La vacuna contra el sarampión es segura y eficaz. No te dejes engañar por los escépticos
Los casos de sarampión están aumentando en Estados Unidos. En el primer trimestre de este año, se registró un número de casos 17 veces mayor con respecto al promedio registrado durante el mismo período en los cuatro años anteriores, según los Centros para el Control y Prevención de Enfermedades (CDC).
Los casos de sarampión están aumentando en Estados Unidos. En el primer trimestre de este año, se registró un número de casos 17 veces mayor con respecto al promedio registrado durante el mismo período en los cuatro años anteriores, según los Centros para el Control y Prevención de Enfermedades (CDC). La mitad de las personas infectadas, principalmente niños, han sido hospitalizadas.
Y se espera que las cifras sigan empeorando, en gran medida porque cada vez más padres deciden no vacunar a sus hijos contra el sarampión y otras enfermedades como la polio y la tos ferina.
Este año, el 80% de los casos ha sido en personas no vacunadas o con un estatus de vacunación desconocido. Muchos padres han sido influenciados por una avalancha de desinformación difundida por políticos y personalidades en redes sociales, podcasts, y en la TV, que repiten falsas creencias, erosionando la confianza en la ciencia que respalda las vacunas infantiles de rutina.
A continuación, examinamos algunos mitos frecuentes de la retórica antivacunas y explicamos por qué está equivocada:
“No es para tanto”
Una idea errónea común es que las vacunas no son necesarias porque las enfermedades que previenen no son peligrosas u ocurren con muy poca frecuencia como para ser motivo de preocupación. Aunque se hayan reportado casos de sarampión en 19 estados, los escépticos acusan a funcionarios de salud pública y a los medios de comunicación de sembrar temor sobre la enfermedad sin fundamento.
Por ejemplo, una nota publicada en el sitio web del National Vaccine Information Center, una fuente habitual de desinformación sobre las vacunas, sostuvo que la preocupación creciente por el sarampión “es una exageración al estilo de ‘el cielo se cae'”. El artículo decía que contraer el sarampión, las paperas, la varicela y la gripe (también llamada influenza) era “políticamente incorrecto”.
Según los CDC, el sarampión resulta fatal en aproximadamente 2 de cada 1,000 niños infectados. Si este nivel de riesgo suena aceptable, vale la pena señalar que un número mucho mayor de niños con sarampión requieren hospitalización por neumonía y otras complicaciones serias.
Por cada 10 casos de sarampión, un niño con la enfermedad desarrolla una infección de oído que puede causar la pérdida auditiva permanente. Otro efecto extraño del virus es que puede destruir la inmunidad de una persona, y así afectar su capacidad para recuperarse de la gripe y otras afecciones comunes.
Las vacunas contra el sarampión han evitado la muerte de alrededor de 94 millones de personas, principalmente niños, en los últimos 50 años, según un análisis de abril de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). Junto con las vacunas contra la polio y otras enfermedades, se estima que las vacunas han salvado 154 millones de vidas en todo el mundo.
Algunos escépticos de las vacunas sostienen que las enfermedades que previenen ya no son una amenaza porque se han vuelto relativamente poco frecuentes en el país. (Lo cual es cierto, gracias a la vacunación). Es el razonamiento que invocó el cirujano general de Florida, Joseph Ladapo, durante un brote de sarampión en febrero, cuando dijo a los padres que sus hijos no vacunados podían seguir yendo a la escuela. “Hay mucha inmunidad”, dijo Ladapo.
A medida que esta actitud relajada hacia las vacunas convence a los padres de no dárselas a sus hijos, la inmunidad colectiva disminuye y los brotes serán cada vez más grandes y se propagarán más rápido.
En 2019, un brote de rápido crecimiento afectó a una comunidad con tasas de vacunación insuficientes en Samoa y mató a 83 personas en cuatro meses. Las tasas persistentemente bajas de vacunación contra el sarampión en la República Democrática del Congo mataron a más de 5,600 personas a causa de la enfermedad en brotes masivos el año pasado.
“Nunca se sabe”
Desde los orígenes de las vacunas, siempre ha existido un grupo que ha desconfiado porque no son naturales, en comparación con las infecciones y plagas que abundan en la naturaleza. Los miedos y dudas sobre las vacunas han ido cambiando a lo largo de las décadas. En el 1800, por ejemplo, los escépticos pensaban que las vacunas contra la viruela hacían que a las personas les salieran cuernos y que se comportaran como bestias.
En tiempos más recientes, los escépticos han vinculado las vacunas con una variedad de afecciones, desde el trastorno por déficit de atención e hiperactividad hasta el autismo y las enfermedades del sistema inmunológico. Los estudios científicos no respaldan estas afirmaciones.
La realidad es que las vacunas están entre las intervenciones médicas más estudiadas. En el siglo pasado, las vacunas han pasado por estudios científicos y ensayos clínicos masivos tanto en las fases de desarrollo como después, durante su uso generalizado.
Más de 12,000 personas participaron en los ensayos clínicos de la última vacuna aprobada para prevenir el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola. Al probar la vacuna en un gran número de personas, los investigadores pueden detectar riesgos poco comunes, lo cual es importante porque se administran a millones de personas sanas.
Para evaluar los riesgos a largo plazo, los científicos analizan grandes cantidades de datos para identificar señales de daño. Por ejemplo, un grupo danés analizó una base de datos de más de 657,000 niños y encontró que aquellos que fueron vacunados contra el sarampión cuando eran bebés no tenían más probabilidades de ser diagnosticados con autismo que aquellos que no fueron vacunados.
En otro estudio, los investigadores analizaron registros de 805,000 niños nacidos entre 1990 y 2001 y no encontraron ninguna prueba de que las vacunaciones múltiples pudieran afectar el sistema inmune de los niños.
Pero las personas que promueven la desinformación sobre las vacunas, como el candidato a la presidencia Robert F. Kennedy Jr., descartan los estudios masivos respaldados por la ciencia.
Por ejemplo, Kennedy sostiene que los ensayos clínicos para las nuevas vacunas no son confiables porque no se compara a los niños vacunados con un grupo que recibe un placebo, como solución salina u otra sustancia sin efecto. En vez de utilizar un placebo, muchos ensayos modernos comparan las vacunas actualizadas con otras más antiguas. Esto se debe a que se considera no ético poner en peligro a los niños al darles una vacuna falsa cuando se conoce el efecto protector de la inmunización.
En un ensayo clínico de vacunas contra la polio realizado en la década de 1950, 16 niños que recibieron un placebo murieron de polio y 34 quedaron paralizados, dijo Paul Offit, director del Centro de Educación Sobre Vacunas del Hospital de Niños de Philadelphia y autor de un libro sobre la primera vacuna contra la polio.
“Demasiadas y demasiado pronto”
Varios de los libros sobre vacunas más vendidos en Amazon promueven la peligrosa idea de que los padres deberían omitir o retrasar la vacunación de sus hijos. “Puede ser que no todas las vacunas en el calendario de los CDC sean adecuadas para todos los niños en todo momento”, escribe Paul Thomas en su libro más vendido “The Vaccine-Friendly Plan”. Para respaldar su argumento, dice que los niños que han seguido “mi protocolo están entre los más sanos del mundo”.
Desde la publicación del libro, la licencia médica de Thomas fue suspendida temporalmente en Oregon y Washington.
La Junta Médica de Oregon documentó cómo Thomas convenció a los padres a omitir vacunas recomendadas por los CDC e “hizo llorar” a una madre que no estaba de acuerdo. Varios niños bajo su cuidado contrajeron tos ferina y rotavirus, ambas enfermedades que se previenen fácilmente con vacunas, escribió la junta.
Thomas le recetó suplementos de aceite de pescado y homeopatía a un niño que tenía una laceración profunda en el cuero cabelludo en lugar de darle una vacuna de emergencia contra el tétanos. El niño desarrolló un cuadro de tétanos grave y estuvo en el hospital por casi dos meses, donde tuvo que someterse a una intubación, una traqueotomía y una sonda de alimentación para sobrevivir.
El calendario de vacunación recomendado por los CDC se diseñó para proteger a los niños en los momentos más vulnerables de su vida y minimizar los efectos secundarios. Por ejemplo, la vacuna combinada contra el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola no se administra durante el primer año de vida del bebé porque los anticuerpos que transmite temporalmente la madre pueden interferir con la respuesta inmunitaria. Y como algunos bebés no generan una respuesta inmunitaria fuerte con esa primera dosis, los CDC recomiendan una segunda dosis alrededor del momento en que los niños comiencen el jardín de infantes, ya que el sarampión y otros virus se propagan rápidamente en contextos grupales.
No se recomienda retrasar mucho más las dosis de esta vacuna ya que los datos sugieren que los niños vacunados a los 10 años o más tienen más probabilidades de desarrollar reacciones adversas, como convulsiones o fatiga.
Alrededor de una docena de otras vacunas siguen su propio esquema cronológico, con superposiciones para obtener la mejor respuesta. Los estudios han demostrado que la vacuna contra el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola se puede administrar de forma segura y eficaz combinada con otras vacunas.
“Ellos no quieren que lo sepas”
En la introducción del nuevo libro de Ladapo sobre cómo superar el miedo en la salud pública, Kennedy compara al cirujano general de Florida con Galileo. Así como la Inquisición católica condenó al famoso astrónomo por promover teorías sobre el universo, sugiere Kennedy, las instituciones científicas reprimen a los disidentes de las vacunas por razones nefastas.
“La persecución de científicos y médicos que se atreven a cuestionar las doctrinas contemporáneas no es nada nuevo”, escribe Kennedy. Su compañera de fórmula, la abogada Nicole Shanahan, ha hecho campaña con la idea de que las conversaciones sobre los peligros de las vacunas se están censurando y que las corporaciones influyen sobre los CDC y otras agencias federales para ocultar datos.
En el podcast más escuchado en Estados Unidos, “The Joe Rogan Experience”, a menudo figuran invitados que desconfían del consenso científico. El año pasado, en el programa, Kennedy repitió el mito muchas veces desmentido de que las vacunas causan autismo.
Lejos de ignorar ese miedo, los epidemiólogos lo han tomado en serio. Han realizado más de una docena de estudios en busca de un vínculo entre las vacunas y el autismo, y no han encontrado ninguno. “Hemos refutado de manera concluyente la teoría de que las vacunas están relacionadas con el autismo”, afirmó Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, epidemiólogo de la Universidad de Wollongong en Australia. “Es por esto que el sistema de salud pública tiende a cerrar esas conversaciones rápidamente”.
Las agencias federales son transparentes con respecto a las reacciones que pueden causar las vacunas, incluyendo convulsiones y dolor en el brazo. Y el gobierno tiene un programa para compensar a las personas si se determina científicamente que sus lesiones son el resultado de las vacunas. Alrededor de 1 a 3.5 de cada millón de dosis de la vacuna contra el sarampión, las paperas y la rubéola pueden provocar una reacción alérgica potencialmente mortal. Se estima que el riesgo de muerte a causa de un rayo durante toda la vida de una persona es hasta cuatro veces mayor.
“Lo más convincente que puedo decir es que mi hija tiene todas sus vacunas y que todos los pediatras y profesionales de salud pública que conozco han vacunado a sus hijos”, dijo Meyerowitz-Katz. “Nadie haría eso si pensara que existen riesgos graves”.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Health Industry, Noticias En Español, Public Health, States, Children's Health, Misinformation, Oregon, vaccines, Washington
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Anti-Abortion Hard-Liners Speak Up
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
With abortion shaping up as a key issue for the November elections, the movement that united to overturn Roe v. Wade is divided over going further, faster — including by punishing those who have abortions and banning contraception or IVF. Politicians who oppose abortion are already experiencing backlash in some states.
Meanwhile, bad actors are bilking the health system in various new ways, from switching people’s insurance plans without their consent to pocket additional commissions, to hacking the records of major health systems and demanding millions of dollars in ransom.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post, and Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins schools of public health and nursing and Politico Magazine.
Panelists
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins University and Politico
Rachel Roubein
The Washington Post
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- It appears that abortion opponents are learning it’s a lot easier to agree on what you’re against than for. Now that the constitutional right to an abortion has been overturned, political leaders are contending with vocal groups that want to push further — such as by banning access to IVF or contraception.
- A Louisiana bill designating abortion pills as controlled substances targets people in the state, where abortion is banned, who are finding ways to get the drug. And abortion providers in Kansas are suing over a new law that requires patients to report their reasons for having an abortion. Such state laws have a cumulative chilling effect on abortion access.
- Some Republican lawmakers seem to be trying to dodge voter dissatisfaction with abortion restrictions in this election year. Sen. Ted Cruz of Texas and Sen. Katie Britt of Alabama introduced legislation to protect IVF by pulling Medicaid funding from states that ban the fertility procedure — but it has holes. And Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland declared he is pro-choice, even though he mostly dodged the issue during his eight years as governor.
- Former President Donald Trump is in the news again for comments that seemed to leave the door open to restrictions on contraception — which may be the case, though he is known to make such vague policy suggestions. Trump’s policies as president did restrict access to contraception, and his allies have proposed going further.
Also this week, Rovner interviews Shefali Luthra of The 19th about her new book on abortion in post-Roe America, “Undue Burden.”
Plus, for “extra credit,” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: The 19th’s “What Happens to Clinics After a State Bans Abortion? They Fight To Survive,” by Shefali Luthra and Chabeli Carrazana.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Stat’s “How Doctors Are Pressuring Sickle Cell Patients Into Unwanted Sterilizations,” by Eric Boodman.
Rachel Roubein: The Washington Post’s “What Science Tells Us About Biden, Trump and Evaluating an Aging Brain,” by Joel Achenbach and Mark Johnson.
Joanne Kenen: ProPublica’s “Toxic Gaslighting: How 3M Executives Convinced a Scientist the Forever Chemicals She Found in Human Blood Were Safe,” by Sharon Lerner; and The Guardian’s “Microplastics Found in Every Human Testicle in Study,” by Damian Carrington.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- NPR’s “Republicans Try To Soften Stance on Abortion as ‘Abolitionists’ Go Farther,” by Sarah McCammon.
- KFF Health News’ “Biden Leans Into Health Care, Asking Voters To Trust Him Over Trump,” by Phil Galewitz.
- KFF Health News’ “Exclusive: Senator Urges Biden Administration To Thwart Fraudulent Obamacare Enrollments,” by Julie Appleby.
- KFF Health News’ “KHN’s ‘What the Health?’: Un-Trumping the ACA,” featuring an interview with journalist Marshall Allen.
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: Anti-Abortion Hard-Liners Speak Up
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Mila Atmos: The future of America is in your hands. This is not a movie trailer, and it’s not a political ad, but it is a call to action. I’m Mila Atmos, and I’m passionate about unlocking the power of everyday citizens. On our podcast Future Hindsight, we take big ideas about civic life and democracy and turn them into action items for you and me. Every Thursday, we talk to bold activists and civic innovators to help you understand your power and your power to change the status quo. Find us at futurehindsight.com or wherever you listen to podcasts.
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, May 23, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might’ve changed by the time you hear this. So, here we go. We are joined today via a video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Rachel Roubein of The Washington Post.
Rachel Roubein: Hi, thanks for having me.
Rovner: And Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins schools of public health and nursing and Politico Magazine.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: Later in this episode, we’ll have my interview with podcast panelist Shefali Luthra of The 19th. Shefali’s new book about abortion in the post-Roe [v. Wade] world, called “Undue Burden,” is out this week. But first, this week’s news. We’re going to start with abortion this week with a topic I’m calling “Abolitionists in Ascendance,” and a shoutout here to NPR’s Sarah McCammon with a great piece on this that we will link to in the show notes. It seems that while Republican politicians, at least at the federal level, are kind of going to ground on this issue, and we’ll talk more about that in a bit, those who would take the ban to the furthest by prosecuting women, and/or banning IVF and contraception, are raising their voices. How much of a split does this portend for what, until the overturn of Roe, had been a pretty unified movement? I mean they were all unified in “Let’s overturn Roe,” and now that Roe has gone, boy are they dividing.
Ollstein: Yeah, it’s a lot easier to agree on what you’re against than on what you’re for. We wrote about the split on IVF specifically a bit ago, and it is really interesting. A lot of anti-abortion advocates are disappointed in the Republican response and the Republican rush to say, “No, let’s leave IVF totally alone” because these groups think, some think it some should be banned, some think that there should be a lot of restrictions on the way it’s currently practiced. So not a total ban, but things like you can only produce a certain number of embryos, you can only implant a certain number of embryos, you can only create the ones you intend to implant, and so that would completely upend the way IVF is currently practiced in the U.S.
So, we know the anti-abortion movement is good at playing the long game, and so some of them have told me that they see this kind of like the campaign to overturn Roe v. Wade. They understand that Republicans are reacting for political reasons right now, and they are confident in winning them over for restrictions in the long term.
Rovner: I’ve been fascinated by, I would say, by things like Kristan Hawkins of Students for Life [of America] who’s been sort of the far-right fringe of the anti-abortion movement looking like she’s the moderate now with some of these people, and their discussions of “We should charge women with murder and have the death penalty if necessary.” Sorry, Rachel, you want to say something?
Roubein: This is something that Republicans, they don’t want to be asked about this on the campaign. The more hard-line abolitionist movement is something more mainstream groups have been taking a lot of pains to distance themselves and say that we don’t prosecute women, and essentially nobody wants to talk about this ahead of 2024. GOP doesn’t want to be seen as that party that’s going after that.
Kenen: And the divisions existed when Roe was still the law of the land, and we would all write about the divisions and what they were pushing for, and it was partly strategic. How far do you push? Do you push for legislation? Do you push for the courts? Do you push for 20 weeks for fetal pain? But it was like rape exceptions and under what terms and things like that. So it was sort of much later in pregnancy, and with more restrictions, and the fight was about exactly where do you draw that line. This abolition of all abortion under all circumstances, or personhood, only a couple of years ago, were the fringe. Personhood was sort of like, “Oh, they’re out there, no one will go for that.” And now I don’t think it’s the dominant voice. I don’t think we yet know what their dominant voice is, but it’s a player in this conversation.
At the same time, on the other side, the pro-abortion rights people, there’s polls showing us this many Americans support abortion, but it’s subtler too. Even if people support abortion rights, it doesn’t mean that they’re not, some subset are in favor of some restrictions, or where that’s going to settle. Right now, a 15-week ban, which would’ve seemed draconian a year or two ago, now seems like the moderate position. It has not shaken out, and …
Rovner: Well, let’s talk …
Kenen: It’s not going to shake out for some time.
Rovner: Let’s talk about a few specifics. The Louisiana State Legislature on Tuesday approved a bill that would put the drugs used in medication abortion, mifepristone and misoprostol, on the state’s list of controlled substances. This has gotten a lot of publicity. I’m wondering what the actual effect might be here though since abortion is already banned in Louisiana. Obviously, these drugs are used for other things, but they wouldn’t be unavailable. They would just be put in this category of dangerous drugs.
Ollstein: So, officials know that people in banned states, including Louisiana, are obtaining abortion pills from out of state, whether through telehealth from states with shield laws or through these gray-area groups overseas that are mailing pills to anyone no matter what state they live in or what restrictions are in place. So I think because it would be very difficult to actually enforce this law, short of going through people’s homes and their mail, this is just one more layer of a chilling effect and making people afraid to seek out those mail order services.
Rovner: So it’s more, again, for the appearance of it than the actuality of it.
Ollstein: It also sets up another state versus federal law clash, potentially. We’ve seen this playing out in courts in West Virginia and in North Carolina, basically. Can states restrict or even completely ban a medication that the FDA says is safe and effective? And that question is percolating in a few different courts right now.
Rovner: Including sort of the Supreme Court. We’re still waiting for their abortion pill decision that we expect now next month. Meanwhile, in Kansas, where voters approved a big abortion rights referendum in 2022 — remember, it was the first one of those — abortion providers are suing to stop a new state law enacted over the governor’s veto that would require them to report to the state women’s reasons for having an abortion. Now it’s not that hard to see how that information could be misused by people with other kinds of intents, right?
Ollstein: Well, it also brings up right to free speech issues, compelled speech. I think I’ve seen this pop up in abortion lawsuits even before Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization], this very issue because there have been instances where either doctors are required to give information that they say that they believe is medically inaccurate. That’s an issue in several states right now. And then this demanding information from patients. A lot of clinics that I’ve spoken to are so afraid of subpoenas from officials in-state, from out of state, that they intentionally don’t ask patients for certain kinds of data even though it would really help medically or organizationally for them to have that data. But they’re so afraid of it being seized, they figure well, they can’t seize it if they’re … doesn’t exist in the first place. And so I think this kind of law is in direct conflict with that.
