are mulling. So we’re going to see where this goes; obviously, it’s an interesting test for the influence of these anti-abortion groups on Capitol Hill. And my colleague and I also scooped that former President Bush, who oversaw the creation of this program, is quietly lobbying certain members, having meetings, and so we will see what kind of pull he still has in the party.
Rovner: Well, this was one of his signature achievements, literally. So it’s something that I know that … and we should point out, unlike the spending bills, the appropriation bills, if this doesn’t happen by Oct. 1, nothing stops, it’s just it becomes theoretically unauthorized, like many programs are, and it’s considered not a good sign for the program.
Luhby: One thing I also wanted to just bring up quickly, tangentially related to health care, but also showing how bipartisan programs are not getting the support that they did, is the WIC program, which is food assistance for women, infants and children, needs more money. Actually participation is up, but even before that, the House Republicans wanted to cut the funding for it, and that was going to be a big divide between them and the Senate. And now because participation is up, the Biden administration is actually asking for another $1.4 billion for the program. This is a program that, again, has always had support and has been fully funded, not had to turn people away. And now it’s looking that many women and small children may not be able to get the assistance if Congress isn’t able to actually fund the program fully.
Rovner: Yes, they’re definitely tied in knots. Well, Oct. 1 turns out to be a key date for a lot of health care issues. It’s also the day drugmakers are supposed to notify Medicare whether they will participate in negotiations for the 10 high-cost drugs Medicare has chosen for the first phase of the program that Congress approved last year. But that might all get blocked if a federal judge rules in favor of a suit brought by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, among others. Rachel, there was a hearing on this last week, where does this lawsuit stand and when do we expect to hear something from the judge?
Cohrs: So the judge didn’t ask any questions of the attorneys, so they were essentially presenting arguments that we’ve already seen previewed in some of the briefing materials. We are expecting some action by Oct. 1, which is when the Chamber had requested a ruling on whether there’s going to be a preliminary injunction, just because drugmakers are supposed to sign paperwork and submit data to CMS by that Oct. 1 date. So I think we are just waiting to see what the ruling might be. Some of the key issues or whether the Chamber actually has standing to file this lawsuit, given it’s not an actual drug manufacturer. And there was some quibbling about what members they listed in the lawsuit. And then I think they only addressed the argument that the negotiation program violated drugmakers’ due process rights, which isn’t the full scope of the lawsuit. It’s not an indicator of success really anywhere else, but it is important because it is the very first test. And if a preliminary injunction is issued, then it brings everything to a halt. So I think it would be very impactful for other drugmakers as well.
Rovner: Nobody told me when I became a health reporter that I was going to have to learn every step of the civil judicial process, and yet here we are. Well, while we are still on the subject of drug prices, a new poll from the AP and the NORC finds that while the public, Republicans and Democrats, still strongly support Medicare being able to negotiate the price of prescription drugs, President [Joe] Biden is getting barely any credit for having accomplished something that Democrats have been pushing for for more than 20 years. Most respondents in the survey either don’t think the plan goes far enough, because, as we point out, it’s only the first 10 drugs, or they don’t realize that he’s the one that helped push it over the finish line. This should have been a huge win and it’s turning out to be a nothing. Is that going to change?
Ollstein: It’s kind of a “Groundhog Day” of the Obamacare experience in which they pass this big, huge reform that people had been fighting for so long, but they’re trying to campaign on it when people aren’t really feeling the effects of it yet. And so when people aren’t really feeling the benefit and they’re hearing, “Oh, we’re lowering your drug prices.” But they’re going to the pharmacy and they’re paying the same very high amount, it’s hard to get a political win from that. The long implementation timeline is against them there. So there are some provisions that kick in more quickly, so we’ll have to see if that makes any kind of difference. I think that’s why you hear them talk a lot about the insulin price cap because that is already in effect, but that hits fewer people than the bigger negotiation will theoretically hit eventually. So it’s tough, and I think it leaves a vacuum where the drug industry and conservatives can fearmonger or raise concerns and say, “This will make drugs inaccessible and they won’t submit new cures for approval.” And all this stuff. And because people aren’t feeling the benefits, but they’re hearing those downsides, yeah, that makes the landscape even tougher for Democrats.
Luhby: This is very much the pattern that the Biden administration has had with a lot of its achievements or successes because it’s also not getting any credit for anything in the economy. The job market is relatively strong still, the economy is relatively strong. Yes, we have high inflation and high prices, even though that’s moderated, prices are still high, and that’s what people are seeing. Gas prices are now up again, which is not good for the administration. But they’re touting their Bidenomics, which also includes lowering drug prices. But generally polling shows, including our CNN polling shows, that people do not think the economy is doing well and they’re not giving Biden any credit for anything.
Cohrs: I think part of the problem is that … it’s different from the Affordable Care Act where it was health care, health care, health care for a very long time. This is lumped into a bill called the Inflation Reduction Act. I think it got lumped in with climate, got looped in with tax. And the media, we did our best, but it was hard to explain everything that was in the bill. And Medicare negotiation is complicated, it’s wonky, and I don’t know that people fully understood everything that was in the Inflation Reduction Act when it passed and they capitulated to Sen. [Joe] Manchin for what he wanted to name it. And so I think some of that got muddled when it first passed and they’re kind of trying to do catch-up work to explain, again, like Alice said, something that hasn’t gone into effect, which is a really tough uphill climb.
Rovner: This has been a continuing frustration for Democrats, which is that actually getting legislation done in Washington always involves some kind of compromise, and it’s always going to be incremental. And the public doesn’t really respond to things that are incremental. It’s like, “Why isn’t it bigger? Why didn’t they do what they promised?” And so the Republicans get more credit for stopping things than the Democrats get for actually passing things. Right. Well, let us turn to abortion. The breaking news today is that the Senate is finally acting to bust the blockade Alabama Republican Sen. Tommy Tuberville has had on military promotion since February to protest a Defense Department policy allowing service people leave to travel to other states for abortions. And Tuberville himself is part of this breakage, right, Alice? And it’s not a full breakage.
Ollstein: Right. And there have also been some interesting interviews that maybe raise questions on how much Tuberville understands the mechanics of what he’s doing because he said in an interview, “Oh, well, the people who were in these jobs before, they’ll just stay in it and it’s fine.” And they had to explain, “Well, statutorily, they can’t after a certain date.” And he seemed surprised by that. And now you’re seeing these attempts to go around his own blockade, and Democrats to go around his blockade. In part, for a while, Democrats were really not wanting to do that, schedule these votes, until he fully relented because they thought that would increase the pressure.
Rovner: They didn’t want to do it nomination by nomination for the big-picture ones because they were afraid that would leave behind the smaller ones.
Ollstein: Exactly. But this is dragging on so long that I think you’re seeing some frustration and desire to do something, even if it’s not fully resolving the standoff.
Rovner: And I’m seeing frustration from other Republicans. Again, the idea of a Republican holding up military promotions for six months is something that was not on my Republican Bingo card five years ago or even two years ago. I’m sure he’s not making a lot of his colleagues very happy with this. So on the Republican presidential campaign trail, abortion continues to be a subject all the candidates are struggling with — all of them, it seems, except former President Donald Trump, who said in an interview with NBC on Sunday that he alone can solve this. Francis, you have the tape.
Donald Trump: We are going to agree to a number of weeks or months or however you want to define it, and both sides are going to come together, and both sides, and this is a big statement, both sides will come together and for the first time in 52 years, you’ll have an issue that we can put behind us.
Rovner: OK. Well, Trump — who actually seemed all over the place about where he is on the issue in a fairly bald attempt to both placate anti-abortion hardliners in the party’s base and those who support abortion rights, whose votes he might need if he wants to win another election — criticized his fellow Republicans, who he called, “inarticulate on the subject.” I imagine that’s not going over very well among all of the other Republican candidates, right?
Ollstein: We have a piece up on this this morning. One, Trump is clearly acting like he has already won the primary, so he is trying to speak to a general audience, as you noted, and go after those votes in the middle that he may need and so he’s pitching this compromise. And we have a piece that the anti-abortion groups are furious about this, but they don’t really know what to do about it because he probably is going to be the nominee and they’re probably going to spend tens of millions to help elect him if he is, even though they’re furious with these comments he’s making. And so it’s a really interesting moment for their influence. Of course, Trump is trying to have it both ways, he also is calling himself the most pro-life president of all time. He is continually taking credit for appointing the justices to the Supreme Court who overturned Roe v. Wade.
Rovner: Which he did.
Ollstein: Exactly.
Rovner: Which is true.
Ollstein: Which he definitely did. But he is not toeing the line anymore that these groups want. These groups want him to endorse some sort of federal ban on abortion and they want him to praise states like Florida that have passed even stricter bans. He is not doing that. And so there’s an interesting dynamic there. And now his primary opponents see this as an opening, they’re trailing him in the polls, and so they’re trying to capitalize on this. [Gov. Ron] DeSantis and a bunch of others came out blasting him for these abortion remarks. But again, he’s acting like he’s already won the primary, he’s brushing it off and ignoring them.
Rovner: I love how confident he is though, that there’s a way to settle this — really, that there is a compromise, it’s just nobody’s been smart enough to get to it.
Ollstein: Well, he also, in the same interview, he said he’ll solve the Ukraine-Russia war in a day. So I mean, I think we should consider it in that context. It was interesting when I talked to all these different anti-abortion groups, they all said the idea of cutting some sort of deal is ludicrous. There is no magic deal that everybody would be happy about. If anything …
Rovner: And those on the other side will say the same thing.
Ollstein: Exactly. How could you watch what’s happened over the past year or 30 years and think that’s remotely possible? However, they did acknowledge that him saying that does appeal to a certain kind of voter, who is like, “Yeah, let’s just compromise. Let’s just get past this. I’m sick of all the fighting.” So it’s another interesting tension.
Rovner: Yeah. And I love how Trump always says the quiet part out loud, which is that this is not a great issue for Republicans and they’re not talking about it right. It’s like Republicans know this is a not-great issue for Republicans, but they don’t usually say that in an interview on national television. That is Trump, and this will continue. Well, finally this week I wanted to talk about what I am calling the dark underbelly of the new weight loss drugs. This is my extra credit this week. It’s a Washington Post story by Daniel Gilbert called “Inside the Gold Rush to Sell Cheaper Imitations of Ozempic.” It’s about the huge swell of sometimes not-so-legitimate websites and wellness spas selling unapproved formulations of semaglutide and tirzepatide — better known by their brand names Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro — to unsuspecting consumers because the demand for these diabetes drugs is so high for people who want to lose weight. The FDA has declared semaglutide at least to be in shortage for the people it was originally approved for, those with Type 2 diabetes. But that designation legally allows compounding pharmacies to manufacture their own versions, at least in some cases, except to quote the piece, “Since then, a parallel marketplace with no modern precedent has sprung up attracting both licensed medical professionals and entrepreneurs with histories ranging from regulatory violations to armed robbery.” Meanwhile, and this is coming from a separate story, both Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk, the manufacturers of the approved versions of the drugs, are suing companies they say are selling unapproved versions of their drug, including, in some cases, drugs that actually pretend to be the brand name drug that aren’t. This is becoming really a big messy buyer-beware market, right? Rachel, you guys have written about this.
Cohrs: It has. Yeah, my colleagues have done great coverage, including I think the lawsuit by manufacturers of these drugs who are seeing their profits slipping through their fingers as patients are turning to these alternatives that aren’t necessarily approved by the FDA. And I think there are also risks because we have seen some side effects from these medications; they range from some very serious GI symptoms to strange dreams. There’s just a whole lot going on there. And I think it is concerning that some patients are getting ahold of these medications, which are expensive if you’re buying them the traditional way. And again, for weight loss, I think some of these medications are still off-label, they’re not FDA-approved. So if they’re getting these without any supervision from a medical provider or somebody who they can ask when they have questions that come up and are monitoring for some of these other side effects, then I think it is a very dangerous game for these patients. And I think it’s just a symptom of this outpouring of interest and the regulators’, I think, failure to keep up with it. And there’s also some supply concerns. So I think it’s just this perfect storm of desperation from patients and the bureaucracy struggling to keep up.
Rovner: Yeah. One of the reasons I chose the story is I really feel like this is unprecedented. I mean, I suppose it could have been predicted because these drugs do seem to be very good at what they do and they are very expensive and very hard to get, so not such a surprise that not-so-honest people might spring up to try and fill the void. But it’s still a little bit scary to see people selling heaven only knows what to people who are very anxious to take things.
Luhby: And in related news, there are more doctors who are interested in obesity medicine now, so everyone is trying to cash in.
Rovner: Yeah, I mean, eventually I imagine this will sort itself out. It’s just that at the beginning when it’s so popular, although I will still … I keep thinking this, is the solution to really throw this much money at it or to try to figure out how to make these drugs cheaper? If it’s going to be such a societal good, maybe we should do something about the price. Anyway, that is my extra credit in this week’s news. Now we will take a quick break and then we’ll come back with the rest of our extra credits.
Hey, “What the Health?” listeners, you already know that few things in health care are ever simple. So, if you like our show, I recommend you also listen to “Tradeoffs,” a podcast that goes even deeper into our costly, complicated, and often counterintuitive health care system. Hosted by longtime health care journalist and friend Dan Gorenstein, “Tradeoffs” digs into the evidence and research data behind health care policies and tells the stories of real people impacted by decisions made in C-suites, doctors’ offices, and even Congress. Subscribe wherever you listen to your podcasts.
OK, we are back and it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it; we will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Tami, why don’t you go first this week?
Luhby: Sure. Well, this week I chose a good story by one of my colleagues, Brenda Goodman. It’s titled “Supply and Insurance Issues Snarl Fall Covid-19 Vaccine Campaign for Some.” And we’ve all been hearing this, I heard this from a friend of mine who’s a doctor, we know Cynthia Cox at KFF tweeted about this. And that even though the new vaccines are ready and the Biden administration has been pushing people to go get them, and many people are eager to get them, they’re not so easy to get. Either because drugstores are running out, that’s what happened to my friend. She went in and said there just wasn’t any supply available. Or for some other people, they’re supposed to be free for most Americans, but the insurance companies haven’t caught up with that yet. So they go in and either they’re denied or the pharmacy tells them that they have to pay potentially $200 for the vaccines. So the problem here is that there’s already an issue with getting vaccines and people getting vaccinated in this country and then putting up extra hurdles for them will only cause more problems and cause fewer people to get vaccinated because some people may not come back.
Rovner: Talk about something that should have been predictable. The distributors knew it was going to be available and pretty much when, and the insurance companies knew it was going to be available and pretty much when, and yet somehow they seem to have not gotten their act together when the predictable surge of people wanting to get the vaccine early came about. Alice, you wanted to add something?
Ollstein: Just anecdotally, the supply and the demand are completely out of whack. My partner is back home in Alabama right now and he was at a pharmacy where they were just wandering around asking random people, “Will you take the shot? Will you take the shot?” And a bunch of people were saying, “No.” And meanwhile, here in D.C., myself and everyone I know is just calling around wanting to get it and not able to. And so you think we’d have figured this out better after so many years of this.
Rovner: Well, I have an appointment for tomorrow. We’ll see if it happens. Rachel, why don’t you go next?
Cohrs: Sure. I chose a KFF Health News story by Arthur Allen, and the headline is “Save Billions or Stick With Humira? Drug Brokers Steer Americans to the Costly Choice.” And I just love a story where it’s off the news cycle a little bit and we see this big splashy announcement. And I think Arthur did a great job of following up here and seeing what actually was happening with formulary placement for Humira and the new biosimilars that just came on the market.
Rovner: Yep. Remind us what Humira is?
Cohrs: Oh, yeah. So it’s one of the most profitable drugs ever. The company that makes it, AbbVie, had created this big patent thicket to try to prevent it from competition for a very long time, but this year saw competition that had been on the market in Europe finally come online in the U.S. So again, a big change for AbbVie, for the market. But I think there was concern about whether people would actually switch to these new medications that have lower prices. But again, as it gets caught up and spit out of our drug supply chain, there are a whole lot of incentives that don’t necessarily result in the cheaper medication being prescribed. And Arthur found that Express Scripts and Optum, which are two of the three biggest pharmacy benefit managers, have the biosimilar versions of Humira at the same price as Humira. So that doesn’t really create a lot of incentive for people to switch. So I think it was just great follow-up reporting and we don’t really have a lot of visibility into these formularies sometimes. So I think it was a illuminating piece.
Rovner: Yeah. And the mess that is drug pricing. Alice.
Ollstein: So I also chose a great piece by my colleague Adam Cancryn and it’s called “The Anti-Vaccine Movement Is on the Rise. The White House Is at a Loss Over What to Do About It.” It’s part of a series we’re doing on anti-vax sentiment and its impacts. And this is just going into how the Biden administration really doesn’t have a plan for combating this, even as it’s posing a bigger and bigger public health threat. And some of their attempts to go after misinformation online were stymied in court and they also are struggling with not wanting to elevate it by debunking it — that that age-old tension of, is it better to just ignore it or is it better to combat it directly? A lot of this is also tying into RFK Jr.’s presidential bid and how much to acknowledge that or not. But the impact is that they’re not really taking this on, even as it’s getting worse and worse in the country.
Rovner: And I got a bunch of emails this week about the anti-vax movement spreading to pets — that people are now resisting getting their dogs and cats vaccinated. Seriously. I mean, it is a serious problem. Obviously, if people stop getting rabies vaccines, that could be a big deal. So something else to watch. All right. Well, I already did my extra credit. So that is it for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our indefatigable engineer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can tweet me; I’m still @jrovner on X and on Bluesky. Tami?
Luhby: You can tweet me at @Luhby. I sometimes check it still.
Rovner: Rachel.
Cohrs: I’m on X @rachelcohrs.
Rovner: Alice.