Roubein: It also gets at the question of medical privacy that we’ve been seeing in the Biden administration’s efforts over HIPAA and protecting patients’ records and making it harder for state officials to attempt to seize.
Rovner: Yeah, this is clearly going to be a struggle in a lot of states where voters versus Republican legislatures, and we will sort of see how that all plays out. So even while this is going on in a bunch of the states, a lot of Republicans, including some who have been and remain strongly anti-abortion, are doing what I’m calling ducking-and-covering on a lot of these issues. Case in point, Texas Republican Sen. Ted Cruz and Alabama Republican Sen. Katie Britt this week introduced a bill they say would protect IVF, which is kind of ironic given that both of them voted against a bill to protect IVF back in, checking notes, February. What’s the difference here? What are these guys trying to do?
Kenen: Theirs is narrower. They say that the original bill, which was a Democratic bill, was larded with abortion rights kinds of things. I have not read the entire bill, I just read the summary of it. And in this one, if a state restricts someone who had — someone feel free to correct me if I am missing something here because I don’t have deep knowledge of this bill — but if a state does not protect IVF, they would lose their Medicaid payment. And I was not clear whether that meant every penny of Medicaid, including nursing homes, or if it’s a subsection of Medicaid, because it seems like a big can of worms.
Ollstein: Yeah, so the key difference in these bills is the word ban. The Republican bill says that if states ban IVF, then these penalties kick in for Medicaid, but they say that there can be “health and safety regulations,” and so that is very open to interpretation. That can include the things we talked about before about you can only produce a certain number of embryos, you can only implant a certain number of embryos, and you can’t discard them. And so even what Alabama did was not an outright ban. So even something like that that cut off services for lots of people wouldn’t be considered a ban under this Republican bill. So I think there’s sort of a semantic game going on here where restrictions would still be allowed if they were short of a blanket ban, whereas the democratic bill would also prevent restrictions.
Rovner: Well, and along those exact same lines, in Maryland, former two-term Republican governor Larry Hogan, who’s managed to dodge the abortion issue in his primary run to become the Senate nominee, now that he is the Republican candidate for the open Senate seat, has declared himself, his words, “pro-choice,” and says he would vote to restore Roe in the Senate if given the opportunity. But as I recall, and I live in Maryland, he vetoed a couple of bills to expand abortion rights in very blue Maryland. Is he going to be able to have this both ways? He seems to be doing the [Sen.] Susan Collins script where he gets to say he’s pro-choice, but he doesn’t necessarily have to vote for abortion rights bills.
Kenen: Hogan is a very popular moderate Republican governor in a Democratic state. He is a strong Senate candidate. His opponent, a Democrat, Angela Alsobrooks, has a stronger abortion rights record. I don’t think that’s going to be the decisive issue in Maryland. I think it may help him a little bit, but I think in Maryland, if the Senate was 55-45, a lot of Democrats like Hogan and might want another moderate Republican in the Senate. But given that this is going to be about control of the Senate, abortion will be a factor, I don’t think abortion is going to be the dominant factor in this particular race.
If she were to win and there’s two black women, I mean that would be the first time that two black women ever served in the Senate at once, and I think they would only be number three and number four in history. So race and Affirmative Action will be factors, but I think that Democrats who might otherwise lean toward him, because he was considered a good governor. He was well-liked. This is a 50-50ish Senate, and that’s the deciding thing for anyone who pays attention, which of course is a whole other can of worms because nobody really pays attention. They just do things.
Roubein: I think it’s also worth noting this tact to the left comes as Maryland voters will be voting on an abortion rights ballot measure in 2024. So that all sort of in context, we’ve seen what’s happened with the other abortion measures, abortion rights have won, so.
Rovner: And Maryland is a really blue state, so one would expect it …
Kenen: There’s no question that the Maryland …
Rovner: Yeah.
Kenen: I mean, and all of us would fall flat on our faces if the abortion measure fails in Maryland. But I believe this is the first one on the ballot alongside a presidential election, and some of them have been in special elections. It’s unclear the correlation between, you can vote for a Republican candidate and still vote for a pro-abortion rights initiative. We will learn a lot more about how that split happens in November. I mean, is Kansas going to go for Biden? Unlikely. But Kansas went really strong for abortion rights. If you’re not a single-issue voter, you can, in fact, have it both ways.
Rovner: Yes, and we are already seeing that in the polls. Well, of course then there is the king of trying to have it both ways: former President Trump. He is either considering restrictions on contraception, as he told an interviewer earlier this week, promising a proposal soon, or he will, all caps, as he put on Truth Social, never advocate imposing restrictions on birth control. So which is it?
Ollstein: So this came out of Trump’s verbal tick of saying “We’ll have a plan in a few weeks,” which he says about everything. But in this context it made it sound like he was leaving the door open to restrictions on contraception, which very well might be the case. So what my colleague and I wrote about is he says he would never restrict contraception. A lot of things he did in his first administration did restrict access to contraception. It was not a ban. Again, we’re getting back into the semantics of ban. It was not a ban, but his Title X rule led to a drop in hundreds of thousands of people accessing contraception. He allowed more kinds of employers to refuse to cover their employees’ contraception on their health plans, and the plans his allies are creating in this Project 2025 blueprint would reimpose those restrictions and go even further in different ways that would have the effect of restricting access to contraception. And so I think this is a good instance of look at what people do, not what they say.
Rovner: So now that we’re on the subject of campaign 2024, President Biden’s campaign launched a $14 million ad buy this week that includes the warning that if Trump becomes president again he’ll try to repeal the Affordable Care Act. Maybe health care will be an issue in this election after all? I don’t have a rooting interest one way or the other. I’m just curious to see how much of an issue health will be beyond reproductive rights.
Kenen: Well, as Alice just pointed out, Trump’s promised plans often do not materialize, and we are still waiting to see his replacement plan eight years later. I think he’s being told to sort of go slow on this. I mean, not that you can control what Trump says, but he didn’t run on health care until the end, in 2016. It was a close race, and he ran against Hillary Clinton, and it was the last 10 or so days that he really came down hard because it was right when ACA enrollment was about to begin and premiums came in and they were high. He pivoted. So is this going to be a health care election from day one? And I’m putting abortion aside for one second in terms of my definition of health care for this particular segment. Is it going to be a health care election in terms of ACA, Medicare, Medicaid? At this point, probably not. But is it going to emerge at various times by one or the other side in politically opportune ways? I would be surprised if Biden’s not raising it. The ACA is thriving under Biden.
Rovner: Well, he is. That’s the whole point. He just took out a $14 million ad buy.
Kenen: Right. But again, we don’t know. Is it a health care election or is it a couple ads? We don’t know. So yes, it’s going to be a health care election because all elections are health care elections. How much it’s defined by health care compared to immigration? No, at this point, that’s not what we’re expecting. Compared to the economy? No, at this point. But is it an issue for some voters? Yes. Is it going to be an issue more prominently depending on how other things play out? It’ll have its peaks. We just don’t know how consistent it’ll be.
Roubein: Biden would love to run on the Inflation Reduction Act and politically popular policies like allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices. One of the problems of that is polls, including from KFF, has shown that the majority of voters don’t know about that. And some of these policies, the big ones, have not even gone into effect. CMS [Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] is going through the negotiation process, but that’s not going to hit people’s pocketbooks until after the election.
Kenen: The cliff for the ACA subsidies, which is in 2025, I mean I would imagine Democrats will be campaigning on, “We will extend the subsidies,” and again, in some places more than others, but that’s a time-sensitive big thing happening next year.
Rovner: But talk about an issue that people have no idea that’s coming. Well, meanwhile, for Trump, reproductive health isn’t the only issue where he’s doing a not-so-delicate dance. Apparently worried about Robert F. Kennedy Jr. stealing anti-vax [vaccine] votes from him, Trump is now calling RFK Jr. a fake anti-vaxxer. Except I’m old enough to remember when Trump bragged repeatedly about how fast his administration developed and brought the covid vaccine to market. That used to be one of his big selling points. Now he’s trying to be anti-vax, too?
Kenen: Not only did he brag about bringing it to the market. The way he used to talk about it, it was like he was there in his lab coat inventing it. Operation Warp Speed was a success. It got vaccines out in record time, way beyond what many people expected. Democrats gave him credit for that one policy in health care. He got a vaccine out and available in less than a year, and he got vaccinated and boasted about being vaccinated. He was open about it. Now we don’t know if he’s been boosted. He really backed off. As soon as somebody booed him, and it wasn’t a lot of boos, at one rally when he talked about vaccination and he got pushed back, that was the end.
Rovner: So, yeah, so I expect that to sort of continue on this election season, too.
Kenen: But we don’t expect RFK to flip.
Rovner: No, we do not. Right. Well, moving on to this weekend’s “Cyber Hacks,” a new feature, the fallout continues from the hack of Ascension [health care company]. That’s the Catholic hospital system with facilities in 19 states. In Michigan, patients have been unable to use hospital pharmacies and their doctors have been unable to send electronic prescriptions, so they’re having to write them out by hand. And in Indiana orders for tests and test results are being delayed by as much as a day for hospital patients. Not a great thing.
And just in time, or maybe a little late, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, through the newly created ARPA-H [Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health] that we have talked about, this week announced the launch of a new program to help hospitals make security patches and updates to their systems without taking them offline, which is obviously a major reason so many of these systems are so vulnerable to cyberhacking.
Of course, this announcement from HHS is just to solicit ideas for grants to help make that happen. So it’s going to be a while before we get any of these security changes. I’m wondering, how many systems are going to try to build a lot more redundancy into them? In the meantime, are we hearing anything about what they can do in the short term? It feels like the entire health care system is kind of a sitting duck for this group of cyberhackers who think they can get in easily and get ransom.
Kenen: There’s a reason they think that.
Rovner: They can.
Roubein: Thinking about hospitals and doctors using this manually, paper-based system and how that’s delaying getting your results and just there’s been these stories about patients. Like the anxiety that that’s understandably causing patients, and we’ll see sort of whether Congress can grapple with this, and there’s not really much legislation that’s going to move, so …
Kenen: But I was surprised that they were calling on ARPA-H. I mean, that’s supposed to be a biotech- curing-diseases thing, and none of the four of us are cybersecurity experts, and none of us really specialize in covering the electronic side of the digital side of health, but it just seems to me, I just thought that was an odd thing. First of all, some of these are just systems that haven’t been upgraded or individual clinicians who don’t upgrade or don’t do their double authorization. Some of it’s sort of cyberhygiene, and some of it’s obviously like the change thing. They’re really sophisticated criminals, but it’s not something that one would think you can’t get ahead of, right? They’re smart, good-guy technology people. It’s not like the bad guys are the only ones who understand technology. So why are the smart good guys not doing their job? And also, probably, health care systems have to have some kind of security checks on their own members to make sure they are following all the safety rules and some kind of consequences if you’re not, other than being embarrassed.
Rovner: I’ve just been sort of bemused by all of this, how both patients and providers complain loudly and frequently about the frustrations of some of these electronic record systems. And of course, in the places that they’re going down and they’ve had to go back to paper, people are like, “Please give us our electronic systems back.” So it doesn’t take long to get used to some of these things and be sorry when they’re gone, even if it’s only temporarily. It’s obviously been …
Kenen: But like what Rachel said, if you’re in the hospital, you’re sick, and do your clinicians need your lab results? Yes. I mean some of them are more important than others, and I would hope that hospitals are figuring out how to prioritize. But yeah, this is a crisis. If you’re in the hospital and they don’t know what’s wrong with you and they’re trying to figure out do you have X, Y, or Z, waiting until next week is not really a great idea.
Rovner: But it wasn’t that many years ago that their existence …
Kenen: Right, no, no, no.
Rovner: … did not involve …
Kenen: [inaudible 00:21:28].
Rovner: … electronic medical record.
Kenen: Right. Right.
Rovner: They knew how to get test results back and forth even if it was sending an intern to go fetch them. Finally, this week, we have some updates on some stories that we’ve talked about in earlier episodes. First, thanks in part to the excellent reporting of my colleague and sometime-pod-panelist Julie Appleby, the Senate Finance Committee Chairman Ron Wyden is demanding that HHS [U.S. Department of Health and Human Services] officials do more to rein in rogue insurance brokers who are reaping extra commissions by switching patients’ Affordable Care Act plans without their knowledge, often subjecting them to higher out-of-pocket costs and separating them from the providers that they’ve chosen. Sen. Wyden said he would introduce legislation to make such schemes a crime, but in the meantime he wants Biden officials to do more, given that they have received more than 90,000 complaints in the first quarter of 2024 alone about unauthorized switches and enrollments. Criminals go where the money is, right? You can either cyberhack or you can become a broker and switch people to ACA plans so you can get more commissions.
Kenen: I would think there could be a bipartisan, I mean it’s hard to get anything done in Congress. There’s no must-pass bills in the immediate future that are relevant. And the idea that a broker is secretly doing something that you don’t want them to do and that’s costing you money and making them money. I could see, those 90,000 people are from red and blue states and they vote, it’s going to affect constituents nationwide. Maybe they’ll do something. Maybe the industry can also… There is the National Association … I forgot the acronym, but there’s a broker’s organization, that there are probably things that they can also do to sanction. States can also do some things to brokers, but whether there’s a national solution or piecemeal, I don’t know, but it’s so outrageous that it’s not a right-left issue.
Rovner: Yes, one would think that there’ll be at least some kind of congressional action built into something …
Kenen: Something or other, right.
Rovner: … Congress that manages to do before the end of the year. Well, and in one of those seemingly rare cases where legislation actually does what it was intended to do, the White House this week announced that it has approved more than a million claims under the 2022 PACT Act, which made veterans injured as a result of exposure to burn pits and other toxic substances eligible for VA [Veterans Affairs] disability benefits. On the other hand, the VA is still working its way through another 3 million claims that have been submitted. I feel like even if it’s not very often, sometimes it’s worth noting that there are bipartisan things from Washington, D.C., that actually get passed and actually help the people that they’re supposed to help. It’s kind of sad that this is notable as an exception of something that happened and is working.
Roubein: In sort of the, I guess, Department of Unintended Side Effects here, my colleague Lisa Rein had a really interesting story out this morning that talked about the PACT Act, but basically that despite a federal law that prohibits charging veterans for help in applying for disability benefits, for-profit companies are making millions. She did a review of up to like a hundred unaccredited for-profit companies who have been charging veterans anywhere from like $5,000 to $20,000 for helping file disability claims because …
Rovner: That’s the theme of this week. Anyplace that there’s a lot of money in health care, there were people who will want to come in and take what’s not theirs. That’s where we will leave the news this week. Now we will play my interview with Shefali Luthra, then we’ll come back with our extra credits.
I am so pleased to welcome back to the podcast my former colleague and current “What The Health?” panelist Shefali Luthra. You haven’t heard from her in a while because she’s been working on her first book, called “Undue Burden,” that’s out this week. Shefali, great to see you.
Luthra: Thank you so much for having me Julie.
Rovner: So as the title suggests, “Undue Burden” is about the difficulties for both patients and providers in the wake of the overturn of Roe v. Wade. We talk so much about the politics of this issue, and so little about the real people who are affected. Why did you want to take this particular angle?
Luthra: To me, this is what makes this topic so important. Health care and abortion are really critical political issues. They sway elections. They are likely to be very consequential in this coming presidential election. But this matters to us as reporters and to us as people because of the life-or-death stakes and even beyond the life-or-death stakes, the stakes of how you choose to live your life and what it means to be pregnant and to be a parent. These are really difficult stories to tell because of the resources involved. And I wanted to write a book that just got at all of the different reasons why people pursue abortion and why they provide abortion and how that’s changed in the past two years. Because it felt to me like one of the few ways we could really understand just how seismic the implications of overturning Roe has been.
Rovner: And unlike those of us who talk to politicians all the time, you were really on the ground talking to patients and doctors, right?
Luthra: That was really, really important to the book. I spent a lot of time traveling the country, in clinics talking to people who were able to get abortions, who were unable to get abortions, and it was just really compelling for me to see how much access to care had the capacity to change their lives.
Rovner: So what kind of barriers then are we talking about that cropped up? And I guess it wasn’t even just the wake of the overturn of Roe. In Texas we had sort of a yearlong dry run.
Luthra: Exactly, and the book starts before Roe is overturned in Texas when the state enacted SB 8, the six-week abortion ban that effectively cut off access. And the first main character readers meet is this young girl named Tiffany, and she’s a teenager when she becomes pregnant, and she would love to get an abortion. But she is a minor. She lives very far from any abortion provider. She does not know how to self-manage an abortion. She does not know where to find pills. She has no connections into the health care system. She has no independent income. And she absolutely cannot travel anywhere for care. As a result, she has a child before she turns 18. And what this story highlights is that there are just so many barriers to getting an abortion. Many already existed: The incredible cost for procedure not covered by health insurance, the geographic distance, people already had to travel, the extra restrictions on minors.
But the overturning of Roe has amplified these, it is so expensive to get an abortion. It can be difficult to know you’re pregnant, especially if you are not trying to become pregnant. You have a very short time window. You may need to find childcare. You may need to find a car, get time off work, and bring all of these different forces together so that you are able to make a journey that can be days and pay for a trip that can cost thousands of dollars.
Rovner: One of the things that I think surprised me was that states that proclaimed themselves abortion “havens” actually did so little to help their clinics that predictably got swamped by out-of-state patients. Why do you think that was the case, and is it any better now?
Luthra: I think things have certainly changed. We have seen much more action in states, such as Illinois, where we see more people traveling there for care than anywhere else in the country. But it is worth going back to the summer that Roe was overturned. The governor promised to call a special session and put all these resources into making sure that Illinois could be a sanctuary. He never called that special session. And clinics felt like they were hanging out to dry, just waiting to get some support, and in the meanwhile, doing the absolute best they could.
One thing that I think this book really gets at is we are starting to see more efforts from these bluer states, the Illinois, the Californias, the New Yorks, and they talk a lot about wanting to be abortion havens, in part because it’s great politics if you’re a Democrat, but there’s only so much you can do. California has seen also quite a large increase in out-of-state patients. But I’ve spoken to so many people who just cannot conceivably go to California. They can barely go to Illinois. Making that journey when you are young, if you don’t have a lot of money, if you live in South Texas, if you live in Louisiana, it’s just not really feasible. And the places that are set up as these access points just can’t really fill in the gaps that they say they will.
Rovner: As you point out in the book, a lot of this was completely predictable. Was there something in your reporting that actually did surprise you?
Luthra: That’s a great question, and what did surprise me was in part something that we’ve begun to see borne out in the reporting, is there are very effective telemedicine strategies. We have begun to see physicians living in blue states, the New Yorks, Massachusetts, Californias, prescribing and mailing abortion pills to people in states with bans. This is pretty powerful. It has expanded access to a lot of people. What was really striking to me, though, even as I reported about the experiences of patients seeking care, is that while that has done so much to expand access in the face of abortion bans, it isn’t a solution that everyone can use. There were lots of people I met who did not want a medication abortion, who did not feel safe having pills mailed into their homes, or whose pregnancy complications and questions were just too complex to be solved by a virtual consult and then pills being mailed to them to take in the comfort of their house.
Rovner: Aren’t these difficulties exactly what the anti-abortion movement wanted? Didn’t they want clinics so swamped they couldn’t serve everybody who wanted to come, and abortion to be so difficult to get that women would end up carrying their pregnancies to term instead?
Luthra: Yes and no, I would argue. I think you are absolutely right that one of the primary goals of the anti-abortion movement was to make abortion unavailable, to make it harder to acquire, to have more people not get abortions and instead have children. But when I speak to folks in the anti-abortion movement, they are very troubled by how many people are traveling out of state to get care. They see those really long wait times in Kansas, in, until recently, Florida, in Illinois, in New Mexico, as a symptom of something that they need to address, which is that so many people are still finding a way to fight incredible odds to access abortion.
Rovner: Is there one thing that you hope people take away after they’re finished reading this?