Ollstein: I’m @AliceOllstein.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 1 month ago
Elections, Health Care Costs, Health Industry, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, Public Health, Abortion, Biden Administration, Drug Costs, HIV/AIDS, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Podcasts, U.S. Congress, Women's Health
Watch: Thinking Big in Public Health, Inspired by the End of Smallpox
One of humanity’s greatest triumphs is the eradication of smallpox. Many doctors and scientists thought it was impossible to eliminate a disease that had been around for millennia and killed nearly 1 in 3 people infected. Smallpox is the first and only human disease to be wiped out globally.
KFF Health News held a web event Thursday that discussed how the lessons from the victory over smallpox could be applied to public health challenges today. The online conversation was led by Céline Gounder, physician-epidemiologist and host of “Eradicating Smallpox,” Season 2 of the Epidemic podcast.
Gounder was joined by:
Helene Gayle, a physician and epidemiologist, is president of Spelman College. She is a board member of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and past director of the foundation’s HIV, tuberculosis, and reproductive health program. She spent two decades with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention focusing primarily on HIV/AIDS prevention and global health.
William “Bill” Foege was a leader in the campaign to end smallpox during the 1970s. An epidemiologist and physician, Foege led the CDC from 1977 to 1983. He appears in the virtual learning series “Becoming Better Ancestors: Applying the Lessons Learned from Smallpox Eradication.” Foege is featured in Episode 2 of the “Eradicating Smallpox” docuseries.
click to open the transcript
Transcript: Thinking Big in Public Health, Inspired by the End of Smallpox
Note: This transcript was generated by a third-party site and may contain errors. Please use the transcript as a tool but check the corresponding audio before quoting the web event.
TRANSCRIPT
[The video trailer for season 2 of the Epidemic podcast, “Eradicating Smallpox,” begins to play]
Céline Gounder: Bangladesh 50 years ago, we were on the cusp of something big, something we had never done before. We were about to wipe smallpox off the planet. It’s one of humanity’s greatest triumphs. One public health has yet to repeat. I’m Dr. Celine Gounder. I’m a physician and epidemiologist.
This season of Epidemic, we’re going to India and Bangladesh, where smallpox made its last stand, to understand how health workers beat the virus. The question I’m asking, “How can we dream big in public health again?” From KFF Health News and just human productions, Epidemic, eradicating smallpox. Listen wherever you get your podcasts.
[Video trailer ends]
Céline Gounder: Good morning everyone, and thanks for joining us today. I’m Dr. Celine Gounder. I’m editor-at-large for Public Health at KFF Health News and I’m the host of the Epidemic Podcast. In today’s conversation, we’re going to talk about lessons to be learned from the eradication of smallpox and how those can be applied to public health challenges today. The eradication of smallpox is one of humanity’s greatest triumphs. Many doctors and scientists thought it was impossible to eliminate a disease that had lasted for millennia and killed nearly one in three people infected. Smallpox remains the first and only human disease to be wiped out globally.
Just a few logistical details before we get started. The briefing is being recorded and the link to the recorded version will be emailed to everyone later today. We also have ASL interpretation available. To access it, please click on the globe icon in your Zoom control panel and select ‘American Sign Language.’ A screen will appear and you will be able to view the interpreter. Questions should be entered using the Q&A function on Zoom and can be sent in during the discussion.
I’d like to move forward with introducing our panelists today. Dr. Bill Foege is an epidemiologist and physician and was a leader in the campaign to end smallpox during the 1970s. Foege is featured in episode two of the Eradicating Smallpox docuseries, and he’s also featured in the Nine Lessons series produced by the Becoming Better Ancestors Project. The Nine Lessons, available at ninelessons.org, is a virtual learning series about how the lessons from smallpox eradication could be applied to COVID and other public health and societal challenges.
Also, joining us today is Dr. Helene Gayle, who’s also an epidemiologist and physician. She’s the president of Spelman College. She’s also a board member of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and past director of the Foundation’s program on HIV, Tuberculosis and reproductive health. She spent two decades with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, focusing primarily on HIV AIDS prevention and Global Health.
So welcome and thank you for joining us today, Bill and Helene. I’d like to start with talking about some of the challenges we face in science communication. And as we’ve seen during the COVID pandemic, one of the big challenges is balancing reassurance with uncertainty. And before I ask you my questions, I’m going to play a clip of Dr. Tony Fauci speaking about this as part of the Nine Lessons series. So let’s give that a listen.
[Video clip from the Nine Lessons series begins to play]
Tony Fauci: If you have a static situation with nothing changing and you get one opinion one day, and then a week later you change, that’s flip-flopping. When you have a dynamic situation that’s evolving week to week and month to month, as a scientist, to be true to yourself and to be true to the discipline of science, you have to collect data as the situation evolves, which almost invariably will necessitate your changing policy, changing guidelines, changing opinion. And that’s exactly what happened with things like mask wearing. We didn’t know until weeks and weeks into the outbreak that a lot of the transmission was by people who were without symptoms. It was that that made the CDC and all of us say, “We really don’t need to be wearing masks.” As soon as we found out that, A, there was no shortage, B, we were getting good data, that outside of the hospital setting masks did work, and three, we found out that 50% of the infections were transmitted from someone who had no symptoms. When you put all those three things together, then the science tells us everybody should be wearing a mask.
[Video clip ends]
Céline Gounder: Bill, how did this play out in the smallpox eradication program, specifically this idea of scientific certainty, uncertainty, and science communication?
Bill Foege: This is actually a balance that goes far beyond public health and medicine and almost everything we do. And on the one hand, you have to have enough certainty in order to get other people to follow you. There’s a book by Gary Wills on Leadership, and it’s entitled Certain Trumpets. He takes this from the Bible verse that says, “If you hear an uncertain trumpet, who would gird for battle?”
So you have to have enough certainty. The other side of that though is Richard Feynman, the physicist who said, “Certainty is the Achilles heel of science.” If we believe something is true, we stop looking for other answers to why this is happening. And I think in smallpox, we always tried to present certainty in what we were doing. And all the time we worried about what could go wrong, what if we lose political support? I didn’t see HIV coming, but boy, if I had, that would’ve been a big problem to deal with.
Céline Gounder: Helene, don’t you think public health officials should still be confident in expressing, particularly in an emergency, what we know and their recommendations for managing a public health crisis, and how do you balance that confidence and reassurance with the lack of certainty?
Helene Gayle: So I think, and building on some of the things that Bill said, I think part of it is building the confidence in the communicator. And I think one of the things, and I point to Tony Fauci, is one of those people who I think Americans developed a sense of confidence with him because of his willingness and ability to say when we were wrong and what we know and when we knew it. And so I think recognizing that a lot of this is about building trust and building trust in the message as well as in the messenger. I think that’s where some of the ability to be confident, letting people know that you’re trying to give them the information as soon as you have it, but also being honest that this is evolving.
A message is just a slice in time. And I think it’s important that we remember that we’re creating a narrative every time we open our mouths and thinking about what’s the narrative that we’re creating and being consistent in that narrative. So I think the consistency, building that trust, being able to say what you know and what you don’t know is what really I think builds the confidence in the messages. I think what we saw through this pandemic as well, the COVID pandemic as well as past, are people who are unwilling to admit what they know and what they don’t know, unwilling to go back and explain why we said something when we said it and why we’re making that explanation of why we’re now changing, as I think Tony Fauci did very clearly about mask wearing.
So I think all of those things that really are about building trust and confidence are what can make us better in our communication as public health officials.
Céline Gounder: So it still amazes me that the global health community decided to take on smallpox eradication. We often hear about sustainability, cost-effectiveness, those kinds of economic concepts. What does it mean, Helene, for a program to be sustainable? And when we say sustainable, for whom?
Helene Gayle: Well, I think what we hope when we talk about sustainability is that efforts that are important for the short run can be sustained over the long run. And I think what we see so often in public health is that we have this massive surge of resources, personnel, effort, that then we let go of in between times.
So each time we have a pandemic, we have to create this big surge all over again. What we need in public health is to be able to have that kind of long-term, sustainable approach, understanding that there will be times when we have to have those surges, but not letting everything go in between time. When you say for whom, it’s really about how do we create a system and have a system that is in place that gets us not only at the times of great need and crisis, but is there for the public’s health for the long-term. And that’s what I hope we can move to as we think about public health in America and around the world.
Céline Gounder: Bill, does that sound like that’s a “sustainable goal” and should we be setting our public health goals based on what some think is sustainable or not?
Bill Foege: Well, sustainability is a problem that I often had because people require evidence of sustainability before they’ll fund something, but you don’t know what is sustainable until you try and do it. One of the lessons that I learned in the seventies was, in this country, the appropriations for measles would go up when there were lots of measles cases and they would go down when cases were reduced.
And inevitably, when they would go down, then the numbers had come up again. And so we had these variations. And we made a decision in the 1970s what would happen if we could interrupt transmission once, and that changes everything. Now the norm would be no transmission, and you could sustain the appropriations and it worked. We finally did that. So sustainability is something that bothers me. The pragmatists demand this, and I understand where they’re coming from, but there was a fellow by the name of Harlan Cleveland who was an American diplomat. He was our ambassador to NATO for many years. And late in his life, he became interested in global health and he was astonished at what happened with so few resources. And he came to the conclusion that global health workers are fueled on unwarranted optimism. And I like that phrase, because that is in fact what we do, is we become very optimistic and we make something happen that could not have been foreseen, that it would happen.
Céline Gounder: So this also reminds me about a conversation we had on the podcast with, believe it or not, a science fiction writer. Her name is adrienne maree brown, and we spoke with her about how she imagines world’s, possibilities different from our own. So let’s hear a short clip of that now.
Where do you find the inspiration to think up, to dream up the world’s that are so wildly different from our present reality?
[Audio clip from episode 1 of the “Eradicating Smallpox” begins to play]
adrienne maree brown: Saying that stuff is just the way it is. That’s one of the greatest ways that those who currently benefit from the way things are keep us from even imagining that things could be different. For centuries in this country, we were told that slavery was just the way things are and that it could never be any different. And yet there are people in those systems who said, “This isn’t right, this isn’t fair. Something else is actually possible.”
So a lot of the work of radical imagination, for me, is the work of saying, can we imagine a world in which our lives actually matter and we structure our society around the care that we can give to each other, the care that we need.
[Audio clip ends]
Céline Gounder: Bill, you just talked about unwarranted optimism and you told me once, in fact, I think more than once to bet on the optimist. But to go back to what you were saying about the pragmatist, doesn’t it make more sense on some level to be pragmatic and realistic if you want to get things done? And how would realism have gotten in the way of efforts to eradicate smallpox?
Bill Foege: Well, I think realism would have kept us from trying many things that we’ve tried. And the clip you just showed about an imagination that goes beyond realism is so important. If I would be director of CDC again, if I had a problem, I would try to get six comedians to come to CDC and I present them with the problem because they think in a different world than realism. And so I think it just makes sense to be unrealistic that we can do these things.
Céline Gounder: Helene, what about you? How did you balance thinking big versus being pragmatic when you were leading public health programs over the course of your career?
Helene Gayle: Well, I didn’t bring in comedians, but I think maybe I missed the boat on that. I love that idea. I like to think that I was able to combine the two. I think if you don’t think big, you will only achieve small progress. So I think you have to have big goals, but big goals can also be chunked into bite-sized pieces. So I think mixing the practical of what are the short-term games that are necessary to get to those big goals, both, give you a sense of what’s pragmatic and possible, but also keeps you inspired towards the bigger goal.
I think it’s also the case in public health where oftentimes we are operating with very difficult political situations. And again, sometimes you have to be the realist and understand what the limits are, but at the same time not give up on what’s your ultimate goal, what’s your ultimate vision, and keeping that front and center, it’s incredibly important, particularly as we think about how we inspire, back to the unwarranted optimism, how we inspire public health workers to keep going. People don’t get inspired by the short term, “Did I get my stock in today?” They get inspired by, “I’m part of eradicating a disease or stopping a pandemic.” So I think we have to combine the two.
Bill Foege: I might say that in India, we would have a meeting every month in the endemic states and go over what we had learned that month, and we would end the meeting by setting goals for the next month. We never once reached those goals until the last month. They were always beyond what we could do, but they gave us a vision of what we hoped we could do.
Céline Gounder: So this also reminds me of another aspect of goal setting. In another episode of the podcast, we spoke with a global health expert, Dr. Madhu Pai at McGill University, and he pointed out that historically it’s been white men in Europe and in the United States who’ve really driven the agenda in global health. Here’s just a short clip from Madhu.
[Audio clip from episode 2 of the “Eradicating Smallpox” begins to play]
Madhukar Pai: We need to flip the switch and recenter global health away from this, what I call default settings in global health, to the front lines. People on the ground, people who are Black, indigenous, people who are in communities, people who are actually dealing with the disease burden, people who are dying off it, people who have actually lived experience of these diseases that we’re talking about, having them run it is the most radical way of re imagining and shifting power and global health.
[Audio clip ends]
Céline Gounder: So Bill, who set the smallpox eradication goals? Was this local or global experts or both? Was it local communities and how were those different perspectives weighed and balanced in the program?
Bill Foege: Well, the global goal was set by WHO. It was originally conceived by the Soviet Union and presented to WHO, and it got only three votes the first time. Later, when the Soviet Union and the United States combined their efforts, they were able to convince the World Health Assembly and WHO took this on. So the global goal was set by WHO, but countries had the ability to say no. And Ethiopia went for a long time not becoming part of the program, they had other priorities. And these are legitimate priorities that World Bank once had a discussion on whether we should get into polio eradication or not. And I agreed to be part of the debate, even though I hate debates. I agreed to be part because I wanted to know what were the strongest arguments against polio eradication. And for me, there were two of them.
One was that this would distract from other global health efforts. People would focus on this. But the other one came from an African leader who said, “This is neocolonialism. You’re telling us how to spend our money on a disease problem and not allowing us to make that decision.” My counter to that was, “I understand that, but I also understand when Gandhi said his idea of the golden rule was that he should not be able to enjoy what other people could not enjoy.” And so I said, “If I can enjoy the fact that my children, my grandchildren, and now my great-grandchildren are free of polio, I have an obligation as a parent to share that with everyone.”
Céline Gounder: Helene, very often it’s scientific experts, physicians, epidemiologists who really lead the goal setting. Is there anything wrong with this technocratic approach to public health goal setting, and isn’t that just “following the science?”
Helene Gayle: Well, it’s obviously following the science at a macro level, but I think, while it’s important to set these global goals and these big overarching goals, it’s also very important to listen to the people whose health we’re actually trying to have an impact on. And I can remember, during the HIV pandemic, where once people realized how important it was to mobilize resources, there was an unprecedented amount of resources available for HIV, and we got from several countries around the world, the pushback just as Bill was talking about, because they said, “Malaria is a bigger problem for me. We have more people who die from malaria, from measles, from other infectious diseases. So where are our resources for the things that are making the biggest difference for our people?”
So I think it’s great to set the global goals and to be able to have these big overarching goals, but we can’t do that in the absence of also listening to the national and local needs and making sure that we’re thinking flexibly about how we use our resources so that what we do really meets the greatest needs of people on the ground.
Céline Gounder: Bill, you once quoted Einstein to me who said, “Perfection of means and confusion of goals seem, in my opinion, to characterize our age.” So are government officials and public health leaders somehow confused about public health goals while being overly focused on perfecting public health tools?
Bill Foege: I think so. You can’t stop scientists from trying to enlarge their area of knowledge. This is what scientists do. They try to figure out what is right and what is wrong. And so yes, we do confuse this. And it doesn’t matter whether you’re talking about a person, a state, a nation or the world, we devalue health until the day we lose it, and then suddenly it becomes so important. And so this idea of conveying what should happen ahead of time so we don’t lose health is problematic. But yes, it’s much easier to concentrate on the specifics and lose our sight of where we’re actually going with this.
Céline Gounder: Can you just give an example of this attempt to perfect a public health tool?
Bill Foege: Well, with vaccines, you see that people keep improving the vaccines, but don’t improve how to get them to everyone. The clip you showed on white people, mainly white men, making the decisions on global health in the past, is so true. And I’ve just finished reviewing the history of global health, and I think the one thing that was most destructive of global health was colonialism. Some people try to justify it on the basis of it brought new science and so forth, but just think of this country and the fact that colonialism killed off so many people that the slave trade became so important.
And so today, we’re still operating with the effects of colonialism in this hemisphere. Not seeing the vision of the big goal and concentrating on small things, it’s easier for all of us to do.
Céline Gounder: Helene, do you agree that public health officials are confused about the goals? And if so, why and how?
Helene Gayle: Well, I think it’s hard to talk about public health officials as a monolith, and it’s part of the challenge, particularly in this country, is that we have such a disjointed public health system. And I think we would benefit from having a much different public health system, such that people can individualize their roles, what they want to focus on, et cetera. But at a national level, and I would argue even at the global level, that there is a system that is consistent about what’s most important and what’s most important to deliver on.
So I do think that there’s a lot of inconsistency in our system. I think we have a fragmented public health system, and we would really benefit by having something that really had a much more of a network that is coordinated than what we have today.
Céline Gounder: I just got back actually from vacation in Morocco and I happened to be staying in the Medina in Marrakesh the night of the earthquake. And it’s now been estimated that nearly 3,000 people have died in that earthquake or from that earthquake, to date. I felt it, but the building where I was staying sustained hardly any damage. And to date, I haven’t heard of any tourists or expats having been reported dead or seriously injured. Now, this was not an infectious disease outbreak, but it is a public health crisis of a kind, and some are more likely to be hurt and die than others. What does this tell us about, Bill, how to build resilience into the system and how was this done in the context of smallpox?
Bill Foege: Well, the resilience is a difficult thing because we think locally. Well, wherever you are in the world, you’re both local and global. So I keep telling students, wherever you’re working, you’re working on global health. And so start thinking that way of how do we incorporate all these people. And see, you’re absolutely right. It doesn’t take an infectious disease. It takes a disaster to show what the social problems are that are causing this. Michael Osterholm once said, “One of the best fire departments we have is at the Minneapolis airport.” He said, “If we go 10 years or 15 years without a crash, no one will reduce their budget.” This is the kind of resilience that we need in public health. The last appropriations hearing that I had as director of CDC was chaired by Senator Hatfield from Oregon. He was the chair of the entire Appropriations Committee, but he asked permission, as a favor to me, to actually share this last one.
He asked me a question that I was not expecting, which is the one you just asked. He asked, “If you were in charge, how would you improve the sustainability of public health?” And I told him that there were three things I would do. Number one, I would identify any program that has a positive benefit cost ratio, that is, for a dollar invested, you save more than a dollar, plus you improve health. Because if you don’t do that, you’re agreeing to spend money and have the disease both. And I said, “If you took these programs,” and I said, “In order to avoid infighting between the Congress and the executive branch, I put this totally in charge of Congress.” You decide when a program has a positive benefit cost ratio. And now it doesn’t compete with other things in the budget, it becomes something that’s an entitlement. We need this because it is cheaper and it improves health.
Number two, I said, “I would index public health to healthcare expenditures, because the ratio of public health to healthcare keeps going down every year.” I said, “I would accept whatever it is right now and say we have to index our public health spending to that.”
And the third, I would come up with mechanisms to improve and reward programs that benefit outcomes. Today, we benefit access and process, but not outcomes. And so, if we could benefit outcomes, it would change the way the insurance companies work and other programs work. So those three things I think would provide sustainability and public health we don’t have now.
Céline Gounder: Helene, how was resilience built into the system in the context of HIV and or TB?
Helene Gayle: I’ll answer that in a minute, but I just want to add on and taking from the example that you gave from Morocco that I think in many cases we’re talking about sustainability and resilience, but we’re also talking about equity. At the end of the day, the reason you probably were less likely to get impacted was you were probably staying in a building where the construction had been done in a way that it was as sustainable and not prone to the conditions of earthquake. And the people who are likely to have lost their lives were probably living in substandard building situations. So I think every time we think about sustainability and resilience, we also have to think about equity and are we making sure that the way in which we design our programs take equity into consideration, because that’s ultimately what is going to make populations and people have the kind of resilience that’s necessary.
I think when I look at the programs like tuberculosis and HIV, I think what we tried to really do was to build up systems as we went along, because the best way to make sure that our efforts were sustainable and had resilience built into them was to actually build systems, not just focus on the program or the effort that we were doing.
So in HIV, clearly when I look back on the public health infrastructure that was built, the human capacity that was developed as a result of HIV, that’s what starts building in resilience because you’re not just building for the HIV pandemic, but you’re really using those dollars in ways that can help to strengthen systems. And that’s what I think we have the kind of resilience and sustainability that we’re talking about.
Céline Gounder: Lately, I’ve been thinking a lot about this concept of “Wicked problems.” And for people who are not familiar with this term, it goes back to the management literature several decades ago. And these are complicated, they’re messy, they’re context specific problems. People may not agree that there is a problem or what the problem is, they disagree on what caused it. And with wicked problems, there’s no one right solution, just some that might be less bad, might often create new problems. And so, these are very much about values and not just science. Bill, how would you apply this idea of wicked problems to public health challenges like smallpox or COVID?
Bill Foege: Well, wicked problems turns out to be a good expression of, a great picture of this. And when I think of vaccines, for instance, in the beginning, in 1796 of the smallpox vaccine, and how they’ve improved in numbers and types, when I was born, my baby book shows I have got only two vaccinations. Children today will get 18 or 19 or 20 different vaccinations. And you look at the future of this, we now have two vaccines against cancer, one against liver cancer and one against cervical cancer. We’re going to see more vaccines against neoplasms. You look at the possibility of having vaccines in the future for certain heart diseases or even for addiction, alcoholism and drug addiction, and the possibilities are so great. And yet at the same time, we have more and more people who don’t trust science, don’t trust government, and they become anti-vaxxers.
So this is the real challenge of vaccines. It will continue to be the foundation of global health, but we have to figure out how to get people incorporated in the solutions. Vashon Island in Puget Sound had a reputation for very low immunization uptake, and many of the people on the island were the hippies of the sixties and they didn’t trust government and so forth. The New York Times actually had a front page article on the rate of immunization in children, and I think about 19% were not being immunized.
Now, they would not listen to the health officers of Seattle or anyone else of authority coming in, but two parents who had been Peace Corps volunteers started their own program of finding out from people what would it take for you to change your mind. What is it that you don’t know that you wish you knew? The vaccination rate decreased from 81%, or increased from 81% up to 88%, 89%. They were doing something at a grassroots level that we could not have done from the top down. And so, there are solutions to wicked problems, but they sure do require energy and organization and the ability to respect culture.
Céline Gounder: Helene, is there a way we can better align people who have different sets of values around some of the same public health goals or strategies when it comes to some of these wicked problems, whether that is COVID or some of the other problems facing us today, whether it may be climate change or disinformation. Bill mentioned some of the challenges with anti-vaxxers and anti-science.
Helene Gayle: Well, this is another time where I think we should bring in the comedians, but I do think, maybe not the comedians, but to take a point from what you were saying earlier, Bill, I do think looking at how do you find the common ground? And sometimes there’s only 5% of common ground, but you can start with that and continue to grow from there. I think oftentimes, we approach these things that are adversarial in a counter adversarial way. So if somebody’s hostile, we up the hostility, instead of thinking, “All right, where can we find common ground? What are the things that we all agree upon?”
And sometimes it’s just the simple fact that we agree that saving lives is a high value and you can start from there and begin to develop the proof points that make nonbelievers believers. So I think we don’t do enough of thinking about where we find common ground, and instead, go to our corners and think by continuing to insist on what we believe and think that that’s what’s going to convince people, versus starting from where we all have a common belief and building from there. I don’t know any other way to do it. It’s not a magic bullet. It won’t work all the time. But I also think there has to be a point at which you recognize there are some people who you will never get on your side, and if you continue to try to wait for that to happen, you’ll get stuck and not move forward.
So there’s always a certain point when you just need to keep moving forward, understanding that if you demonstrate effectiveness, that may be the most likely way of bringing others along.
Bill Foege: When I’ve had an opportunity to meet with anti-vaxxers, I always start with the fact that I know no parent does this, withholding vaccines, to hurt their child.
Helene Gayle: Exactly.
Bill Foege: They do it only because they believe it’s the best thing for their child. And so if you can start there, you’re in a different position than if you just say, “Well, don’t you read the literature? Don’t you listen to…?” So I think understanding that there’s a reason why people feel this way is the beginning.
Céline Gounder: So earlier we were talking a bit about public health tools and this desire to perfect public health tools, but at the same time, innovations in medical technology were in fact key to eradicating smallpox, especially a simple little tool called the bifurcated needle. Here’s a clip of some smallpox eradication workers discussing this tool from episode four of the podcast.
In the early 1970s, smallpox was still stalking parts of South Asia. India had launched its eradication program more than a decade before, but public health workers couldn’t keep up with the virus. Enter the bifurcated needle.
[Audio clip from episode 4 of the “Eradicating Smallpox” podcast begins to play]
Tim Miner: It was a marvelous invention. In its simplicity, it looks like a little cocktail fork.
Céline Gounder: You dip the prongs into a bit of vaccine.
Tim Miner: And you would just prick the skin about 12 or 15 times until there was a little trace of blood, and then you’d take another one.
Céline Gounder: It barely took 30 seconds to vaccinate someone. And it didn’t hurt.
Yogesh Parashar: No.
Céline Gounder: Well, it didn’t hurt too much.
Yogesh Parashar: It was just like a pin prick rapidly done on your forearm. You had a huge supply with you and you just went about and dot, dot, dot, vaccinated people. Carry hundreds with you at one go.
Tim Miner: And you could train somebody in a matter of minutes to do it.
Céline Gounder: Easy to use, easy to clean, and a big improvement over the twisting teeth of the vaccine instrument health workers had to use before. The bifurcated needle was maybe two and a half, three inches long, small but sturdy enough for rough-and-tumble field work.
Yogesh Parashar: It was made of steel, and it used to come in something that looked like a brick. It was just like one of those gold bricks that you see in the movies.
Céline Gounder: And maybe worth its weight in gold.
[Audio clip ends]
Céline Gounder: So, Bill, public health officials say, in the context of COVID, that we now have the tools to diagnose and treat and prevent COVID, but are these tools enough for us to declare victory over COVID when not everyone has access to those tools? And in the context of smallpox, how did non-biomedical tools compliment biomedical innovations like the bifurcated needle?
Bill Foege: Well, going back to what Helene said, we have to be thinking of this globally and everyone and realize that these tools for smallpox, that is the vaccine, at least some way of giving it, existed long before WHO decided to have a program. But the people that were getting smallpox were the ones who were disenfranchised. They were the ones who were unemployed, in poverty, who had bias, that sort of thing. And so, it was very important to include the non-technical things. And in smallpox, I can tell you that every school and every church and every chief of a village and every volunteer that became involved was part of the solution of this.
Now, on the other hand, I can’t quite give up on smallpox eradication, even now, 40 plus years later. And I keep thinking of ways we could have improved. Nowadays, I would train dogs to pick up the scent of smallpox, because sometimes you would have beggar communities, people actually at the railroad station covered with a cloth with smallpox, but nobody knew that, but a dog would’ve picked that up right away. I’ve even come to the conclusion, if we were well enough organized, we could get rid of smallpox without vaccine and without the technical tools, the bifurcated needle, the jet injector and so forth. You would simply get people who are sick with smallpox and you would isolate them immediately and then you would follow all of their contacts. And the first symptom in a contact would get isolated and so on. And if you were organized well enough, you could get rid of smallpox without vaccine. So the tools are very important, but they’re not the last word.
Céline Gounder: Well, and in fact, that’s the approach that was used for Ebola. And now we have a vaccine. But most of the Ebola control efforts during the West African epidemic were really about that, identifying and isolating.
Helene, are we overly reliant on biomedical tools? And if we are overly reliant, should we pave the way for greater use of non-biomedical tools?
Helene Gayle: Well, as we know, the social determinants of health contribute more to health status than access to healthcare itself. So access to healthcare, including all the biomedical advances is necessary but not sufficient. I think we have to continue to think about why do we have some of the gaps in health that we know already exists. We look at the COVID pandemic as an example, where we know that the populations that were at greatest risk outside of age are people who lived in houses that were overcrowded or who had jobs that put them at risk, low wage earners, et cetera. So I think we have to think about both things. And I think back to your earlier question that is about people’s trust and mistrust, part of the trust in people being willing to access some of our biomedical tools comes from feeling that the rest of their needs are also being taken care of.
So if we just think of populations as we’ve got these great tools and we are going to give you these tools when your greatest challenge is whether or not you’re going to be able to feed your children at night or whether or not you’re going to have a roof over your head, you’re not going to be as eager and the uptake of our biomedical tools will not be as great. So I just think it’s about combining both and making sure that we’re thinking about some of these root causes that will also be part of helping to enhance, focusing on those will also be part of enhancing people’s trust and belief in some of the other approaches, that biomedical approaches that we know also make a huge difference.
Céline Gounder: Public health is different from clinical medicine, in that it focuses on the public or the ‘we’ so to speak, while clinical medicine focuses on the ‘I’ or the patient. There seems to be very little appetite in this moment for thinking about the ‘we.’
Bill, is there anything wrong with that? And if so, how do we shift that perspective that thinking about ‘we’ and public health and beyond?
Bill Foege: People often say clinical medicine deals with the numerator, the people that come to clinics and hospitals for care, while public health deals with the denominator. That’s simplistic because the denominator includes the numerator. And so, public health really is concentrated on everybody, on the ‘we’ and how to get everybody together on this.
There are two things from history that always impressed me. Confucius was asked by a student once, “Could you tell us in one word how best to live?” And Confucius said, “Is not reciprocity that word.” And so, this is ‘we’ that everybody’s dealing with each other. And then Gandhi said, his idea of the golden rule was that he should not enjoy something not enjoyed by everyone, the ‘we.’
So we keep hearing this from the wise people of history to stop thinking about just ourselves. Gandhi also said, “We should seek interdependence with the same zeal that we seek self-reliance.” And then he added in a soft voice, “There is no alternative.” And this is true. There is no alternative. And we’ve just got to take that approach in school, that’s much of school is built around how to improve your self-reliance, how to develop, how get money in the future and so forth. And we have to figure out how to teach interdependence.
Céline Gounder: Helene, should we be moving from an ‘I’ to a ‘we’ framing? And if so, how do we do that?
Helene Gayle: I think we have to. I think we recognize, and when we have pandemics, it’s very obvious. You can’t just think about what’s happening to you as an individual without recognizing that if we don’t stem transmission for something like a COVID, all of us are at risk.
So I think this sense of reciprocity is critical as we think about it. And it’s more broadly in our society. We can’t think that crime happens in one part of the city and it won’t also impact our economy, the economy of the city overall and ultimately impact other neighborhoods. I think we continue to think that we can wall off problems when we have to realize how interconnected we are, whether it’s health, whether it’s our economies, whether it’s the issue of climate change. I think as a species, we’re at a point where the ‘I’ thinking is having huge impacts for all of us. And unless we start having that ‘we’ mindset, we really are not going to be able to tackle some of these difficult wicked problems.
Bill Foege: If I could add one thing that Will Durant once said, ‘We will never do things globally unless we fear an alien invasion.” And what we’ve come up with are surrogates for alien invasions. So we see nuclear weapons as threatening of all of us. So we think ‘we.’ But there are other things. Our synthetic biology might be another one of these. Climate change may be a third one. We have four or five things that could totally eliminate people and we should be thinking ‘we’ in order to solve those problems.
Céline Gounder: So I’m now going to shift gears a little bit and take some of the questions our audience has been sending in. The first comes from Paurvi Bhatt who asks, “As we try to deal with new pandemics and eliminate older ones, how can we balance attention spans, science and safety in a world where “failing fast” and disruption define how we think about innovation?”
Helene, do you want to take a stab at that one?
Helene Gayle: Well, I just think we have to stay the course and continue to find ways. And we started out talking about health communications. I think we need to get better at our communications and in keeping people engaged in issues, because we are living in this 24/7 news cycle and a new issue coming up all the time. I think we as health professionals have an obligation to make sure that we are keeping these issues that are front and center in people’s minds and continuing to share what progress is happening. I think when people recognize there’s progress and you’re not just telling the same old story, I think you can keep people engaged, but I think it’s on us to do a better job in that regard.
Céline Gounder: Bill?
Bill Foege: I tell students now, and it took me a long time to reach this conclusion, that whenever they’re faced with these big problems, to think of three things.
Number one, try to get the science right. We’ve talked about you can’t always do that and you have to apologize and go back, but try to get the science right.
Number two, add art to the science. Will Durant says, “The first scientist that we know by name was Imhotep in Egypt, who was a physician and an artist and designed the step pyramid.” Because he said, “Then you get creative common sense at its best.” It was Huxley that says science is simply common sense at its best. So you get creative common sense at its best.
And then I go back 700 years to Roger Bacon who did a report for the Pope. And he said, “One of the problems with science is it has no moral compass.” And so you have to develop scientists with a moral compass. And when you do this, now you have moral creative common sense at its best, and this is a great approach to wicked problems.
Céline Gounder: Is public health science with a moral compass?
Bill Foege: It’s supposed to be. And sometimes we see it drifting off, but in general, public health people have a social mind that they’re trying to do this with a moral compass, including everyone.
Céline Gounder: Our next question comes from Merina Pradhan. Can you touch upon how the message needs to be as simple and brief as possible? Dr. Fauci’s message was very on point from a public health point of view, but how many in the general population would be able to assimilate that? Helene?
Helene Gayle: I would just say we have to tailor the message to the audience. When I saw the background that Dr. Fauci was talking against, I think he was talking to an audience of people who could incorporate that message. I might be wrong, but I think regardless, the point is if you’re sitting and talking to a group of public health professionals, you have one message. If you’re talking to the general public, you have another.
And I think it is true that we sometimes get confused with our own language because there’s so many nuances to public health that we put out these messages, that by the time we’re done, it’s hard to know. Do you believe yes, or do you believe no? So I agree. I think we have to keep it simple, but I think we also have to keep it truthful. And sometimes that’s a real challenge with the nuances of public health messaging. But I think again, tailoring it to the different audiences and recognizing that hopefully you have more than one bite at the apple, if you will, to make it short and concise, but then have other opportunities where you can explain it in greater detail.
Céline Gounder: Bill, this question is for you, from Mark Rosenberg, one of the new epidemics is the public health crisis of gun violence, now the leading cause of death for children and teens in the United States. Are there lessons from the eradication of smallpox that could be applied to help solve this new epidemic?
Bill Foege: I think all of the lessons from smallpox, knowing the truth, having coalitions, making sure that you progressing in the right way, having respect for culture, all of these things do apply. But I would end that answer, with becoming better ancestors, we’re saying that the ultimate expression of love from any of us is to become a better ancestor. And we certainly can do better on gun violence. And don’t put up with the discussion that says this is due to mental health problems and this and that, when other countries don’t have the same problem and they have just as much mental health problems as we do, but they don’t have the guns available.
Céline Gounder: Helene, this is a question from Ayo Femi-Osinubi. “Bill mentions that we don’t know what is sustainable till we try. How would you approach sustainability for pandemic preparedness in the midst of trying to prioritize basic health service delivery?”
Helene Gayle: Well, I think that the two aren’t necessarily in opposition. I think we need to have basic health services and building on basic services, making sure that we are thinking about how are those services available and sustainable so that when we have crises, public health crises, those systems are there and functional in a way that allows us to ramp up for public health emergencies.