Luthra: There are two things that I have spent a lot of time thinking about as I’ve reported this book. The first is just who gets abortions and under what circumstances. And so often in the national press, in national politics, we talk about these really extreme life-or-death cases. We talk about people who became septic and needed an abortion because their water broke early, or we talk about children who have been sexually assaulted and become pregnant. But we don’t talk about most people who get abortions; who are usually mothers, who are usually people of color, who are in their 20s and just know that they can’t be pregnant. I think those are really important stories to tell because they’re the true face of who is most affected by this, and it was important to me that this book include that.
The other thing that I have thought about so often in reporting this and writing this is abortion demands have an unequal impact. That is true if you are poor, if you are a person of color, if you live in a rural area, et cetera. You will in all likelihood see a greater effect. That said, the overturning of Roe v. Wade is so tremendous that it has affected people in every state. It affects you if you can get pregnant. It affects you if you want birth control. It affects you if you require reproductive health care in some form. This is just such a seismic change to our health care system that I really hope people who read this book understand that this is not a niche issue. This is something worthy of our collective attention and concern as journalists and as people.
Rovner: Shefali Luthra, thank you so much for this, and we will see you soon on the panel, right?
Luthra: Absolutely. Thank you, Julie. I’m so glad we got to do this.
Rovner: OK, we are back. It’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Joanne, why don’t you go first this week?
Kenen: This was a pair of articles, a long one and a shorter, related one. There’s an amazingly wonderful piece in ProPublica by Sharon Lerner, and it’s called “Toxic Gaslighting: How 3M Executives Convinced a Scientist the Forever Chemicals She Found in Human Blood Were Safe.” I’m going to come back and talk about it briefly in a second, but the related story was in The Guardian by Damian Carrington: “Microplastics Found in Every Human Testicle in Study.” Now, that was a small study, but there may be a link to the declining sperm count because of these forever chemicals.
The ProPublica story, it was a young woman scientist. She worked for 3M. They kept telling her her results was wrong, her machinery was dirty, over and over and over again until she questioned herself and her findings. She was supposed to be looking at the blood of 3M workers who were, it turned out, the company knew all this already and they were hiding it, and she compared the blood of the 3M workers to non-3M workers, and she found these plastic chemicals in everybody’s blood everywhere, and she was basically gaslit out of her job. She continued to work for 3M, but in a different capacity.
The article’s really scary about the impact for human health. It also has wonderfully interesting little nuggets throughout about how various 3M products were developed, some by accident. Something spilled on somebody’s sneaker and it didn’t stain it, and that’s how we got those sprays for our upholstery. Or somebody needed something to find the pages in their church hymnal, and that’s how we got Post-it notes. It’s a devastating but very readable, and it makes you angry.
Rovner: Yeah, I feel like there’s a lot more we’re going to have to say about forever chemicals going forward. Alice.
Ollstein: So I have a pretty depressing story from Stats. It’s called “How Doctors Are Pressuring Sickle Cell Patients Into Unwanted Sterilizations,” by Eric Boodman. And it is about people with sickle cell, and that is overwhelmingly black women, and they felt pressured to agree to be permanently sterilized when they were going to give birth because of the higher risks. And the doctors said, because we’re already doing a C-section and we’re already doing surgery on you, to not have to do an additional surgery with additional risks, they felt pressured to just sign that they could be sterilized right then and there and came to regret it later and really wanted more children. And so, this is an instance of people feeling coerced, and when people think about pro-choice or the choice debate about reproduction they mostly think about the right to an abortion. But I think that the right to have more children, if you want to, is the other side of that coin.
Rovner: It is. Rachel.
Roubein: My extra credit, it’s called “What Science Tells Us About Biden, Trump and Evaluating an Aging Brain,” by Joel Achenbach and Mark Johnson from The Washington Post. And basically, they kind of took a very science-based look at the 2024 election. They basically called it a crash course in gerontology because former President Donald Trump will be 78 years old. President Biden will be a couple weeks away from turning 82. And obviously that is getting a lot of attention on the campaign trail. They talked to medical and scientific experts who were essentially warning that news reports, political punditry about the candidates’ mental fitness, has essentially been marred by misinformation here about the aging process. One of the things they dived into was these gaffes or what the public sees as senior moments and what experts had told them is, that’s not necessarily a sign of dementia or predictive of cognitive decline. There need to be kind of further clinical evaluation for that. But there have been some calls for just how to kind of standardize and require a certain level of transparency for candidates in terms of disclosing their health information.
Rovner: Yes, which we’ve been talking about for a while, and will continue to. My extra credit this week is from our guest, Shefali Luthra, and her colleague at The 19th Chabeli Carrazana, and it’s called “What Happens to Clinics After a State Bans Abortion? They Fight To Survive.” And for all the talk about doctors and other staffers either moving out of or not moving into states with abortion bans, I think less has been written about entire enterprises that often provide far more than just abortion services having to shut down as well. We saw this in Texas in the mid-2010s, when a law that shut down many of the clinics there was struck down by the Supreme Court in 2016. But many of those clinics were unable to reopen. They just could not reassemble, basically, their leases and equipment and staff. The same could well happen in states that this November vote to reverse some of those bans. And it’s not just abortion, as we’ve discussed. When these clinics close, it often means less family planning, less STI [sexually transmitted infection] screening and other preventive services as well, so it’s definitely something to continue to watch.
Before we go this week, I want to note the passing of a health policy journalism giant with the death of Marshall Allen. Marshall, who worked tirelessly, first in Las Vegas and more recently at ProPublica, to expose some of the most unfair and infuriating parts of the U.S. health care system, was on the podcast in 2021 to talk about his book, “Never Pay the First Bill, and Other Ways to Fight the Health Care System and Win.” I will post a link to the interview in this week’s show notes. Condolences to Marshall’s friends and family.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcast. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review. That helps other people find us too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org, or you can still find me at X, @jrovner. Joanne, where are you?
Kenen: We’re at Threads @JoanneKenen.
Rovner: Alice.
Ollstein: Still on X @AliceOllstein.
Rovner: Rachel.
Roubein: On X, @rachel_roubein.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Aging, Courts, Elections, Insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, Public Health, States, Abortion, Contraception, Kansas, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Louisiana, Podcasts, Pregnancy, reproductive health, texas, Women's Health
Médicos que atendieron a manifestantes en la protesta estudiantil en la UCLA dicen que la policía dejó huesos rotos y hemorragias
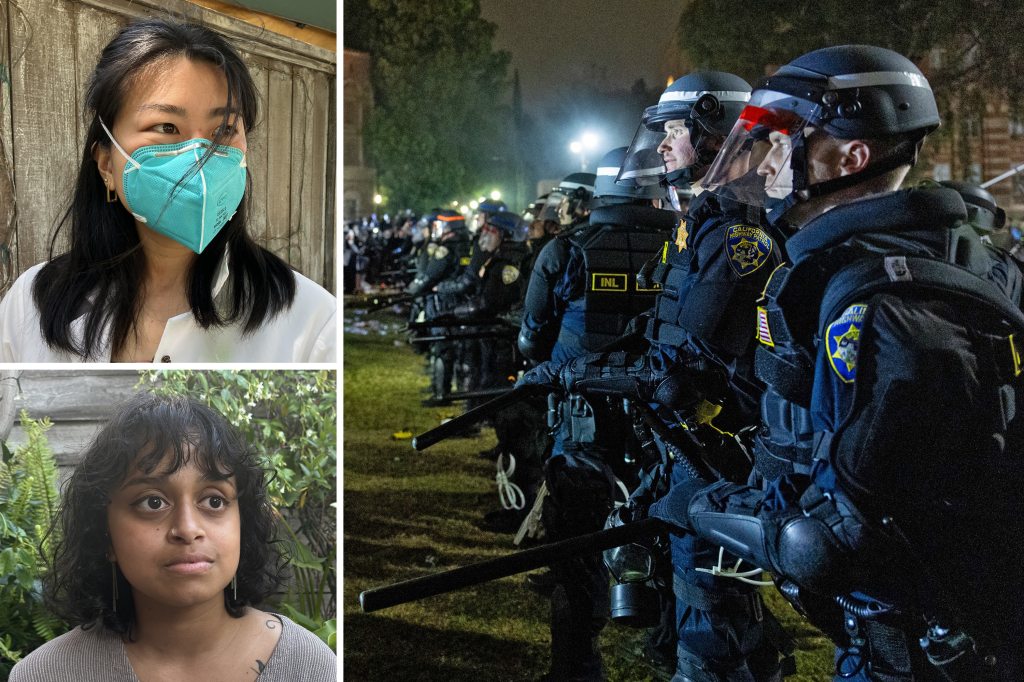
En el campamento que habían montado los estudiantes dentro del campus de la Universidad de California en Los Ángeles (UCLA), de repente la ginecóloga y obstetra residente Elaine Chan se sintió como una médica en un campo de batalla.
La policía avanzó hacia el campamento luego de horas de enfrentamiento y tensión.
En el campamento que habían montado los estudiantes dentro del campus de la Universidad de California en Los Ángeles (UCLA), de repente la ginecóloga y obstetra residente Elaine Chan se sintió como una médica en un campo de batalla.
La policía avanzó hacia el campamento luego de horas de enfrentamiento y tensión.
Chan, de 31 años, voluntaria en el puesto de atención médica, dijo que los manifestantes llegaban con dificultades para caminar y con graves heridas punzantes. Pero, por el caos que reinaba afuera, había pocas posibilidades de trasladarlos a un hospital donde se les pudiera brindar otro tipo de cuidados.
Chan expresó su sospecha de que esas lesiones habían sido causadas por balas de goma u otros proyectiles “menos letales”. Después del desalojo del campamento, la policía confirmó que había usado estos dispositivos.
“Los proyectiles atravesaron la piel y se clavaron profundamente en el cuerpo de las personas”, explicó Chan. “Todos sangraban profusamente. Los médicos que nos especializamos en obstetricia y ginecología no hemos sido capacitados para atender heridos por balas de goma… No podía creer que se permitiera atacar de ese modo a civiles, a estudiantes, que tenían ningún equipo de protección”.
La protesta de la UCLA, que reunió a miles de personas que se oponen a los continuos bombardeos de Israel sobre la Franja de Gaza, comenzó en abril y alcanzó un peligroso crescendo en mayo, cuando manifestantes pro Israel y la policía se enfrentaron a los activistas y a los que los apoyaban.
En entrevistas con KFF Health News, Chan y otros tres médicos voluntarios describieron cómo debieron atender a manifestantes con heridas sangrantes, lesiones en la cabeza y huesos presuntamente fracturados en una clínica improvisada en tiendas de campaña, sin electricidad ni agua corriente.
En los puestos sanitarios del campamento hubo día y noche médicos, enfermeras, estudiantes de medicina, paramédicos y voluntarios sin formación médica formal.
En muchos momentos, la escalada de la violencia fuera de la carpa sanitaria fue de tal magnitud que impedía que los manifestantes heridos llegaran hasta las ambulancias, explicaron los médicos. Esto obligó a que los heridos fueran caminando por sus propios medios hasta algún hospital cercano. A otros los llevaron más allá de los límites de la protesta para trasladarlos a una sala de emergencias.
“Nunca había estado en una situación en la que se nos impidiera ofrecer una atención de mayor nivel”, dijo Chan. “Y eso me aterrorizó”.
Tres de los médicos entrevistados por KFF Health News dijeron que estaban presentes el 2 de mayo, cuando la policía arrasó el campamento, y describieron que debieron ocuparse de múltiples lesiones que parecían haber sido causadas por proyectiles “menos letales”.
Estos proyectiles “menos letales” incluyen balas llenas de perdigones de metales pesados o plomo; y municiones comúnmente conocidas como balas de goma. Los utiliza la policía para controlar a sospechosos o para dispersar multitudes y protestas.
La policía recibió una condena generalizada por haber utilizado estas armas contra las manifestaciones del movimiento Black Lives Matter, que se extendieron por todo el país tras el asesinato de George Floyd en 2020.
Aunque el nombre de estas armas parece minimizar su peligrosidad, los proyectiles menos letales pueden viajar a más de 200 mph y está comprobada su capacidad de herir, mutilar o matar.
Las entrevistas a los médicos que atendieron en la posta sanitaria contradicen directamente la versión del Departamento de Policía de Los Ángeles (LAPD). Después que los agentes desalojaran el campamento, el jefe de Policía, Dominic Choi, afirmó en una publicación en la plataforma social X que “no hubo heridos graves entre los agentes ni entre los manifestantes” durante el operativo en el hubo más de 200 arrestos.
En las respuestas enviadas por correo electrónico a las preguntas de KFF Health News, tanto el Departamento de Policía de Los Ángeles como la Patrulla de Carreteras de California afirmaron que investigarían cómo habían actuado sus agentes durante la protesta en la UCLA. Esas indagaciones, dijeron, darán lugar a un “informe detallado”.
La declaración de la Patrulla de Carreteras asegura que los oficiales advirtieron previamente a los manifestantes que si no se dispersaban podrían utilizar “municiones no letales”.
Después que algunos manifestantes se convirtieran en una “amenaza inmediata” porque “lanzaban objetos y armas”, algunos oficiales utilizaron “balas cinéticas especiales para protegerse a sí mismos, a otros oficiales y a los miembros del público”. Un agente resultó con heridas leves, según el comunicado.
Las imágenes de un video que circuló por Internet después del desalojo del campamento parecían mostrar a un oficial de la Patrulla de Carreteras disparando con una escopeta estos proyectiles de menor letalidad contra los manifestantes.
“El uso de la fuerza y cualquier incidente que implique el uso de un arma por parte del personal de la CHP es un asunto serio, y la CHP llevará a cabo una investigación justa e imparcial para garantizar que las acciones fueron coherentes con la política y la ley”, respondió la Patrulla de Carreteras en su declaración.
El Departamento de Policía de la UCLA, que también participó en el operativo vinculado a la protesta, no respondió al pedido de testimonio de KFF Health News.
Jack Fukushima, de 28 años, estudiante de medicina de la UCLA y socorrista voluntario, contó que presenció cómo un agente de policía les disparó a por lo menos dos manifestantes con proyectiles de menor letalidad.
Entre ellos, a un hombre que se desplomó tras recibir un impacto “justo en el pecho”. Fukushima explicó que, junto con otros médicos, acompañaron al hombre, aturdido, a la carpa sanitaria. Luego volvieron a la zona de los enfrentamientos para buscar más heridos.
“Realmente lo sentí como una guerra”, aseguró Fukushima. “Encontrarse con semejante brutalidad policial fue muy descorazonador”.
Cuando los médicos estuvieron de regreso en la primera línea, la Policía ya había traspasado los límites del campamento y se encontraba forcejeando directamente con los manifestantes, recordó Fukushima.
En esa situación, el socorrista vio como el mismo policía que antes le había disparado al herido que habían llevado al puesto sanitario ahora le disparaba a otro manifestante en el cuello. El muchacho cayó al suelo. Fukushima supuso lo peor y corrió a su lado.
“Cuando logré acercarme le pregunté: ‘Oye, ¿estás bien?’”, contó Fukushima. “Y él, con una valentía impresionante, me respondió: ‘Sí, no es mi primera vez’. Y volvió de inmediato a la acción”.
Sonia Raghuram, de 27 años, otra estudiante de medicina que colaboró en la carpa sanitaria dijo que durante el operativo policial atendió a un manifestante que tenía una herida punzante abierta en la espalda, a otro con un moretón del tamaño de una moneda en el centro del pecho y a un tercero con un corte que sangraba “a borbotones” sobre el ojo derecho y que probablemente tenía una costilla rota.
Raghuram contó que los pacientes le dijeron que las heridas habían sido causadas por los proyectiles policiales, lo que, según ella, coincidía con la gravedad de sus lesiones.
Los pacientes les advirtieron claramente que los agentes de policía se estaban acercando a la posta sanitaria, dijo Raghuram, pero ella no se movió.
“Nunca abandonaremos a un paciente”, aseguró, aludiendo al mantra de la carpa médica. “No me importa que nos detengan. Si estoy atendiendo a un paciente, eso es lo prioritario”, concluyó.
La protesta de la UCLA es una de las muchas que se han organizado en campus universitarios de todo el país. Los estudiantes que se oponen a la guerra que Israel mantiene en Gaza exigen que la universidad apoye un alto el fuego y que se retiren las inversiones que pueda tener en empresas vinculadas a Israel.
La Policía utilizó la fuerza para desalojar a los manifestantes de campamentos en la Universidad de Columbia, la Universidad de Emory y las universidades de Arizona, Utah y el sur de Florida, entre otras.
En el campus de la UCLA, el 25 de abril los estudiantes que protestaban instalaron tiendas de campaña en una plaza cubierta de césped frente al teatro Royce Hall.
El asentamiento atrajo a miles de simpatizantes, según Los Angeles Times. Días más tarde, una “violenta turba” de manifestantes de signo contrario “atacó el campamento”, informó el Times, e intentó derribar las barricadas que protegían sus límites, arrojando fuegos artificiales contra las carpas que había en su interior.
La noche siguiente, la Policía declaró ilegal la demostración y luego desalojó el campamento en las primeras horas del 2 de mayo. Hubo cientos de arrestos.
La Policía ha sido muy criticada por no haber intervenido durante el enfrentamiento entre los manifestantes que acampaban y los que fueron a atacarlos, una confrontación que se prolongó durante horas.
La red de Universidades de California anunció que había contratado a un consultor independiente en materia policial para que investigara los actos de violencia y para “resolver las preguntas sin respuesta sobre la planificación y los protocolos de la UCLA, así como sobre el trabajo de colaboración interinstitucional”.
Charlotte Austin, de 34 años, residente de cirugía, dijo que cuando los manifestantes opositores atacaron el campamento de protesta, vio a unos 10 agentes de seguridad privada del campus de pie, “con las manos en los bolsillos”, mientras los estudiantes eran golpeados y ensangrentados.
Austin asegura que atendió a pacientes con cortes en la cara y posibles fracturas de cráneo. La posta médica envió al menos a 20 personas al hospital esa noche, agregó.
“Cualquier profesional de la medicina calificaría esas lesiones de graves”, dijo Austin. “Hubo personas que debieron ser internadas, no se limitó solo a una visita a la sala de emergencias, sino que necesitaron una hospitalización real”.
Tácticas policiales: “lícitas pero horribles”
Los manifestantes de la UCLA no son los primeros heridos por proyectiles de menor letalidad, ni mucho menos.
En los últimos años, la policía de todo Estados Unidos ha disparado cientos de veces estas armas contra manifestantes, sin que prácticamente exista una normativa general que regule su uso o su seguridad. Algunos de los heridos nunca han vuelto a ser los mismos y las ciudades han gastado millones para responder a las demandas de los damnificados.
Durante las protestas que se produjeron en todo el país tras la muerte de George Floyd a manos de la policía en 2020, al menos 60 manifestantes sufrieron lesiones graves —incluso ceguera y fractura de mandíbula— por disparos de estos proyectiles, a veces en aparente violación de las políticas de los departamentos de policía, según una investigación conjunta de KFF Health News y USA Today.
En 2004, en Boston, una estudiante universitaria que celebraba la victoria de los Red Sox murió por el impacto de un proyectil lleno de gas pimienta, que le atravesó el ojo y le llegó al cerebro.
“Se llaman ‘menos letales’ por una razón”, sentenció Jim Bueermann, ex jefe de policía de Redlands, en California, que ahora lidera el Future Policing Institute. “Pueden matarte”.
Bueermann, que a petición de KFF Health News revisó las imágenes de video de la intervención de la policía en la UCLA, dijo que muestran a agentes de la Patrulla de Carreteras de California disparando balas de salva con una escopeta.
Bueermann opinó que las imágenes no proporcionaban suficiente contexto como para determinar si los proyectiles se estaban utilizando “razonablemente”, según indica la norma establecida por los tribunales federales, o se estaban disparando “indiscriminadamente”, lo que fue prohibido por una ley de California en 2021.
“Hay un dicho en la Policía — “legal pero horrible”— lo que significa que es razonable bajo los estándares legales, pero se ve terrible”, explicó Bueermann. “Y creo que un policía cargando múltiples balas en una escopeta y disparando contra los manifestantes, no es algo que se vea muy bien”.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Noticias En Español, Public Health, States, Arizona, california, Florida, Georgia, Massachusetts, New York, Utah
Could Better Inhalers Help Patients, and the Planet?