So I think those things are not in opposition. It’s what I was talking about earlier. I think we need a more clear and comprehensive public health system that doesn’t just get ramped up every time we have a crisis, that it’s there, that it’s stable, that we have the kind of workforce that we need, that we have the kind of tools that we need, and that those are in place and that we build upon those than the other services that are important for individual care.
So again, I go back to a lot of this is about how we build systems that can be sustained and that are flexible and nimble so that they can respond when we have these public health crises.
Céline Gounder: So one last question. I’m going to give this one to Bill from David Torres. “I teach my global health students about the history of smallpox eradication. Given the coercive nature of the final push to vaccinate some people for smallpox and today’s resistance to and mistrust of public health measures, including vaccination campaigns and masking for COVID, would the elimination of smallpox be conceivable today? And if so, how would it be accomplished?”
Bill Foege: It would be very difficult today because of HIV and not knowing about immune systems, but you could still do it. The question about coercion, we hear this often, and most of this comes from one paper by Dr. Greenough, where he has interviewed people who worked on smallpox who used coercion. They would break into huts at 2:00 in the morning with the police officer to do that. None of that was necessary.
And so particular people were so enthusiastic about smallpox eradication that they did this. But think about it for a moment. If you have a village with three people who have refused vaccination, if they get smallpox, everyone around them is already vaccinated. They’re the ones that suffer. You don’t have to go in and use coercion. And so, when I’ve talked to other people who worked in smallpox, they’re surprised that anyone used coercion. You don’t have to do that, and that’s part of respecting the culture, is that you find other ways to do this.
Céline Gounder: Well, I really want to thank both of you, Bill and Helene for joining us today and for answering all of my questions, the audience’s questions. Between the two of you, you have over a century’s worth of wisdom in public health, and I always love hearing what you both have to say about these issues.
I just want to remind the audience that a recording of the event will be posted online later today and that all registrants will be sent an email when the recording is available. Also, please check out the podcast, Epidemic. It’s available on Apple, Spotify, wherever you get your podcasts. Season two is the season on eradication of smallpox. And also check out the Nine Lessons at ninelessons.org. And thanks everyone for joining us today.
Helene Gayle: Thank you.
Bill Foege: Thank you.
Season 2 of the ‘Epidemic’ Podcast Is ‘Eradicating Smallpox’
The eight-episode audio series “Eradicating Smallpox” documents one of humanity’s greatest public health triumphs.
By the late 1960s and early 1970s, smallpox was gone from most parts of the world. But in South Asia, the virus continued to kill. Public health heroes had to conquer social stigma, local politics, and more to wipe out the 3,000-year-old virus, an achievement many scientists thought was impossible.
Host Céline Gounder traveled to India and Bangladesh and brought back never-before-heard stories, many from public health workers whose voices have been missing in the coverage of the history of smallpox eradication. Gounder brings decades of experience working on tuberculosis and HIV in Brazil and South Africa; Ebola during the outbreak in Guinea, West Africa; and covid-19 in New York City at the height of the pandemic.
Season 2 of “Epidemic” is a co-production of KFF Health News and Just Human Productions.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 1 month ago
Multimedia, Public Health, Epidemic, Video
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Underinsured Is the New Uninsured
The Host
Emmarie Huetteman
KFF Health News
Emmarie Huetteman, associate Washington editor, previously spent more than a decade reporting on the federal government, most recently covering surprise medical bills, drug pricing reform, and other health policy debates in Washington and on the campaign trail.
The Host
Emmarie Huetteman
KFF Health News
Emmarie Huetteman, associate Washington editor, previously spent more than a decade reporting on the federal government, most recently covering surprise medical bills, drug pricing reform, and other health policy debates in Washington and on the campaign trail.
The annual U.S. Census Bureau report this week revealed a drop in the uninsured rate last year as more working-age people obtained employer coverage. However, this year’s end of pandemic-era protections — which allowed many people to stay on Medicaid — is likely to have changed that picture quite a bit since. Meanwhile, reports show even many of those with insurance continue to struggle to afford their health care costs, and some providers are encouraging patients to take out loans that tack interest onto their medical debt.
Also, a mystery is unfolding in the federal budget: Why has recent Medicare spending per beneficiary leveled off? And the CDC recommends anyone who isat least 6 months old get the new covid booster.
This week’s panelists are Emmarie Huetteman of KFF Health News, Margot Sanger-Katz of The New York Times, Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet, and Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico.
Panelists
Sarah Karlin-Smith
Pink Sheet
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico
Margot Sanger-Katz
The New York Times
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- The Census Bureau reported this week that the uninsured rate dropped to 10.8% in 2022, down from 11.6% in 2021, driven largely by a rise in employer-sponsored coverage. Since then, pandemic-era coverage protections have lapsed, though it remains to be seen exactly how many people could lose Medicaid coverage and stay uninsured.
- A concerning number of people who have insurance nonetheless struggle to afford their out-of-pocket costs. Medical debt is a common, escalating problem, exacerbated now as hospitals and other providers direct patients toward bank loans, credit cards, and other options that also saddle them with interest.
- Some state officials are worried that people who lose their Medicaid coverage could choose short-term health insurance plans with limited benefits — so-called junk plans — and find themselves owing more than they’d expect for future care.
- Meanwhile, a mystery is unfolding in the federal budget: After decades of warnings about runaway government spending, why has spending per Medicare beneficiary defied predictions and leveled off? At the same time, private insurance costs are increasing, with employer-sponsored plans expecting their largest increase in more than a decade.
- And the push for people to get the new covid booster is seeking to enshrine it in Americans’ annual preventive care regimen.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Emmarie Huetteman: KFF Health News’ “The Shrinking Number of Primary Care Physicians Is Reaching a Tipping Point,” by Elisabeth Rosenthal.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: MedPage Today’s “Rural Hospital Turns to GoFundMe to Stay Afloat,” by Kristina Fiore.
Joanne Kenen: ProPublica’s “How Columbia Ignored Women, Undermined Prosecutors and Protected a Predator for More Than 20 Years,” by Bianca Fortis and Laura Beil.
Margot Sanger-Katz: Congressional Budget Office’s “Raising the Excise Tax on Cigarettes: Effects on Health and the Federal Budget.”
Also mentioned in this week’s episode:
- U.S. Census Bureau’s “Health Insurance Coverage of U.S. Workers Increased in 2022,” by Rachel Lindstrom, Katherine Keisler-Starkey, and Lisa Bunch.
- The Commonwealth Fund’s “Can Older Adults with Employer Coverage Afford Their Health Care?” by Lauren A. Haynes and Sara R. Collins.
- KFF Health News’ “What One Lending Company’s Hospital Contracts Reveal About Financing Patient Debt,” by Noam N. Levey.
- The New York Times’ “A Huge Threat to the U.S. Budget Has Receded. And No One Is Sure Why,” by Margot Sanger-Katz, Alicia Parlapiano, and Josh Katz.
- The Wall Street Journal’s “Health-Insurance Costs Are Taking Biggest Jumps in Years,” by Anna Wilde Mathews.
- The New York Times’ “The N.Y.C. Neighborhood That’s Getting Even Thinner on Ozempic,” by Joseph Goldstein.
click to open the transcript
Transcript: Underinsured Is the New Uninsured
KFF Health News’ ‘What the Health?’
Episode Title: Underinsured Is the New Uninsured
Episode Number: 314
Published: Sept. 14, 2023
[Editor’s note: This transcript, generated using transcription software, has been edited for style and clarity.]
Emmarie Huetteman: Hello and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Emmarie Huetteman, a Washington editor for KFF Health News. I’m filling in for Julie [Rovner] this week, who’s on vacation. And I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, Sept. 14, at 11 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So, here we go. We’re joined today by video conference by Margot Sanger-Katz of The New York Times.
Margot Sanger-Katz: Good morning, everybody.
Huetteman: Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: Hi there.
Huetteman: And Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Huetteman: No interview this week, so let’s get right to the news. The percentage of working-age adults with health insurance went up last year, according to the annual Census report out this week. As a result, the uninsured rate dropped to 10.8% in 2022. But lower uninsured rates may be obscuring another problem: the number of people who are underinsured and facing high out-of-pocket costs. The Commonwealth Fund released a report last month on how difficult it is for many older adults with employer coverage to afford care. And recent reporting here at KFF Health News has probed how medical providers are steering patients toward bank loans and credit cards that saddled them with interest on top of their medical debt. So, the number of people without insurance is dropping. But that doesn’t mean that health care is becoming more affordable. So what does it mean to be underinsured? Are the policy conversations that focus on the uninsured rate missing the mark?
Sanger-Katz: So, two things I would say. One is that I even think that the Census report on what’s happening with the uninsured is obscuring a different issue, which is that there’s been this artificial increase in the number of people who are enrolled in Medicaid as a result of this pandemic policy. So the Congress said to the states, if you want to get extra money for your Medicaid program through the public health emergency, then you can’t kick anyone out of Medicaid regardless of whether they are no longer eligible for the program. And that provision expired this spring. And so this is one of the big stories in health policy that’s happening this year. States are trying to figure out how to reevaluate all of these people who have been in their Medicaid program for all these years and determine who’s eligible and who’s not eligible. And there’s been quite a lot of very good reporting on what’s going on. And I think there’s a combination of people who are losing their Medicaid coverage because they really genuinely are no longer eligible for Medicaid. And there also appears to be quite a large number of people who are losing their Medicaid coverage for administrative hiccup reasons — because there’s some paperwork error, or because they moved and they didn’t get a letter, or some other glitch in the system. And so when I looked at these numbers on the uninsured rate, in some ways what it told us is we gave a whole bunch of people insurance through these public programs during the pandemic and that depressed the uninsured rate. But we know right now that millions of people have lost insurance, even in the last few months, with more to come later this year. And so I’m very interested in the next installment of the Census report when we get back to more or less a normal Medicaid system, how many people will be without insurance. So that’s just one thing. And then just to get to your question, I think having insurance does not always mean that you can actually afford to pay for the health care that you need. We’ve seen over the last few decades a shift towards higher-deductible health care plans where people have to pay more money out-of-pocket before their insurance kicks in. We’ve also seen other kinds of cost sharing increase, where people have to pay higher copayments or a percentage of the cost of their care. And we’ve also seen, particularly in the Obamacare exchanges, but also in the employer market, that there’s a lot of insurance that doesn’t include any kind of out-of-network benefit. So it means, you know, if you can go to a provider who is covered by your insurance, your insurance will pay for it. But if you can’t find someone who’s covered by your insurance, you could still get hit with a big bill. The sort of surprise bills of old are banned. But, you know, the doctor can tell you in advance, and you can go and get all these medical services and then end up with some big bills. So whether or not just having an insurance card is really enough to ensure that people have access to health care remains an open question. And I think we have seen a lot of evidence over recent years that even people with insurance encounter a lot of financial difficulties when they get sick and often incur quite a lot of debt despite having insurance that protects them from the unlimited costs that they might face if they were uninsured.
Huetteman: Joanne.
Kenen: I would say two big things. The uninsurance rate, which we all think is going to go up because of this Medicaid unwinding, it’s worth stopping and thinking about. It’s what? 7.9[%]? Was that the number?
Huetteman: It was 10.8, was the uninsured rate last year.
Sanger-Katz: It depends if you look at any time of the year or all of the year.
Kenen: Back when the ACA [Affordable Care Act] was passed, it was closer to something like 18. So in terms of really changing the magnitude of the uninsurance problem in America, the work isn’t done. But this is a really significant change. Secondly, some aspects of care are better — or within reach because the ACA made so many preventive and primary care services free. That, too, is a gain. Obviously, through the medical debt, which KFF [Health News] now has done a great job — oh, and believe me, and other reporters, you’ve done an amazing job, story after story. You know, the “Bill of the Month” series that you edited, it’s … but they’re not isolated cases. It’s not like, oh, this person ran into this, you know, cost buzz saw. There’s insane pricing issues! And out-of-pocket and, you know, deductibles and extras, and incredibly hard to sort out even if you are a sophisticated, insured consumer of health care. Pricing is a mess. There have been changes to the health care market, in terms of consolidation of ownership, more private equity, bigger entities that just have created … added a new dimension to this problem. So have we made gains? We’ve made really important gains. Under the original ACA passed under the Obama administration and the changes, the access and generosity of subsidy changes that the Biden administration has made, even though they’re time-limited, they have to be renewed. But, you know, are people still being completely hit over the head and every other body part by really expensive costs? Yes. That is still a heartbreaking and really serious problem. I mean, I can just give one tiny incident where somebody … I needed a routine imaging thing in network. The doctor in that hospital wasn’t reachable. I had my primary care person send in the order because she’s not part of that health care system. She’s in network. The imaging center is in network. The doctor who told me I needed this test is in network. But because the actual order came from somebody not in their hospital and in … on the Maryland side of the line, instead of the D.C. side of the line, the hospital imaging center decided it was going to be out of network. And because she’s not ours and wanted to charge me an insane amount of money. I sorted it out. But it took me an insane amount of time and I shouldn’t have needed to do that.
Huetteman: Yeah, that’s absolutely true.
Kenen: I could have paid it, if I had to.
Huetteman: Absolutely. And as you noted, I do edit the “Bill of the Month” series. And we see that with all kinds of patients, even the most enterprising patients can’t get an answer to simple questions like, is this in network or out of network? Why did I get this bill? And it’s asking way too much of most people to try and fit that into the rest of the things that they do every day. You know, Margot brought up the Medicaid unwinding. Well, let’s speaking of insurance, let’s catch up there for a moment because there was a little news this week. We’re keeping an eye on those efforts to strip ineligible beneficiaries from state Medicaid rolls since the covid-19 public health emergency ended. Now, some state officials are worried that people who lose coverage could opt to replace it with short-term insurance plans. You might know them as “junk plans.” They often come with lower price tags, but these short-term plans do not have to follow the Affordable Care Act’s rules about what to cover. And people in the plans have found themselves owing for care they thought would be covered. The Trump administration expanded these plans, but this summer the Biden administration proposed limiting them once more. Remind us: What changes has Biden proposed for so-called junk plans and for people who lose their coverage during the Medicaid unwinding? What other options are available to them?
Sanger-Katz: So the Biden administration’s proposal was to basically return these short-term plans to actual short-term coverage, which is what they were designed to do. Part of what the Trump administration did is they kept this category of short-term plans. But then they said basically, well, you can just keep them for several years. And so they really became a more affordable but less comprehensive substitute for ACA-compliant insurance. So the Biden administration just wants to kind of squish ’em back down and say, OK, you can have them for like a couple of months, but you can’t keep them forever. I will say that a lot of people who are losing their Medicaid coverage as a result of the unwinding are probably pretty low on the income scale, just as a result of them having qualified for Medicaid in the first place. And so a very large share of them are eligible for free or close-to-free health plans on the Obamacare exchanges. Those enhanced subsidies that Joanne mentioned, they’re temporary, but they’re there for a few years. They really make a big difference for exactly this population that’s losing Medicaid coverage. If you’re just over the poverty line, you can often get a free plan that’s a — this is very technical, but — it’s a silver plan with these cost-sharing wraparound benefits. And so you end up with a plan where you really don’t have to pay very much at the point of care. You don’t have to pay anything in a premium. So I think, in general, that is the most obvious answer for most of these people who are losing their Medicaid. But I think it is a challenge to navigate that system, for states to help steer people towards these other options, and for them to get enrolled in a timely way. Because, of course, Obamacare markets are not open all the time. They’re open during an open enrollment period or for a short period after you lose another type of coverage.
Huetteman: Absolutely. And a lot of these states actually have efforts that are normally focused on open enrollment right now. And some officials say that they are redirecting those efforts toward helping these folks who are losing their Medicaid coverage to find the options, like those exchange plans that are available for zero-dollar premiums or low premiums under the subsidies available.
Kenen: I have seen some online ads from HHS [the Department of Health and Human Services], saying, you know, “Did you lose your Medicaid?” and it’s state-specific — “Did you lose your Medicaid in Virginia?” I don’t live in Virginia, so I’m not sure why I’m getting it. My phone is telling me the Virginia one. But there is an HHS [ad], and it is saying if you lost your Medicaid, go to healthcare.gov, we can help. You know, we may be able to help you. So they are outreaching, although I’m afraid that somebody who actually lost it in Virginia might be getting an ad about Nebraska or whatever. I live close to Virginia. It’s close enough. But there is some effort to reach people in a plain English, accessible pop-up on your phone, or your web browser, kind of way. So I have seen that over the last few weeks because the special enrollment period, I mean, most people who are no longer eligible for Medicaid are eligible for something, and something other than a junk plan. Some of them have insurance at work now because the job market is better than it was in 2020, obviously. Many people will be eligible for these highly subsidized plans that Margot just talked about. Very few people should be left out in the cold, but there’s a lot of work to be done to make those connections.
Huetteman: Absolutely. Absolutely. And going back to the Census report for a second, it had noted that a big part of the increase in coverage came from employer-sponsored coverage among working-age adults, although we have, of course, seen those reports that say … and then they try to afford their health care costs. And it’s really difficult for a lot of them, even when they have that insurance, as we talked about. All right. So let’s move on. The New York Times is reporting a mystery unfolding in the federal budget. And I’d like to call it “The Case of Flat Medicare Spending.” After decades of warnings about runaway government spending, a recent Times analysis shows that spending per Medicare beneficiary has actually leveled off over more than a decade. Meanwhile, The Wall Street Journal reports that private health insurance costs are climbing. Next year, employer-sponsored plans could see their biggest cost increase in more than a decade, and that trend could continue. So what’s going on with insurance costs? Let’s start with Medicare. Margot, you were the lead reporter on the Times analysis. What explains this Medicare spending slowdown?
Sanger-Katz: So part of the reason why I have found it to be a somewhat enjoyable story is that I think there is a bit of a mystery. I talked to lots of people who have studied and written about this phenomenon over the years, and I think there was no one I talked to who said “I 100% understand what is going on here. And I can tell you, here’s the thing.” But there are a bunch of factors that I think a lot of people think are contributing, and I’ll just run through them quickly. One of them is Medicare is getting a little younger. The baby boomers are retiring generally, like, 65-year-olds are a little cheaper to take care of than 85-year-olds. So as the age mix gets younger, we’ve seen the average cost of taking care of someone in Medicare get a little smaller. That’s like the easiest one. I think another one is that Obamacare and other legislative changes that Congress has passed during this period have just mechanically reduced the amount of money that Medicare is spending. So the two most obvious ways are, in the Affordable Care Act, Congress took money away from Medicare Advantage plans, paid them a smaller premium for taking care of patients, and they also reduced the amount that hospitals get every year, as what’s called a productivity adjustment. So hospitals get a little raise on their pay rates every year. And the legislation tamped that down. There was also, some listeners may remember, the budget sequester that happened in 2011, 2012, where there was kind of a haircut that Medicare had to take across the board. So there have been these kind of legislative changes. They explain like a little bit of what is going on. And now I think the rest of it really has to do with the health care system itself. And part of that seems to be that this has been a period of relatively limited technological improvement. So, you know, for years medicine just kept getting better and better. We had these miracle cures, we had these amazing surgeries. We, you know, especially like in the area of cardiovascular disease, just enormous advances in recent decades where, you know, first bypass surgery and then stents and then, you know, drugs that could prevent heart attacks. And so I think, you know, health care spending kept climbing and climbing in part because there was better stuff to spend it on. It was expensive, but it really improved people’s health. And in recent years, there’s just been a little less of that. There have clearly been medical advances, particularly in the pharmaceutical space. You know, we have better treatments for cancer, for certain types of cancers, than we had before and for other important diseases. But these expensive innovations tend to affect smaller percentages of people. We haven’t had a lot of really big blockbusters that everyone in Medicare is taking. And so that seems to explain some of the slowdown. And then I think the last piece is, like, kind of the piece that’s the hardest to really explain or pin down, but it seems like there’s just something different that doctors and hospitals are doing. They’re getting more efficient. They’re not always buying the latest and greatest thing, if there’s not evidence to support it. They’re reducing their medical errors. And, you know, I think Obamacare probably gets a share of the credit here. It really created a lot of changes in the way we pay for medical care and in the Medicare program itself. And it created this innovation center that’s supposed to test out all of these different things. But I think also over the same period, we’ve seen the private sector make many of the same moves. You know, private insurers have gotten a little bit more stingy about covering new technologies without evidence. They’ve tended to pay physicians and hospitals in bundles, or paying them incentives for quality, not paying them for certain types of care that involve errors. And so a lot of people I talked to said that they think the medical system is reacting to all of the payers crunching down on them. And so they’re just not being quite as aggressive and they’re trying to think more about value, which I feel like is like kind of a lame buzzword that often doesn’t mean anything. But I think, you know, it’s a way of thinking about this change. And, you know, that’s the kind of thing, if culturally that endures, you know, could continue into the future. Whereas some of these other factors, like the demographics, the lack of technological development, those — the Obamacare, which was kind of a one-time legislative change, you know — those things may not continue into the future, which is why the fact that we’ve had 15 years of flat Medicare spending is no guarantee that Medicare spending won’t spike again in the future. And I think you were right to point to what’s happening in the private sector, because private sector insurance premiums also have been like a little bit on the flat side through this period. And I think there is potential for them to take off again.
Huetteman: Absolutely. And that’s what The Wall Street Journal’s reporting had just said, that the health care costs for coming into next year are climbing. Let’s talk about that for a minute. Why are private insurance costs rising as Medicare spending levels off? One of the things that I noticed is we talked about technological innovation. Pharmaceutical innovation seems to be one of the things that’s contributing to rising private health insurance costs and elsewhere, in particular, those weight-loss drugs I know.
Kenen: And the Alzheimer’s drugs.
Huetteman: And the Alzheimer’s drugs.
Kenen: Eventually they’ll become more widely available. Sarah knows way more than the rest of us.
Karlin-Smith: The Alzheimer’s drugs will probably be less of an issue for the private health insurance population. But certainly weight-loss drugs are something that private insurers are worried about what percentage of the population they will cover with these drugs. And I think insurance companies, they have to balance that … difficult balance between what percentage of the drug cost rate you put on patients and what do you build into premiums. And sometimes there’s only so much flexibility they can have there. So I think that’s a big reason for what you’re seeing here.
Huetteman: Yeah, absolutely.
Sanger-Katz: I think the weight-loss drugs are interesting because they kind of are, potentially, an example of the kind of technology that is both expensive and good for public health, right? So, you know, when we have all these improvements in cardiac disease, like, that was great. People didn’t have heart attacks. They didn’t have disability in old age. They lived longer lives. That was great. But it cost a ton of money. And I think because we have been going through this period in which costs have been kind of level, and there hasn’t been a lot of expensive breakthrough technology, we haven’t had to weigh those things against each other in the way that we might now, where we might have to say, OK, well, like, this is really expensive, but also, like, it has a lot of benefits. and how do we decide what the right cost benefit is as a society, as an employer, as a public insurance program? And I think we’re going to see a lot of payers and economists and other analysts really thinking hard about these trade-offs in a way that they, I think, haven’t really been forced to do very much in the last few years with … I mean, maybe with the possible exception of those breakthrough therapies for hepatitis C —also expensive, huge public health benefit. And it was a struggle for our system to figure out what to do with them.
Kenen: But, like the statins, which, you know, revolutionized heart health, these drugs that are useful for both diabetes and … weight loss, the demand of people who just want them because they want to lose those 20 pounds, insurers are not — Medicare at least is not — covering it. Insurers have some rules about “Are you pre-diabetic?” and etc., etc., but they cost a lot of money and a lot of people want to take them. So I think they’re clearly great for diabetes. They clearly are a whole new class of drugs that are going to do good things. We still don’t. … There’s still questions about who should be using them for the rest of their lives, for weight control, etc., etc. Yes, there are going to be benefits, but this era of … what is the typical cost per month, Sarah?
Karlin-Smith: The list price of these drugs are thousands of dollars per month. But I think to your point, Joanne, though, the trouble for insurance companies who are figuring out how to cover this is they’re starting to get more research that there are these actual health benefits outside of just weight loss. And once you start to say, you know, that these drugs help prevent heart attacks and have hard evidence of that, it becomes harder for them to deny coverage. I think to Margot’s point of the long-term benefits, you might see to health because of it, we get back to another issue in the U.S. health system is, which is these private health insurance companies might essentially basically be footing the bill for benefits that Medicare is going to reap, not necessarily the insurance companies, right? So if somebody, you know, doesn’t have a heart attack at 50 because they’re on these drugs, that’s great. But if the savings is actually going to Medicare down the line, you know, the private health insurer doesn’t see the benefit of that. And that’s where some of the tensions you get into it in terms of, like, how we cover these products and who we give them to.
Kenen: Because that trade-off: quality of life and longevity of life. That’s what health is about, right? I mean, is having people live healthy, good lives, and it costs money. But there’s this issue of the drug prices have gotten very high, and hepatitis C is a perfect example. I mean, now it’s like we were freaked out about $84,000 in, you know, 2013, 2015, whenever that came out. You know, now that looks quaint. But that price was still so high that we didn’t get it to people. We could have wiped out hepatitis C or come damn close to wiping out hepatitis C, but the price the drug was an obstacle. So we’re still, I mean, there’s a big White House initiative now, you know, there’s creative … the Louisiana model of, you know, what they call the Netflix model where, you know, you have a contract to buy a whole ton of it for less per unit. I mean, these are still questions. Yes. I mean, we all know that certain drugs make a big difference. But if they’re priced at a point where people who need them the most can’t get them, then you’re not seeing what they’re really invented for.
Sanger-Katz: Oh, I was just going to say, I think that part of what interests me about this particular class of drugs and the debates that we are likely to have about them, and there are, you know, the way that they’re going to be adopted into our health care system is that setting aside the diabetes indication for a moment, the idea of drugs that effectively treat obesity, I think obesity is a very stigmatized disease in our country. And in fact, Medicare has statutory language that says that Medicare cannot cover drugs for weight loss. So it would actually require an act of Congress for these drugs to be approved for that purpose in Medicare. And in Medicaid, in general, states are required to cover FDA-approved drugs. You know, they can put some limitations, but they’re supposed to cover them. Again, there is a special statutory exclusion for weight-loss drugs where the states really have discretion they don’t have for a cancer drug, for a drug for diabetes, a drug for other common diseases. And so I do think that, you know, a lot of this debate is colored by people’s prejudices against people who have obesity, and the way that our medical care system has thought about them and the treatment for their disease over time. And I’m curious about that aspect of it as well. I mean, of course, I think that Joanne is absolutely right that we do not know long term how these drugs are going to help people with obesity, whether it’s really going to reduce the burden of disease down the road for them, whether it’s going to have other health consequences in an enduring way. You know, I think there are unknowns, but I think if you take the most optimistic possible look at these drugs, that there’s quite a lot of evidence that they really do improve people’s health. And if we treat these drugs differently than we would an expensive drug for an infectious disease like hepatitis C or different from an expensive drug for cancer diseases that are less stigmatized, I think that would maybe be a little bit sad.
Karlin-Smith: I mean certainly the reason why the initial restrictions in Medicare and other programs are baked in goes back to stigma to some degree. But also, I mean … because they were thinking of these as weight-loss drugs and sort of vanity treatments people would only be using for vanity. And at that time, the drugs that were available did not work quite as well and had a lot of dangers and certainly did not show any of these other health benefits that we’re starting to see with this new class of medicine. So I think that would be the hope that, you know, as the science and the products shift, as well as our medical understanding around what causes obesity, what doesn’t cause obesity, how much of it is … right, again, just as medical as any other condition and not all about a person’s behavior. And I think we will see that the benefits of some of these drugs for certain people, in particular, are probably a lot bigger than maybe the benefits of certain cancer treatments that we pay a lot more money for. The challenge is going to be the amount of people and the amount of time they are going to be on these drugs, right? You know, if you’re talking about these hepatitis C drugs, I think one reason they didn’t shock the budgets in the way people were expecting, besides the fact that, unfortunately, we didn’t get them to everybody, is they’re actually really short-term cures, right? I think it’s like 10 weeks or something.
Kenen: Some are like eight.
Karlin-Smith: Right. Ballpark. And with the obesity drugs, what we know … these new drugs so far is that you seem like you have to consistently take them. Once you get off them, the weight comes back. And then the assumption would be you lose all those health benefits. So we’re talking about a high-cost drug on a chronic basis that our system can’t afford.
Kenen: Margot, do you know? I mean, my guess is that the ban on covering weight-loss drugs was written into MMA [the Medicare Modernization Act] in 2003. That’s my guess. I don’t know if anyone …
Sanger-Katz: That’s right. Yeah. It was part of the creation of the drug benefit program.
Kenen: So I think that you’re totally right that it’s what both of you said. You know, we tended to say it was someone’s fault, like they didn’t have enough willpower. Or they, you know, didn’t do what they were supposed to do. And there was stigma and we thought about it diffrently. I also think the science, you know, Sarah alluded to this, I think the science of obesity has really changed, that we didn’t talk about it — even though obesity experts — really didn’t talk about it as a disease a generation ago. We thought of it as maybe as a risk factor, but we didn’t think of it as a disease in and of itself. And we now do know that. So I think that the coverage issues are going to change. But what are the criteria? How fast do they change, for who do they change? Do you really want to put somebody on a drug because they want to lose 10 or 15 punds, which is … versus someone who really has struggled with weight and has physical risk factors because of it, including, you know, heart disease, diabetes, all these other things we know about. I mean, I just think we don’t know. I mean, there was a piece in the Times about the Upper East Side of Manhattan is like this beehive of people taking these weight loss drugs because they can afford it, but they’re also thinner than the rest of the population. So it becomes, you know, a luxury good or another disparity.
Sanger-Katz: If insurance won’t cover these drugs ,of course, rich people are going to take them more than people of limited means. Right? Like, I think you can only really test the hypothesis of, like, who are these drugs meant to reach once … if you have coverage for them, right? I thought that story was very good, and it did reveal something that’s happening. But I also thought … it felt like it was focusing on the idea that that rich people were taking these drugs just for vanity. And I think …
Kenen: Some of them, not all clearly some of them.
Sanger-Katz: Some of them are, of course. But I thought the thing that was less explored in that story is all of the people in poor neighborhoods of New York who were not accessing those drugs. Was it because they couldn’t find any way to get them?
Kenen: Right, and some of them were pre-diabetic. Some of them. I mean, the other thing is people who are overweight are often pre-diabetic. And that is an indication. I mean, you can … it’s in flux. It’s going to change over the coming months, you know, but what a cost and how those benefits paid off and who’s going to end up paying and where the cost shifting is going to come, because there is always cost shifting. We just don’t know yet. But these drugs are here to stay. And there are questions. There are a lot of questions. The mounting evidence is that they are going to be a benefit. It’s just, you know, what do we pay for them? Who gets them? How long do the people stay on them, etc., etc., etc.
Sanger-Katz: And just to come back to Emmarie’s first question, like, what is this going to mean for our insurance premiums, right? With something like 40% of adults in the United States have obesity. If we start to see more and more people taking these drugs to treat this disease, all of us are going to have to pay for that in some way. And, you know, that affects overall health care.
Huetteman: Absolutely. Well, let’s move to the week’s big covid news now. This week, the FDA approved a new booster, which comes amid an uptick in cases and concerns about a surge this fall and winter. Before the CDC made its recommendations, though, there was debate over whether the booster should be recommended only for a couple of higher-risk groups. So who does the CDC say should get the shot? And what’s the response been like from the health care community so far?
Karlin-Smith: So the CDC decided their advisers and the CDC themselves to recommend the shot for everybody. That really didn’t surprise me because I think that was the direction FDA wanted to go as well. I think the majority came down to the fact that a broad recommendation would be the best for health equity and actually ensuring the people we really want to get the shots get them. If you start siphoning off the population and so forth, it actually might prevent people that really should get the shots from getting it. I think the booster debate has actually been really similar since we started approving covid boosters, which is that the companies that provided for the boosters is not the same as the original data they presented to get the vaccines approved. So we don’t have as much understanding with the type of rigorous research some people would like to know: OK, what is the added benefit you’re getting from these boosters? We know they provide some added benefit of protection for infection, but that’s very short-lived. And then I think there’s … people have differences of opinions of how much added protection it’s giving you from severe disease and death. And so there are factions who argue, and I think Paul Offit has become one of the most known and vocal cheerleaders of this mindset, which is that, well, actually, if you’ve already had, you know, two, three, four shots, you’ve already had covid, you’re probably really well protected against the worst outcomes. And these shots are not really going to do that much to protect you from an infection. “So why take them anymore?” — essentially, is sort of his mindset. And there are people that disagree. I think the thing that probably might help change mindsets is, at least in this country, probably not going to happen, which is, you know, more rigorous outcomes research here. But I think the sentiment of the CDC and its advice has been, well, these shots are extremely low risk and there’s at least some added benefit. So for most people, the risk-benefit balance is: Get it. And if you make it kind of simple, if you say, OK, you know, everybody, it’s time to get your next covid booster, the feeling is that will get the most people in the U.S. to go out and do it. Unfortunately, most covid booster recommendations have been fairly broad — the last, at least, and that hasn’t translated. But we’ll see. This is actually the first time that everyone, except for babies under 6 months — because you can’t start your covid vaccination until then —everybody is really included in the booster recommendation at the same time. In previous rounds, particularly for younger kids, it was more staggered. So this will be the simplest recommendation we have yet.
Kenen: And that’s part of the public health strategy, is to not talk about it so much as boosters, just as an annual shot. The way you get an annual flu shot. I mean, most people don’t get them. But the idea is that to normalize this, you know, you get an annual flu shot, you get an annual covid shot, for certain age groups you get annual RSV now that’ll be available. But that’s not for everybody. I mean, I think they really want to make this simple. OK, it’s fall, get your covid shot. We don’t think uptake is going to be real high. It hasn’t been for boosters. But in terms of trying to change, this is just, you know, this is one of those things to add to your to-do list this year and to, sort of, less “pandemicize” it. I don’t think that’s a word. But, you know, everyone will forgive me. And more just, you know, OK, you know, this is one of the things you got to do in the fall. Maybe “pandemicize” is a word or maybe it should be.
Sanger-Katz: I like it. Maybe we should use it.
Huetteman: Pandemicize your care.
Kenen: Right. You know, it’s part of your preventive care and just … I mean, good luck trying to de-politicize it. But that’s part of it. I mean, the CDC director, Mandy Cohen, she wrote an op-ed this week and it was all about, you know, I’m a doctor, I’m the CDC director, and I’m a mom. And, you know, my family is going to get it. You know, Ashish Jha was tweeting about how he’s going to get it, his elderly parents are going to get theirs as soon as possible, etc., etc. So it’s not going to be … the hard-core people who really don’t want these shots and haven’t taken the shots and believe the shots cause more harm than good, etc. It won’t change a lot of their minds. But there are a lot of people who are uncertain in the middle and their minds can be changed. And they have … they were changed in the initial round of shots. So that’s who the messaging is … it’s sort of a reminder to people who take the shots and an invitation to those who … haven’t been getting boosted that just start doing this every year.