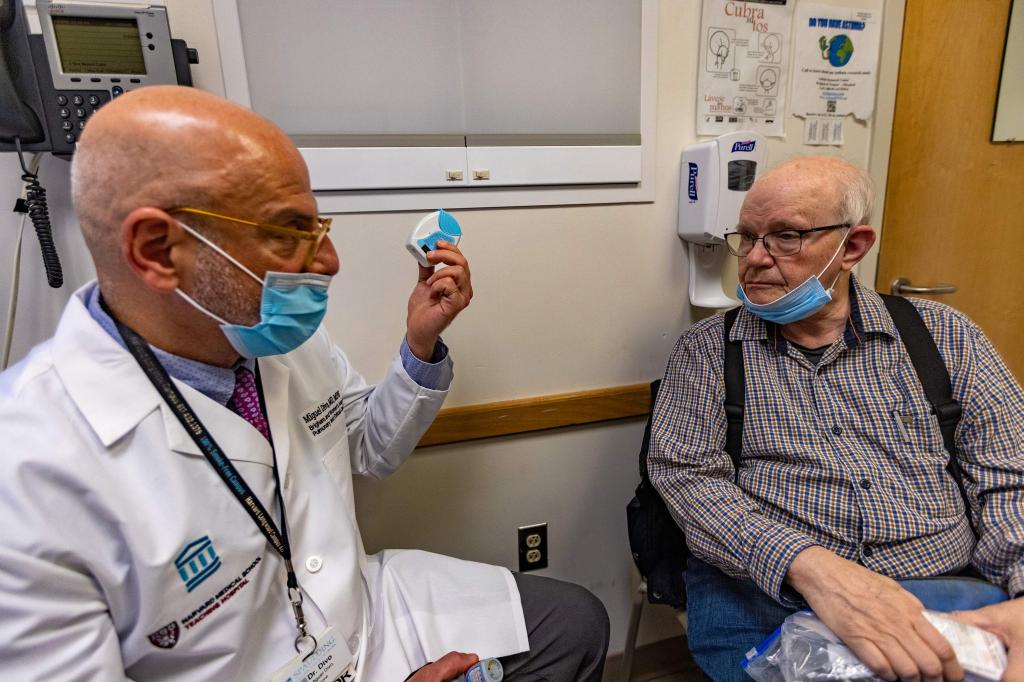
Miguel Divo, a lung specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, sits in an exam room across from Joel Rubinstein, who has asthma. Rubinstein, a retired psychiatrist, is about to get a checkup and hear a surprising pitch — for the planet, as well as his health.
Miguel Divo, a lung specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, sits in an exam room across from Joel Rubinstein, who has asthma. Rubinstein, a retired psychiatrist, is about to get a checkup and hear a surprising pitch — for the planet, as well as his health.
Divo explains that boot-shaped inhalers, which represent nearly 90% of the U.S. market for asthma medication, save lives but also contribute to climate change. Each puff from an inhaler releases a hydrofluorocarbon gas that is 1,430 to 3,000 times as powerful as the most commonly known greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide.
“That absolutely never occurred to me,” said Rubinstein. “Especially, I mean, these are little, teeny things.”
So Divo has begun offering a more eco-friendly option to some patients with asthma and other lung diseases: a plastic, gray cylinder about the size and shape of a hockey puck that contains powdered medicine. Patients suck the powder into their lungs — no puff of gas required and no greenhouse gas emissions.
“You have the same medications, two different delivery systems,” Divo said.
Patients in the United States are prescribed roughly 144 million of what doctors call metered-dose inhalers each year, according to the most recently available data published in 2020. The cumulative amount of gas released is the equivalent of driving half a million gas-powered cars for a year. So, the benefits of moving to dry powder inhalers from gas inhalers could add up.
Hydrofluorocarbon gas contributes to climate change, which is creating more wildfire smoke, other types of air pollution, and longer allergy seasons. These conditions can make breathing more difficult — especially for people with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD — and increase the use of inhalers.
Divo is one of a small but growing number of U.S. physicians determined to reverse what they see as an unhealthy cycle.
“There is only one planet and one human race,” Divo said. “We are creating our own problems and we need to do something.”
So Divo is working with patients like Rubinstein who may be willing to switch to dry powder inhalers. Rubinstein said no to the idea at first because the powder inhaler would have been more expensive. Then his insurer increased the copay on the metered-dose inhaler so Rubinstein decided to try the dry powder.
“For me, price is a big thing,” said Rubinstein, who has tracked health care and pharmaceutical spending in his professional roles for years. Inhaling the medicine using more of his own lung power was an adjustment. “The powder is a very strange thing, to blow powder into your mouth and lungs.”
But for Rubinstein, the new inhaler works and his asthma is under control. A recent study found that some patients in the United Kingdom who use dry powder inhalers have better asthma control while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. In Sweden, where the vast majority of patients use dry powder inhalers, rates of severe asthma are lower than in the United States.
Rubinstein is one of a small number of U.S. patients who have made the transition. Divo said that, for a variety of reasons, only about a quarter of his patients even consider switching. Dry powder inhalers are often more expensive than gas propellant inhalers. For some, dry powder isn’t a good option because not all asthma or COPD sufferers can get their medications in this form. And dry powder inhalers aren’t recommended for young children or elderly patients with diminished lung strength.
Also, some patients using dry powder inhalers worry that without the noise from the spray, they may not be receiving the proper dose. Other patients don’t like the taste powder inhalers can leave in their mouths.
Divo said his priority is making sure patients have an inhaler they are comfortable using and that they can afford. But, when appropriate, he’ll keep offering the dry powder option.
Advocacy groups for asthma and COPD patients support more conversations about the connection between inhalers and climate change.
“The climate crisis makes these individuals have a higher risk of exacerbation and worsening disease,” said Albert Rizzo, chief medical officer of the American Lung Association. “We don’t want medications to contribute to that.”
Rizzo said there is work being done to make metered-dose inhalers more climate-friendly. The United States and many other countries are phasing down the use of hydrofluorocarbons, which are also used in refrigerators and air conditioners. It’s part of the global attempt to avoid the worst possible impacts of climate change. But inhaler manufacturers are largely exempt from those requirements and can continue to use the gases while they explore new options.
Some leading inhaler manufacturers have pledged to produce canisters with less potent greenhouse gases and to submit them for regulatory review by next year. It’s not clear when these inhalers might be available in pharmacies. Separately, the FDA is spending about $6 million on a study about the challenges of developing inhalers with a smaller carbon footprint.
Rizzo and other lung specialists worry these changes will translate into higher prices. That’s what happened in the early to mid-2000s when ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were phased out of inhalers. Manufacturers changed the gas in metered-dose inhalers and the cost to patients nearly doubled. Today, many of those re-engineered inhalers remain expensive.
William Feldman, a pulmonologist and health policy researcher at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said these dramatic price increases occur because manufacturers register updated inhalers as new products, even though they deliver medications already on the market. The manufacturers are then awarded patents, which prevent the production of competing generic medications for decades. The Federal Trade Commission says it is cracking down on this practice.
After the CFC ban, “manufacturers earned billions of dollars from the inhalers,” Feldman said of the re-engineered inhalers.
When inhaler costs went up, physicians say, patients cut back on puffs and suffered more asthma attacks. Gregg Furie, medical director for climate and sustainability at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is worried that’s about to happen again.
“While these new propellants are potentially a real positive development, there’s also a significant risk that we’re going to see patients and payers face significant cost hikes,” Furie said.
Some of the largest inhaler manufacturers, including GSK, are already under scrutiny for allegedly inflating prices in the United States. Sydney Dodson-Nease told NPR and KFF Health News that the company has a strong record for keeping medicines accessible to patients but that it’s too early to comment on the price of the more environmentally sensitive inhalers the company is developing.
Developing affordable, effective, and climate-friendly inhalers will be important for hospitals as well as patients. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality recommends that hospitals looking to shrink their carbon footprint reduce inhaler emissions. Some hospital administrators see switching inhalers as low-hanging fruit on the list of climate-change improvements a hospital might make.
But Brian Chesebro, medical director of environmental stewardship at Providence, a hospital network in Oregon, said, “It’s not as easy as swapping inhalers.”
Chesebro said that even among metered-dose inhalers, the climate impact varies. So pharmacists should suggest the inhalers with the fewest greenhouse gas emissions. Insurers should also adjust reimbursements to favor climate-friendly alternatives, he said, and regulators could consider emissions when reviewing hospital performance.
Samantha Green, a family physician in Toronto, said clinicians can make a big difference with inhaler emissions by starting with the question: Does the patient in front of me really need one?
Green, who works on a project to make inhalers more environmentally sustainable, said that research shows a third of adults diagnosed with asthma may not have the disease.
“So that’s an easy place to start,” Green said. “Make sure the patient prescribed an inhaler is actually benefiting from it.”
Green said educating patients has a measurable effect. In her experience, patients are moved to learn that emissions from the approximately 200 puffs in one inhaler are equivalent to driving about 100 miles in a gas-powered car. Some researchers say switching to dry powder inhalers may be as beneficial for the climate as a patient adopting a vegetarian diet.
One of the hospitals in Green’s health care network, St. Joseph’s Health Centre, found that talking to patients about inhalers led to a significant decrease in the use of metered-dose devices. Over six months, the hospital went from 70% of patients using the puffers, to 30%.
Green said patients who switched to dry powder inhalers have largely stuck with them and appreciate using a device that is less likely to exacerbate environmental conditions that inflame asthma.
This article is from a partnership that includes WBUR, NPR, and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Multimedia, States, Audio, Environmental Health, Massachusetts
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Abortion Access Changing Again in Florida and Arizona
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
The national abortion landscape was shaken again this week as Florida’s six-week abortion ban took effect. That leaves North Carolina and Virginia as the lone Southern states where abortion remains widely available. Clinics in those states already were overflowing with patients from across the region.
Meanwhile, in a wide-ranging interview with Time magazine, former President Donald Trump took credit for appointing the Supreme Court justices who overturned Roe v. Wade, but he steadfastly refused to say what he might do on the abortion issue if he is returned to office.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet, Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico, and Rachana Pradhan of KFF Health News.
Panelists
Sarah Karlin-Smith
Pink Sheet
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Rachana Pradhan
KFF Health News
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- Florida’s new, six-week abortion ban is a big deal for the entire South, as the state had been an abortion haven for patients as other states cut access to the procedure. Some clinics in North Carolina and southern Virginia are considering expansions to their waiting and recovery rooms to accommodate patients who now must travel there for care. This also means, though, that those traveling patients could make waits even longer for local patients, including many who rely on the clinics for non-abortion services.
- Passage of a bill to repeal Arizona’s near-total abortion ban nonetheless leaves the state’s patients and providers with plenty of uncertainty — including whether the ban will temporarily take effect anyway. Plus, voters in Arizona, as well as those in Florida, will have an opportunity in November to weigh in on whether the procedure should be available in their state.
- The FDA’s decision that laboratory-developed tests must be subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as medical devices comes as the tests have become more prevalent — and as concerns have grown amid high-profile examples of problems occurring because they evaded federal review. (See: Theranos.) There’s a reasonable chance the FDA will be sued over whether it has the authority to make these changes without congressional action.
- Also, the Biden administration has quietly decided to shelve a potential ban on menthol cigarettes. The issue raised tensions over its links between health and criminal justice, and it ultimately appears to have run into electoral-year headwinds that prompted the administration to put it aside rather than risk alienating Black voters.
- In drug news, the Federal Trade Commission is challenging what it sees as “junk” patents that make it tougher for generics to come to market, and another court ruling delivers bad news for the pharmaceutical industry’s fight against Medicare drug negotiations.
Plus, for “extra credit” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: ProPublica’s “A Doctor at Cigna Said Her Bosses Pressured Her To Review Patients’ Cases Too Quickly. Cigna Threatened To Fire Her,” by Patrick Rucker, The Capitol Forum, and David Armstrong, ProPublica.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: The Associated Press’ “Dozens of Deaths Reveal Risks of Injecting Sedatives Into People Restrained by Police,” by Ryan J. Foley, Carla K. Johnson, and Shelby Lum.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: The Atlantic’s “America’s Infectious-Disease Barometer Is Off,” by Katherine J. Wu.
Rachana Pradhan: The Wall Street Journal’s “Millions of American Kids Are Caregivers Now: ‘The Hardest Part Is That I’m Only 17,” by Clare Ansberry.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- Time’s “How Far Trump Would Go,” by Eric Cortellessa.
- NPR’s “Why Is a 6-Week Abortion Ban Nearly a Total Ban? It’s About How We Date a Pregnancy,” by Selena Simmons-Duffin.
- NPR’s “’Sicko’s’ Peeno Sees Few Gains in Health Insurance,” by Julie Rovner.
- CNN’s “Walmart Will Close All of Its Health Care Clinics,” by Nathaniel Meyersohn.
Click to open the Transcript
Transcript: Abortion Access Changing Again in Florida and Arizona
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Mila Atmos: The future of America is in your hands. This is not a movie trailer, and it’s not a political ad, but it is a call-to-action. I’m Mila Atmos, and I’m passionate about unlocking the power of everyday citizens. On our podcast “Future Hindsight,” we take big ideas about civic life and democracy, and turn them into action items for you and me. Every Thursday, we talk to bold activists and civic innovators to help you understand your power and your power to change the status quo. Find us at futurehindsight.com or wherever you listen to podcasts.
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, May 2, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this. So here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Sarah Karlin-Smith of the Pink Sheet.
Sarah Karlin-Smith: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: And my KFF Health News colleague Rachana Pradhan.
Rachana Pradhan: Hello.
Rovner: No interview this week, but more than enough news to make up for it, so we will dig right in. We will start, again, with abortion. On Wednesday, Florida’s six-week abortion ban took effect. Alice, what does this mean for people seeking abortions in Florida, and what’s the spillover to other states?
Ollstein: Yeah, this is a really huge deal not only because Florida is so populous, but because Florida, somewhat ironically given its leadership, has been a real abortion haven since Roe vs. Wade was overturned. A lot of its surrounding states had near-total bans go into effect right away. Florida has had a 15-week ban for a while, but that has still allowed for a lot of abortions to take place, and so a lot of people have been coming to Florida from Alabama, Louisiana, those surrounding states for abortions. Now, Florida’s six-week ban is taking effect and that means that a lot of the patients that had been going there will now need to go elsewhere, and a lot of Floridians will have to travel out of state.
And so there are concerns about whether the closest clinics they can get to, in North Carolina and southern Virginia, will have the capacity to handle that patient overload. I talked to some clinics that are trying to staff up. They’re even thinking about physical changes to their clinics, like building bigger waiting rooms and recovery rooms. This is going to cause a real crunch, in terms of health care provision. That is set to not only affect abortion, but with these clinics overwhelmed, that takes up appointments for people seeking other services as well. My colleagues and I have been talking to people in the sending states, like Alabama, who worry that the low-income patients they serve who were barely able to make it to Florida will not be able to make it even further. Then, we’ve talked to providers in the receiving states, like Virginia, who are worried that there just are simply not enough appointments to handle the tens of thousands of people who had been getting abortions in Florida up to this point.
Rovner: Of course, what ends up happening is that, if people have to wait longer, it pushes those abortions into later types of abortions, which are more complicated and more dangerous and more expensive.
Ollstein: Yes. While the rate of complication is low, the later in pregnancy you go, it does get higher. That’s another consideration as well.
I will flag, though, that restrictions on abortion pills in North Carolina, which is now one of the states set to receive a lot of people, those did get a little bit loosened by a court ruling this week so people will not have to have a mandatory in-person follow-up appointment for abortion pills like they used to have to have. That could help some patients who are traveling in from out of state, but a lot of restrictions remain, and it’ll be tough for a lot of folks to navigate.
Rovner: While we think of that, well there’s at least, you can get abortions up to six weeks, my friend Selena Simmons-Duffin over at NPR had a really good explainer about why six weeks isn’t really six weeks, because of the way that we measure pregnancy, that six weeks is really two weeks. It really is a very, very small window in which people will be able to get abortions in Florida. It’s not quite a full ban, but it is quite close to it.
Well, speaking of full bans, after several false starts, the Arizona Senate Wednesday voted to repeal the 1864 abortion ban that its Supreme Court ruled could take effect. The Democratic governor is expected to sign it. Where does that leave abortion law in the very swing state of Arizona? It’s kind of a muddle, isn’t it?
Ollstein: It is. The basics are that a 15-week ban is already in place and will continue to be in place once this repeal takes effect. What we don’t know is whether the total ban from before Arizona was even a state will take effect temporarily, because of the weird timing of the court’s implementation of that old ban, and the new repeal bill that just passed that the governor is expected to sign very soon. The total ban could go into effect, at least for a little bit over the summer. Planned Parenthood is positioning the court to not let that happen, to stay the implementation until the repeal bill can take effect. All of this is very much in flux. Of course, as we’ve seen in so many states, that leads to patients and providers just being very scared, and not knowing what’s legal and what’s not, and folks being unable to access care that may, in fact, be legal because of that. Of course, this is all in the context of Arizona, as well as Florida, being poised to vote directly on abortion access this fall. If the total ban does go into effect temporarily, it’s sure to pour fuel on that fire and really rile people up ahead of that vote.
Rovner: Yeah, I was going to mention that. Well, now that we’re talking about politics. This week, we heard a little bit more about how former President Trump wants to handle the abortion issue, via a long sit-down interview with Time magazine. I will link to that interview in the show notes. The biggest “news” he made was to suggest that he’d have an announcement soon about his views on the abortion pill. But he said that would come in the next two weeks, the interview was of course more than two weeks ago. They did a follow-up two weeks later and he still said it was coming. In the follow-up interview, he said it would be next week, which this has already passed. Do we really expect Trump to say something about this, or was that just him deflecting, as we know he is wont to do?
Pradhan: Well, I’m sure that he’s getting pressure to say something, because as people have noted now quite widely, regardless of individual state laws, there are certainly conservatives that are pushing for him and his future administration to ban the mailing of abortion pills using the Comstock Act from the 1800s, which would basically annihilate access to that form of terminating pregnancies.
Rovner: There are also some who want him to just repeal the FDA approval, right?
Ollstein: Right. Of course, the Biden administration has made it easier for folks to get access to those, to mifepristone, in particular, one of two pills that are used in medication abortion. But yeah, will it be two weeks? I think he obviously knows that this is a potential political liability for him, so whether he’ll say something, I’m sure he will get competing advice as to whether it’s a good idea to say something at all, so we’ll have to see.
Rovner: Well, speaking of Trump deflecting, he seemed to be pretty disciplined about the rest of the abortion questions — and there were a lot of abortion questions in that interview — insisting that, while he takes credit for appointing the justices who made the majority to overturn Roe, everything else is now up to the state. But by refusing to oppose some pretty-out-there suggestions of what states might do, Trump has now opened himself up to apparently accepting some fairly unpopular things, like tracking women’s menstrual periods. Lest you think that’s an overstatement, the Missouri state health director testified at a hearing last week that he kept a spreadsheet to track the periods of women who went to Planned Parenthood, which, according to The Kansas City Star, “helped to identify patients who had undergone failed abortions.” Yet, none of these things ever seem to stick to Trump. Is any of this going to matter in the long run? He’s clearly trying to walk this line between not angering his very anti-abortion base and not seeming to side too much with them, lest he anger a majority of the rest of the people he needs to vote for him.
Ollstein: Well, he’s also not been consistent in saying it’s totally up to states, whatever states want to do is fine. He’s repeatedly criticized Florida’s six-week ban. He refused to say how he would vote on the referendum to override it. He has criticized the Arizona ruling to implement the 1864 ban. This isn’t a pure “whatever states do is fine” stance, this is “whatever states do, unless it’s something really unpopular, in which case I oppose it.” That is a tough line to walk. The Biden administration and the Biden campaign have really seized on this and are trying to say, “OK, if you are going to have a leave-it-to-states stance, then we’re going to try to hang on you every single thing states do, whether it’s the legislature, or a court, or whatever, and say you own all of this.” That’s what’s playing out right now.
Rovner: I highly recommend reading the interview, because the interviewer was very skilled at trying to pin him down. He was pretty skilled at trying to evade being pinned down. Well, meanwhile, Republican attorneys general from 17 states are suing the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission from including abortion in a list of conditions that employers can’t discriminate against and must provide accommodations for, under rules implementing the Pregnant Workers Fairness Act. The new rules don’t require anyone to pay for anything, but they could require employers to provide leave or other accommodations to people seeking pregnancy-related health care. The EEOC has included abortion as pregnancy-related health care. This is yet another case that we could see making its way to the Supreme Court. Ironically, the Pregnant Workers Fairness Act was a very bipartisan bill, so there are a lot of anti-abortion groups that are extremely angry that this has been included in the regulation. This is one of those abortion-adjacent issues that tends to drag abortion in, even when it was never expected to be there. And we’re going to see more of these. We’re going to get back into the spending bills, as Congress tries to muddle its way through another session.