Karlin-Smith: And it is important to emphasize when the boosters have been tweaked and, you know, updated to try to match as close as they possibly can the current version of the virus. The virus has evolved and shifted a lot over time to the point where even these boosters, you know, they can’t quite keep up with the virus. But the idea is that we’re helping broaden everybody’s protection by keeping it as up to date with the science. So I think that’s an important element of that, that people don’t appreciate. They’re not just giving you the exact same shot over and over again. They’re trying to, like we do with the flu vaccine every year, be as close to what is circulating as possible.
Kenen: And there’s a new, new, new, new variant that looked very — do I have enough “news” in there? — that looked, and I don’t remember the initials; I can’t keep track — that is really quite different than the other ones. And there was a lot of initial concern that this vaccine would not work or that we wouldn’t … that our protection would not work against that. The follow-up research is much more reassuring that the fall shot will work against that. But that one really is different, and it’s got a lot of mutations. And, you know, we don’t know yet how … some of these things come and go pretty quickly. I mean, who remembers Mu? That one people were very worried about and it seemed quite dangerous and luckily it didn’t take root. You know, people don’t even know there was a Greek letter called Mu. M-u, not m-o-o, in case anyone’s wondering. If relatives ask me if they should take it, the two things that struck me in reading about it are, yes, it works against this new variant, and we’re not really sure what are the new, new, new, new, new, new, new, new ones. And also, I mean, there’s some research that it does protect against long covid. And I think that’s a big selling point for people. I think there are people who still, with reason, worry about long covid, and that vaccination does provide some protection against that as well.
Huetteman: That’s a great point. I mean, anecdotally, you talk to your friends who’ve had covid, there’s going to be at least a few of them who say they haven’t quite felt like themselves ever since they had covid. And I think that is one of the things that really motivates people who aren’t in those higher-risk categories, to think about whether they need the booster or not.
Kenen: Yeah, and also the myocarditis … Sarah, correct … you follow this more closely than I do, so correct me if I’m wrong here, but I believe that they’re finding that the myocarditis risk in the newer formulations of the vaccine has dropped, that it is not as much of a concern for young men. And covid itself can cause myocarditis in some individuals. Did I get that right?
Karlin-Smith: Yeah, I think that that’s right. The general sense has been that the risk was more with the initial shots, and it seems to have gone down. I think that there are people that still worry about particular age groups of, like, young men in certain age groups, that maybe for them the benefit-risk balance with the myocarditis risk is, you know, might be a little bit different. And that’s where a lot of the pushback comes through. But right, like you said, there is a fairly high … there’s myocarditis risk from covid itself that needs to be balanced.
Huetteman: Well, OK. That’s this week’s news. Now we’ll take a quick break and then we’ll come back with extra credits.
Julie Rovner: Hey, “What the Health?” listeners, you already know that few things in health care are ever simple. So, if you like our show, I recommend you also listen to “Tradeoffs,” a podcast that goes even deeper into our costly, complicated, and often counterintuitive health care system. Hosted by longtime health care journalist and friend Dan Gorenstein, “Tradeoffs” digs into the evidence and research data behind health care policies and tells the stories of real people impacted by decisions made in C-suites, doctors’ offices, and even Congress. Subscribe wherever you listen to your podcasts.
Huetteman: OK, we’re back. And it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week that we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it; we’ll post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Sarah, why don’t you go first?
Karlin-Smith: Sure. So I looked at a MedPage Today page by Kristina Fiore that talks about a GoFundMe campaign that was started by a small rural hospital in Pennsylvania. They’re trying to raise $1.5 million to basically keep the hospital open. It’s the only hospital in the county. It’s a small critical-access hospital. And I think people who follow health care and health policy in the U.S. are probably used to seeing GoFundMe campaigns for individual health care, as we talked about earlier in the episode, right? The unaffordability that can happen even for people with good insurance if you … depending on your medical situation. But this situation, I thought, was really unique, a whole hospital, which is, I guess, community-owned, and they’re essentially turning to the internet to try and stay open. And it touches on some of the payment differences in how rural hospitals make their money, or the payment rates they get reimbursed versus more urban hospitals. Other issues it brings up is just, you know, how do you keep an institution open that’s serving a relatively small population of people? So, you don’t necessarily want to have people going to the hospital, but they’re basically arguing that if we don’t get this amount of people in our ER per day, we can’t stay open. But then that means you don’t have an ER for anybody. And I think it’s just worth looking at, looking at the facts they put on their GoFundMe page, just thinking about, you know, what this says about various policies in the U.S. health system. And, unfortunately for them right now, they’re well short of their $1.5 billion goal.
Huetteman: Yeah, it’s amazing to see this get translated into an institution-saving effort as opposed to an individual-saving effort. Joanne, you want to go next?
Kenen: Sure. This is a story that it was by Bianca Fortis from ProPublica, Laura Biel, who wrote this for ProPublica and New York Magazine, and also Laura, who’s a friend of mine, also has a fabulous podcast called “Exposed.” And in this case, I want to mention the photographer, too, because if you click on this, it’s quite extraordinary visuals. Hannah Whitaker from New York Magazine. And the title is “How Columbia …” — and this is the university, not the country — “How Columbia Ignored Women, Undermined Prosecutors and Protected a Predator for More Than 20 Years.” This is an OB-GYN who was abusing his patients, and it’s hundreds, hundreds that have been identified and known. We knew about him because some of the patients had come forward, including Evelyn Wang, who was Andrew Wang — is Andrew Wang’s wife, the presidential candidate last cycle. But we didn’t know this. You know, first of all, it’s even bigger than we knew three years ago, and he has been prosecuted — finally. But it took 20 years. And this is really more of a story about how the medical system, the health care system, had warning after warning after warning after warning, and they didn’t do anything. And also, many of the people who tried to give the warnings, some of the employees, including the medical assistants, and the nurses, and the receptionists, knew what was going on. And they thought that they, as lower-level women going up against a white male doctor, wouldn’t be believed. And they didn’t even try. They just felt like he’s the guy, he’s the doctor. I’m the, you know, I’m the nurse. They won’t listen to me. So that was another subtheme that came out to me. I had known vaguely about this. It’s really long, and I read every word. It’s a really horrifying saga of an abdication of responsibility to women who were really harmed. Vulnerable women who were really harmed.
Huetteman: Yeah, it’s a really troubling story, but it’s an important piece of journalism. And I advise that people give it a little time. Margot, would you like to go next?
Sanger-Katz: Yeah. So this is a very nerdy, deep cut. I wanted to talk about a CBO [Congressional Budget Office] report from 2012 called “Raising the Excise Tax on Cigarettes: Effects on Health and the Federal Budget.” So when I published this article about how Medicare spending has sort of flattened out, we got so many reader comments and emails and tweets and several people asked, “Could it be that the decline in smoking has led to lower costs for Medicare?” And that caused me to do some reporting and to read this paper. And I think the finding, the sort of counterintuitive finding that I will tell you about in a minute, from the CBO really speaks to some of the discussion that we were having earlier about these obesity drugs, which is that there are many beneficial preventive therapies in health care that are great for people’s health. They make them healthier, they have happier lives, they live longer, they have less burden of disease, but they are not cost-effective in the sense that they reduce our total spending on health care. And the simplest way to think about this is that if everyone in America just died at age 65, Medicare’s budget would look amazing. You know, it would be great. We would save so much money if we could just kill everyone at age 65. But that’s not what the goal of Medicare is. It’s not to save the maximum amount of money. It’s to get a good value, to improve people’s life and health as much as possible for a good value. And so this report was looking at what would happen if we had a really effective policy to reduce smoking in the United States. They looked at a tax that they estimated would reduce the smoking rate by a further 5 percentage points. And what they found is that it would cost the government more money, that people would be healthier, they would live longer lives, more of them would spend more years in Medicare, and they would end up having some other health problem that was expensive that they weren’t going to have before. And also they would collect a lot of Social Security payments because they would live a lot longer. And so I found it so stunning because the economics of it, I think, make a lot of sense. And when you think about it, it’s true. But it does go to show how, I think, that sometimes when we, and when politicians, talk about preventive health care, they always talk about it like it’s a win-win. You know, this is going to be great for people and it’s going to save money. And I think that in health care, many times things that are good and beneficial improve health and they cost money and we have to decide if it’s worth it.
Huetteman: Absolutely. That’s great. Thank you. My extra credit this week comes from KFF Health News. Dr. Elisabeth Rosenthal, our senior contributing editor, writes: “The Shrinking Number of Primary Care Physicians Is Reaching a Tipping Point.” And we’ve seen some great coverage lately on the disappearance of the primary care doctor in this country. And Dr. Rosenthal also offers some solutions to this yawning gap in our health care system. She reports that the percent of U.S. doctors that have moved into primary care is now at about 25%, which is much lower than in previous decades. And one point she makes, in particular, about a problem that’s leading to this is the payment structure that we have in our country favors surgeries and procedures, of course, not diagnostic tests, preventative care, when it comes to reimbursing doctors. And of course, this lack of primary care doctors has implications for our overall health, both individually and as a country. So I recommend that you give that article a little bit of your time this week.
All right. That’s our show for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, to our amazing engineer, Francis Ying. And as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can tweet me. I’m @emmarieDC. Sarah?
Karlin-Smith: I’m @SarahKarlin.
Huetteman: Joanne?
Kenen: @JoanneKenen on Twitter, @joannekenen1 on Threads.
Huetteman: And Margot.
Sanger-Katz: @sangerkatz in all the places.
Huetteman: We’ll be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Terry Byrne
Copy chief
Gabe Brison-Trezise
Deputy copy chief
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 1 month ago
COVID-19, Health Care Costs, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Public Health, Uninsured, FDA, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Podcasts, vaccines
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Welcome Back, Congress. Now Get to Work.
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Congress returns from its August recess with a long list of things to do and not a lot of time to do them. The fiscal year ends Sept. 30, and it’s possible that lawmakers will fail to finish work not only on the annual appropriations bills, but also on any short-term spending bill to keep the government open.
Meanwhile, Medicare has announced the first 10 drugs whose prices will be negotiated under the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. Exactly how the program will work remains a question, however. Even how the process will begin is uncertain, as drugmakers and other groups have filed lawsuits to stop it.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Rachel Cohrs of Stat, Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico, and Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Panelists
Rachel Cohrs
Stat News
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Hard-line Republicans are refusing to back even a temporary government spending bill, suggesting a government shutdown looms — with repercussions for health programs. While the Senate and House have come to intra-chamber agreements on subjects like community health center funding or even have passed spending bills, Congress as a whole has been unable to broker an overarching deal.
- A coalition of House Republicans is falsely claiming that global HIV/AIDS funding through PEPFAR promotes abortion and is battling efforts to extend the program’s funding. PEPFAR is a bipartisan effort spearheaded by then-President George W. Bush and credited with saving millions of lives.
- The PEPFAR fight underscores the dysfunction of the current Congress, which is struggling to fund even a highly regarded, lifesaving program. Another example is the months-long blockade of military promotions by a freshman Republican senator, Alabama’s Tommy Tuberville, a member of the Senate Armed Services Committee. His objections over an abortion-related Pentagon policy have placed him at odds with top military leaders, who recently warned that his heavy-handed approach is weakening military readiness.
- The Biden administration recently announced new staffing requirements for nursing homes, as a way to get more nurses into such facilities. But how long will compliance take, considering ongoing nursing shortages? And the drug industry is reacting to the news of which 10 drugs will be up first for Medicare negotiation, with much left to be sorted out.
- In abortion news, a Texas effort to block patients seeking abortions from using the state’s roads is spreading town to town — and, despite being dubiously enforceable, it could still have a chilling effect.
Also this week, Rovner interviews Meena Seshamani, who leads the federal Medicare program, about the plan to start negotiating drug prices.
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: JAMA Health Forum’s “Health Systems and Social Services — A Bridge Too Far?” by Sherry Glied and Thomas D’Aunno.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: The Washington Post’s “Heat’s Hidden Risk,” by Shannon Osaka, Erin Patrick O’Connor, and John Muyskens.
Rachel Cohrs: The Wall Street Journal’s “How Novartis’s CEO Learned From His Mistakes and Got Help From an Unlikely Quarter,” by Jared S. Hopkins.
Joanne Kenen: Politico’s “How to Wage War on Conspiracy Theories,” by Joanne Kenen, and “Court Revives Doctors’ Lawsuit Saying FDA Overstepped Its Authority With Anti-Ivermectin Campaign,” by Kevin McGill.
Also mentioned in this week’s episode:
- The Washington Post’s “Highways Are the Next Antiabortion Target. One Texas Town Is Resisting,” by Caroline Kitchener.
- KFF Health News’ “Biden Administration Proposes New Standards to Boost Nursing Home Staffing,” by Jordan Rau.
- Stat’s “The Curious Case of J&J’s Stelara, The Unluckiest Drug on Medicare’s List,” by Rachel Cohrs.
Click to open the transcript
Transcript: Welcome Back, Congress. Now Get to Work.
[Editor’s note: This transcript, generated using transcription software, has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, Sept. 7, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast, and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go. We are joined today via video conference by Rachel Cohrs of Stat News.
Rachel Cohrs: Good morning.
Rovner: Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Politico.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Later in this episode, we’ll have an interview with Meena Seshamani, who runs the Medicare program for the federal government, with an update on the Medicare drug negotiation debate as, we’ll discuss, the first 10 drugs that will be subject to negotiation were announced last week. But first, this week’s news. So Labor Day is behind us, and Congress is back — sort of. The Senate is back. The House returns next week. And there are lots of questions to be answered this fall, starting with whether or not Congress can finish the annual spending bills before the start of fiscal 2024 on Oct. 1. Spoiler: They cannot. But there’s also a real question whether Congress can even pass a short-term bill to keep the government running while lawmakers continue to work on the rest of the appropriations. As of now, what do you guys think are the odds that we’re going to end up with some kind of government shutdown at the end of the month?
Ollstein: Well, it’s whether it happens at the end of the month or at the end of the year, really. Folks seem pretty convinced that it will happen at some point. It could be short-lived. But, yeah, like you said, you have some hard-line House Republicans who say they won’t support even a temporary stopgap bill without spending cuts, policy changes, without sort of extracting some of their demands from leadership. And you could work around that in the House by cobbling together a coalition of Republicans and Democrats. But that also puts [House Speaker Kevin] McCarthy’s leadership in jeopardy. And so, we’re having sort of the same dynamic play out that we saw earlier this year, trying to navigate between the hard-line House Republicans and, you know, the more vulnerable swing districts’ members. So it’s … tough.
Rovner: Yeah, it’s the Republicans from districts that [President Joe] Biden won … basically.
Ollstein: Yeah. And so you have this weird game of chicken right now where both the House and Senate are trying to pass whatever they can to give themselves more leverage in the ultimate House-Senate negotiations. They think, OK, if we pass five bills and they only pass one, you know, then we have the upper hand. So we’ll see where that goes.
Rovner: It’s funny, because the Senate has been a well-oiled machine this year on the spending bills, which is unusual. I was about to say I will point out that there are two women: the chairman and ranking member. But that’s actually also true in the House. We do have women running the appropriations process this year. But I was amused that Kevin McCarthy, sometime during August, a couple of weeks ago, said, you know, very confidently, well, we’ll pass a short-term spending bill. You know, we won’t let the government shut down. And by the next day, the hard-line Republicans, the right wing, were saying, yeah, no you won’t. You’re going to have to deal with us first. And, obviously, there’s lots of health stuff that’s going to get caught up in that. The end of the fiscal year also marks the end of funding authority for a number of prominent programs. This is not the same as the appropriations programs whose authorizations lapse can continue, although things can get complicated. PEPFAR, the two-decade-old bipartisan program that provides AIDS and HIV prevention and treatment around the world, is one of those programs that, at least as of now, looks pretty stuck. Alice, is there any movement on this? We’ve talked about it before.
Ollstein: Not yet. So the latest we know, and we got this last night, is that [Foreign Relations Committee] Chairman [Bob] Menendez in the Senate is floating a new compromise. Basically, supporters of PEPFAR have been pushing for the full five-year standard reauthorization. And a coalition of House Republicans who are claiming that PEPFAR money is going to abortion say they want no reauthorization at all. They just want the program to sort of limp along through appropriations. So between five years and zero, Menendez is now suggesting a three-year extension. There is a huge desire not to just have the one-year funding patch because that would kick all of this into the heat of the 2024 season. And if you think the debate is ugly now over abortion and federal spending, just wait until 2024.
Kenen: I mean, this … [unintelligible] money … it’s saved tens of millions of lives — and with bipartisan support in the past.
Rovner: It was a Republican initiative.
Kenen: Right. It was President Bush, George the second.
Rovner: George W. Bush. Yeah.
Kenen: And they’re not saying they’re actually going out and using the AIDS dollars to conduct, to actually do abortions. They’re saying that there’s, you know, they’re in the world of abortion and they’re promoting abortion, etc., etc. So the conversation gets really, really, really, really muddled. Under U.S. law, they cannot use U.S. dollars for abortion under the Hyde Amendment, you know, all sorts of other foreign policy rules. So it’s hard to overstate how important this program has been, particularly in Africa. It has saved millions and millions of lives. And I think Alice might have broken the story originally, but it got caught up in abortion politics, and it caught people by surprise. This is not something … everything in Washington gets caught up in politics, except this! So I think it’s been quite shocking to people. And it’s, I mean — life-and-death sounds like a, you know, it’s a Washington cliché — this is life-and-death.
Ollstein: Yeah, absolutely. And, you know, even though the program won’t shut down if they don’t manage to get a reauthorization through, you know, I talked to people who run PEPFAR services in other countries, and they said that, you know, having this year-to-year funding and instability and uncertainty — you know, they won’t be able to hire, they won’t be able to do long-term planning. They said this will really undermine the goal to eliminate HIV transmission by 2030.
Cohrs: Oh, I actually did just want to jump in about another Sept. 30 deadline, because there was a big development this week. I know we were just talking about long-term planning. There is funding for community health centers that’s expiring at the end of September as well. DSH cuts could go into effect for hospitals. We do this routine every so often, but the House is actually more in step than the Senate on this issue; they released — at least Republicans released — a draft legislation, where all three committees of jurisdiction are in agreement about how to proceed. There are some transparency measures in there.
Rovner: The three committees in the House.
Cohrs: In the House. Yes, yes, we’re talking about the House. Yeah. So, they have reconciled their differences here and are hoping to go to the floor this month. So, I think they are out of the gate first, certainly with some sort of longer-term solution here. Again, could get punted. But I think it is a pretty big development when we’re talking about these extenders that the industry cares about very much.
Kenen: Congress is so polarized that it can’t even do the things that it agrees on. And we have seen this before where CHIP [Children’s Health Insurance Program] got caught up a few years ago. Community health clinics have gotten caught right in that same bill, right? But, you know, we really have this situation where it’s so dysfunctional they can’t even move fully on things that everybody likes. And community health centers date back to the early ’60s. However, they got a really big expansion, again, under second President Bush. And they’re popular, and they serve a need, and everybody likes them.
Rovner: They got a bigger expansion under the Affordable Care Act.
Kenen: Right, but they, you know — but I think that the Bush years was like the biggest in many years. And then they got more. So again, I mean, are they going to shut their doors? No. Is it going to be a mess? It is already a mess. They can’t — they don’t know what’s coming next. That’s no way to run a railroad or a health clinic.
Rovner: All right, well, one more while we’re on the subject of abortion-related delays: Alabama Sen. Tommy Tuberville is still blocking Senate approval of routine military promotions to protest the Biden administration’s policy of allowing funding for servicewomen and military dependents to travel for abortions if they’re posted to states where it’s banned. Now, the secretaries of the Army, Navy, and Air Force are joining together to warn that Tuberville’s hold is threatening military readiness. Tuberville apparently went on Fox News last night and said he’s got more people who are coming to support him. Is there any end to this standoff in sight? I mean, people seem to be getting kind of upset about it. It’s been going on since, what, February?
Ollstein: Yeah, there is not yet an end in sight. So far, all of the attempts to pressure Tuberville to back down have only hardened his resolve, it seems, you know, and he’s gone beyond sort of his original statement of, you know, all of this is just to get rid of this policy that doesn’t pay for abortions; it just allows people to travel out of state if they’re stationed — they don’t get to choose where they’re stationed — if they’re stationed somewhere where abortion is not legal or accessible. And so now he’s making claims about other things in the military he considers too woke. He’s criticized some of these individual nominees themselves that he’s blocking, which was not sort of part of the original stand he took. And so, it’s tough, and there isn’t enough floor time to move all of these and go around him. And so this pressure campaign doesn’t seem to be really making any headway. So I don’t really see how this gets resolved at this point.
Kenen: Except that other Republicans are getting a little bit more public. I mean, they were sort of letting him run out for a while. And there’s more Republicans who are clearly getting enough of this. But I mean, unless McConnell can really get him to move — and we don’t know what’s gone on behind closed doors, but we’re certainly not seeing any sign of movement. In fact, as Alice said, he’s digging in more. I mean, like, Marines and woke are not the two words you usually hear in one sentence, but in his worldview, they are. So, I think it’s unprecedented. I mean, I don’t think anyone’s ever done this. It’s not like one or two people. It’s like the entire U.S. military command can’t move ahead.
Rovner: I’ve been doing this a very long time, and I don’t remember anything quite like this. Well, the one thing that we do expect to happen this fall is legislation on — and Rachel, you were referring to this already — sort of health care price transparency and PBMs, the pharmacy benefit managers. Where are we with that? They were supposed to work on it over the August break. Did they?
Cohrs: They were supposed to work on it. The House was clearly working on it and reconciling some of their differences. They’re planning to introduce legislative text on Friday. So, I think Democrats aren’t on board yet, so things could change from the draft they had been circulating early this week. But again, Republicans don’t really need Democrats to move forward, at least in the House. The Senate has been pretty quiet so far. Not to say that no work has gone on, but they certainly weren’t ready for the rollout in the same way that the House was. You know, I think there are still some big questions about, you know, what they’re planning to accomplish with insulin policy, how they’re planning to fit together this jigsaw puzzle of PBM transparency and reforms that have come out of different committees. And I think it’ll come down to [Senate Majority Leader] Sen. Schumer making some tough choices. And from my understanding, that hasn’t quite happened yet. But if the actual showdown happens November, December, they still have some time.
Rovner: Yeah. Now they’re not going out early. They’re clearly going to be fighting over the appropriation. So, the legislative committees have plenty of time to work on these other things. All right. Well, let’s turn to Medicaid for a moment. The quote-unquote “unwinding” continues as states move to redetermine who remains eligible for the program and who doesn’t following the pandemic pause. As predicted, it’s been a bit of a bumpy road. And now it seems a bunch of states have been incorrectly dropping children from Medicaid coverage because their parents are no longer eligible. That’s a problem because nationwide, income limits for children’s eligibility is higher than parents’. In some states, it is much higher. I remember after Hurricane Katrina, in Louisiana, parents were only eligible if they earned 15% of poverty. Somebody said 50, and the Medicaid director said, “No, 15, one-five.” Whereas kids are eligible to, I believe it’s 200% of poverty. And I think that’s a national level.
Kenen: Now, in some states it’s higher.
Rovner: Yes. But I say this is happening in a bunch of states because federal government won’t tell us how many or which ones. We do know it’s more than a dozen, but this is the second time the administration has admonished states for wrongly canceling Medicaid coverage. And they wouldn’t say which states were involved at that time either. Is this an effort to keep this as apolitical as possible, given that the states most likely to be doing this are red states who are trying to remove ineligible people from Medicaid as fast as they can, that they’re trying to sort of keep this from becoming a Republican versus Democrat thing.
Ollstein: It seems like, from what we’re hearing, that the administration is really wary of publicly picking a fight with these states. They want the states to work with them. And so, even if the states are going about this in a way they think is totally wrong, they don’t want to just put them publicly on blast, because they think that’ll make them, again, double down and refuse to work with the government at all. And so, they’re trying to maintain some veneer of cooperation. But at the same time, you’re having, you know, millions of people, including children, falling through the cracks. And so, you know, we have sort of this sternly-worded-letter approach and we’ll see if that accomplishes anything, and if not, you know, what measures can be taken. You know, the administration also created a way for states to hit pause on the process and take a little more time and do a little more verification of people’s eligibility. And some — a couple states — have taken advantage of that, and it’s been successful in, you know, having fewer people dropped for paperwork reasons, but it’s not really happening in the states where it sort of most needs to happen, according to experts.
Rovner: The administration has had fingers pointed at it, too, because apparently it approved some of these plans from the states that were going to look at total family income without realizing that, oh, that meant that kids who are still eligible could end up losing coverage because their parents are no longer eligible.
Kenen: Right. And I also read something yesterday that in some cases it’s sort of a technical issue rather than a “how much outreach and what your intentions are,” that it’s a programing issue, which is related to what Julie just said about the plan. So, it’s not that these states set about to drop these kids, and there may be some kind of goodwill to fix it, in which case you don’t want to get in — and I don’t know that it’s 100% red states either. So —
Rovner: No, that’s clear. We assume, because they’re the ones going fastest, but we do not know.
Kenen: Right, so that there seems to be some kind of — the way it was set up, technically, that can be remedied. And if it’s a technical fix as opposed to an ideological fight, you don’t really want to — you want to figure out how to reprogram the computer or whatever it is they have to do and then go back and catch the people that were lost. So, they’ve been pretty low-key about politicizing rewinding in general. But on the kids, I think they’re going to be even more — CHIP passed, another thing with bipartisan support that’s a mess. I mean, it seems to be the theme of the day. But, you know, CHIP was created on a bipartisan basis, and it’s always been sustained on a bipartisan basis. So, I think that the issue, I don’t know how technically easy it is to fix, but there’s a big difference in how the administration goes after someone that’s intentionally doing something versus someone who wrote their computer programmer set something up wrong.
Rovner: Well, we will definitely keep on this one.
Kenen: But it’s a big mess. It’s a lot of kids.
Rovner: It is a big mess. And let’s turn to the thing that is not bipartisan in Congress, and that is —
Kenen: That’ll be a bigger mess.
Rovner: — Medicare drug negotiations. Yes. While we were away, the federal government released its much-anticipated list of the 10 brand-name drugs that will be the first tranche up for potential price negotiation. I say potential, because the companies have the option of negotiating or not — sort of — and because there are now, I think, nine lawsuits challenging the entire program. My interview with Medicare administrator Meena Seshamani will get into the nuts and bolts of how the negotiation program is supposed to work. But Rachel, tell us a little bit about the drugs on the list and how their makers are trying to cancel this entire enterprise before it even begins.
Cohrs: Sure. So, a lot of these drugs that we’re seeing on the list are blood thinners. Some are diabetes medications. There are drugs for heart failure, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and there’s also a cancer treatment, too. But I think overall, the drugs were chosen because they have high cost to Medicare. And it was —
Rovner: So that either could mean a lot of people use an inexpensive drug —
Cohrs: Yes.
Rovner: — or a few people use a very expensive drug.
Cohrs: Correct. And it was Wall Street’s favorite parlor game to try to guess what drugs were going to be on this list of 10 drugs that are going to be the guinea pigs to go through this program for the very first time. But it was interesting, because there were a few surprises. Medicare officials were using newer data than Wall Street analysts had access to. So, there were a couple drugs, especially further down on the list, that people used more in the period CMS [Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] was studying than had been used previously. So, we saw a couple very interesting instances of a drug being chosen for the list, even though it just kind of fell through the cracks. It was J&J’s [Johnson & Johnson’s] Stelara. It’s a Crohn’s disease treatment, and it does have competition coming in the market soon, but just because of a fluke of kind of when it was approved by the FDA, it just missed cutoffs for some of these exemptions and is now subject to some pretty significant discounts through the program.
Rovner: We’ll link to your very sad story about Stelara.
Cohrs: Sad for the company, but not sad for the patients who will hopefully be paying less for this medication. And there’s also the case of Astellas [Pharma Inc.], which makes a prostate cancer drug that’s very expensive. A lot of people expected that to be selected, but actually wasn’t. And Astellas had sued the Biden administration already before the list came out and then had to withdraw their lawsuit yesterday because their argument that they were going to be harmed by this legislation was made much weaker by the fact that they weren’t selected for this first year of the program. So, who knows? They could dust off their arguments a year from now or two years from now. But it was interesting to see kind of some of these surprises on the list. Again, there are still several, like you mentioned, outstanding lawsuits in several different jurisdictions. I think the main one that we’re watching is by the [U.S.] Chamber of Commerce, which requested a preliminary injunction by the end of this month. So, we’ll see if that comes through. But it is a very long road to 2026. There might be a new administration by then. So, I think there are still a lot of questions about whether this reaches the finish line. But I think it’s a very important step for CMS to get this list out there in the world.
Rovner: So, I spent some time digging in my notes from earlier years, and I dug up notes from an interview I did on Aug. 26 with a spokesperson from the drug industry about how the Medicare drug benefit, quote, “impact the ability of companies to research new medicines. And if that happens, the elderly would be the ones hurt the most.” That quote, by the way, was from Aug. 26 of 1987. Some things truly never change. But is this maybe, possibly, the beginning of the end of drugmakers being able to charge whatever they want in the United States? Because it’s the only country where they can.
Cohrs: Oh, they can still charge whatever they want. This law doesn’t change that. It just changes the fact that Medicare won’t be paying whatever drugmakers happen to charge for an unlimited amount of time. Like, they can still charge whatever they want to Medicare for as long as they can get on the market before they’re selected for this negotiation program. But certainly there could be significant cost — significant savings to Medicare, even if those prices are high. And it’s just kind of a measure that forces price reductions, even if the generic or biosimilar market isn’t functioning to lower those prices through competition.
Kenen: Right. And it’s only Medicare. So, people who are not on Medicare — insurance companies also negotiate prices, but they’re not the government. It’s different. But I mean, these drugs are not going to start being, you know, three bucks.
Rovner: But they may stop being 300,000.
Kenen: Well, we don’t know, because there are some people who think that if Medicare is paying less, they’re going to charge everybody else more. We just don’t know. We don’t know what their behavior is going to be. But no, this does not solve the question of affordability of medication in the United States.
Rovner: The drug companies certainly think it’s the camel’s nose under the tent.
Kenen: They have some medicine for camels’ noses that they can charge a lot of money for, I’m sure.
Rovner: I bet they do. While we are on the subject of things that I have covered since the 1980s, last week the Biden administration finally put out its regulation requiring that nursing homes be staffed 24/7/365 by, you know, an actual nurse. One of the first big reconciliation bills I covered was in 1987 — that was a big year for health policy — and it completely overhauled federal regulation of nursing homes, except for mandating staffing standards, because the nursing homes said they couldn’t afford it. Basically, that same fight has been going on ever since. Except now the industry also says there aren’t enough nurses to hire, even if they could afford it. Yet patient advocates say these admittedly low staffing ratios that the Biden administration has put out are still not enough. So, what happens now? Is this going to be like the prescription drug industry, where they’re going to try to sue their way out of it? Or is it going to be more like the hospital transparency, where they’re just not going to do it and say, “Come and get us”?
Kenen: My suspicion is litigation, but it’s too soon to know. I assume that either one of the nursing home chains — because there are some very big corporations that own a lot of nursing homes — there are several nursing home trade industry groups, for-profit, nonprofit. Does one owner — is in an area where there is a workforce shortage, because that does exist. I mean, I’d be surprised if we don’t see some litigation, because when don’t we see that? I mean, it’s rare. That’s the norm in health care, is somebody sues. Some of the workforce issues are real, but also this proposal doesn’t go into effect tomorrow. It’s not like — but I mean, there are issues of the nursing workforce. There are issues about not just the number of nurses, but do we have them in the right places doing the right jobs? It’s not just RNs [registered nurses]; there are also shortages of other direct care workers. I did a story a few months ago on this, and there are actually nursing homes that have closed entire wings because they don’t have enough staff, and those are some of the nonprofits. There are nursing issues.
Rovner: And a lot of nursing home staff got sick at the beginning of the covid pandemic, and many of them died before there were good treatments. I mean, it’s always been a very hard and not very well-paid job to care for people in nursing homes. And then it became a not very pleasant, not very well-paid, and very deadly job. So I don’t think that’s probably helping the recruitment of people to work in nursing.
Kenen: Right, but the issue — I think a lot of people, when you have your first family experience with a nursing home or, you know, or those of us reporters who hadn’t been familiar with them until we went and did some stories on them, I think people are surprised at how little nursing there actually is. It’s nurses’ aides; it’s, you know, what they used to call licensed practical nurses or nursing assistants; and CNAs, certified nursing assistants. They’re various; different states have different names. But these are not four-year RNs. The amount of actual nursing — forget doctors. I mean, there’s just not a lot of RNs in nursing homes. There’s not a lot of doctors who spend time in nursing homes. A lot of the care is done through people with less training. So, this is trying to get more nurses in nursing homes. And there’s been a lot of stories about inadequate care. KFF Health News — I think it was Jordan Rau who did them. There have been some good stories about particularly nights and weekends, just really nobody there. These are fragile people. And they wouldn’t be in a nursing home if they weren’t fragile people. There are a lot of horror stories. At the same time, there are some legitimate — How fast can you do this? And how well can you do it? And can you do it across the country? I mean, it’s going to take some working out, but I don’t think anybody thinks that nursing home care in this country is, you know, a paragon of what we want our elders to experience.
Rovner: And the nursing home industry points out, truthfully, that most nursing home payments now come from Medicaid, because even people who start out being able to afford it themselves often run out of money and then they end up — then they qualify for Medicaid. And Medicaid in many states doesn’t pay very much, doesn’t pay nursing homes very much. So it’s hard for these companies. We’re not even talking about the private equity companies. A lot of nursing homes operate on the financial edge. I mean, there are —our long-term care policy in this country is, you know, just: What happens, happens, and we’ll worry about it later. And this has been going on for 50 years. And now we have baby boomers retiring and getting older and needing nursing home care. And at some point, this is all going to come to a head. All right. Well, let us turn to abortion. This week marks the second anniversary of the Texas abortion ban, the so-called heartbeat bill, that bans most abortion and lets individuals sue other individuals for helping anyone getting an abortion, which the Supreme Court, if you’ll recall, allowed to take effect months before it formally overturned Roe v. Wade. And, I guess not surprisingly, Texas is still in the news about abortion. This time. The same people who brought us Texas SB 8, which is the heartbeat bill, are going town by town and trying to pass ordinances that make it illegal to use roads within that town’s borders to help anyone obtain an abortion. They’re calling it abortion “trafficking.” Now, it’s not only not clear to me whether a local ordinance can even impact a state or an interstate highway, which is what these laws are mostly aimed at; but how on earth would you enforce something like this, even if you want to?
Ollstein: So, my impression is that they do not want to. These are not meant to be practical. They are not meant to be enforced, because how would you do it other than implementing a very totalitarian checkpoint system? This is meant to —
Rovner: Yes, have you been drinking and are you on your way to get an abortion?
Ollstein: Right. Right, right, right. So, it seems like the main purpose is to have a chilling effect, which it very well could have, even if it doesn’t stand up in court. You know, you also have this situation that we’ve had play out in other ways, where people are challenging laws in courts for having a chilling effect, and courts are saying, look, you have to wait till you actually get prosecuted and challenge it, you know, do an as-applied challenge. If you can’t challenge unless there’s a prosecution but there’s no prosecutions, then you sort of just have it hanging over your head like a cloud.