Pradhan: I think, when I think about this, even though there’s a regulatory battle and a legal one now, too, like in the immediate aftermath of the Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] decision, when there were employers, I think about it more practically. Which is that there were employers that were saying, “We would cover expenses.” Or they would pay for people to travel out of state if that was something that they needed. I wonder how many people would actually do it, even if it exists, because that’s a whole other … Getting an abortion, or even things related to pregnancy, are incredibly private things, so I don’t know how many women would be willing to stand up and say, “Hey, I need this accommodation and you have to give it to me under federal regulations.” In a way, I think it’s notable both that the EEOC put out those regulations and that there’s litigation over it, but I wonder if it, practically speaking, just how much of an impact it would really have, just because of those privacy and practical hurdles associated with divulging information in that regard.
Rovner: As we were just talking about, somebody in Alabama, the closest place they can go to get an abortion is in North Carolina or Virginia, and go, “Hey, I need three days off so I can drive halfway across the country to get an abortion because I can’t get one here.” I see that might be an awkward conversation.
Pradhan: Just like any sensitive medical- or health-related needs, it’s not like people are rushing to tell their employers necessarily that it’s something that they’re dealing with.
Rovner: That’s true. It doesn’t have anything to do with privacy. Most people are not anxious to advertise any health-related issues that they are having. Speaking of people and their sensitive medical information, that Change Healthcare hack that we’ve been talking about since February, well the CEO of Change’s owner, UnitedHealth Group, was on Capitol Hill on Wednesday, taking incoming from both the Senate Finance Committee in the morning, and the House Energy and Commerce Committee in the afternoon. Among the other things that Andrew Witty told lawmakers was that the portal that was hacked did not have multifactor authentication and he confirmed that United paid $22 million in bitcoin to the hackers, although as we discussed last week, they might not have paid the hackers who actually had possession of the information. Nobody actually seemed to follow up on that, which I found curious. My favorite moment in the Senate hearing was when North Carolina Republican Thom Tillis offered CEO Witty a copy of the book “Hacking For Dummies.” Is anything going to result from these hearings? Other than what it seemed a lot of lawmakers getting to express their frustration in person.
Pradhan: Can I just say how incredible it is to me that a company that their net worth is almost $450 billion, one of the largest companies in the world, apparently does not know how to enforce rules on two-factor authentication, which is something I think that is very routine and commonplace among the modern industrialized workforce.
Rovner: I have it for my Facebook account!
Pradhan: Right. I think everyone, even in our newsroom, knows how to do it or has been told that this is necessary for so many things. I just find it absolutely unbelievable that the CEO of United would go to senators and say this, and think that it would be well-received, which it was not.
Rovner: I will say his body language seemed to be very apologetic. He didn’t come in guns blazing. He definitely came in thinking that, “Oh, I’m going to get kicked around, and I’m just going to have to smile and take it.” But obviously, this is still a really serious thing and a lot of members of Congress, a lot of the senators and the House members, said they’re still hearing from providers who still can’t get their claims processed, and from people who can’t get their medications because pharmacies can’t process the claims. There’s a lot of dispute about how long it’s going to take to get things back up and running. One of the interesting tidbits that I took away is that, as much of health care that goes through Change, it’s like 40% of all claims, it’s actually a minimum part of United’s health claims. United doesn’t use Change for most of its claims, which surprised me. Which is maybe why United isn’t quite as freaked out about this as a lot of others are. Is there anything Congress is going to be able to do here, other than say to their constituents, “Hey, I took your complaints right to the CEO?”
Karlin-Smith: I think there’s two things they may focus on. One is just cybersecurity risks in health care, which is broader than just these incidents. In some ways, it could be much worse, if you think about hospitals and medical equipment being hacked where there could be direct patient impacts in care because of it. The other thing is, United is such a large company and the amount of Americans impacted by this, but also the amount of different parts of health care they have expanded into, is really under scrutiny. I think it’s going to bring a light onto how big they’ve become, the amount of vertical integration in our health system, and the risks from that.
Rovner: We went through this in the ’90s. Vertical integration would make things more efficient, because everybody would have what they called aligned incentives, everybody would be working towards the same goal. Instead, we’ve seen that vertical integration has just created big, behemoth companies like United. I don’t know whether Congress will get into all of that, but at least it brought it up into their faces.
There’s lots of regulatory news this week. I want to start with the FDA, which finalized a rule basically making laboratory-developed tests medical devices that would require FDA review. Sarah, this has been a really controversial topic. What does this rule mean and why has there been such a big fight?
Karlin-Smith: This rule means that diagnostic tests that are developed, manufactured, and then actually get processed, and the results get processed at the lab, will now no longer be exempted from FDA’s medical device regulations and they’ll have to go through the process of medical devices. The idea is to basically have more oversight over them, to ensure that these tests are actually doing what they’re supposed to do, you’re getting the right results and so forth. Initially, over the years, the prevalence of these tests has grown, and what they’re used for, I think, has changed and developed where FDA is more concerned about the safety and the types of health decisions people may be making without proper oversight of the tests. One, I think, really infamous example that maybe can people use to understand this is Theranos was a company that was exempted from a lot of regulations because of being considered an LDT. The initial impact is going to be interesting because they’re actually basically exempting all already-on-the-market products. There’s also going to be some other exemptions, such as for tests that meet an unmet medical need, so I think that will have to be defined. There is a reasonable chance that there’s going to be lawsuits challenging whether FDA can do this on their own or need Congress to write new legislation. There have been battles over the years for Congress to do that. FDA, I think, has finally gotten tired of waiting for them to lead. I think initially, we’re going to see a lot of battles going forth and FDA also just has limited capacity to review some of this stuff.
Rovner: We already know that FDA has limited capacity on the medical device side. I was amused to see, oh, we’re going to make these medical devices, where there’s already a huge problem with FDA either exempting things that shouldn’t really be exempt, or just not being able to look at everything they should be looking at.
Karlin-Smith: Right. They’re going to take what they call a risk-based approach, which is a common terminology used at the FDA, I think, to focus on the things where they think there’s the most risk of something problematic happening to people’s health and safety if something goes wrong. It’s also an admission, to some extent, of something that’s not necessarily their fault, which is they only have so much budget and so many people, and that really comes down to Congress deciding they want to fix it. Now, FDA has user-fee programs and so forth, so perhaps they could convince the industry to pony up more money. But as you alluded to early on, one of the fights over this has been their different segments of companies that make these tests that have different feelings about the regulations. Because you have more traditional, medical device makers that are used to dealing with the FDA that probably feel like they have this leg up, they know how to handle a regulatory agency like FDA and get through. Then you have other companies that are smaller, and do not have that expertise, maybe don’t feel like they have the manpower and, just, money to deal with FDA. I think that’s where you get into some of these business fights that have also kept this on the sidelines for a while.
Pradhan: Well, also I wonder, hospitals also use laboratory developed tests, too, and they develop them. I feel like, and Sarah, correct me if I’m wrong, but I think previously when there was debate over whether FDA was going to do this, I think hospitals were pretty critical of any move of FDA to start regulating these more aggressively, right? Because they said for tests used for cancer detection or other health issues, I think that they were not thrilled at the idea. I don’t know that they’ve had to really deal with FDA in this regard either when it comes to devices.
Karlin-Smith: Yeah. I know one big exemption that people were looking for was whether they were going to exempt academic medical centers, and they did not. We’ll see what happens with that moving forward. But obviously, again, the older ones will have this exemption.
Rovner: Well, speaking of controversial regulations, the administration has basically decided that it’s not going to decide about the potential menthol ban that we’ve been talking about on and off. There was a statement from HHS [Department of Health and Human Services] last week that just said, “We need to look at this more.” Somebody remind us why this is so controversial. Obviously, health interests say, really, we should ban menthol, it helps a lot of people to continue smoking and it’s not good for health. Why would the administration not want to ban menthol?
Pradhan: It’s controversial because, I’ll just say, that it’s an election year and they are worried about backlash from Black voters not supporting President Biden in his reelection campaign, because they do this.
Karlin-Smith: It’s a health versus criminal justice issue, because the concern is that yes, in theory, if Black people make up the majority of people who use menthol cigarettes, you’re obviously protecting their health by not having it. But the concern has been among how this would be enforced in practice and whether it would lead to overpolicing of Black communities and people being charged or facing some kind of police brutality for what a lot of people would consider a minor crime. That’s where the tension has been. Although notably, some groups like the NAACP and stuff have been gotten on board with banning menthol. It’s an interesting thing where we’re trying to solve a policing or criminal justice problem through a health problem, rather than just solving the policing problem.
Ollstein: Like Sarah said, you have civil rights groups lined up on both sides of this fight. You have some saying that banning menthol cigarettes would be racist because they’re predominantly used by the Black population. But then you have people saying, well it’s racist to continue letting their health be harmed, and pointing out that those flavored cigarettes have been targeted in their marketing towards Black consumers, and that being a racist legacy that’s been around for a while. There’s these accusations on both sides and it seems like the politics of it are scaring the administration away a little bit.
Rovner: Well, just speaking of things that are political and that people smoke, the Drug Enforcement Administration announced its plan to downgrade the classification of marijuana, which until now has been included in the category of most dangerous drugs, like heroin and LSD, to what’s called Schedule III, which includes drugs with medicinal use that can also be abused, like Tylenol with codeine. But apparently, it could be awhile before it takes effect. This may not happen in time for this year’s election, right?
Karlin-Smith: Right. They have to release a proposed rule, you got to do comments, you got to get to the final rule. OMB [Office of Management and Budget] even. It’s supposedly at OMB now. OMB could hold it up for a while if they want to. As anybody who follows health policy in [Washington] D.C. knows, nothing moves fast here when it comes to regulations.
Rovner: Yes. A regulation that we thought was taken care of, but that actually only came out last week would protect LGBTQ+ Americans from discrimination in health care settings. This was a provision of the Affordable Care Act that the Trump administration had reversed. The Biden administration announced in 2021 that it wouldn’t enforce the Trump rules. But this is still a live issue in many courts and it’s significant to have these final regulations back on the books, yes?
Pradhan: It is. I think this is one of the ACA regulations that has ping-ponged the most, ever since the law was passed, because there have been lawsuits. I want to say it took the Obama administration years to even issue the first one, I think knowing how controversial it was. I believe it was the second, I think it was his second term and it was when there was no fear of repercussions for his reelection. Yeah, it’s been a very, very long-fought battle and I imagine this is also not the end of it. But no, it is very significant, the way that they defined the regulations.
Rovner: I confess, I was surprised when they came out because I thought it had already happened. I’m like, “Oh, we were still kicking this around.” So, now they appear to be final.
Well, finally this week, lots of news in health business. First, an update from last week. The Federal Trade Commission is challenging so-called junk patents from some pretty blockbuster drugs, charging that the patents are unfairly blocking generic competition. Sarah, what is this and why does it matter?
Karlin-Smith: FDA has what’s known as an orange book, as a part of a very complicated process set up by the 1984, I believe, Hatch-Waxman Act that was a compromise between the brand and the generic drug industries to get generic drugs to market a bit faster. FTC has been accusing companies of improperly listing patents in the orange book that shouldn’t be there, and thus making it harder to get generic products on the market. In particular, they’ve been actually going against drugs that have a device component, basically saying these components’ patents are not supposed to be in the orange book. They are basically asking the companies to delist the patents. They actually have gotten some concessions so far, from some of the other products they’ve targeted.
The idea would be this should help speed some of the generic entrants. It’s not quite as simple, because you do have lots of patents covering these drugs, so it does make it a little bit easier, but it’s not like it automatically opens the door. But it is unique and interesting that they have focused in on these targets because, typically, what are sometimes known as complex generics, are a lot harder for companies to make and get into the market because of the devices. Because for safety reasons FDA wants the devices to be very similar. If you pick up your product at the pharmacy, you have to be able to just know how to use it, really, without thinking about it, even if it’s a …
Rovner: Obviously, this covers things like inhalers and injectables.
Karlin-Smith: Right. The new weight loss drugs everybody is focused on, inhalers has been a big one as well. Things like an EpiPen, or stuff like that.
I think it’s been interesting because it does seem like FTC’s had more immediate results, I guess, than you sometimes see in Washington. [Sen.] Bernie Sanders has piggybacked on what they’re doing and targeted these companies and products in other ways, and gotten some small pricing cost concessions for consumers as well. But it will take a little bit of time for, even if patents get delisted, for generic drugmakers to actually then go through the whole rigamarole of getting cheaper products to market.
Rovner: Yes. This is part of what I call the “30 Years War,” to do something about drug prices. Before we leave drug prices, we’re still fighting in court about the Medicare drug negotiation, right? There, the drug industry continues to lose. Is that where we are?
Karlin-Smith: Correct. They have their fourth negative ruling this week. Basically, in this case, the judge ruled on two main arguments the industry was trying to push forward. One is that the drug negotiation program would constitute a takings violation under the Fifth Amendment. One of the main reasons the judge in this district in New Jersey said no is because they’re saying basically participation in Medicare and this drug price negotiation program are voluntary, the government is not forcibly taking any of your property, you don’t have to participate.
Another big ruling from this judge was that this program does not constitute First Amendment violations. What’s happening here is a regulation of conduct, not speech. One of the more amusing things in the decision to me, that I enjoyed, is the industry has argued that they’re basically being forced under this program to say, “Oh, this is … when CMS [Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services]” … and then work out a price, that the price they work out is the maximum fair price because that’s the technical terminology used in the law, that they’re then somehow making an admission that any other price that they’ve charged has not been fair. The judge basically said, “Well, this is a public relations problem, not a constitutional problem. Nobody is telling you you can’t go out and publicly disagree with CMS about this program and about their prices that you end up having to enter into.”
It’s another blow. They have a lot of different legal arguments they’re trying out in different cases. As I said, they’ve thrown a lot of spaghetti at the wall. So far, other arguments have failed. Some of the cases are stalled on more technicalities, like the districts they’ve filed in. There was another case that was heard, an appeal was heard yesterday, in PhRMA, the main trade group’s case, where they’re trying to push on because of that. There’s going to be a lot of more action, but so far, looks good for the government.
Pradhan: When this was first rolling out, including when CMS announced the initial 10 drugs that would first be on the list, lawyers that I talked with at the time said that the arguments that the industry was making, it was a reach, to be diplomatic about it. I don’t think anyone really thought that they would be successful and it seems like that is, at least to date, that’s how it’s playing out.
Rovner: I’ll repeat, it’s a good time to be a lawyer for the drug industry, at least you’re very busy.
All right, well, finally this week, we spend so much time talking about how big health care is getting, Walmart this week announced that it’s basically getting out of the primary care business. It’s closing down its two dozen clinics and ending its telehealth programs. This feels like another case of that, “Wow, it looked so easy to make money in health care.” Until you discover that it’s not.
Pradhan: Right. I think making money in primary care, certainly that’s not where the people say, “Oh, that’s a real big cash cow, let’s go in there.” It’s other parts of the health care industry.
Karlin-Smith: One thing that struck me about a quote in a CNN article from Walmart was how they were focusing on they wanted to do this, but they found it wasn’t a sustainable business model. To me, that then just brings up the question of “Should health care be a business?” and the problems. There’s a difference between being able to operate primary care and make enough money to pay your doctors and cover all your costs, and a big company like Walmart that wants to be able to show big returns for their investors and so forth. There’s also that distinction that something that’s not attractive for a business model like that can still be viable in the U.S.
Rovner: This reminds me a lot of ways of the ill-fated Haven Healthcare, which was when Amazon and JPMorgan Chase and Berkshire Hathaway all thought they could get together because they were big, smart companies, could solve health care. They hired Atul Gawande, he was one of the biggest brains in health care, and it didn’t work out. We shall continue.
Anyway, that is the news for this week. Now it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device.
Rachana, why don’t you go first this week?
Pradhan: This story that I’m going to suggest, [“Millions of American Kids Are Caregivers Now: ‘The Hardest Part Is That I’m Only 17.”] it’s in The Wall Street Journal, depressing like most health care things are. It’s about how millions of children, I think it’s over 5 million children under the age of 18, are providing care to siblings, grandparents, and parents with chronic medical needs, and how they are becoming caregivers at such young ages. In part, because it is so hard to find and afford in-home care for people. That is my extra credit.
Rovner: Right, good story. Sarah?
Karlin-Smith: I looked at a piece in The Atlantic by Katherine J. Wu, “America’s Infectious-Disease Barometer Is Off.” It’s focused on our initial response in this country to bird flu, and maybe where the focus should and shouldn’t be. It has some interesting points about repeat mistakes we seem to be making, in terms of inadequate testing, inadequate focus on the most vulnerable workers, and what we need to do to protect them in this crisis right now.
Rovner: Alice?
Ollstein: I chose [“Dozens of Deaths Reveal Risks of Injecting Sedatives Into People Restrained by Police“] an AP investigation, collaborating with Frontline, about the use of sedatives when police are arresting someone. This is supposed to be a way to safely restrain someone who’s combative, or maybe they’re on drugs, or maybe they’re having a mental health episode, and this is supposed to be a nonlethal way to detain someone. It has led to a lot of deaths, nearly 100 over the past several years. These drugs can make someone’s heart stop. The reporting shows it’s not totally clear if just the drugs themselves are what is killing people, or if it’s in combination with other drugs they might be on, or it’s because they’re being held down in a way by the cops that prevent them from breathing properly, or what. But this is a lot of deaths of people who have received these injections and is leading to discussions of whether this is a best practice. Pretty depressing stuff, but important.
Rovner: Yeah. It was something that was supposed to help and has not so much in many cases. My story this week is from ProPublica. It’s called “A Doctor at Cigna Said Her Bosses Pressured Her To Review Patients’ Cases Too Quickly. Cigna Threatened To Fire Her.” It’s by Patrick Rucker and David Armstrong. It’s about exactly what the headline says. A doctor who spent too much time reviewing potential insurance denials because she wanted to be sure the cases were being decided correctly. It’s obviously not the first story of this kind, but I chose it because it so reminded me of a story that I did in 2007, which was about a physician who worked for a managed-care company, it was Humana in that case, who was pushed to deny care and first testified to Congress about it in 1996. I honestly can’t believe that, 28 years later, we are still arguing about pretty much the exact same types of practices at insurance companies. At some point you would think we would figure out how to solve these things, but apparently not yet.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions. We’re at whatthehealth@kff.org, or you can still find me at X @jrovner.
Rachana, where are you hanging these days?
Pradhan: I am also on X, @rachanadpradhan.
Rovner: Sarah?
Karlin-Smith: I’m at @SarahKarlin or @sarahkarlin-smith on Bluesky.
Rovner: Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein on X, and @alicemiranda on Bluesky.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Courts, Multimedia, Pharmaceuticals, States, Abortion, Arizona, Biden Administration, FDA, Florida, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Medical Devices, Podcasts, Prescription Drugs, Tobacco, Trump Administration, Women's Health
Toxic Gas Adds to a Long History of Pollution in Southwest Memphis
MEMPHIS, Tenn. — For many years, Rose Sims had no idea what was going on inside a nondescript brick building on Florida Street a couple of miles from her modest one-story home on the southwestern side of town.
Like other residents, she got an unwelcome surprise in October 2022 at a public forum held by the Environmental Protection Agency at the historic Monumental Baptist Church, known for its role in the civil rights movement. The EPA notified the predominantly Black community that Sterilization Services of Tennessee —which began operations in the brick building in the 1970s — had been emitting unacceptably high levels of ethylene oxide, a toxic gas commonly used to disinfect medical devices.
Airborne emissions of the colorless gas can increase the risk of certain medical conditions, including breast cancer. Sims, who is 59 and Black, said she developed breast cancer in 2019, despite having no family history of it, and she suspects ethylene oxide was a contributing factor.
“I used to be outside a lot. I was in good health. All of a sudden, I got breast cancer,” she said.
Local advocates say the emissions are part of a pattern of environmental racism. The term is often applied when areas populated primarily by racial and ethnic minorities and members of low-socioeconomic backgrounds, like southwest Memphis, are burdened with a disproportionate amount of health hazards.