Kenen: Like Alice said, there’s no way you could do this. Like, what do you do, stop every car and give every person a pregnancy test? Are you going to, like, have, you know, ultrasounds on the E-ZPass monitors? Like, you go through it, it checks your uterus. So, I mean, it’s just not — you can’t do this. But I think one of the things that was really interesting in one of the stories I read about it, I think it was in The Washington Post, was that when they interviewed people about it, they thought it was trafficking, like really trafficking, that there were pregnant woman being kidnapped and forced to have an abortion. So even if you’re pro-choice, you might say, “Oh, I’m against abortion trafficking. I mean, I don’t want anyone to be forced to have an abortion.” You know, so, it’s — the wording and the whole design of it is, they know what they’re doing. I mean, they want to create this confusion. They want to create a disincentive. There’s no way — you know, radar guns? I mean, it’s just, there’s no way of doing this. But it is part of the effort to clamp down even further on a state that has already really, really, really clamped down.
Rovner: Although, I mean, if one could sue and if one could then know about something that’s happening and then you could presumably take the person to court and say, I know you were pregnant and now you’re not, and somebody took you in a car to New Mexico or whatever …
Kenen: You can’t even prove — how do you prove that it wasn’t a miscarriage?
Rovner: That’s —
Kenen: Right? I mean …
Rovner: I’m not saying — I’m not talking about the burden of proof. I’m just saying in theory, somebody could try to have a case here. I mean, but we certainly know that Texas has done a very good job creating a chilling effect, because we still have this lawsuit from the women who were not seeking abortions, who had pregnancy complications and were unable to get health-saving and, in some cases, lifesaving care promptly. And that’s still being litigated. But meanwhile, we have, you know, just today a study out from the Guttmacher Institute that showed that despite how well these states that are banning abortion have done in banning abortion, there were presumably more abortions in the first half of 2023 than there were before these bans took effect, because women from ban states were going to states where it is not banned. And there has been, ironically, better access in those states where it is not banned. I can’t imagine that this is going to please the anti-abortion community. One would think it would make them double down, wouldn’t it?
Ollstein: We know that people are leaving their states to obtain an abortion. We also know that that’s not an option for a lot of people, and not just because a lot of people can’t afford it or they can’t take time off work, they can’t get child care — tons of reasons why somebody might not be able to travel out of state. They have a disability, they’re undocumented. We also have — it’s become easier and easier and easier to obtain abortion pills online through, you know, a variety of ways: individual doctors in more progressive states, big online pharmacies are engaged in this, overseas activist groups are engaged in this. And so, you know, that’s also become an option for a lot of people. And anti-abortion groups know that those are the two main methods. People are still continuing to have abortions. And so, they’re continuing to just throw out different ways to try to either, you know, deter people or actually block them from either of those paths.
Rovner: This fight will also continue on. So, that is this week’s news. Now we will play my interview with Meena Seshamani, and then we will come back and do our extra credits.
Hey, “What the Health?” listeners, you already know that few things in health care are ever simple. So, if you like our show, I recommend you also listen to “Tradeoffs,” a podcast that goes even deeper into our costly, complicated, and often counterintuitive health care system. Hosted by longtime health care journalist and friend Dan Gorenstein, “Tradeoffs” digs into the evidence and research data behind health care policies and tells the stories of real people impacted by decisions made in C-suites, doctors’ offices, and even Congress. Subscribe wherever you listen to your podcasts.
I am pleased to welcome back to the podcast Dr. Meena Seshamani, deputy administrator and director of the Center for Medicare at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Meena was with us to talk generally about Medicare’s new prescription drug negotiation program earlier this summer. But now that the first 10 drugs subject to negotiation have been announced, we’re pleased to have her back. Welcome.
Meena Seshamani: Thank you for having me.
Rovner: So, remind our listeners, why hasn’t Medicare been able to negotiate drug prices until now — they negotiate prices of everything else — and what changed to make that happen?
Seshamani: That’s right. It was because of the Medicare law that Medicare did not have the ability to negotiate drugs. And thanks to the new drug law, the Inflation Reduction Act, now Medicare has the ability to negotiate the prices of the highest-cost drugs that don’t have competition. And that is part of the announcement that we had on what the first 10 drugs are that have been selected.
Rovner: So, as you say, last week, for the first time and in time for the Sept. 1 deadline, Medicare announced the list of the first 10 drugs that will be part of the first round of price negotiations. Why these 10 specifically? I imagine it’s not a coincidence that the list includes some of the drugs whose ads we see the most often on TV: drugs like Eliquis, Xarelto, and Jardiance, which I of course know how to pronounce because I see the ads all the time.
Seshamani: Well, the process of selection really was laid out in the drug law and also through the guidance that we put out that we had incorporated everybody’s comment for. So, what we did is we started with the, you know, over 7,500 drugs that are covered in the Part D Medicare prescription drug program. From there, we picked those drugs that had been on the market for seven years for a drug product or 11 years for a larger molecule or biologic product that did not have competition. And then from there, there are various exemptions and exclusions that, again, are laid out in the law: for example, drugs that have low Medicare spend, of less than $200 million; drugs that are plasma-derived products; certain orphan drugs. An orphan drug is a drug that is indicated for a rarer disease. So that, again, those specific criteria are laid out in the law and in our guidance. And then there were opportunities for manufacturers to apply, for example, for a small biotech exemption; if their drug was, you know, 80% of their, you know, Medicare Part D revenue, they could say, “Hey, I’m a small biotech.” Again, a lot of these criteria were laid out in the law. Or for a manufacturer of a biosimilar, which is kind of like a generic drug for one of these biologic drugs, they could say, “Hey, we have a biosimilar that’s going to be coming on the market, has a high likelihood of coming on the market, so you should delay negotiating” the brand, if you will, drug. So, again, all of these steps were laid out in the drug law, and those are the steps and criteria that we followed that came to that list of 10 drugs that we published.
Rovner: I did see the makers of one drug — and forgive me, I can’t remember which one it was — saying, “But our drug isn’t that expensive.” On the other hand, their drug is used by a lot of people on Medicare. So, it’s not just the list price of the drug, right? It’s how much it costs Medicare overall.
Seshamani: That’s right. The list is made up of those drugs that have the highest gross total cost to the program — so, price per unit times units of volume that is used.
Rovner: So, how does this negotiation process work? What happens now? Now we have this list of 10 drugs.
Seshamani: Yeah, a lot of this is also laid out in the law, and then we fleshed out further in our guidance. So, from the list of 10 drugs, on Oct. 1, manufacturers now have to decide if they want to participate in the negotiation program. It is a voluntary program. It is our hope that they will come to the table and want to negotiate, because I think we all have shared goals of improving access and affordability and really driving innovation for the cures and therapies that people need. So, Oct. 1, they sign agreements for the negotiation program if they decide to participate. And Oct. 2 is the deadline for gathering data. We put out what’s called an information collection request to say, this is the kind of data we’re thinking about collecting. We got lots of comments and incorporated that. So, that provides the framework for the data that we’re requesting both from the manufacturer of the selected drug, but also, there are aspects open to the public on, you know, how the drug benefits populations, for example. So that’s Oct. 2. Then we’re going to have patient-focused listening sessions, a session for each drug, for patients, their caregivers, you know, other advocates, to be able to share what they see as the benefits of the drugs that are selected. And, we will have meetings with each of the manufacturers. All of that information will come together in an initial offer that CMS will make Feb. 1, 2024, and that is a date that is stipulated in the law. The manufacturer then has about 30 days to evaluate that. If they like that offer, they can agree. If they want, they can make a counteroffer. From that counteroffer, CMS has the ability to agree or to say, “You know, we don’t agree, so let’s now have a series of negotiation meetings.” There can be up to three negotiation meetings that provides that back-and-forth, ultimately leading to an agreed-upon what’s called maximum fair price in the law. And those maximum fair prices are published by Sept. 1, 2024. Again, that Sept. 1 is stipulated in the law. And also as part of this process, CMS will publish a narrative about that negotiation process — you know, the data that was received, you know, the back-and-forth, and also we’ll publish ultimately the maximum fair prices that are agreed to.
Rovner: And does that maximum fair price just apply to Medicare?
Seshamani: The maximum fair price just applies to Medicare. The information will be available. I mean, we don’t have any authority. You know, the commercial sector, they do their own negotiations, and they will continue to do so. But part of this is an opportunity to really further the conversation about how drugs impact the lives of people. We have an opportunity now with some drugs that have been on the market for quite a while, right? Minimum of seven years or 11 years, to see how these drugs work in the real world, in people’s communities, so that we can incorporate that into what it is that we need and want for people to be healthy, to stay out of the hospital, to live meaningful lives. So it’s really an opportunity to further that conversation. And a lot of that data, a lot of those listening sessions, that will all go into our negotiation process and will be part of the narrative that we publish.
Rovner: And what happens if the drug company says either we don’t want to negotiate or we don’t like our final offer? If they say they don’t want to play, what happens?
Seshamani: Julie, I will say again, to start with, we are hopeful that the drug companies will come forward and will want to negotiate because, again, through many conversations that we have had, we do have shared goals of access and affordability and really driving innovation and procures and therapies that people need. And it is a choice for drug companies if they want to participate or not, as stipulated in the law. If a drug company decides not to sign, you know, the negotiation agreement, not to participate in negotiation, then we would refer them to the Department of Treasury for an excise tax. That excise tax is also described in the law. If a drug company has this excise tax applied, they can get out of paying the excise tax. If, No. 1, they decide to come to the table and negotiate, or No. 2, if they exit the Medicare and Medicaid market. So those are kind of their off-ramps, if you will, for that excise tax.
Rovner: So they don’t have to participate in the negotiation, but they also don’t have to participate in Medicare and Medicaid.
Seshamani: Correct.
Rovner: So I saw a lot of complaining last week with the first group of drugs that this is really only going to benefit the people on Medicare who take those drugs. But, in fact, if there really is a lot of money saved, the benefits could go well beyond this, right?
Seshamani: Yeah, I think two points. So, yes, this negotiation is for, you know, some of the highest-cost drugs to the Medicare program that don’t have competition. And the negotiated drug prices apply to the Medicare program. However, as we talked about, this really drives a conversation around drugs and really grounding this negotiation process in the clinical benefit that a drug provides. Considering things like if a drug is easier for someone to take and it’s easier for a caregiver, that can have tangible improvements to the health of the person they’re caring for, right? And I think we have that opportunity to really drive the conversation. And as we know in many aspects of health care, people look to Medicare to see what Medicare is doing. And also, the transparency around providing that narrative of the negotiation, publishing the maximum fair prices that are agreed to. That’s all data that anybody can use as they would like. And I think the second piece that’s important to remember is that negotiation is one very important piece of a very big change to Medicare prescription drug coverage. You know, alongside the $2,000 out-of-pocket tab that’s going to go into effect in 2025, the no-cost vaccines, $35 copay cap for insulin that have already gone into effect. So, really, it is part of a larger sea change in Medicare drug coverage that will help millions of people and their families. You know, I did a roundtable with seniors as we were rolling out the insulin copay cap. And one woman was telling me that she was providing money to her brother every month so that he could pay for his insulin on Medicare. So, really, I mean, this has tremendous impact not just for people on Medicare, but their families, their communities, and really furthers the conversation for the entire system.
Rovner: I was actually thinking of more nitty-gritty money, which is if you save money for Medicare, premiums will be lower for people who are getting drug coverage, and taxpayers will save money, too, right? I mean, this is not just for these people and their families.
Seshamani: Our priority is being able to reach agreement on a fair price for the people who rely on these medications for their lives and the American taxpayer in the Medicare program.
Rovner: I know you can’t comment on lawsuits, and there are many lawsuits already challenging this. But the drug companies, one of their major arguments is that if you limit what they can charge for their drugs, particularly in the United States, the last country where they can charge whatever they want for their drugs, they will not be able to afford to keep the pipeline going to discover more new, important drugs. This is an argument they’ve been making since, I told somebody earlier, since I covered this in the late 1980s. What is your response just to that argument?
Seshamani: Well, I think there were several articles, many articles were written about this on the day that the 10 selected drugs were published. They were published before the stock market opened. And there really was no impact on the stocks of the companies. There were many financial pieces written about this. So I think that is one indication of the fact that the pharmaceutical industry is strong, it is thriving, and it is designed to innovate. And what we’re hoping to do through this negotiation program is really reward the kinds of innovations that we all need, the cures and therapies that people need. Recently, the venture fund that backed Moderna invested in a new startup for small molecules. Bayer has recently invested a billion dollars in the U.S. So you see, the industry very much is thriving. That is what the stock market response also shows. And it’s also the way that we are approaching negotiation to make sure that we’re rewarding the kinds of innovations that people need.
Rovner: Well, Meena Seshamani, thank you so much. I hope we can come back to you as this negotiation process for the first time proceeds.
Seshamani: Absolutely. Thanks again, Julie.
Rovner: OK. We are back, and it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Alice, why don’t you go first this week?
Ollstein: Yeah, I picked a very sad story from The Washington Post about how people who have schizophrenia are a lot more vulnerable to extreme heat. And it’s rare to find one of these health care stories where you’re just astonished. You know, I had no idea about this. You know, it really walks through not only are people more vulnerable for mental health reasons, you know, it profiles this terrible story of a guy in Phoenix who wandered off into the desert and died because he was experiencing paranoid delusions. But also, just physically, people with schizophrenia have difficulty regulating their body temperature. A lot of medications people take make people more dehydrated, less able to cope. And just an astonishingly high percentage of people hospitalized and killed by extreme heat have these mental illnesses. Of course, they’re also more likely to have housing instability or be out on the street. So just a fascinating piece, and I hope it spurs cities to think of ways to address it. One other small thing I want to compliment is it just, technically, on this article online, they have a little widget where you can convert all of the temperatures cited in the lengthy story from Fahrenheit to Celsius. And I just really appreciated that for allowing, you know, no matter where you live, you sort of get what these high temperatures mean.
Rovner: Yeah, graphics can be really helpful sometimes. Rachel.
Cohrs: Yeah. So I chose a story in The Wall Street Journal and the headline is “How Novartis’s CEO Learned From His Mistakes and Got Help From an Unlikely Quarter,” by Jared S. Hopkins. And I think it was a really interesting and rare look inside one of these pharmaceutical companies. And Novartis hired a Wall Street analyst, Ronny Gal, to help advise them. And I think I had read his analysis before he crossed over to Novartis. So I think it was interesting to just hear how that has integrated into Novartis’ strategy and just how they’re changing their business. But I think as we’re, you know, having these conversations about drug pricing and how strategies are changing due to some of these policies, it is helpful to look at who these executives are listening to and what they’re prioritizing, whose voices in this decision-making process that really has impacts for so many people who are waiting for treatments. And I think there are tough choices that are made all the time. So I just thought it was very illuminating and helpful as we’re talking about how medicines get made in D.C.
Rovner: Yeah, maybe there will be a little more transparency to actually how the drug industry works. We will see. Joanne.
Kenen: With Julie’s permission, I have two that are both short and related. I wrote a piece for Politico Nightly called “How to Wage War on Conspiracy Theories,” and I liked it because it really linked political trends and disinformation and attempts to debunk, with very parallel things going on in the world of health care and efforts to the motivations and efforts to sow trust and what we do and do not know about how to debunk, which we’re not very good at yet. And then the classic example, of course, is the related AP story, which has a very long headline, so bear with me. It’s by Kevin McGill: “Court Revives Doctors’ Lawsuit Saying FDA Overstepped Its Authority With Anti-Ivermectin Campaign.” And, basically, it’s that the 5th Circuit, a conservative court that we’ve talked about before, is saying that the FDA is allowed to inform doctors, but it can’t advise doctors. And I’m not really sure what the difference is there, because if the FDA is informing doctors that ivermectin, we now know, does not work against covid, and it can in fact harm people, there’s ample data, that the FDA is not allowed to tell doctors not to use it. So the ivermectin campaign is a form of disinformation, or misinformation, whatever you want to call it, that at the very beginning, people had, you know, there were some test-tube experiments. We had nothing else. You can sort of see why people wanted … might have wanted to try it. But we have lots and lots and lots of good solid clinical research and human beings and, no, it does not cure covid. It does not improve covid. And it can be damaging. It’s for parasites, not viruses.
Rovner: It can cure worms. Well, I’m going to channel my inner Margot Sanger-Katz this week and choose a story from a medical journal, in this case the Journal of the American Medical Association. Its lead author is Sherry Glied, who’s dean of the NYU Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service and former assistant HHS [Department of Health and Human Services] secretary for planning and evaluation during the Obama administration — and I daresay one of the most respected health policy analysts anywhere. The piece is called “Health Systems and Social Services — A Bridge Too Far?” And it’s the first article I’ve seen that really does question whether what’s become dogma in health policy over the past decade that — tending to what are called social determinants of health, things like housing, education, and nutrition — can improve health as much as medical care can. Rather, argues Glied, quote, “There are fundamental mismatches between the priorities and capabilities of hospitals and health systems and the task of addressing social determinants of health,” and that, basically, medical providers should leave social services to those who are professional social service providers. That is obviously a gross oversimplification of the argument of the piece, however, but I found it really thought-provoking and really, for the first time, someone saying, maybe we shouldn’t be spending all of this health care money on social determinants of health. Maybe we should let social service money go to the social service determinants of health. Anyway, we will see if this is the start of a trend or just sort of one outlier voice. OK, that is our show for this week. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks, as always, to our amazing engineer, Francis Ying. Also, as always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org. Or you can tweet me, or X me, or whatever. I’m still there @jrovner, also on Bluesky and Threads. Rachel?
Cohrs: I’m @rachelcohrs on X.
Rovner: Alice.
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein.
Rovner: Joanne.
Kenen: @JoanneKenen on Twitter, @joannekenen1 on Threads.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
2 years 1 month ago
Aging, Health Industry, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, Public Health, States, Abortion, Biden Administration, Drug Costs, HIV/AIDS, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Long-Term Care, Nursing Homes, Podcasts, U.S. Congress, Women's Health