The drivers of environmental racism include the promise of tax breaks for industry to locate a facility in a heavily minority community, said Malini Ranganathan, an urban geographer at American University in Washington, D.C. The cheaper cost of land also is a factor, as is the concept of NIMBY — or “not in my backyard” — in which power brokers steer possible polluters to poorer areas of cities.
A manager at Sterilization Services’ corporate office in Richmond, Virginia, declined to answer questions from KFF Health News. An attorney with Leitner, Williams, Dooley & Napolitan, a law firm that represents the company, also declined to comment. Sterilization Services, in a legal filing asking for an ethylene oxide-related lawsuit to be dismissed, said the use of the gas, which sterilizes about half the medical devices in the U.S., is highly regulated to ensure public safety.
Besides southwest Memphis, there are nearly two dozen locales, mostly small cities — from Athens, Texas, to Groveland, Florida, and Ardmore, Oklahoma — where the EPA said in 2022 that plants sterilizing medical devices emit the gas at unusually high levels, potentially increasing a person’s risk of developing cancer.
The pollution issue is so bad in southwest Memphis that even though Sterilization Services planned to close shop by April 30, local community leaders have been hesitant to celebrate. In a letter last year to a local Congress member, the company said it has always complied with federal, state, and local regulations. The reason for its closure, it said, was a problem with renewing the building lease.
But many residents see it as just one small win in a bigger battle over environmental safety in the neighborhood.
“It’s still a cesspool of pollution,’’ said Yolonda Spinks, of the environmental advocacy organization Memphis Community Against Pollution, about a host of hazards the community faces.
The air in this part of the city has long been considered dangerous. An oil refinery spews a steady plume of white smoke. A coal plant, which is now closed, leaked components of coal ash, such as arsenic, into the ground and groundwater, according to a corrective action report from the Tennessee Valley Authority. The TVA is proposing to gut an existing gas plant and replace turbines in the facility with new ones. A continual stream of heavy trucks chug along nearby highways and roads. Other transportation sources of air pollution include the Memphis International Airport and barge traffic on the nearby Mississippi River.
Lead contamination is also a concern, not just in drinking water but in the soil from now-closed lead smelters, said Chunrong Jia, a professor of environmental health at the University of Memphis. Almost all the heavy industry in Shelby County — and the associated pollutants — are located in southwest Memphis, Jia added.
Sources of pollution are often “clustered in particular communities,” said Darya Minovi, a senior analyst with the Union of Concerned Scientists, a nonprofit that advocates for environmental justice. When it comes to sterilizing facilities that emit ethylene oxide, areas inhabited largely by Black, Hispanic, low-income, and non-English-speaking people are disproportionately exposed, the group has found.
Four sites that the EPA labeled high-risk are in low-income areas of Puerto Rico. Seven sterilizer plants operate in that U.S. territory.
The EPA, responding to public concerns and to deepened scientific understanding of the hazards of ethylene oxide, recently released rules that the agency said would greatly reduce emissions of the toxic gas from sterilizing facilities.
KeShaun Pearson, who was born and raised in south Memphis and has been active in fighting environmental threats, said he is frustrated that companies with dangerous emissions are allowed to create “toxic soup” in minority communities.
In the area where the sterilization plant is located, 87% of the residents are people of color, and, according to the Southern Environmental Law Center, life expectancy there is about 10 years lower than the average for the county and state. The population within 5 miles of the sterilizer plant is mostly low-income, according to the Union of Concerned Scientists.
Pearson was part of Memphis Community Against the Pipeline, a group formed in 2020 to stop a crude oil pipeline that would have run through Boxtown, a neighborhood established by emancipated slaves and freedmen after the signing of the Emancipation Proclamation of 1863.
That campaign, which received public support from former Vice President Al Gore and actress-activist Jane Fonda, succeeded. After the ethylene oxide danger surfaced in 2022, the group changed the last word of its name from “pipeline” to “pollution.”
Besides breast and lymphoid cancers, animal studies have linked inhaling the gas to tumors of the brain, lungs, connective tissue, uterus, and mammary glands.
Last year, with the help of the Southern Environmental Law Center, the south Memphis community group urged the Shelby County Health Department to declare the ethylene oxide situation a public health emergency and shut down the sterilizing plant. But the health department said the company had complied with its existing air permit and with the EPA’s rules and regulations.
A health department spokesperson, Joan Carr, said Shelby County enforces EPA regulations to ensure that companies comply with the federal Clean Air Act and that the agency has five air monitoring stations around the county to detect levels of other pollutants.
When the county and the Tennessee Department of Health did a cancer cluster study in 2023, the agencies found no evidence of the clustering of high rates of leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, or breast or stomach cancer near the facility. There were “hot and cold spots” of breast cancer found, but the study said it could not conclude that the clusters were linked to the facility.
Scientists have criticized the study’s methodology, saying it did not follow the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendations for designing a cancer cluster investigation.
Meanwhile, several people have sued the sterilizing company, claiming their health has been affected by the ethylene oxide emissions. In a lawsuit seeking class-action status, Reginaé Kendrick, 21, said she was diagnosed with a brain tumor at age 6. Chemotherapy and radiation have stunted her growth, destroyed her hair follicles, and prevented her from going through puberty, said her mother, Robbie Kendrick.
In response to proposed stricter EPA regulations, meanwhile, the Tennessee attorney general helped lead 19 other state AGs in urging the agency to “forgo or defer regulating the use of EtO by commercial sterilizers.”
Sims said she’s glad her neighborhood will have one less thing to worry about once Sterilization Services departs. But her feelings about the closure remain tempered.
“Hope they don’t go to another residential area,” she said.
[Clarification: This article was updated at 3:15 p.m. ET on May 1, 2024, to specify which substances leaked into the ground and groundwater and what changes will occur related to the Tennessee Valley Authority’s activities in Shelby County, Tennessee.]
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 5 months ago
Public Health, Race and Health, States, Disparities, Environmental Health, Florida, Oklahoma, Tennessee, texas, Virginia
KFF Health News' 'What the Health?': Abortion — Again — At the Supreme Court
The Host
Julie Rovner
KFF Health News
Julie Rovner is chief Washington correspondent and host of KFF Health News’ weekly health policy news podcast, “What the Health?” A noted expert on health policy issues, Julie is the author of the critically praised reference book “Health Care Politics and Policy A to Z,” now in its third edition.
Some justices suggested the Supreme Court had said its piece on abortion law when it overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022. This term, however, the court has agreed to review another abortion case. At issue is whether a federal law requiring emergency care in hospitals overrides Idaho’s near-total abortion ban. A decision is expected by summer.
Meanwhile, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid finalized the first-ever minimum staffing requirements for nursing homes participating in the programs. But the industry argues that there are not enough workers to hire to meet the standards.
This week’s panelists are Julie Rovner of KFF Health News, Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University’s nursing and public health schools and Politico Magazine, Tami Luhby of CNN, and Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Panelists
Joanne Kenen
Johns Hopkins University and Politico
Tami Luhby
CNN
Alice Miranda Ollstein
Politico
Among the takeaways from this week’s episode:
- This week’s Supreme Court hearing on emergency abortion care in Idaho was the first challenge to a state’s abortion ban since the overturn of the constitutional right to an abortion. Unlike previous abortion cases, this one focused on the everyday impacts of bans on abortion care — cases in which pregnant patients experienced medical emergencies.
- Establishment medical groups and doctors themselves are getting more vocal and active as states set laws on abortion access. In a departure from earlier political moments, some major medical groups are campaigning on state ballot measures.
- Medicaid officials this week finalized new rules intended to more closely regulate managed-care plans that enroll Medicaid patients. The rules are intended to ensure, among other things, that patients have prompt access to needed primary care doctors and specialists.
- Also this week, the Federal Trade Commission voted to ban most “noncompete” clauses in employment contracts. Such language has become common in health care and prevents not just doctors but other health workers from changing jobs — often forcing those workers to move or commute to leave a position. Business interests are already suing to block the new rules, claiming they would be too expensive and risk the loss of proprietary information to competitors.
- The fallout from the cyberattack of Change Healthcare continues, as yet another group is demanding ransom from UnitedHealth Group, Change’s owner. UnitedHealth said in a statement this week that the records of “a substantial portion of America” may be involved in the breach.
Plus for “extra credit” the panelists suggest health policy stories they read this week that they think you should read, too:
Julie Rovner: NBC News’ “Women Are Less Likely To Die When Treated by Female Doctors, Study Suggests,” by Liz Szabo.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: States Newsroom’s “Loss of Federal Protection in Idaho Spurs Pregnant Patients To Plan for Emergency Air Transport,” by Kelcie Moseley-Morris.
Tami Luhby: The Associated Press’ “Mississippi Lawmakers Haggle Over Possible Medicaid Expansion as Their Legislative Session Nears End,” by Emily Wagster Pettus.
Joanne Kenen: States Newsroom’s “Missouri Prison Agency To Pay $60K for Sunshine Law Violations Over Inmate Death Records,” by Rudi Keller.
Also mentioned on this week’s podcast:
- American Economic Review’s “Is There Too Little Antitrust Enforcement in the U.S. Hospital Sector?” by Zarek Brot-Goldberg, Zack Cooper, Stuart Craig, and Lev Klarnet.
- KFF Health News’ “Medical Providers Still Grappling With UnitedHealth Cyberattack: ‘More Devastating Than Covid,” by Samantha Liss.
CLICK TO OPEN THE TRANSCRIPT
Transcript: Abortion — Again — At the Supreme Court
[Editor’s note: This transcript was generated using both transcription software and a human’s light touch. It has been edited for style and clarity.]
Julie Rovner: Hello, and welcome back to “What the Health?” I’m Julie Rovner, chief Washington correspondent for KFF Health News, and I’m joined by some of the best and smartest health reporters in Washington. We’re taping this week on Thursday, April 25, at 10 a.m. As always, news happens fast and things might have changed by the time you hear this, so here we go.
We are joined today via video conference by Alice Miranda Ollstein of Politico.
Alice Miranda Ollstein: Hello.
Rovner: Tami Luhby of CNN.
Tami Luhby: Hello.
Rovner: And Joanne Kenen of the Johns Hopkins University schools of public health and nursing and Politico Magazine.
Joanne Kenen: Hi, everybody.
Rovner: No interview this week, but wow, tons of news, so we are going to get right to it. We will start at the Supreme Court, which yesterday heard oral arguments in a case out of Idaho over whether the federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act, or EMTALA, trumps Idaho’s almost complete abortion ban. This is the second abortion case the high court has heard in as many months and the first to actively challenge a state’s abortion ban since the overturn of Roe v. Wade in 2022. Last month’s case, for those who have forgotten already, was about the FDA approval of the abortion pill mifepristone. Alice, you and I both listened to these arguments. Did you hear any hints on which way the court might be leaning here?
Ollstein: The usual caveat that you can’t always tell by the questions they ask. Sometimes they play devil’s advocate or it’s not indicative of how they will rule on the case, but it did seem that at least a couple of the court’s conservatives were interested in really taking a tough look at Idaho’s argument. Obviously, some of the other conservatives were very much in support of Idaho’s argument that its doctors should not be compelled to perform abortions for patients experiencing a medical emergency. It really struck me from the arguments how much it focused on what’s actually going on on the ground.
That was a huge departure from a lot of other Supreme Court arguments and a lot of Supreme Court arguments on abortion where it’s a lot of hypotheticals and getting into the legal weeds. This was just like they were reading these concrete, reported stories of what’s been happening in Idaho and other states because of these abortion bans. People turned away while they were actively miscarrying, people being flown across state lines to receive timely care. I think whether that will make a difference that the justices are sort of being confronted with the concrete ramifications of the Dobbs [v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization] decision or not remains to be seen.
Rovner: I thought one of the things that it looked like very much like last month’s argument is that the women justices were very much about real details and talking about medical conditions, about ectopic pregnancies and premature rupture of membranes and things that none of the men mentioned at all. The men were sort of very legalistic and the women, including Amy Coney Barrett, who voted to overturn Roe v. Wade, were very much all about, as you said, what’s going on on the ground and what this distinction means. I mean, where we are is that Idaho has an exception in its abortion ban, but only for the life of the woman. Whereas EMTALA says you have to stabilize someone in an emergency situation and it’s been interpreted by the federal government to say sometimes that stabilization means terminating a pregnancy, as in the case of premature rupture of membranes or an ectopic pregnancy or a case where the woman is going to hemorrhage and is actively hemorrhaging.
That question of where that line is, between what’s an immediate threat to life and what’s just a threat to health or a threat to life soon, was the crux of this case. And it really does feel uncomfortably like we have nine Supreme Court justices making, really, medical decisions.
Ollstein: Yeah, it struck me how Amy Coney Barrett seemed to get pretty frustrated with Idaho’s attorney at a couple points. Idaho’s attorney was saying kind of, “Nothing to see here. There’s no problem. Since we allow lifesaving abortions and that’s what is required under EMTALA, there’s no conflict.” So Amy Coney Barrett was like, “Well, why are you here then? Why are you before us?” The reason is that they’re trying to get this lower-court injunction lifted even though it’s not in effect right now. The other point she got kinda testy was when Idaho was saying that their law is clear, doctors know what to do, and Amy Coney Barrett asked, “Well, couldn’t a prosecutor come in later and disagree and said, “Oh, you performed an abortion you said was to save someone’s life, but I don’t think it was necessary to save her life and I’m going to charge you criminally?” And the Idaho attorney conceded that that could happen.
So I think her vote could potentially be in play, but I don’t know if it’s going to be enough to overcome the court’s conservatives who are very skeptical that EMTALA should compel states to do anything.
Rovner: So the medical community has been quite outspoken in this case. The American Medical Association, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American College of Emergency Physicians have all filed briefs saying the Idaho ban could require them to violate professional ethics, wrote the immediate president of the AMA, Jack Resnick, in an op-ed. “It is reckless for Idaho to tell emergency physicians that they must ignore their moral and ethical standards and stand by while a septic patient begins to lose kidney function or when a hemorrhaging patient faces only a 30% chance of death.” But I feel like the medical profession has long since lost control of the abortion issue. I mean, is there any chance here that they might prevail? I have to say this week I’ve gotten so many emails from so many doctor groups saying, “Oh my goodness, look what’s happening. They’re going to put us in this impossible situation.” To which I want my response to be, “Where have you been for the last 20 years?”
Ollstein: I mean, I think it is notable that these establishment medical groups are becoming more vocal. I mean, some might say better late than never, and I think in some instances they are having an impact at the state level. They have pushed some state legislatures to add or expand exemptions to abortion bans. But a lot of times Republican lawmakers have rejected calls from state medical associations to do that, and so I think filing amicus briefs is a way to have your say, lobbying at the state level is a way to have your say. Some doctors are even running for office specifically on this issue. And also, medical groups are campaigning hard on these state abortion referendums. I reported on doctor groups door-knocking in Ohio, for instance, before that referendum won big.
I think it’s really interesting to see the medical community get a lot more vocal on something they’ve either tried to stay out of or been vocal on the other side on in the past, but we’ll have to see how much impact that actually has.
Rovner: Well, one thing this case highlights is how pregnant women who experience complications that can threaten their health or future fertility, but are not immediately life-threatening, can end up in really terrible circumstances, as we heard in a number of anecdotes at the oral arguments. The Associated Press “FOIA’d”[requested Freedom of Information Act] EMTALA pregnancy complaint records from several states with abortion bans and found some pretty horrific examples, including one woman who miscarried in the emergency room lobby restroom after she was turned away from the registration desk. Another who was turned away and ended up giving birth in a car on the way to another hospital. That baby died. These are not people who go to the emergency room in search of abortions. They’re women who are trying to maintain pregnancies. Is the concept that people ending up in the most horrific situations are often those who most want children, is that finally getting through here?
Ollstein: What struck me most about that reporting is that the documents they got were just from the first few months after Roe v. Wade was overturned, so we have no idea what’s happening now. It could be better, it could be much worse, it could be the same. I think that lack of transparency makes this really hard to report on accurately. And the fact that it took The AP a year to even get those few heavily redacted documents speaks to the challenge here. We want an accurate picture of how these bans are impacting the provision of health care around the country, and it’s really hard to get.
Rovner: I know the Biden administration has been kind of trying to keep this quiet. I mean, not out there sort of blaring what’s happening. They’ve been sort of leaving that to the politics side and this is obviously the policy side. Obviously on the politics side, the Biden administration is getting bolder about using abortion as a campaign issue. The president himself gave a speech in Florida where a six-week ban is set to take effect next week and pinned all the abortion restrictions directly on former President Trump, who he pointed out has taken credit for them. Biden actually said the word abortion twice in that speech. I was listening very closely and went back and counted. I think that’s a first. They’re definitely stepping up the pressure politically, right?
Ollstein: Yes. The Biden campaign is leaning very hard on this. Even in states where it’s debatable whether they have a chance, like Florida, I think that there’s an interest, especially after seeing all of these referendums and ballot measures win big. It’s really shown Democrats that this is a very popular issue to run on, that they shouldn’t be afraid of it, that they should lean into it. I think you are seeing attempts to do that. It’s not always the language that the abortion rights advocacy community wants to hear, but it’s definitely more than we’ve heard from the Biden administration in the past.
I think you’re also seeing an attempt to sort of take the air out of Trump’s “Let’s leave it to states. I am reasonable and moderate” sort-of pitch. By highlighting what’s happening on the ground in certain states, it’s an attempt to say, “OK, you want to leave it to states? Then you own all of this. You own every woman being turned away from a hospital while she’s miscarrying. You own every instance of a ban going into effect and people having to travel across state lines,” et cetera. But whether just blaming Trump and arguing that he would be worse is enough versus saying what Biden would actually do and continue to do, I think that’s what we’ve heard people want to hear more of. Although there has been some action from the Biden administration recently.
Rovner: That was just going to be my next question. The one policy change the Biden administration did do this week was finalized a rule expanding the health records protections under HIPAA to abortion information. Why was this important? It sounds pretty nerdy.
Ollstein: This has been in the works for more than a year. A lot of people have been wondering why it’s been taking so long and worried that if it took even longer, it would be easier to get rid of it if a new administration takes over. But essentially this is to make it harder for states to reach across state lines to try to obtain information and use it to prosecute for having an abortion. It’s an attempt to better protect that data and so we heard a lot of praise after the announcement came out from abortion rights groups and some medical groups, and I would anticipate some groups on the right would sue. I’ve seen some complaints saying this will prevent law enforcement from investigating actual crimes against people, and so I expect to see some legal challenges soon.
Kenen: There are all sorts of efforts to stop both travel for abortion. There are also laws on books already, there have been for a number of years, about helping a minor cross state lines for abortion. There’s the attempts to stop the shipment of abortion pills from a legal state into a state that has a ban. There’s all sorts of things where, whether the intent is to actually prosecute a woman or a pregnant person, versus collecting evidence for some kind of larger crackdown or prosecution, this is potentially a piece … patient records are potentially a piece of that. We’ve talked a few weeks ago, maybe a month or two ago by now, about some Texas communities that wanted to say, “If you drive on the road in our town on the way to an abortion, we’re going to arrest you.” How they figure out logistically and practically … What are you going to do? Stop everybody on the road and give them a pregnancy test?
I mean, I don’t know how you enforce that, but just that these ideas are out there and on the books through this privacy shield. We have privacy under HIPAA, all of us, so to interpret it this way, or reinforce it depending on your political point of view, undermine excessively, whatever, but this is sort of pivotal because there’s so many ways these records could be used in various kinds of legislative and prosecutorial ways.
Rovner: As you point out, it’s not theoretical. We’ve seen attorneys general — Indiana and Kansas — and some other states, actually, and Texas say that they want to go after these records, so it’s not …
Kenen: Right and we’ve seen cases of the child rape victim and the prosecutor, what happened with the doctor, and so it’s not theoretical. It’s not widespread right now, but it’s not theoretical. Whether the pregnancy was planned and wanted or it was unplanned and ended up being wanted, going through a pregnancy loss is not just medically difficult, depending on when in pregnancy it occurs and under what circumstances. It can be medically quite complicated and it’s emotionally devastating. So to just get pulled into these political legal fights when you’ve already been bleeding in the parking lot or whatever, or having lost a pregnancy, it’s like you forget these are human beings. These are people going through medical crises.
Rovner: Indeed. Well, abortion is far from the only big health news this week. On Monday, the Biden administration finalized more long-awaited rules regarding staffing in nursing homes that participate in Medicare or Medicaid. Tami, what’s in these rules and why is the concept that nursing homes should have nurses on duty so controversial?
Luhby: It is very controversial and it’s also very consequential. So on Monday, as you said, the Biden administration finalized the first-ever minimum staffing rules at nursing homes involved in Medicare and Medicaid, and they say it’s crucial for patient safety and quality of care. It requires that all nursing homes provide a total of at least 3.48 hours of nursing care per resident per day, including defined periods of care from registered nurses and from nurses’ aides. Plus, nursing homes must have a registered nurse on-site at all times, which is different than the rules now. Now, CMS [Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] is giving the nursing homes some time to staff up. The mandate will be phased in over three years with rural communities having up to five years and they’re also giving temporary exemptions for facilities in areas with workforce shortages that demonstrate a good faith effort to hire. When I spoke to [Department of Health and Human Services] Secretary [Xavier] Becerra about the nursing home industry’s vocal concerns that this could cause a lot of nursing homes to close or limit admissions, he said, “Well, a business model that is based on understaffing is not a very good business model and is dangerous for patients.”
So, it’s going to be a heavy lift for nursing homes. According to HHS, 75% of them will have to hire staff, including 12,000 registered nurses and 77,000 aides. And also, 22% of them will need to hire registered nurses to meet the around-the-clock mandate. The nursing home operators, not surprisingly, have strongly pushed back on this rule even back when it was first proposed in September, saying that they’re already having staffing problems amid a nationwide shortage of nurses. The American Health Care Association called the mandate an unreasonable standard that only threatens to shut down more nursing homes, displace hundreds of thousands of residents, and restrict seniors’ access to care.
Rovner: We should point out the American Health Care Association is the lobbying group for nursing homes.
Luhby: Yes. What’s interesting also, though, is that on the other side, you have advocacy groups that are saying that it doesn’t go far enough and they’re citing a 2001 CMS study that found that nursing home residents need at least 4.1 hours of daily care. To add to all of this, if it’s not complicated and controversial enough, Congress is getting involved and is also split over the rules. Some lawmakers, like Sens. Elizabeth Warren and Bob Casey, generally support it, but nearly a hundred House members from both parties wrote to HHS Secretary Becerra expressing their concern that the mandate could lead to nursing home closures. And there’s a bipartisan Senate bill and a House Republican bill that would prohibit HHS from finalizing the rule. So we have time before this goes into effect. It goes into effect in phases, and we’ll see if lawmakers move to block the mandate or if the courts do, but it’s going to be interesting to watch how this plays out.
Rovner: Joanne wanted to add something.
Kenen: Well, first of all, as we say frequently, there’s always lawsuits. We have a health care/lawsuit system, so it’s not over. But I think the other thing is I think families who put a loved one in a nursing home don’t understand how little nursing, let alone doctoring, goes on. The name is “nursing” home and people expect there to be a nurse there, meaning a registered nurse. I think people often think there’s a doctor there, where the doctors are not there very much. That’s one reason the lack of medical care on-site, not only could there be emergencies, but I mean even things that could be treated in place if there is a physician. I mean, it’s just dial 911 and put them in an ambulance and send them to the hospital. And we do have this problem with hospital readmission, which is not just a cost problem and a regulatory problem, it’s really bad for patients to … the continuity of care is good and lack of continuity and handoffs and change, sending people back-and-forth is not good for them.
Obviously, there are times there’s an emergency and you need to send someone to a hospital, but not always. If there was a doctor or nurse, there’s some things that you don’t have to call 911 for. Because you don’t know or don’t learn about nursing homes until you have a relative there or until you’re a reporter who has to write about them. You don’t realize that they’re very custodial and there’s not a lot of taken care of in terms of getting assistance in bathing and walking and things like that. There’s less medical care, including nursing care, than people realize until your loved one is there. I mean, when I covered them the first time, I was really shocked. I mean, it’s 20 years ago the first time I wrote about it, but my assumption of what was there and what is actually there was a big gap.
Rovner: Tami.
Luhby: One thing also, though is … I mean, yes, that is definitely true about the medical care, but we’re also talking about just the care, not only the nursing. But that’s why so many aides need to be hired because you also have situations in nursing homes where people aren’t getting help to go to the bathroom, aren’t getting showered regularly, aren’t being watched. Maybe they’re trying to go to the bathroom themselves and they’re falling because they have to go. I mean, unfortunately, I’ve had experience with nursing homes with my family and I’ve seen this. But also I think it’s been pretty well reported in a lot of publications and studies and such. But there are a lot of problems in nursing homes, in general, and staffing.
Rovner: Well, just to talk about how long this is going on, former Sen. David Pryor died this week. When he was a House member, he rather famously went undercover at a nursing home to try and spotlight. That was when we first started to hear about some of the conditions in nursing homes. He was instrumental in doing the work that got the original federal nursing home standards passed in 1987, which was the first time I covered this issue, and even then there was a big fight in 1987 about should there be a staffing mandate? It’s like, hello, if we’re going to improve care in nursing homes, maybe we should make sure there are enough people to provide care. Even then the nursing home industry was saying, “But we have a shortage. We can’t hire enough people to actually do this if you give us a staffing mandate.” So literally, this has gone back-and-forth since 1987. And, as Joanne points out, it’s still in all likelihood not over, but one could sort of think, gee, they’ve had two generations now to come up with enough people to work in these nursing homes. Maybe Becerra is right. Maybe there’s something wrong with the business model?
Luhby: I was going to say, we know the business model is also moving more towards private equity, which is not necessarily going to be as concerned with the staffing levels. We know that the staffing levels … I think there’ve been studies that show that staffing levels are generally lower in investor-owned nursing homes. So there’s that.
Kenen: There’ve been a lot of demographic changes. I mean, you live longer, but you don’t always live healthier. We have families that are spread out. Not everybody’s living in the same town anymore. I mean, they haven’t for a number of decades now, but your daughter-in-law is 3,000 miles away. She can’t come to your house every day. At the same time, we do have a push and it’s not brand-new, it’s a number of years now, to do more home- and community-based care, but there are shortages and waiting lists and problems there, too. So there are a lot of people who need institutional care. Whether they wanted to have that or not, that’s where they go because either there’s not enough community support or they don’t have the family to fill in the gaps or they’re too medically complicated or whatever. Given the demographic trends and the degree of chronic disease and disability, this is not going away. It’s like Julie said, it’s way overdue. We need to figure it out. There are workforce shortages to train more CRNAs [certified registered nurse anesthetists] like the trained aides. It’s not a five-, six-year program. I mean, this can be done and is done somewhere in community colleges. You can do this. You can improve at all levels. You need more nurse RNs, nurses or advanced practice nurses, but you also need more of everything else. People who go to work in these jobs, by and large, do want to provide quality, compassionate care, and it’s hard to do if there are not enough of you.
Rovner: But they’re also super hard jobs and super stressful and super physically demanding.
Kenen: Hoisting and …
Rovner: Yeah, yeah. And not well-paid.
Kenen: Keeping track of a lot of stuff.
Rovner: Well, in a related move, the Biden administration this week also finalized rules that will attempt to make the quality of Medicaid managed-care plans more transparent. Among other things, the rules establish national wait time limits for certain types of medical care and require states to conduct secret shopper surveys of insurance provider networks to make sure there are enough practitioners available to serve the patient population. The administration says these rules are needed because so many Medicaid patients are now in managed care and regulations just haven’t kept up. Will these be enough to actually protect these often very vulnerable populations? I mean, obviously these people are not quite as vulnerable as people in nursing homes, but they’re kind of the next level down.
Kenen: Well, I think that we’ve seen a history of waves of regulation. Then whatever the status quo becomes, it doesn’t stay the status quo. Whether, as Tami mentioned, there’s more private equity or there’s monopolization and consolidation or just new state regulation. I mean, it’s not static. Do we know how this move is going to play out? No. Do we assume that the bad actors who don’t want to comply will find new ways of doing things that in five years we’ll have another set of regulations that we’ll be talking about? I mean, unfortunately, that’s the way things work. Some regulatory approaches or legal approaches work and others just sort of morph. There’s a lot of history of innovative great actors and lousy bad actors.
Rovner: I say it’s been a big week for federal regulation because we also have breaking news from the Federal Trade Commission, of all places. On Tuesday, the commissioners voted to finalize rules banning most noncompete clauses in employment contracts. At an event here at KFF, the FTC chair, Lina Kahn, said a surprisingly large number of comments about that proposed rule came from health care workers. Here’s a snippet from that conversation.
Lina Khan: There were a whole bunch of comments that said, “I signed this, but it’s not like I was exercising real choice. It felt coercive.” We also heard a lot about the effect of these noncompetes and the way that, especially in rural areas, if you want to switch employers and there’s really only one other option locally, if a noncompete is barring you from taking a job with that other hospital, practically to change jobs you have to leave the state. Right? And just how destructive and devastating that is for people and their families, especially if they’re choosing between staying in a job where the employer realizes that this is a captive employee and they don’t really have to compete in offering them better opportunities, better wages, and having to instead think about uprooting their family. We also heard from doctors who did not uproot their families, but instead just commuted hours and hours a day driving. People saying, “For five years I didn’t really see my kids at all awake, ever, because I was always on the road because of this noncompete.” So just really vivid stories from people.
Rovner: So even though the vote was less than 48 hours ago, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce has already filed suit to block the rules as have some smaller business groups. Why do businesses think they need to prevent workers from changing jobs near where they live? I mean, you could see it for people who’ve invented something. You don’t want them to walk out the door with proprietary secrets, but baristas at Starbucks and even nurses are not walking out with trade secrets.
Kenen: Well, I mean, this is common in doctors’ employment contracts, nurses, it’s everything. I think it’s partly because there are provider shortages in some places and they want to keep the workforce they have instead of having them be lured across town to a competitor where they could be paid more and then you have to pay even more to hire the next one. So that’s part of it. It’s economic. A lot of it’s economic. I mean, there’s some fear of patients going with a certain beloved provider, a doctor goes somewhere else. But I think it’s basically they don’t want churn. They don’t want to have to keep paying more. Somebody gets a job offer across the street and they don’t want to take it. They like where they are, but they’re going to ask for more money. It’s largely economic in a market where there’s scarcity of some specialties and certainly nursing. I mean, there’s questions about are there are not enough nurses? Or are we just putting them in the wrong places? But speaking generally, there’s a nursing shortage and physicians, we don’t have enough primary care providers. We certainly don’t have enough geriatricians. We don’t have enough mental health providers. We don’t have enough of a lot of things. This helps the employer, in this case, the health system, usually.
Rovner: I have to say it was only in the last couple of years that I even became aware there were noncompetes in health care. I mean, I knew about them for weathercasters on local stations. It’s like if you leave, you have to go to another station in another city. I had absolutely no idea that they were so common, as you point out, for so many economic reasons. Obviously this has also already been challenged in court, so we’ll have to see how that plays out.
Also this week on the antitrust front, we have a paper from three health economists published in the American Economic Review who calculated that if the Federal Trade Commission had been more aggressive about flagging and potentially blocking hospital mergers just between 2010 and 2015, health care prices could have been 5% lower. Researchers blame the FTC’s limited budget, but you have to wonder if that budget is limited because business has so much clout in Washington and really doesn’t want eager regulators snooping into their potentially anticompetitive practices. I mean, the FTC has been around for 120-some years now. Occasionally it tries to do big things like with these noncompetes, but mostly it doesn’t do as much as obviously economists and people who study it think that it could do. I mean, we certainly have problems with lack of competition in health care.
Ollstein: I think we have an unusually aggressive FTC right now, so it’ll be really interesting to see what they can accomplish in whatever time this administration has remaining to it, which remains to be seen. I have seen some more aggressive action from the agency in the past on things like payday lending and some of these other sort of maybe more fringy sectors of the economy. So to take on health care, which is so central and such a behemoth and, like you said, there’s so much political power behind it, as Joanne said, guarantee of lawsuits and coverage from us forever basically.
Kenen: The other point that’s worth making, I don’t think any of us have said this, it doesn’t apply to nonprofit hospitals or health systems, and that’s a lot of … market-dominant health care systems that are nonprofits, nominally their tax status is nonprofit. It’s a very confusing term to normal people, but these bans on noncompetes do not apply to the nonprofit sector, which is a lot of health care.
Rovner: Yet still it’s set off quite a conflagration since they passed this on Tuesday. Well, finally this week, speaking of big health care business, we are still seeing ramifications from that Change Healthcare hack back in February. While UnitedHealth Group, which owns Change, says things are approaching normality, that’s not the case for providers who still can’t submit bills or collect payments except doing it on paper. Meanwhile, in what’s going to be some kind of movie or miniseries someday, a second group is now demanding ransom after publishing some of the stolen data. If you’ve been following this story along with us, you’ll remember that United reportedly already paid a ransom of $22 million, except that it appears that the group that got that money stiffed the group that actually has control of the pirated data.
Oh, and buried in UnitedHealthcare’s news “update” posted on its website, it says protected health information, “which could cover a substantial proportion of people of America,” is involved in the hack. Can this get any worse?
Kenen: Snakes? I don’t think any of us journalists can quite comprehend. I mean, we understand intellectually, but I don’t think we understand what it’s like to be the billing clerk at a major practice right now trying to figure out what’s where and how to get paid and what it means for patients and what’s next. I mean, this is a tremendous hack, but it’s not the last.
Rovner: Yeah, and the idea that I think — what did they say? — 1 out of every 3 health care transactions goes through Change, I certainly wasn’t aware of. I think most reporters who are covering this weren’t aware of. I think certainly none of the public was aware of, that there’s that much of the money-changing that goes on from one, as we now know, vulnerable organization is a little bit scary.
Luhby: It shows the power of UnitedHealth[care] in the market. I mean, it’s the largest insurer and people think of it, “OK, I have insurance through it,” but they don’t realize all of the other tentacles that are attached.
Kenen: It also shows that there’s hack after hack after hack after hack. This company knew that they were big and powerful and central, and many of us never heard of them or barely knew what they were. But they knew what they were and despite all the warnings of the need for better and higher protection, cybersecurity protections, these things are going on still. I don’t have the technical expertise to know, well, OK, everybody’s doing everything they’re supposed to do as a health system, but the hackers are just always a step ahead. Or whether they’re really not doing everything they’re supposed to do and weak links in their own chains. Is it the diabolical geniuses? Or is it people still not taking this seriously enough?
Rovner: I will add that in our discussion with FTC Chair Lina Kahn, she did talk about cybersecurity as something that the FTC is going to be looking at in deciding whether there is unfair competition going on. Also, she has promised to come on the podcast, so hopefully we will get her in the next several weeks.
All right, that is the news for this week. Now it’s time for our extra-credit segment. That’s when we each recommend a story we read this week we think you should read, too. As always, don’t worry if you miss it. We will post the links on the podcast page at kffhealthnews.org and in our show notes on your phone or other mobile device. Tami, you were the first in, why don’t you go first this week?
Luhby: Well, my extra credit is an AP story by Emily Wagster Pettus titled “Mississippi Lawmakers Haggle Over Possible Medicaid Expansion as Their Legislative Session Nears End.” This story brings us up to date on the negotiations between the House and Senate in Mississippi over expanding Medicaid. Just a quick refresher for listeners: Mississippi is one of 10 states that hasn’t expanded Medicaid yet, and this is the first time, and it’s really very consequential that the Republican-led legislature has seriously considered doing so. The problem is the House and Senate versions are very, very different. The House bill is more like a traditional Medicaid expansion, providing coverage for those earning up to 138% of the poverty level, although it would also try to institute a work requirement, and about 200,000 people would gain coverage. But the Senate version would only extend coverage to those earning up to 100% of the poverty level, which the Senate Medicaid committee chair thought would add about 40,000 to the program, and it would also come with a very strict work requirement.
So on Tuesday, lawmakers met to try to hash out a compromise. They did so in public. It was a public meeting recorded, which was very unusual, and apparently there were people waiting hours to get in. It was standing room only. The House offered a plan that would cover people earning up to 100% of the poverty level under Medicaid, while those earning between 100% and 138% would receive subsidies to buy insurance through the ACA exchange. But the Senate did not offer a proposal nor immediately respond to the one in the House. There are more meetings scheduled. I think there was another one yesterday. It remains to be seen what will happen, but the clock is ticking. The state legislature only is in session until May 5, and it doesn’t give them much time.
Another wrinkle is that it’s important to note that Gov. Tate Reeves, a Republican, has repeatedly voiced his opposition to Medicaid expansion in recent months and is likely to veto any bill. So if lawmakers do eventually agree on a compromise, they may very well also have to vote on whether to override the veto by the governor. This happened in Kansas in 2017 where the legislature did pass Medicaid expansion, Republican governor vetoed it, and the legislature was not able to override the veto and it never got that far again.
Rovner: So yes, we will keep our eyes on Mississippi. Thank you for the update. Alice, why don’t you go next?
Ollstein: I have a piece from States Newsroom related to the Supreme Court arguments on Idaho’s abortion ban and its impact on pregnant patients. The piece [“Loss of Federal Protection in Idaho Spurs Pregnant Patients To Plan for Emergency Air Transport”] is about the increase in patients being airlifted out of the state on these Life Flight [Network] emergency transports and the situation and doctors’ hesitancy to provide abortion care, even when they feel it’s medically necessary, is leading to this increase in flying patients to Oregon and Washington and Utah and neighboring states. It’s getting to the point where some doctors are even recommending people who are pregnant or planning to be pregnant purchase memberships in these flight companies, which normally is only recommended for people who do extreme outdoor sports who may need to be rescued or who ride motorcycles. So the fact that just being pregnant is becoming a category in which you are recommended to have this kind of insurance is pretty wild.
Rovner: Yeah. Welcome to 2024. Joanne.
Kenen: This is a piece from the Missouri Independent, which is also part of the States Newsroom, by Rudi Keller, and the headline is “Missouri Prison Agency To Pay $60K for Sunshine Law Violations Over Inmate Death Records.” That doesn’t sound quite as dramatic as this story really is. It’s about a mother who’s been trying to find out how her son was left unprotected, and he died by suicide, hanged himself in solitary confinement, when he had a history of mental illness. He was serving time for robbery. He wasn’t a murderer. I mean, he was obviously in prison. He had done something wrong, very wrong. He had had a 13-year sentence. But he had a history of mental illness. He had a history of past suicide attempts. He had been taken off some of his drugs, and she has been trying to find out what happened. But it’s not just her. There are other cases. The number of deaths in Missouri prisons has actually gone up in the last few years, even though the prison population itself has gone down. The headline is sort of the tip of a rather sad iceberg.
Rovner: Prison health care, I think, is something that people are starting to look at more closely, but there’s a lot of stories there to be done. Well, my story this week is from my friend and former colleague Liz Szabo, and it’s called “Women Are Less Likely To Die When Treated by Female Doctors, Study Suggests.” Now, this was a study of women on Medicare who were hospitalized, so not everybody, and the difference was small, but statistically significant. Those women treated by women doctors were slightly less likely to die in the ensuing 30 days than those treated by male doctors. It’s not entirely clear why, but at least part of it is that women tend to take other women’s problems more seriously, and women patients may be more likely to open up to other women doctors.
It’s another data point in trying to close the gap between women and men and the gap between people of color and white people when it comes to health care. So more studies to come.
OK, that is our show. As always, if you enjoy the podcast, you can subscribe wherever you get your podcasts. We’d appreciate it if you left us a review; that helps other people find us, too. Special thanks as always to our technical guru, Francis Ying, and our editor, Emmarie Huetteman. As always, you can email us your comments or questions to whatthehealth, all one word, @kff.org. Or you can still find me at X, I’m @jrovner. Joanne, where do you hang these days?
Kenen: Occasionally on X @JoanneKenen, but not very much, and on threads @joannekenen1.
Rovner: Tami?
Luhby: Best place is cnn.com.
Rovner: There you go. Alice?
Ollstein: @AliceOllstein on X, and @alicemiranda on Bluesky.
Rovner: We will be back in your feed next week. Until then, be healthy.
Credits
Francis Ying
Audio producer
Emmarie Huetteman
Editor
To hear all our podcasts, click here.
And subscribe to KFF Health News’ “What the Health?” on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Pocket Casts, or wherever you listen to podcasts.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
Courts, Elections, Health Industry, Medicaid, Medicare, Multimedia, States, Abortion, Health IT, Hospitals, KFF Health News' 'What The Health?', Legislation, Podcasts, reproductive health, Women's Health
Neumáticos tóxicos están matando a los peces. ¿Qué pasa con los humanos?
Durante décadas, las preocupaciones sobre la contaminación automovilística se han centrado en lo que sale del tubo de escape. Ahora, investigadores y reguladores dicen que se necesita prestar más atención a las emisiones tóxicas de los neumáticos mientras los vehículos circulan por las carreteras.
Y primero en la lista de preocupaciones se encuentra un producto químico llamado 6PPD, que se agrega a los neumáticos para que duren más tiempo. Cuando los neumáticos se van desgastando por el roce con el pavimento, liberan 6PPD.
Al entrar en contacto con el ozono, esta sustancia reacciona y se convierte en un producto químico diferente, el 6PPD-q, que puede ser extremadamente tóxico, tanto que se ha relacionado con muertes de peces en el estado de Washington.
Pero los problemas no terminan ahí.
Los neumáticos están hechos principalmente de goma natural y goma sintética, pero contienen cientos de otros ingredientes, que a menudo incluyen acero y metales pesados como cobre, plomo, cadmio y zinc.
A medida que los neumáticos se desgastan, la goma desaparece en partículas, tanto trozos que se pueden ver a simple vista como micropartículas. Las pruebas realizadas por una empresa británica, Emissions Analytics, encontraron que los neumáticos de un automóvil emiten 1,000 millones de partículas ultrafinas por kilómetro conducido: entre 5 y 9 libras de goma por automóvil de combustión interna por año.
Y lo que hay en esas partículas es un misterio, porque los ingredientes de los neumáticos son de propiedad exclusiva.
“Tienes un cóctel químico en estos neumáticos que nadie realmente entiende y que los fabricantes de neumáticos mantienen en secreto”, dijo Nick Molden, CEO de Emissions Analytics. “Nos resulta difícil pensar en otro producto de consumo tan prevalente en el mundo y utilizado prácticamente por todos, donde se sepa tan poco sobre lo que contiene”.
Los reguladores apenas han comenzado a abordar el problema de la toxicidad en los neumáticos, aunque ha habido algunas acciones sobre el 6PPD.
El producto químico fue identificado por un equipo de investigadores, dirigido por científicos de la Universidad Estatal de Washington y de la Universidad de Washington, que estaban tratando de determinar por qué estaban muriendo masivamente los salmones coho que regresaban a arroyos del área de Seattle para desovar.
Trabajando para el Washington Stormwater Center, los científicos probaron alrededor de 2,000 sustancias para determinar cuál estaba causando las muertes, y en 2020 anunciaron que habían encontrado al culpable: 6PPD.
La Tribu Yurok en el norte de California, junto con otras dos tribus nativas de la costa oeste, han pedido a la Agencia de Protección Ambiental (EPA) que prohíba el producto químico. La EPA dijo que está considerando nuevas normas que lo regulen.
“No podríamos quedarnos de brazos cruzados mientras el 6PPD mata a los peces que nos sostienen”, dijo Joseph L. James, presidente de la Tribu Yurok, en un comunicado. “Esta toxina letal no tiene lugar en ninguna cuenca salmonera”.
California ha comenzado a tomar medidas para regular el producto químico. El año pasado comenzó a calificar a los neumáticos que lo contienen como un “producto prioritario”, lo que requiere que los fabricantes busquen y prueben sustitutos.
“El 6PPD juega un papel crucial en la seguridad de los neumáticos en las carreteras de California y, actualmente, no hay alternativas más seguras ampliamente disponibles”, dijo Karl Palmer, subdirector del Departamento de Control de Sustancias Tóxicas del estado. “Por esta razón, nuestro marco es ideal para identificar alternativas al 6PPD que sigan garantizado la seguridad de los neumáticos en las carreteras de California, protegiendo al mismo tiempo las poblaciones de peces y las comunidades que dependen de ellas”.
La Asociación de Fabricantes de Neumáticos de EE.UU. (USTMA) dice que ha movilizado un consorcio de 16 fabricantes para llevar a cabo un análisis de alternativas. Anne Forristall Luke, presidenta y CEO de la USTMA, dijo que “proporcionará la revisión más efectiva y exhaustiva posible de si existe una alternativa más segura al 6PPD en los neumáticos”.
Sin embargo, Molden dijo que hay un inconveniente. “Si no investigan, no se les permite vender en el estado de California”, dijo. “Si investigan y no encuentran una alternativa, pueden seguir vendiendo. No tienen que encontrar un sustituto. Y hoy no hay alternativa al 6PPD”.
California también está estudiando una solicitud de la California Stormwater Quality Association para clasificar los neumáticos que contienen zinc, un metal pesado, como un producto prioritario, lo que requeriría que los fabricantes busquen una alternativa. El zinc se utiliza en el proceso de vulcanización para aumentar la resistencia del caucho.
Sin embargo, cuando se trata de partículas de neumáticos, no ha habido ninguna acción, incluso cuando el problema empeora con la proliferación de automóviles eléctricos. Debido a su aceleración más rápida, los vehículos eléctricos desgastan los neumáticos más rápido y emiten aproximadamente un 20% más de partículas que los de un automóvil de gasolina promedio.
Un estudio reciente en el sur de California encontró que las emisiones de neumáticos y frenos en Anaheim representaban el 30% de PM2.5, un contaminante atmosférico de partículas pequeñas, mientras que las emisiones de escape representaban el 19%.
Las pruebas realizadas por Emissions Analytics han encontrado que los neumáticos producen hasta 2,000 veces más contaminación por partículas en masa que los tubos de escape. Estas partículas acaban en el agua y el aire y a menudo se ingieren. Los neumáticos también emiten partículas ultrafinas, incluso más pequeñas que PM2.5, que pueden ser inhaladas y viajar directamente al cerebro.
Nuevas investigaciones sugieren que las micropartículas de neumáticos deberían ser clasificadas como un contaminante de “alta preocupación”. En un informe el año pasado, investigadores del Imperial College de Londres dijeron que las partículas podrían afectar al corazón, los pulmones y los órganos reproductivos, y causar cáncer.
Las personas que viven o trabajan junto a carreteras, muchas veces de bajos ingresos, están expuestas a más de estas sustancias tóxicas.
Los neumáticos también son una fuente importante de microplásticos. Más de tres cuartas partes de los microplásticos que llegan al océano provienen de la goma sintética de los neumáticos, según un informe del Pew Charitable Trusts y la empresa británica Systemiq.
Y todavía hay muchas incógnitas sobre las emisiones de neumáticos, que pueden ser especialmente complejas de analizar porque el calor y la presión pueden transformar los ingredientes del neumático en otros compuestos.
Una pregunta pendiente de investigación es si el 6PPD-q afecta a las personas y qué problemas de salud, si los hay, podría causar. Un estudio reciente publicado en Environmental Science & Technology Letters encontró altos niveles del producto químico en muestras de orina de una región del sur de China, con niveles más altos en mujeres embarazadas.
Molden dijo que el descubrimiento del 6PPD-q ha generado un nuevo interés en el impacto sanitario y ambiental de los neumáticos, y espera una gran cantidad de nuevas investigaciones en los próximos años. “Las piezas del rompecabezas se están armando”, dijo. “Pero es un rompecabezas de mil piezas, no de doscientas”.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
california, Noticias En Español, States, Environmental Health, Indigenous Health, Study
California Health Workers May Face Rude Awakening With $25 Minimum Wage Law
SACRAMENTO, Calif.
— Nearly a half-million health workers who stand to benefit from California’s nation-leading $25 minimum wage law could be in for a rude awakening if hospitals and other health care providers follow through on potential cuts to hours and benefits.
A medical industry challenge to a new minimum wage ordinance in one Southern California city suggests layoffs and reductions in hours and benefits, including cuts to premium pay and vacation time, could be one result of a state law set to begin phasing in in June. However, some experts are skeptical of that possibility.
The California Hospital Association brought a partly successful legal challenge to Inglewood’s $25 minimum wage ordinance, which barred employers from taking those sorts of steps to offset their higher costs.
“Layoffs, reductions in premium pay rates, reductions in non-wage benefits, reductions in hours, and increased charges are consequences of an employer having less money to spend—which will necessarily be the case given the significant increase in spending on wages due to the minimum wage,” the association said in its lawsuit. Additional examples include reducing health coverage and charging for parking or work-related equipment.
Inglewood voters approved the ordinance in November 2022, nearly a year before California legislators enacted a $25 minimum wage for health workers. Those statewide higher wages are to be phased in starting in June under California’s first-in-the-nation law, but Gov. Gavin Newsom has since said they are too expensive as the state faces a deficit estimated between $38 billion and $73 billion. It’s unclear if lawmakers will agree to a delay or take other steps to reduce the cost.
U.S. District Judge Dale S. Fischer agreed with the hospital industry in a March 11 tentative ruling when he shot down the portion of Inglewood’s ordinance banning layoffs and clawbacks by employers, while allowing the rest of the ordinance to remain in effect. He gave the sides time to object to his preliminary decision, though none did.
The California Hospital Association represents more than 400 hospitals and was a key backer of the state’s carefully crafted compromise law, which notably contains none of the employee safeguards included in the Inglewood ordinance.
Spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea said the association doesn’t know how providers will react once the state law takes effect. “We don’t have any insights,” she said.
“The challenge for any health care organization is figuring out how to pay for the higher wages,” said Joanne Spetz, director of the Philip R. Lee Institute for Health Policy Studies at the University of California-San Francisco. “Since labor costs are the largest part of any health care organization’s costs, it’s hard to figure out how to reduce spending without looking at labor costs.”
Providers can try to increase revenues by bargaining for higher reimbursements from commercial insurers, she said. Public hospitals, nursing homes, and community clinics get most of their money through Medi-Cal, the state’s Medicaid program.
Providers could reduce the services they offer, pare back charity care, and cut or delay capital investments, Spetz said. In the long term, she expects some combination of spending cuts and revenue increases.
Both the state law and local ordinance cover far more than doctors and nurses, with a definition of health worker that includes janitors, housekeepers, groundskeepers, security guards, food service workers, laundry workers, and clerical staff.
The most recent estimate by the Health Care Program at the University of California-Berkeley Labor Center is that as many as 426,000 health workers would make an average of $6,400 extra in the law’s first year, a 19% average pay bump mainly benefiting lower-income workers of color and women. State finance officials project that well over 500,000 workers will benefit.
Researchers didn’t include layoffs and other potential staffing and benefit reductions when they projected the state law’s costs and benefits, said Laurel Lucia, the program’s director. But she pointed to initial projections by hospitals, doctors, and business and taxpayer groups that the wage hike would cost $8 billion annually, thereby imperiling services and resulting in higher premiums and higher costs for state and local governments.
“It seems like a contradiction to say this law’s going to cost billions of dollars while at the same time saying it’s going to reduce workers’ total compensation,” said Lucia, who projects a far lower price tag.
She added that state finance officials had anticipated that Medi-Cal reimbursements would reflect the increased labor costs, while Medicare would eventually at least partially compensate for the higher labor costs.
Michael Reich, chair of the Center on Wage and Employment Dynamics at UC Berkeley’s Institute for Research on Labor and Employment, and affiliated economist Justin Wiltshire recently argued that California’s new $20 minimum wage law for fast-food workers won’t result in mass layoffs and price increases, as some have predicted.
Health care is much different than fast food, Reich acknowledged, but he argued for much the same positive result.
“A higher minimum wage will make it easier and cheaper for hospitals to recruit and retain these workers. The cost savings, and the productivity benefits of more experienced workers, could offset much of the labor cost increase,” Reich said.
The hospital association filed its lawsuit against Inglewood’s ordinance in July, while it was still opposing early versions of the statewide minimum wage legislation. Among many other provisions, the statewide law put on hold an initiative to cap hospital executives’ salaries in Los Angeles.
The hospital association’s legal challenge referenced in part layoffs and reduced working hours imposed by Centinela Hospital Medical Center after Inglewood’s ordinance took effect.
But Centinela said the reduction was entirely unrelated to the ordinance and that all staff were offered alternate positions, which many accepted.
“Centinela Hospital also has since added many more jobs in new clinical positions above minimum wage scale,” the hospital said in a statement.
Service Employees International Union-United Healthcare Workers West, the prime backer of both the local ordinance and the statewide law, sued the hospital in April 2023 alleging that it cut workers’ hours to offset the higher minimum wage. The case is still pending.
The union did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
In a court filing, however, the union and city of Inglewood said similar employer restrictions in previous minimum wage laws have survived.
The ordinance “merely sets the backdrop for collective bargaining negotiations,” and does not bar employers from locking out employees or hiring replacement workers during a strike. Employers can still lay off workers or reduce their hours, they said, so long as they don’t do so to fund the higher minimum wage.
But Fischer agreed with the hospital association that layoffs and reductions in employees’ total compensation packages are “obvious responses by an employer to rising compensation costs.”
Restricting employers’ options would violate federal labor relations rules, he said.
“The minimum wage an employer has to pay its employees will invariably affect the total amount of compensation it is able or willing to pay,” he wrote “This will then invariably affect the number of employees it can retain and the number of hours those employees will be scheduled to work.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
california, Health Industry, States, Cost of Living, Hospitals, Legislation
Swap Funds or Add Services? Use of Opioid Settlement Cash Sparks Strong Disagreements
State and local governments are receiving billions of dollars in opioid settlements to address the drug crisis that has ravaged America for decades.
State and local governments are receiving billions of dollars in opioid settlements to address the drug crisis that has ravaged America for decades. But instead of spending the money on new addiction treatment and prevention services they couldn’t afford before, some jurisdictions are using it to replace existing funding and stretch tight budgets.
Scott County, Indiana, for example, has spent more than $250,000 of opioid settlement dollars on salaries for its health director and emergency medical services staff. The money usually budgeted for those salaries was freed to buy an ambulance and create a financial cushion for the health department.
In Blair County, Pennsylvania, about $320,000 went to a drug court the county has been operating with other sources of money for more than two decades.
And in New York, some lawmakers and treatment advocates say the governor’s proposed budget substitutes millions of opioid settlement dollars for a portion of the state addiction agency’s normal funding.
The national opioid settlements don’t prohibit the use of money for initiatives already supported by other means. But families affected by addiction, recovery advocates, and legal and public health experts say doing so squanders a rare opportunity to direct additional resources toward saving lives.
“To think that replacing what you’re already spending with settlement funds is going to make things better — it’s not,” said Robert Kent, former general counsel for the Office of National Drug Control Policy. “Certainly, the spirit of the settlements wasn’t to keep doing what you’re doing. It was to do more.”
Settlement money is a new funding stream, separate from tax dollars. It comes from more than a dozen companies that were accused of aggressively marketing and distributing prescription painkillers. States are required to spend at least 85% of the funds on addressing the opioid crisis. Now, with illicit fentanyl flooding the drug market and killing tens of thousands of Americans annually, the need for treatment and social services is more urgent.
Thirteen states and Washington, D.C., have restricted the practice of substituting opioid settlement funds for existing dollars, according to state guides created by OpioidSettlementTracker.com and the public health organization Vital Strategies. A national set of principles created by Johns Hopkins University also advises against the practice, known as supplantation.
Paying Staff Salaries
Scott County, Indiana — a small, rural place known nationally as the site of an HIV outbreak in 2015 sparked by intravenous drug use — received more than $570,000 in opioid settlement funds in 2022.
From August 2022 to July 2023, the county reported using roughly $191,000 for the salaries of its EMS director, deputy director, and training officer/clinical coordinator, as well as about $60,000 for its health administrator. The county also awarded about $151,000 total to three community organizations that address addiction and related issues.
In a public meeting discussing the settlement dollars, county attorney Zachary Stewart voiced concerns. “I don’t know whether or not we’re supposed to be using that money to add, rather than supplement, already existing resources,” he said.
But a couple of months later, the county council approved the allocations.
Council President Lyndi Hughbanks did not respond to repeated requests to explain this decision. But council members and county commissioners said in public meetings that they hoped to compensate county departments for resources expended during the HIV outbreak.
Their conversations echoed the struggles of many rural counties nationwide, which have tight budgets, in part because they poured money into addressing the opioid crisis for years. Now as they receive settlement funds, they want to recoup some of those expenses.
The Scott County Health Department did not respond to questions about how the funds typically allocated for salary were used instead. But at the public meeting, it was suggested they could be used at the department’s discretion.
EMS Chief Nick Oleck told KFF Health News the money saved on salaries was put toward loan payments for a new ambulance, purchased in spring 2023.
Unlike other departments, which are funded from local tax dollars and start each year with a full budget, the county EMS is mostly funded through insurance reimbursements for transporting patients, Oleck said. The opioid settlement funds provided enough cash flow to make payments on the new ambulance while his department waited for reimbursements.
Oleck said this use of settlement dollars will save lives. His staff needs vehicles to respond to overdose calls, and his department regularly trains area emergency responders on overdose response.
“It can be played that it was just money used to buy an ambulance, but there’s a lot more behind the scenes,” Oleck said.
Still, Jonathan White — the only council member to vote against using settlement funds for EMS salaries — said he felt the expense did not fit the money’s intended purpose.
The settlement “was written to pay for certain things: helping people get off drugs,” White told KFF Health News. “We got drug rehab facilities and stuff like that that I believe could have used that money more.”
Phil Stucky, executive director of a local nonprofit called Thrive, said his organization could have used the money too. Founded in the wake of the HIV outbreak, Thrive employs people in recovery to provide support to peers with mental health and substance use disorders.
Stucky, who is in recovery himself, asked Scott County for $300,000 in opioid settlement funds to hire three peer specialists and purchase a vehicle to transport people to treatment. He ultimately received one-sixth of that amount — enough to hire one person.
In Blair County, Pennsylvania, Marianne Sinisi was frustrated to learn her county used about $322,000 of opioid settlement funds to pay for a drug court that has existed for decades.
“This is an opioid epidemic, which is not being treated enough as it is now,” said Sinisi, who lost her 26-year-old son to an overdose in 2018. The county received extra money to help people, but instead it pulled back its own money, she said. “How do you expect that to change? Isn’t that the definition of insanity?”
Blair County Commissioner Laura Burke told KFF Health News that salaries for drug court probation officers and aides were previously covered by a state grant and parole fees. But in recent years that funding has been inadequate, and the county general fund has picked up the slack. Using opioid settlement funds provides a small reprieve since the general fund is overburdened, she said. The county’s most recent budget faces a $2 million deficit.
Forfeited Federal Dollars
Supplantation can take many forms, said Shelly Weizman, project director of the addiction and public policy initiative at Georgetown University’s O’Neill Institute. Replacing general funds with opioid settlement dollars is an obvious one, but there are subtler approaches.
The federal government pours billions of dollars into addiction-related initiatives annually. But some states forfeit federal grants or decline to expand Medicaid, which is the largest payer of mental health and addiction treatment.
If those jurisdictions then use opioid settlement funds for activities that could have been covered with federal money, Weizman considers it supplantation.
“It’s really letting down the citizens of their state,” she said.
Officials in Bucks County, Pennsylvania, forfeited more than $1 million in federal funds from September 2022 to September 2023, the bulk of which was meant to support the construction of a behavioral health crisis stabilization center.
“We were probably overly optimistic” about spending the money by the grant deadline, said Diane Rosati, executive director of the Bucks County Drug and Alcohol Commission.
Now the county plans to use $3.9 million in local and state opioid settlement funds to support the center.
Susan Ousterman finds these developments difficult to stomach. Her 24-year-old son died of an overdose in 2020, and she later joined the Bucks County Opioid Settlement Advisory Committee, which developed a plan to spend the funds.
In a September 2022 email to other committee members, she expressed disappointment in the suggested uses: “Please keep in mind, the settlement funds are not meant to fund existing programs or programs that can be funded by other sources, such as federal grants.”
But Rosati said the county is maximizing its resources. Settlement funds will create a host of services, including grief groups for families and transportation to treatment facilities.
“We’re determined to utilize every bit of funding that’s available to Bucks County, using every funding source, every stream, and frankly every grant opportunity that comes our way,” Rosati said.
The county’s guiding principles for settlement funds demand as much. They say, “Whenever possible, use existing resources in order that Opioid Settlement funds can be directed to addressing gaps in services.”
Ed Mahon of Spotlight PA contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
1 year 6 months ago
Courts, Rural Health, States, Indiana, Investigation, New York, Opioid Settlements, Opioids, Pennsylvania